b8a5f9b3924b7d67e4016623338e5799.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 The Learning-to-Learn NETWORK presents a 4 -session certificate course Developing Good Learners in Your Subject
The Learning-to-Learn NETWORK presents a 4 -session certificate course Developing Good Learners in Your Subject
 UGC funded teaching development project Learning to Learn Developing students’ Cognitive, Motivational & Interpersonal strategies for learning
UGC funded teaching development project Learning to Learn Developing students’ Cognitive, Motivational & Interpersonal strategies for learning
 Participating departments 1. BSE 7. ITC 2. BUSS 8. LSGI 3. COMP 9. ME 4. EDC 10. ISE 5. ENGL 11. OR 6. GEC
Participating departments 1. BSE 7. ITC 2. BUSS 8. LSGI 3. COMP 9. ME 4. EDC 10. ISE 5. ENGL 11. OR 6. GEC
 Developing Good Learners in Your Subject 4 -session Certificate Course Session 1: 21 Jan (Tue) Learning-to-Learn Instruments for Use & Research Session 2: 28 Jan (Tue) Learn to Review: Learning Review Table Review Session 3: 11 Feb (Tue) Learn to Reflect: Reflective Learning Journal Reflect Session 4: 19 Feb (Wed) Learn to Relate: O-diagram Relate
Developing Good Learners in Your Subject 4 -session Certificate Course Session 1: 21 Jan (Tue) Learning-to-Learn Instruments for Use & Research Session 2: 28 Jan (Tue) Learn to Review: Learning Review Table Review Session 3: 11 Feb (Tue) Learn to Reflect: Reflective Learning Journal Reflect Session 4: 19 Feb (Wed) Learn to Relate: O-diagram Relate
 What will you get from this 4 -session Certificate Course? a) Ready-to-use worksheets and interesting ideas for developing students’ learning abilities b) Reports from teachers and students on their experience of using these worksheets c) Assistance in planning your own research on helping students learn to learn d) A certificate
What will you get from this 4 -session Certificate Course? a) Ready-to-use worksheets and interesting ideas for developing students’ learning abilities b) Reports from teachers and students on their experience of using these worksheets c) Assistance in planning your own research on helping students learn to learn d) A certificate
 Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning to Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our L 2 L materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to scholarship of researching into learning to learn
Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning to Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our L 2 L materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to scholarship of researching into learning to learn
 Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university
Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university
 L 2 L in-context of academic subject ‘… in such general terms we don’t know how to apply them … do it for every subject…’ Students lack abilities to transfer generic knowledge about learning to academic learning, hence, they prefer L 2 L to be ¨ Associated with the learning of academic subjects to allow easy application ¨ Done for every subject
L 2 L in-context of academic subject ‘… in such general terms we don’t know how to apply them … do it for every subject…’ Students lack abilities to transfer generic knowledge about learning to academic learning, hence, they prefer L 2 L to be ¨ Associated with the learning of academic subjects to allow easy application ¨ Done for every subject
![L 2 L in-task (academic learning task) ‘[L 2 L] should go along with L 2 L in-task (academic learning task) ‘[L 2 L] should go along with](https://present5.com/presentation/b8a5f9b3924b7d67e4016623338e5799/image-9.jpg) L 2 L in-task (academic learning task) ‘[L 2 L] should go along with the process of learning … understand more of [L 2 L], …. Could see its usefulness. ’ ‘… force us to do those things, then we would learn them’ Merits of integrating L 2 L in academic learning tasks ¨ Allows effective understanding and application of L 2 L concepts
L 2 L in-task (academic learning task) ‘[L 2 L] should go along with the process of learning … understand more of [L 2 L], …. Could see its usefulness. ’ ‘… force us to do those things, then we would learn them’ Merits of integrating L 2 L in academic learning tasks ¨ Allows effective understanding and application of L 2 L concepts
![L 2 L in-assessment ‘No assignment [on L 2 L] will not spare time L 2 L in-assessment ‘No assignment [on L 2 L] will not spare time](https://present5.com/presentation/b8a5f9b3924b7d67e4016623338e5799/image-10.jpg) L 2 L in-assessment ‘No assignment [on L 2 L] will not spare time for it. ’ ‘In exam no time to think about quality … write down everything’ ‘Use this [SOLO] as marking scheme. . . ’ Students explicitly point out the need to ¨ Include learning abilities as part of the assessment ¨ Use assessment methods and assessment criteria which encourage use of good learning approaches
L 2 L in-assessment ‘No assignment [on L 2 L] will not spare time for it. ’ ‘In exam no time to think about quality … write down everything’ ‘Use this [SOLO] as marking scheme. . . ’ Students explicitly point out the need to ¨ Include learning abilities as part of the assessment ¨ Use assessment methods and assessment criteria which encourage use of good learning approaches
 L 2 L Incessant throughout course of study ‘We have been spoon-fed for so long, … hard to change the habit. … Need to follow up, perhaps every week. ’ Students expressed a felt need for continuous support and development in L 2 L, because L 2 L ¨ New L 2 L concepts / methods require time and effort to develop ¨ Old L 2 L habits take time and effort to change
L 2 L Incessant throughout course of study ‘We have been spoon-fed for so long, … hard to change the habit. … Need to follow up, perhaps every week. ’ Students expressed a felt need for continuous support and development in L 2 L, because L 2 L ¨ New L 2 L concepts / methods require time and effort to develop ¨ Old L 2 L habits take time and effort to change
 How should L 2 L be addressed in Poly. U? ¨ In-context with reference to academic subject matter ¨ In-task integrated into academic learning tasks ¨ In-assessment Including L 2 L as part of the assessment ¨ Incessant continues throughout course of study
How should L 2 L be addressed in Poly. U? ¨ In-context with reference to academic subject matter ¨ In-task integrated into academic learning tasks ¨ In-assessment Including L 2 L as part of the assessment ¨ Incessant continues throughout course of study
 Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning-to-Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to simple methods for researching into learning to learn
Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning-to-Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to simple methods for researching into learning to learn
 What is Learning to Learn? Developing in students the following ¨ Understanding of what learning means ¨ Abilities for carrying out learning ¨ Attributes as a self-regulated learner
What is Learning to Learn? Developing in students the following ¨ Understanding of what learning means ¨ Abilities for carrying out learning ¨ Attributes as a self-regulated learner
 Understanding of what learning means – underpinning theories ¨ Conceptions of learning Quantitative conception VS Qualitative conception ¨ Levels of learning outcomes SOLO taxonomy – Extended abstract (think beyond given) – Relational understanding (able to relate ideas) – Multi-structural (memorization of unrelated facts) ¨ Qualities of a preferred graduate
Understanding of what learning means – underpinning theories ¨ Conceptions of learning Quantitative conception VS Qualitative conception ¨ Levels of learning outcomes SOLO taxonomy – Extended abstract (think beyond given) – Relational understanding (able to relate ideas) – Multi-structural (memorization of unrelated facts) ¨ Qualities of a preferred graduate
 Abilities for carrying out learning ¨ Motivation ¨ Cognitive abilities ¨ Interpersonal abilities
Abilities for carrying out learning ¨ Motivation ¨ Cognitive abilities ¨ Interpersonal abilities
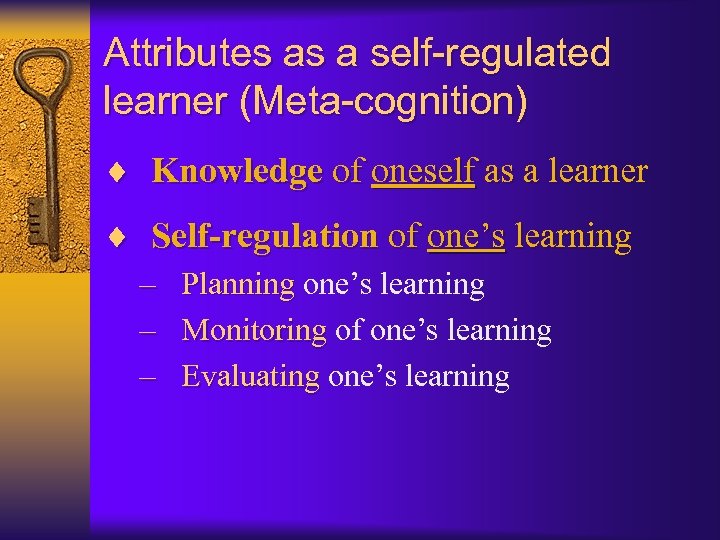 Attributes as a self-regulated learner (Meta-cognition) ¨ Knowledge of oneself as a learner ¨ Self-regulation of one’s learning – Planning one’s learning – Monitoring of one’s learning – Evaluating one’s learning
Attributes as a self-regulated learner (Meta-cognition) ¨ Knowledge of oneself as a learner ¨ Self-regulation of one’s learning – Planning one’s learning – Monitoring of one’s learning – Evaluating one’s learning
 Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning to Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our L 2 L materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to scholarship of researching into learning to learn
Session 1: ‘Learning-to-Learn’ Instruments for Use and Research ¨ Learning to Learn and L 2 L instruments The learning abilities that our L 2 L materials attempt to develop ¨ Use Students’ opinions about how learning to learn should be addressed in university ¨ Research Introduction to scholarship of researching into learning to learn
 Scholarship of helping student L 2 L – practice, research and publication L 2 L work in the Poly. U is contributing to the literature in the following ways: ¨ New realms of L 2 L are explored, e. g. explored – learning goals – Conceptions of learning – 4 -INs of L 2 L (in-context, in-task, in-assessment, incessant) ¨ New materials are developed and tested, e. g. tested – O-Diagram – Knowledge Building Worksheet ¨ Renowned theories are used to underpin L 2 L, e. g. L 2 L – SOLO taxonomy – Conceptions of learning – Meta-cognition
Scholarship of helping student L 2 L – practice, research and publication L 2 L work in the Poly. U is contributing to the literature in the following ways: ¨ New realms of L 2 L are explored, e. g. explored – learning goals – Conceptions of learning – 4 -INs of L 2 L (in-context, in-task, in-assessment, incessant) ¨ New materials are developed and tested, e. g. tested – O-Diagram – Knowledge Building Worksheet ¨ Renowned theories are used to underpin L 2 L, e. g. L 2 L – SOLO taxonomy – Conceptions of learning – Meta-cognition
 Researching into L 2 L: Publications and Presentations ¨ UGC 2001 Conference on ‘The Scholarship of Teaching – 2 papers on the project – 1 paper on implementation of 3 -Column Table – 1 paper on survey of students’ L 2 L needs (selected for publication in printed proceedings) ¨ Forum of Higher Education Reform, Society of HK Scholars – invited speech ¨ 2002 International Conference of HK Educational Research Association – 1 paper on evaluation results (qualitative interviews) ¨ 2003 International Conference of European Association for Research on Learning and Instruction – 1 paper on evaluation results (findings on SPQ)
Researching into L 2 L: Publications and Presentations ¨ UGC 2001 Conference on ‘The Scholarship of Teaching – 2 papers on the project – 1 paper on implementation of 3 -Column Table – 1 paper on survey of students’ L 2 L needs (selected for publication in printed proceedings) ¨ Forum of Higher Education Reform, Society of HK Scholars – invited speech ¨ 2002 International Conference of HK Educational Research Association – 1 paper on evaluation results (qualitative interviews) ¨ 2003 International Conference of European Association for Research on Learning and Instruction – 1 paper on evaluation results (findings on SPQ)
 Sustaining and extending development in Learning to Learn by Integrating L 2 L into Teaching and Piloting Approaches to Assessing Learning and Metacognitive Abilities
Sustaining and extending development in Learning to Learn by Integrating L 2 L into Teaching and Piloting Approaches to Assessing Learning and Metacognitive Abilities


