6fc37d8f0bd1530d10eb11103500668c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 The Internet: A Resource for All of Us Chapter 8
The Internet: A Resource for All of Us Chapter 8
 Objectives • Briefly describe the history of the Internet • Explain what is needed to get on the Internet • Describe generally what an Internet service provider does • Describe the rudimentary functions of a browser • Describe how to search the Internet • List and describe the non-Web parts of the Internet • Explain some of the ongoing problems associated with the Internet
Objectives • Briefly describe the history of the Internet • Explain what is needed to get on the Internet • Describe generally what an Internet service provider does • Describe the rudimentary functions of a browser • Describe how to search the Internet • List and describe the non-Web parts of the Internet • Explain some of the ongoing problems associated with the Internet
 Contents • • • History of the Internet URL Getting Started Internet Service Provider Browser Support Moving Between Sites Searching the Internet Other Uses of the Internet Issues
Contents • • • History of the Internet URL Getting Started Internet Service Provider Browser Support Moving Between Sites Searching the Internet Other Uses of the Internet Issues
 History of the Internet • Government and Universities over 30 years • Who’s connected today? – – – – Individuals Educational institutions Government Research Medical Businesses Everyone!
History of the Internet • Government and Universities over 30 years • Who’s connected today? – – – – Individuals Educational institutions Government Research Medical Businesses Everyone!
 ARPANet Advanced Research Projects Agency Network • 1969 – US Department of Defense and Rand Corporation • Origins – Cold War – fear that a bomb could demolish computing capabilities – Several computers, geographically dispersed, networked together – Plan – if one computer was disabled, others could carry on using alternative communication routes
ARPANet Advanced Research Projects Agency Network • 1969 – US Department of Defense and Rand Corporation • Origins – Cold War – fear that a bomb could demolish computing capabilities – Several computers, geographically dispersed, networked together – Plan – if one computer was disabled, others could carry on using alternative communication routes
 ARPANet Transmitting the Message • Messages divided into packets • TCP/IP protocol – TCP – does the packeting and reassembling of the message – IP – handles the addressing
ARPANet Transmitting the Message • Messages divided into packets • TCP/IP protocol – TCP – does the packeting and reassembling of the message – IP – handles the addressing
 ARPANet Expands Beyond the Military • Research computers from universities • Defense contractors • Needed technical expertise to work on Internet
ARPANet Expands Beyond the Military • Research computers from universities • Defense contractors • Needed technical expertise to work on Internet
 Tim Berners-Lee • 1990 • Perceived a spider’s web of computers with links from computer to computer • CERN site – Dr. Berners-Lee’s physics laboratory – Birthplace of the World Wide Web • Easy movement due to links – Hypertext – Hyper-region
Tim Berners-Lee • 1990 • Perceived a spider’s web of computers with links from computer to computer • CERN site – Dr. Berners-Lee’s physics laboratory – Birthplace of the World Wide Web • Easy movement due to links – Hypertext – Hyper-region
 Marc Andreessen • 1993 • Created browser software • Mosaic – first browser • Provided attractive images and a graphical interface permitting users to click on pictures as well as text
Marc Andreessen • 1993 • Created browser software • Mosaic – first browser • Provided attractive images and a graphical interface permitting users to click on pictures as well as text
 ARPANet to Internet • TCP/IP software is public domain • Network became more valuable as it embraced other networks • ARPANet disappears
ARPANet to Internet • TCP/IP software is public domain • Network became more valuable as it embraced other networks • ARPANet disappears
 Internet Explosion • Mid 1990 s • Estimate over 333 million users worldwide • Part of our daily lives • Four factors – – TCP/IP standard Ability to link from site to site Ease of use of browser Growth of PC and LANs that can connect
Internet Explosion • Mid 1990 s • Estimate over 333 million users worldwide • Part of our daily lives • Four factors – – TCP/IP standard Ability to link from site to site Ease of use of browser Growth of PC and LANs that can connect
 URL Uniform Resource Locator http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Unique address of a web page or file on the Internet • Case-sensitive
URL Uniform Resource Locator http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Unique address of a web page or file on the Internet • Case-sensitive
 http hypertext transfer protocol http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Protocol – rules • Communication using links
http hypertext transfer protocol http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Protocol – rules • Communication using links
 Domain name http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Address of the ISP • Domain names are registered • Ongoing fee is paid for each domain name
Domain name http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section • Address of the ISP • Domain names are registered • Ongoing fee is paid for each domain name
 Top-level Domain Represent the purpose of the organization of entity. com. gov. edu. org. net May be a two-letter country code
Top-level Domain Represent the purpose of the organization of entity. com. gov. edu. org. net May be a two-letter country code
 Last section http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section Directories and file names that specify a particular web page
Last section http: //domain-name. top-level-domain/last-section Directories and file names that specify a particular web page
 Getting Started • Computer with a modem or NIC • Internet service provider (ISP) • Browser • Related software
Getting Started • Computer with a modem or NIC • Internet service provider (ISP) • Browser • Related software
 Internet Service Provider • Vehicle to access the Internet • Provides – Server computer – Software to connect
Internet Service Provider • Vehicle to access the Internet • Provides – Server computer – Software to connect
 Online service • ISP • Members-only services and information • Simple interface with clickable topics • Parent controls
Online service • ISP • Members-only services and information • Simple interface with clickable topics • Parent controls
 Wireless Internet Access • Supports mobile handheld devices – – Text pagers PDAs Pocket computers Web-enabled cellular phones • Applications – E-mail – Checking weather – Making airline reservations
Wireless Internet Access • Supports mobile handheld devices – – Text pagers PDAs Pocket computers Web-enabled cellular phones • Applications – E-mail – Checking weather – Making airline reservations
 Wireless Internet Access • Need – Account with wireless access provider – Cellular modem card or adapter • Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) – Convert web pages into format for mobile devices – Resized for limited display area – Fewer graphics transmitted • Slow download speeds
Wireless Internet Access • Need – Account with wireless access provider – Cellular modem card or adapter • Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) – Convert web pages into format for mobile devices – Resized for limited display area – Fewer graphics transmitted • Slow download speeds
 Browser Netscape Communicator Microsoft Internet Explorer
Browser Netscape Communicator Microsoft Internet Explorer
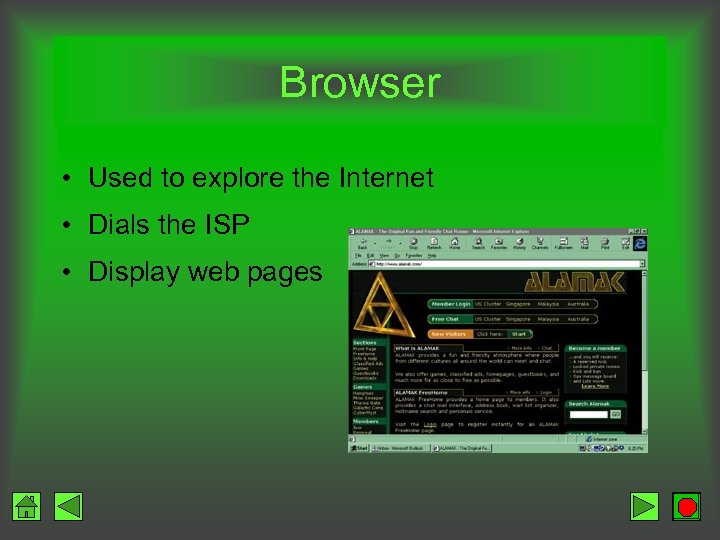 Browser • Used to explore the Internet • Dials the ISP • Display web pages
Browser • Used to explore the Internet • Dials the ISP • Display web pages
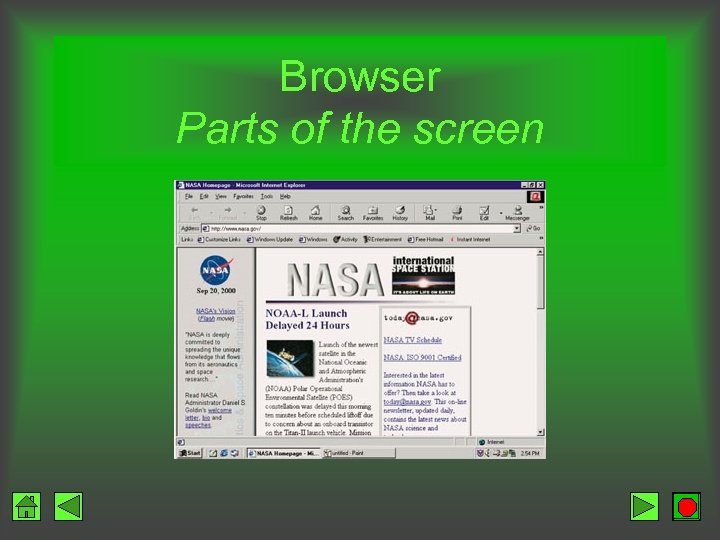 Browser Parts of the screen
Browser Parts of the screen
 Browser Functions and Features • Browser display window – Displays contents of web page from each Internet site visited – Screen limits how much of the site you can view at a time. The page can be scrolled using the scroll bar to see its entire contents • Status line – progress of data being transferred and other messages
Browser Functions and Features • Browser display window – Displays contents of web page from each Internet site visited – Screen limits how much of the site you can view at a time. The page can be scrolled using the scroll bar to see its entire contents • Status line – progress of data being transferred and other messages
 Browser Functions and Features • Welcome banner on title bar • Browser logo – animation indicates you are in the process of moving to a new site • Hot list – Bookmark – Favorites – Store your favorite URLs • Browser control panel – menus and buttons
Browser Functions and Features • Welcome banner on title bar • Browser logo – animation indicates you are in the process of moving to a new site • Hot list – Bookmark – Favorites – Store your favorite URLs • Browser control panel – menus and buttons
 Browser Menus and Buttons • Pull-down menu • Buttons – Convenient shortcuts for commonly used functions – Click button rather than locate command from pull-down menu
Browser Menus and Buttons • Pull-down menu • Buttons – Convenient shortcuts for commonly used functions – Click button rather than locate command from pull-down menu
 Browser Support Frames • Divides page into rectangular sections • Each section displays web pages independently • Several small pages on one screen – Can be scrolled independently – Can be replaced with other pages independently
Browser Support Frames • Divides page into rectangular sections • Each section displays web pages independently • Several small pages on one screen – Can be scrolled independently – Can be replaced with other pages independently
 Plug-ins • Software that increases the functionality of a browser – Audio-video – Image viewing • Download from web sites • Install • Example – Adobe Acrobat Reader – Shockwave
Plug-ins • Software that increases the functionality of a browser – Audio-video – Image viewing • Download from web sites • Install • Example – Adobe Acrobat Reader – Shockwave
 Programming Java • Write software that is machine independent • Programming language – – Dancing icons Sound clips Flashing messages Banners that scroll • Applets – Permits dynamic web pages – Display animations – Receive input – Perform calculations
Programming Java • Write software that is machine independent • Programming language – – Dancing icons Sound clips Flashing messages Banners that scroll • Applets – Permits dynamic web pages – Display animations – Receive input – Perform calculations
 Programming Active. X Controls Capabilities similar to Java Browser must be enabled to support applets / Active. X Controls Security issues
Programming Active. X Controls Capabilities similar to Java Browser must be enabled to support applets / Active. X Controls Security issues
 Moving Between Sites • Clickable categories in the browser – Sports – Weather – News – Technology – Comic strips • Enter the URL in the address text box and press
Moving Between Sites • Clickable categories in the browser – Sports – Weather – News – Technology – Comic strips • Enter the URL in the address text box and press
 Processing Requests URL • User enters a URL • User computer sends request to the ISP server • ISP server sends request across networks of TCP/IP computers • Destination site is reached • Content is transmitted back to your computer (process in reverse)
Processing Requests URL • User enters a URL • User computer sends request to the ISP server • ISP server sends request across networks of TCP/IP computers • Destination site is reached • Content is transmitted back to your computer (process in reverse)
 Searching the Internet Search engine • User specifies a search request • Browser links to Search Engine • Request returns matching pages based upon the Search Engine’s database • Results presented
Searching the Internet Search engine • User specifies a search request • Browser links to Search Engine • Request returns matching pages based upon the Search Engine’s database • Results presented
 Processing Requests Search Engine Database • Search Engine builds database – Searchable terms – Related web sites • Spider, robot, bot – Follows links across the web – Automatically indexes pages to a database • One word • All words • Pages may be submitted by the owner
Processing Requests Search Engine Database • Search Engine builds database – Searchable terms – Related web sites • Spider, robot, bot – Follows links across the web – Automatically indexes pages to a database • One word • All words • Pages may be submitted by the owner
 Processing Requests Search Engine Database • Request same search using different engines yields different results • Databases built independently – Size – Content – Search methodology • Metasearch – atomically puts the same request to several search engines
Processing Requests Search Engine Database • Request same search using different engines yields different results • Databases built independently – Size – Content – Search methodology • Metasearch – atomically puts the same request to several search engines
 Processing Requests Directory vs. Search Engine • Directory – – Human involvement Sites organized by content category May concentrate on specific content areas Subjective decisions regarding inclusion and importance • Search Engine – Spider, robot, or bot automatically builds database – Index on a few keywords – Index on all words on web page
Processing Requests Directory vs. Search Engine • Directory – – Human involvement Sites organized by content category May concentrate on specific content areas Subjective decisions regarding inclusion and importance • Search Engine – Spider, robot, or bot automatically builds database – Index on a few keywords – Index on all words on web page
 Processing Requests Search Engine Limitations • Index only a fraction of the Web • Approximately 20% to 33% of sites • More web pages added daily • Solution – Same request to several search engines – Metasearch
Processing Requests Search Engine Limitations • Index only a fraction of the Web • Approximately 20% to 33% of sites • More web pages added daily • Solution – Same request to several search engines – Metasearch
 Search Tools Directories Search Engines • Yahoo! • Alta. Vista • Net. Guide • Excite • Google Metasearch Sites • Hot. Bot • Meta. Crawler • Infoseek • Dogpile • Lycos • Northern Light
Search Tools Directories Search Engines • Yahoo! • Alta. Vista • Net. Guide • Excite • Google Metasearch Sites • Hot. Bot • Meta. Crawler • Infoseek • Dogpile • Lycos • Northern Light
 Refine the Search • Add words • Enclose words in “quotes” • Use Boolean logic • Examples – “World Trade Center” – Jordan AND NOT Michael
Refine the Search • Add words • Enclose words in “quotes” • Use Boolean logic • Examples – “World Trade Center” – Jordan AND NOT Michael
 Other Uses of the Internet • Newsgroups • FTP • Telnet • E-mail • Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
Other Uses of the Internet • Newsgroups • FTP • Telnet • E-mail • Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
 Newsgroups / Usenet • Large bulletin board divided by category • Posting and reading of messages that focus on specific topics • Over 20, 000 newsgroups • Functions – Conversation – File download • Newsreader software required (included with most browsers)
Newsgroups / Usenet • Large bulletin board divided by category • Posting and reading of messages that focus on specific topics • Over 20, 000 newsgroups • Functions – Conversation – File download • Newsreader software required (included with most browsers)
 Newsgroup Operations • Lurking • Posting material – Inappropriate material • Flame war – Moderated newsgroup
Newsgroup Operations • Lurking • Posting material – Inappropriate material • Flame war – Moderated newsgroup
 FTP File Transfer Protocol • Download files to your local computer • Upload files to another computer • Requirements to download file – Permission to download from a site – File is available for copying • Anonymous FTP – do not need to identify yourself to the remote computer
FTP File Transfer Protocol • Download files to your local computer • Upload files to another computer • Requirements to download file – Permission to download from a site – File is available for copying • Anonymous FTP – do not need to identify yourself to the remote computer
 Public Archives Free files provided by educational institution or the government
Public Archives Free files provided by educational institution or the government
 Telnet • Use your PC as a terminal providing remote access to another computer • Permits – Log on to a host – Use as if you are sitting at a local terminal • Need account on the host system • Telnet software required (provided with most browsers)
Telnet • Use your PC as a terminal providing remote access to another computer • Permits – Log on to a host – Use as if you are sitting at a local terminal • Need account on the host system • Telnet software required (provided with most browsers)
 e-mail • Send/receive written messages • Most used feature of the Internet • Mail server – Collects and stores e-mail • Mailbox – Assigned to each user • E-mail address – User name – @ – Domain of the mail server
e-mail • Send/receive written messages • Most used feature of the Internet • Mail server – Collects and stores e-mail • Mailbox – Assigned to each user • E-mail address – User name – @ – Domain of the mail server
 e-mail Client Software Functions Retrieve Print Create Delete Send Address book Store Attach files Filters
e-mail Client Software Functions Retrieve Print Create Delete Send Address book Store Attach files Filters
 IRC Internet Relay Chat
IRC Internet Relay Chat
 Not Quite Perfect Yet • Unregulated • Useless web sites • Misinformation and misstatements on web sites • Concern over government censorship
Not Quite Perfect Yet • Unregulated • Useless web sites • Misinformation and misstatements on web sites • Concern over government censorship
 Not Quite Perfect Yet Social Issues • Behavior problems – Who is out there? – What are they doing? • Netiquette – Suggestions for appropriate behavior – Example: TYPING IN CAPS is shouting
Not Quite Perfect Yet Social Issues • Behavior problems – Who is out there? – What are they doing? • Netiquette – Suggestions for appropriate behavior – Example: TYPING IN CAPS is shouting



