08744982b2adc1607a098506715c7524.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 The Late Roman Empire, and the Papacy
The Late Roman Empire, and the Papacy
 Late Roman Empire, Papacy l How can we compare/contrast political and temporal circumstances in east and west? l Spiritual?
Late Roman Empire, Papacy l How can we compare/contrast political and temporal circumstances in east and west? l Spiritual?
 The Later Roman Empire The Roman Empire
The Later Roman Empire The Roman Empire
 The Late Roman Empire n Romulus Augustulus (r. 475 -76) The Latin West (5 th century) – Romans ruled fragments – Barbarians! – The Huns – Roman rule ended 476
The Late Roman Empire n Romulus Augustulus (r. 475 -76) The Latin West (5 th century) – Romans ruled fragments – Barbarians! – The Huns – Roman rule ended 476
 The Late Roman Empire The Germanic Kingdoms (ca. 530)
The Late Roman Empire The Germanic Kingdoms (ca. 530)
 The Late Roman Empire n The Greek East – Survived Byzantine Empire – Hellenistic culture – Capital: Constantinople – Four patriarchs Constantine and Constantinople
The Late Roman Empire n The Greek East – Survived Byzantine Empire – Hellenistic culture – Capital: Constantinople – Four patriarchs Constantine and Constantinople
 The Late Roman Empire
The Late Roman Empire
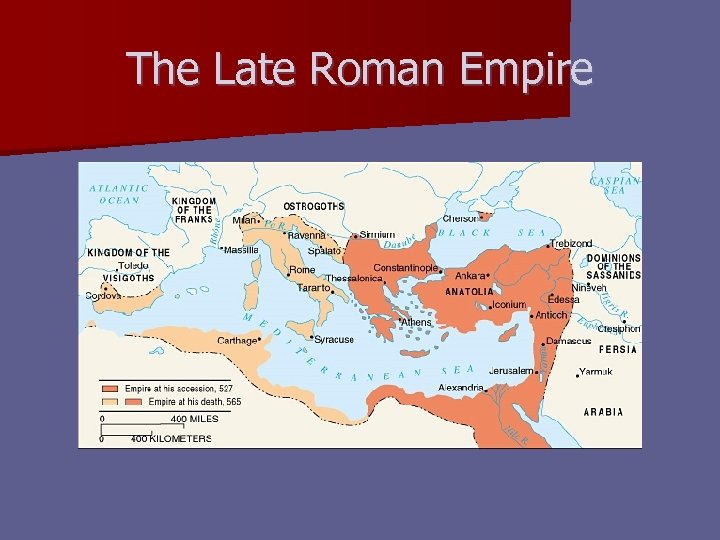
 The Late Roman Empire n Emperor Justinian I (r. 527 -565) – Autocrat – Well-versed in theology – Accomplishments § Code of Justinian § Reconquest of much of Latin West § Hagia Sophia
The Late Roman Empire n Emperor Justinian I (r. 527 -565) – Autocrat – Well-versed in theology – Accomplishments § Code of Justinian § Reconquest of much of Latin West § Hagia Sophia
 The Late Roman Empire n Empress Theodora (ca. 500 -548) – Of low birth, had “reputation” – “Partner in our counsels” – Champion of women
The Late Roman Empire n Empress Theodora (ca. 500 -548) – Of low birth, had “reputation” – “Partner in our counsels” – Champion of women
 The Late Roman Empire
The Late Roman Empire
 The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia (532 -37), exterior
The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia (532 -37), exterior
 The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia, floor plan
The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia, floor plan
 The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia, interior
The Late Roman Empire Hagia Sophia, interior
 The Late Roman Empire Graffiti in Hagia Sophia? !
The Late Roman Empire Graffiti in Hagia Sophia? !
 The Late Roman Empire The Basilica Cistern, Istanbul
The Late Roman Empire The Basilica Cistern, Istanbul
 The Late Roman Empire
The Late Roman Empire
 The Late Roman Empire n Justinian’s Religious Policies – Functioned as head of the Church – Goal: empire of orthodox Christians – Measures taken against… § Judaism § Heretics § Paganism
The Late Roman Empire n Justinian’s Religious Policies – Functioned as head of the Church – Goal: empire of orthodox Christians – Measures taken against… § Judaism § Heretics § Paganism
 The Late Roman Empire
The Late Roman Empire
 The Late Roman Empire
The Late Roman Empire
 The Late Roman Empire n Questions?
The Late Roman Empire n Questions?
 The Papacy n The Papacy – Office of bishop of Rome – Patriarch of Latin West – Successor of St. Peter
The Papacy n The Papacy – Office of bishop of Rome – Patriarch of Latin West – Successor of St. Peter
 The Papacy n Foundational Text – “And I say to you that you are Peter, and upon this rock I will build my Church; and the gates of Hades shall not overpower it. I will give you the keys of the kingdom of heaven; and whatever you shall bind on earth shall be bound in heaven, and whatever you loose on earth shall be loosed in heaven” (Matt. 16: 18 -19)
The Papacy n Foundational Text – “And I say to you that you are Peter, and upon this rock I will build my Church; and the gates of Hades shall not overpower it. I will give you the keys of the kingdom of heaven; and whatever you shall bind on earth shall be bound in heaven, and whatever you loose on earth shall be loosed in heaven” (Matt. 16: 18 -19)
 The Papacy n Steps toward Papal Supremacy – Had faced competition in east and west – Called “Apostolic See” – Supreme spiritual authority in west (455)
The Papacy n Steps toward Papal Supremacy – Had faced competition in east and west – Called “Apostolic See” – Supreme spiritual authority in west (455)
 The Papacy n Pope Leo I (r. 440 -461) – Literary remains: letters, sermons – Papal theory § Peter: “prince of the apostles” § Pope: representative of Peter (“cuius vice fungimur”) § St. Peter writes, speaks through pope – Intervened in eastern affairs
The Papacy n Pope Leo I (r. 440 -461) – Literary remains: letters, sermons – Papal theory § Peter: “prince of the apostles” § Pope: representative of Peter (“cuius vice fungimur”) § St. Peter writes, speaks through pope – Intervened in eastern affairs
 The Papacy Alessandro Algardi, The Meeting between Leo the Great and Attila, St. Peter’s Basilica
The Papacy Alessandro Algardi, The Meeting between Leo the Great and Attila, St. Peter’s Basilica
 The Papacy
The Papacy
 The Papacy n Pope Gregory I (r. 590 -604) – Prefect of Rome first monk-pope – “Servant of the servants of God” – Pastoral Rule
The Papacy n Pope Gregory I (r. 590 -604) – Prefect of Rome first monk-pope – “Servant of the servants of God” – Pastoral Rule
 The Papacy n Gregory and the West – Monitored affairs of Latin Church – Western rulers: “our sons” – Administered Patrimony of St. Peter
The Papacy n Gregory and the West – Monitored affairs of Latin Church – Western rulers: “our sons” – Administered Patrimony of St. Peter
 The Papacy n Gregory and the East – Loyal subject of emperor – Cordial with patriarchs – Offended by title “ecumenical patriarch”
The Papacy n Gregory and the East – Loyal subject of emperor – Cordial with patriarchs – Offended by title “ecumenical patriarch”
 The Papacy n Gregory’s Temporal Authority – – – City provisions Magister militum Organized defenses in Rome, elsewhere – Negotiated peaces, ransomed captives
The Papacy n Gregory’s Temporal Authority – – – City provisions Magister militum Organized defenses in Rome, elsewhere – Negotiated peaces, ransomed captives
 The Papacy Tomb of Gregory the Great, St. Peter’s Basilica
The Papacy Tomb of Gregory the Great, St. Peter’s Basilica
 The Papacy S. Gregorio Magno al Celio, Rome
The Papacy S. Gregorio Magno al Celio, Rome
 The Papacy Gregory’s cathedra, S. Gregorio Magno Gregory’s cell, S. Gregorio Magno
The Papacy Gregory’s cathedra, S. Gregorio Magno Gregory’s cell, S. Gregorio Magno
 The Papacy Gregory’s Table, Gardens of Santa Barbara, S. Gregorio Magno
The Papacy Gregory’s Table, Gardens of Santa Barbara, S. Gregorio Magno
 The Papacy S. Gregorio della Divina Pietà, Rome Gregory serving at his table
The Papacy S. Gregorio della Divina Pietà, Rome Gregory serving at his table
 The Papacy n Questions?
The Papacy n Questions?
 Late Roman Empire, Papacy l How can we compare/contrast political and temporal circumstances in east and west? l Spiritual?
Late Roman Empire, Papacy l How can we compare/contrast political and temporal circumstances in east and west? l Spiritual?


