7fd5363751d315fc0b173a6579ef9ca8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 The Introduction of Lean Manufacturing Concepts at Qualcomm
The Introduction of Lean Manufacturing Concepts at Qualcomm
 Introduction: Agenda n The Value Chain n Lean Concepts n Benefits of Lean Manufacturing n 2 Oracle Instances l The QCT instance l The Quantum instance n Why 2 instances? n Separation of Production and Non-Prod Procurement n 2007 Implementation Sites 1
Introduction: Agenda n The Value Chain n Lean Concepts n Benefits of Lean Manufacturing n 2 Oracle Instances l The QCT instance l The Quantum instance n Why 2 instances? n Separation of Production and Non-Prod Procurement n 2007 Implementation Sites 1
 The Value Chain The Quantum value chain is driven by Qualcomm’s leadership position as the developer of CDMA technologies. QCT CDMA technologies accounts for 90 -95% of QSCO demand, principally FFA’s and SURFS (test equipment used to test chip quality and functionality). The remaining 5 -10% of QSCO demand is generated by QWBS (Qualcomm Wireless Business Solutions), which manufactures Omni. Vision and other wireless products. Value Chain Processes Generate Demand Develop-Introduce Products / Services Market Products / Services Fulfill Demand Sell Products / Services 2 Procure Materials / Services Plan / Manufacture Distribution / Service & Support
The Value Chain The Quantum value chain is driven by Qualcomm’s leadership position as the developer of CDMA technologies. QCT CDMA technologies accounts for 90 -95% of QSCO demand, principally FFA’s and SURFS (test equipment used to test chip quality and functionality). The remaining 5 -10% of QSCO demand is generated by QWBS (Qualcomm Wireless Business Solutions), which manufactures Omni. Vision and other wireless products. Value Chain Processes Generate Demand Develop-Introduce Products / Services Market Products / Services Fulfill Demand Sell Products / Services 2 Procure Materials / Services Plan / Manufacture Distribution / Service & Support
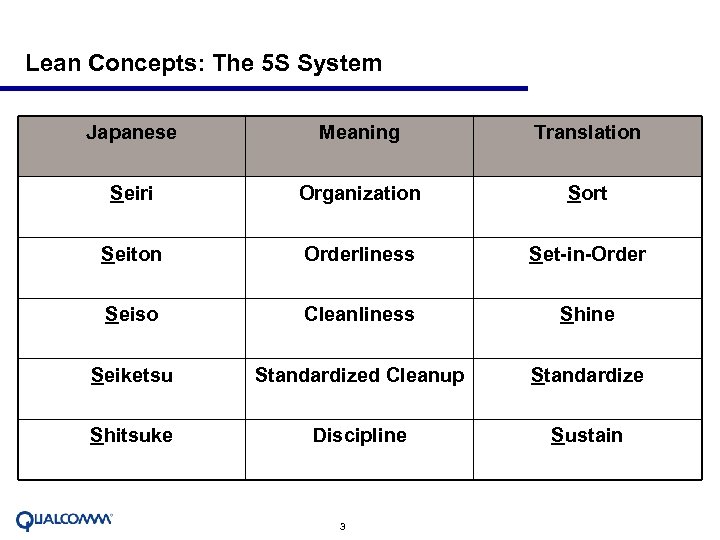 Lean Concepts: The 5 S System Japanese Meaning Translation Seiri Organization Sort Seiton Orderliness Set-in-Order Seiso Cleanliness Shine Seiketsu Standardized Cleanup Standardize Shitsuke Discipline Sustain 3
Lean Concepts: The 5 S System Japanese Meaning Translation Seiri Organization Sort Seiton Orderliness Set-in-Order Seiso Cleanliness Shine Seiketsu Standardized Cleanup Standardize Shitsuke Discipline Sustain 3
 Lean Concepts FROM: TO: Predominately “Push” “Pull” from the Partner Inconsistent Inventory Kanbans, Min/Max and Safety Stock Demand Triggers Disconnected Forecasts Intelligent Forecasts Inconsistent Signal to Partner Defined Signal to CM Partner Complex Processes Radical Simplification 4
Lean Concepts FROM: TO: Predominately “Push” “Pull” from the Partner Inconsistent Inventory Kanbans, Min/Max and Safety Stock Demand Triggers Disconnected Forecasts Intelligent Forecasts Inconsistent Signal to Partner Defined Signal to CM Partner Complex Processes Radical Simplification 4
 Benefits of Lean Manufacturing n Reduced inventory across the supply chain n Greater predictability around lead times and on-time shipments n Increased reliability the right product at the right time at the right price n Better customer satisfaction due to greater accuracy in forecast delivery n Better data, robust processes and systems management effectiveness n Increase control over quality, defects and root cause of defects (6 Sigma) n Optimize operations between existing QSCO and “shelter” organization n Better manage throughput with new Contract Manufacturing partner n Position Qualcomm for rapid growth in emerging business and markets 5
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing n Reduced inventory across the supply chain n Greater predictability around lead times and on-time shipments n Increased reliability the right product at the right time at the right price n Better customer satisfaction due to greater accuracy in forecast delivery n Better data, robust processes and systems management effectiveness n Increase control over quality, defects and root cause of defects (6 Sigma) n Optimize operations between existing QSCO and “shelter” organization n Better manage throughput with new Contract Manufacturing partner n Position Qualcomm for rapid growth in emerging business and markets 5
 2 Oracle instances: The QCT Instance n QCT instance has two application servers: 11. 5. 8 and 11. 5. 9 (lot controlled) n Quantum instance is an Oracle 11. 5. 10 instance, with min. customizations n Each organization “owns” its own inventory; common inventory items n QSCO (manufacturing) has no P&L, and will liquidate costs to other BU’s QCT Instance FAB Suppliers Qualcomm 6 4 B 2 message from SAT 3 B 2_C-O message to SAT 3 B 2_C-I message from FAB PO for DIE items SAT Organizations Service PO for FG items
2 Oracle instances: The QCT Instance n QCT instance has two application servers: 11. 5. 8 and 11. 5. 9 (lot controlled) n Quantum instance is an Oracle 11. 5. 10 instance, with min. customizations n Each organization “owns” its own inventory; common inventory items n QSCO (manufacturing) has no P&L, and will liquidate costs to other BU’s QCT Instance FAB Suppliers Qualcomm 6 4 B 2 message from SAT 3 B 2_C-O message to SAT 3 B 2_C-I message from FAB PO for DIE items SAT Organizations Service PO for FG items
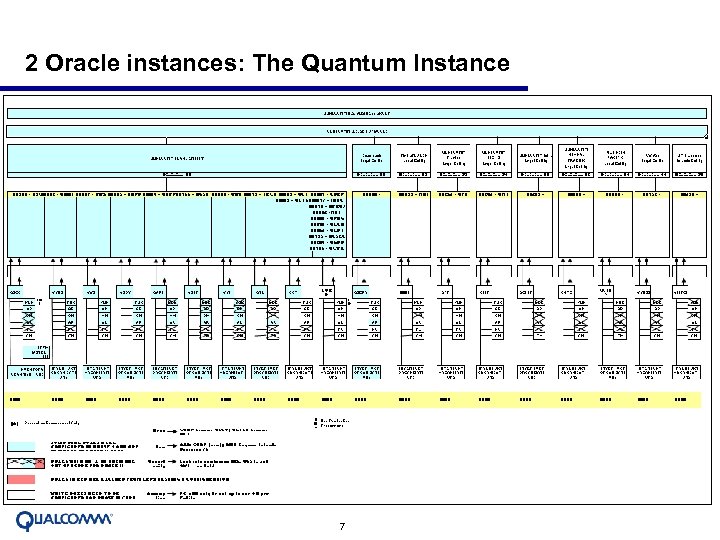 2 Oracle instances: The Quantum Instance 7
2 Oracle instances: The Quantum Instance 7
 Why two instances? The QCT instance is geared to Qualcomm’s chip manufacturing business, is heavily customized, and uses “lot control” and other features that are not attractive to the Qualcomm discrete manufacturing businesses n The QCT instance uses two application servers, one Oracle 11. 5. 8 and the other, an Oracle 11. 5. 9 instance, primarily to support Oracle’s Advanced Supply Chain Planning (ASCP) engine n The QCT instance does not include project accounting, nor does it make allowance for international rollout n There is continuing discussion in the press about “spinning off” the chip business n 8
Why two instances? The QCT instance is geared to Qualcomm’s chip manufacturing business, is heavily customized, and uses “lot control” and other features that are not attractive to the Qualcomm discrete manufacturing businesses n The QCT instance uses two application servers, one Oracle 11. 5. 8 and the other, an Oracle 11. 5. 9 instance, primarily to support Oracle’s Advanced Supply Chain Planning (ASCP) engine n The QCT instance does not include project accounting, nor does it make allowance for international rollout n There is continuing discussion in the press about “spinning off” the chip business n 8
 Separation of Prod & Non-Prod Procurement Direct and NPI Indirect and Services Shelter and Bldg M Corp Procure 9
Separation of Prod & Non-Prod Procurement Direct and NPI Indirect and Services Shelter and Bldg M Corp Procure 9
 Quantum Implementation Sites Russia (2) Canada (1) UK(5) San Diego SD 1 QMT San Jose Tijuana, Mexico SD 2 Mexico(6) EU (DE, ES, FR, IT, NE, SE) (6) Korea(2) Japan(2) China(3) Israel(1) Taiwan (3) QMT Taiwan India(3) Vietnam(1) Singapore (1) Indonesia (1) Brazil (1) South Africa (1) Australia (2) Argentina (1) Actual sites, 2007 rollout Potential sites, 2008 + global rollout 10
Quantum Implementation Sites Russia (2) Canada (1) UK(5) San Diego SD 1 QMT San Jose Tijuana, Mexico SD 2 Mexico(6) EU (DE, ES, FR, IT, NE, SE) (6) Korea(2) Japan(2) China(3) Israel(1) Taiwan (3) QMT Taiwan India(3) Vietnam(1) Singapore (1) Indonesia (1) Brazil (1) South Africa (1) Australia (2) Argentina (1) Actual sites, 2007 rollout Potential sites, 2008 + global rollout 10
 Lean Manufacturing: Agenda n Inventory Orgs Structure n ASCP Overview n Forecasts and Sales Order Drive Demand n Business Processes l SCO (Supply Chain Organization) Procurement l Shelter Manufacturing and CM Procurement l NPI Procurement n Quality and RTS Highlights n The concept of a “Virtual MRB” n Lean Manufacturing “to be” Model n Conclusion 11
Lean Manufacturing: Agenda n Inventory Orgs Structure n ASCP Overview n Forecasts and Sales Order Drive Demand n Business Processes l SCO (Supply Chain Organization) Procurement l Shelter Manufacturing and CM Procurement l NPI Procurement n Quality and RTS Highlights n The concept of a “Virtual MRB” n Lean Manufacturing “to be” Model n Conclusion 11
 Qualcomm Inventory Orgs Structure 12
Qualcomm Inventory Orgs Structure 12
 ASCP Overview • Demand driven by forecasts and Sales Orders (depending on OU) • As Demand drops into the Planners Workbench, Planners route “make” orders to MES (“Shop Floor Control”), material requirements are identified, and PO’s are created and transmitted to Suppliers via EDI (Harbinger) • Entire production procurement process is automated, end-to-end Generate Baseline Forecast Generate Constrained Long Term Supply Plan Collaborative Demand Planning Generate Short Term Manufacturing Plan Generate Consensus Forecast Release Work Orders to Contract Manufacturer Capture Inventory Visibility Release Purchase Orders to Component Vendor(s) Collaborate with Contract Manufacturer Check Availability & Capacity (ATP) Oracle Modules: ODP ASCP Collaborative Planning i. Supplier Portal In addition, DBI may be used for KPI / Metric reporting 13 Order Management
ASCP Overview • Demand driven by forecasts and Sales Orders (depending on OU) • As Demand drops into the Planners Workbench, Planners route “make” orders to MES (“Shop Floor Control”), material requirements are identified, and PO’s are created and transmitted to Suppliers via EDI (Harbinger) • Entire production procurement process is automated, end-to-end Generate Baseline Forecast Generate Constrained Long Term Supply Plan Collaborative Demand Planning Generate Short Term Manufacturing Plan Generate Consensus Forecast Release Work Orders to Contract Manufacturer Capture Inventory Visibility Release Purchase Orders to Component Vendor(s) Collaborate with Contract Manufacturer Check Availability & Capacity (ATP) Oracle Modules: ODP ASCP Collaborative Planning i. Supplier Portal In addition, DBI may be used for KPI / Metric reporting 13 Order Management
 Forecasts Drive Demand into QSCO • Forecasts or SO’s created in QCT, MUI, QMT OU • Demand is placed against QSCO OU, 3 inventory orgs • PO’s are generated and sent via EDI to suppliers 14
Forecasts Drive Demand into QSCO • Forecasts or SO’s created in QCT, MUI, QMT OU • Demand is placed against QSCO OU, 3 inventory orgs • PO’s are generated and sent via EDI to suppliers 14
 Forecasts entered via spreadsheet Releases against Blanket PO (EDI 850) Sales Orders Drive Demand Forecast (EDI 830) Adjustments to Plan made with Arrow 15 Includes VMI, SOI, “toll manufacture”
Forecasts entered via spreadsheet Releases against Blanket PO (EDI 850) Sales Orders Drive Demand Forecast (EDI 830) Adjustments to Plan made with Arrow 15 Includes VMI, SOI, “toll manufacture”
 Sales Orders Drive Demand Run ASCP Engine SIM versus REGEN Run PO’s using EDI 850 Forecast using EDI 830 16
Sales Orders Drive Demand Run ASCP Engine SIM versus REGEN Run PO’s using EDI 850 Forecast using EDI 830 16
 ICG Process: Item is “Planning Enabled” PO’s marked with an “-NPI” 17
ICG Process: Item is “Planning Enabled” PO’s marked with an “-NPI” 17
 Oracle Configuration: Item Master (1 of 2) Indicates an “Active Item” Create Supply to Match Demand Defines period for which releases created 18
Oracle Configuration: Item Master (1 of 2) Indicates an “Active Item” Create Supply to Match Demand Defines period for which releases created 18
 Oracle Configuration: ASCP Engine (2 of 2) ASCP Plan is not Constrained Enforced Demand Drives the Planning Engine 19
Oracle Configuration: ASCP Engine (2 of 2) ASCP Plan is not Constrained Enforced Demand Drives the Planning Engine 19
 Quality and RTS Design Highlights § Uses standard Oracle hooks from Procurement to Quality § 8 Quality Collection Plans developed for each “state” an NC’ed item may take § Handles RTS for both Production and Ancillary Items § Covers all RTS scenarios: § Credit § Outside Rework § SOI (Supplier Owned Inventory) § Legacy Receipts § Utilizes standard Quantum shipping process (custom, integration with RTS) § Leverages standard Oracle WO/PO process to capture all relevant inventory consumption, item conversions, labor charges and other variances § Improves A/P debit memo process using the AP Open Invoices API for automatic debit memo creation 20
Quality and RTS Design Highlights § Uses standard Oracle hooks from Procurement to Quality § 8 Quality Collection Plans developed for each “state” an NC’ed item may take § Handles RTS for both Production and Ancillary Items § Covers all RTS scenarios: § Credit § Outside Rework § SOI (Supplier Owned Inventory) § Legacy Receipts § Utilizes standard Quantum shipping process (custom, integration with RTS) § Leverages standard Oracle WO/PO process to capture all relevant inventory consumption, item conversions, labor charges and other variances § Improves A/P debit memo process using the AP Open Invoices API for automatic debit memo creation 20
 QUALCOMM “Virtual” MRB Process Rework: Manually Create Work Order for internal rework items Collection Plans Material Receipt into MRB Inventory Factory receives part, and after inspection (“reject”), transfers NC part to MRB Inventory. • RCV INSP Work Order NC Rework MRB Sub NC part is retuned to MRB Sub-inventory Repair Vendor Inv Move OSP NC part is sent to outsourced repair facility Supplier NC Process Start RTS (Buyer) RTS/RTV ( Credit/ SOI) Disposition “Accept, Sub (SQE) Use as Is” Scrap Part is not salvageable and is scrapped. Hold Scrap RTS Process: Create OM Shipping Lines from Receipt Lines. Key • Master Main • Audit • Detail • Disp Master • Ro. HS-WEES • WFR Master • RTS Master • OSP Master Automated Manual 21
QUALCOMM “Virtual” MRB Process Rework: Manually Create Work Order for internal rework items Collection Plans Material Receipt into MRB Inventory Factory receives part, and after inspection (“reject”), transfers NC part to MRB Inventory. • RCV INSP Work Order NC Rework MRB Sub NC part is retuned to MRB Sub-inventory Repair Vendor Inv Move OSP NC part is sent to outsourced repair facility Supplier NC Process Start RTS (Buyer) RTS/RTV ( Credit/ SOI) Disposition “Accept, Sub (SQE) Use as Is” Scrap Part is not salvageable and is scrapped. Hold Scrap RTS Process: Create OM Shipping Lines from Receipt Lines. Key • Master Main • Audit • Detail • Disp Master • Ro. HS-WEES • WFR Master • RTS Master • OSP Master Automated Manual 21
 Quality Automated Processes (incl. RTS) § Automatic Creation of Sales Orders § Trigger on RTS disposition § Utilize Item set up § “Feed” Shipping documents § Create Vendor address (site) § Automatic E-mail Notification to next Person in Chain § Reports 22
Quality Automated Processes (incl. RTS) § Automatic Creation of Sales Orders § Trigger on RTS disposition § Utilize Item set up § “Feed” Shipping documents § Create Vendor address (site) § Automatic E-mail Notification to next Person in Chain § Reports 22
 LEAN Process Flow “To Be” Model On line Orders Qualcomm Supply Chain Partner SLC ERP Order Mgmt Costing Customer Resp Pack-out Transit Eng Change Mgmt MPS Planning Cde. C Site Kanban/ROP Sizing Health Monitoring Kanban/ROP ERP CM Dist Site #`1 CM Pack -out Kanban/ROP Component Mgmt MRP Planning Contract Manufacturer CM Dist Site #2 23 Transfer FGI to Company Bad Board/ Virtual MRB Process
LEAN Process Flow “To Be” Model On line Orders Qualcomm Supply Chain Partner SLC ERP Order Mgmt Costing Customer Resp Pack-out Transit Eng Change Mgmt MPS Planning Cde. C Site Kanban/ROP Sizing Health Monitoring Kanban/ROP ERP CM Dist Site #`1 CM Pack -out Kanban/ROP Component Mgmt MRP Planning Contract Manufacturer CM Dist Site #2 23 Transfer FGI to Company Bad Board/ Virtual MRB Process
 Conclusion
Conclusion


