Alfa_Bank_presentation.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 15

The internationalization of Alfa Bank The Netherlands case Victoria Eliseeva Maria Navalikhina Daria Plotnikova Elena Kruglyakova Caroline Ringauf José Pedro Luxo Maia

Agenda • Company profile – Main data – History • Banking industry overview: 5 forces • Internationalization of Russian banks – Theoretical background – Main patterns & trends • Internationalization of Alfa Bank • The Netherlands case • Recommendations 2

Company Profile Alfa Bank at a glance • Largest private bank in Russia • Headquartered in Moscow • Main activities: Retail Banking, Corporate Banking, Investment Banking • Belongs to Alfa Group (one of Russia‘s largest privately owned investment groups) • 460 offices • 7 countries • 18, 000 employees Financial performance 2011 Net income $ 641 million Total assets $ 31, 365 billion Total equity $ 3, 435 billion • OJSC; ultimately owned by 6 shareholders 3
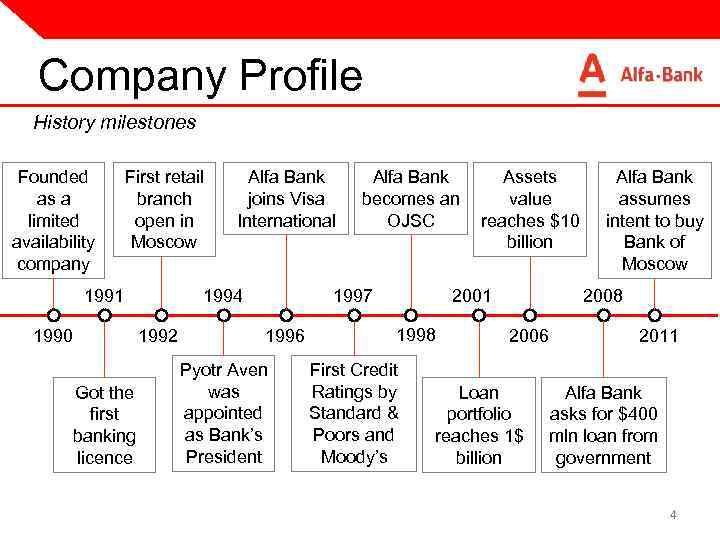
Company Profile History milestones Founded as a limited availability company First retail branch open in Moscow 1991 1990 1994 1992 Got the first banking licence Alfa Bank joins Visa International Alfa Bank becomes an OJSC 1997 1996 Pyotr Aven was appointed as Bank’s President Assets value reaches $10 billion 2001 1998 First Credit Ratings by Standard & Poors and Moody’s Alfa Bank assumes intent to buy Bank of Moscow 2008 2006 Loan portfolio reaches 1$ billion 2011 Alfa Bank asks for $400 mln loan from government 4

Banking Industry analysis: 5 forces Intensity of competitive rivalry We need to analyze the saturation particularly in Russia taking into account the general level of economic development. Number of banks 10000 5000 0 Russia USA EU China Brazil Intensive rivalry in the sector, Number of participants is excessive Market share of major banks in Russia Dominating state-owned banks: Sberbank and VTB Leading competitors: Unicredit, VTB 24, Alfa. Bank, RAB, Bank of Moscow and Gazprombank 5

Banking Industry analysis: 5 forces Bargaining power of suppliers • High differentiation of channels decreases possible risks and provides diverse sources of inputs with different conditions. • 59, 7% of funds is generated from personal, legal entity’s and organizational accounts – influenced by market and competitors • . Additional financial activities (issuing bonds) or partnership with third parties (with Central Bank and funds) – more predictable Bargaining power of customers • Credits and loans accounts for 68, 7% of all assets. • Banks are highly depended on customers’ expectations and level of consumption • Bargaining power of customers is not significant enough as it is mostly bank’s priority to choose or reject clients in the end 6

Banking Industry analysis: 5 forces Threat of substitutes Emergence of substitute products that could compete with existing is hardly possible due to complex legal regulation But, there are exceptions! Threat of new entrants • High entry barriers • Legal procedure is complex and time consuming + bureaucracy • To open a bank you need: 9 documents and 300 million rubles Universal Electronic Card 87 banks were opened during 2000 -2012. 25 banks stopped their activities in 2012 Very poor dynamic of new banks emergence Near Field Communication (NFC) • Existence of non-banking financial institutions 62 NBFI operate in Russia 6 of them emerged in 2012, Yandex. Money, Dengi. Mail. ru, Delta. Kei 7
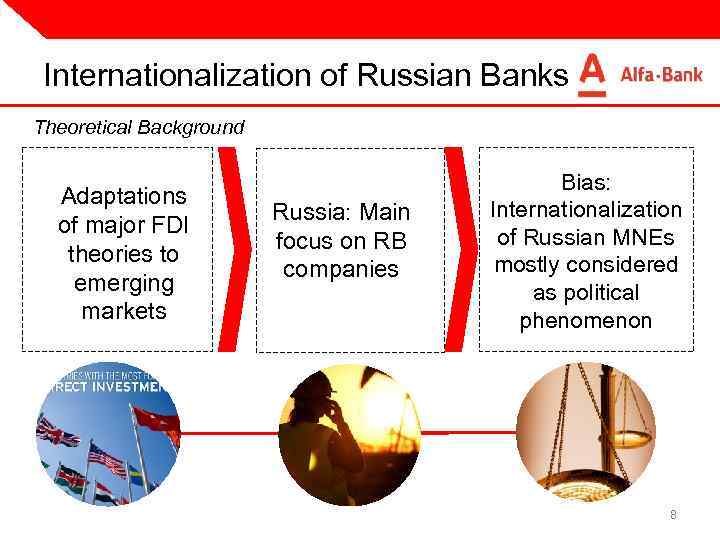
Internationalization of Russian Banks Theoretical Background Adaptations of major FDI theories to emerging markets Russia: Main focus on RB companies Bias: Internationalization of Russian MNEs mostly considered as political phenomenon 8

Internationalization of Russian Banks Theoretical Background: Main Implications Strategy of organic growth differs from RB companies In contrast to RB companies, can’t use export as an entry mode Don’t merely follow parent RB company, open subsidiaries 9
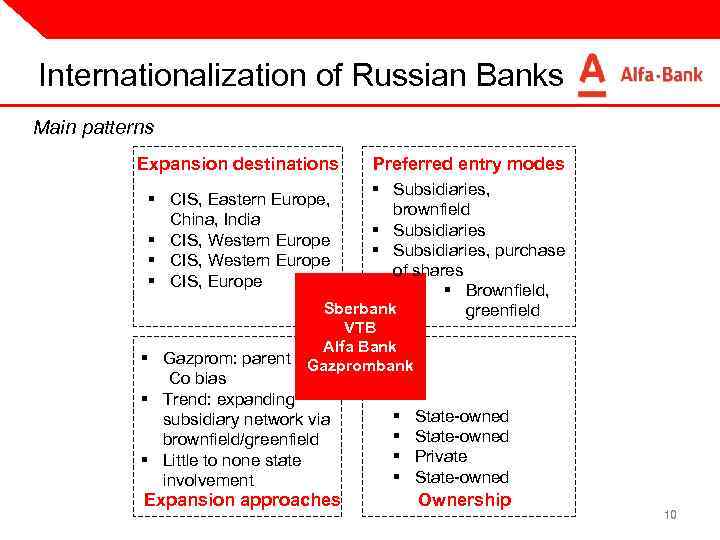
Internationalization of Russian Banks Main patterns Expansion destinations § CIS, Eastern Europe, China, India § CIS, Western Europe § CIS, Europe Preferred entry modes § Subsidiaries, brownfield § Subsidiaries, purchase of shares § Brownfield, Sberbank greenfield VTB Alfa Bank Gazprombank § Gazprom: parent Co bias § Trend: expanding subsidiary network via brownfield/greenfield § Little to none state involvement Expansion approaches § § State-owned Private State-owned Ownership 10

Internationalization of Alfa Bank The CIS The UK The US, Cyprus Netherlands KAZ – 1994, Year of entry Bel – 1999, 2000 1994 Ukr – 2001 Greenfield & Greenfield Brownfield Entry Brownfield investment: strategy investment representative office acquisition Full-service Equity and Russia-related and bank working Main investment project finance + with individual activities operations; only retail banking and corporate banking since 2003 clients Expertise in Emerging Expertise in securities Competitive markets export/import advantage transactions, LSE expertise finance knowledge 2001, 2005 Wholly-owned subsidiary: representative office Brokerage services and investment services Full range of most up -to date investment products 11
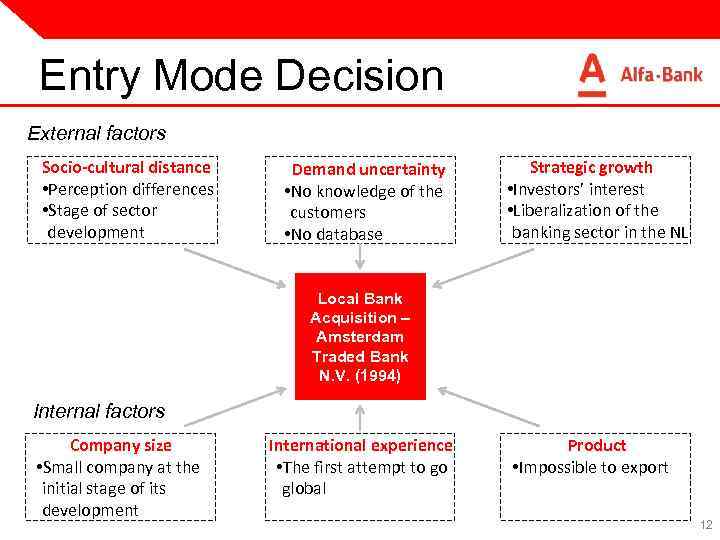
Entry Mode Decision External factors Socio-cultural distance • Perception differences • Stage of sector development Demand uncertainty • No knowledge of the customers • No database Strategic growth • Investors’ interest • Liberalization of the banking sector in the NL Local Bank Acquisition – Amsterdam Traded Bank N. V. (1994) Internal factors Company size • Small company at the initial stage of its development International experience • The first attempt to go global Product • Impossible to export 12
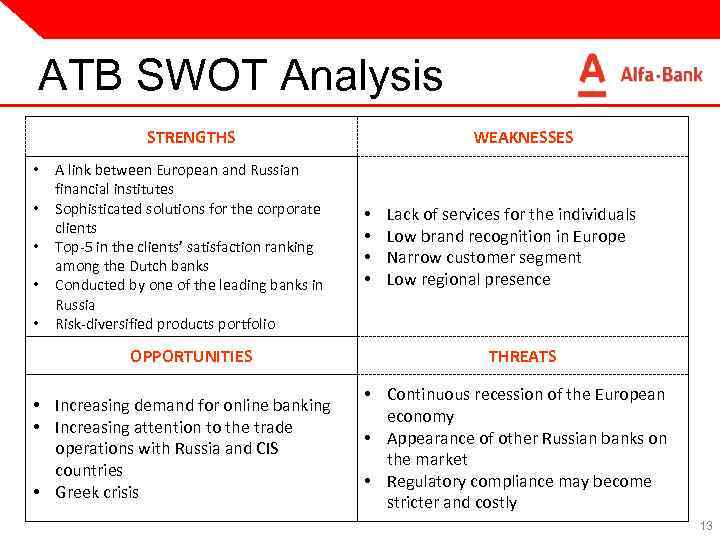
ATB SWOT Analysis STRENGTHS • • • A link between European and Russian financial institutes Sophisticated solutions for the corporate clients Top-5 in the clients’ satisfaction ranking among the Dutch banks Conducted by one of the leading banks in Russia Risk-diversified products portfolio OPPORTUNITIES • Increasing demand for online banking • Increasing attention to the trade operations with Russia and CIS countries • Greek crisis WEAKNESSES • • Lack of services for the individuals Low brand recognition in Europe Narrow customer segment Low regional presence THREATS • Continuous recession of the European economy • Appearance of other Russian banks on the market • Regulatory compliance may become stricter and costly 13

Recommendations 1. 2. 3. 4. Private individuals focus Online banking Brand recognition Regional presence 14

Thank you for your time 15
Alfa_Bank_presentation.pptx