633a2f5a482aa68c28e728e53c3f6eee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 The International Pharmacopoeia Overview Caroline Mendy Technical Officer - Quality Assurance and Safety: Medicines Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia Overview Caroline Mendy Technical Officer - Quality Assurance and Safety: Medicines Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia – Ph. Int l Scope l WHO Consultative procedure l 4 th Edition l APIs monographs features l What's new 2 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia – Ph. Int l Scope l WHO Consultative procedure l 4 th Edition l APIs monographs features l What's new 2 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Pharmacopoeias may be: l National e. g. Brazilian, British, Chinese, Indian, Japanese, Mexican, Spanish, United States l Regional e. g. European l International The International Pharmacopoeia 3 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Pharmacopoeias may be: l National e. g. Brazilian, British, Chinese, Indian, Japanese, Mexican, Spanish, United States l Regional e. g. European l International The International Pharmacopoeia 3 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Pharmacopoeias National and regional pharmacopoeias l Cover medicines used in the relevant country or region l Are legally binding "official" in the relevant country or region l Are prepared by a national or regional authority 4 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Pharmacopoeias National and regional pharmacopoeias l Cover medicines used in the relevant country or region l Are legally binding "official" in the relevant country or region l Are prepared by a national or regional authority 4 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia A few dates… The history of the International Pharmacopoeia dates back 1874… ® 1948 First World Health Assembly established Expert Committee on Unification of Pharmacopoeia ® 1950 WHA approved publication of Pharmacopoeia Internationalis (Ph. Int) 5 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia A few dates… The history of the International Pharmacopoeia dates back 1874… ® 1948 First World Health Assembly established Expert Committee on Unification of Pharmacopoeia ® 1950 WHA approved publication of Pharmacopoeia Internationalis (Ph. Int) 5 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia A collection of monographs and requirements for: ® Drug substances ® Excipients ® Finished dosage forms ® General methods and requirements: ® dosage forms, e. g. tablets, liquid preparation for oral use ® dissolution testing ® Supplementary information, e. g. General guidelines for Chemical Reference Substances ® Infrared reference spectra 6 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia A collection of monographs and requirements for: ® Drug substances ® Excipients ® Finished dosage forms ® General methods and requirements: ® dosage forms, e. g. tablets, liquid preparation for oral use ® dissolution testing ® Supplementary information, e. g. General guidelines for Chemical Reference Substances ® Infrared reference spectra 6 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia Scope since 1975 ® Model Lists of Essential Medicines Essential medicines are selected with due regard to disease prevalence, evidence on efficacy and safety, and comparative -effectiveness. cost ® Medicines recommended and specifications needed by WHO Programmes e. g. treatment guidelines for Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS and for children! 7 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia Scope since 1975 ® Model Lists of Essential Medicines Essential medicines are selected with due regard to disease prevalence, evidence on efficacy and safety, and comparative -effectiveness. cost ® Medicines recommended and specifications needed by WHO Programmes e. g. treatment guidelines for Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS and for children! 7 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia ® implementation: “ready for use” by Member States "The Ph. Int [… ] is intended to serve as source material for reference or adaptation by any WHO Member State wishing to establish pharmaceutical requirements. The pharmacopoeia, or any part of it, shall have legal status, whenever a national or regional authority expressly introduces it into appropriate legislation. " [Reference to World Health Assembly resolution WHA 3. 10, WHO Handbook of Resolutions and Decisions, Vol. 1, 1977, p. 127] 8 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia ® implementation: “ready for use” by Member States "The Ph. Int [… ] is intended to serve as source material for reference or adaptation by any WHO Member State wishing to establish pharmaceutical requirements. The pharmacopoeia, or any part of it, shall have legal status, whenever a national or regional authority expressly introduces it into appropriate legislation. " [Reference to World Health Assembly resolution WHA 3. 10, WHO Handbook of Resolutions and Decisions, Vol. 1, 1977, p. 127] 8 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 How does the Ph. Int function? l The Ph. Int is based on the work and decisions of the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations l Aim over the last 60 years: "to promote quality assurance and quality control of pharmaceuticals" 9 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
How does the Ph. Int function? l The Ph. Int is based on the work and decisions of the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations l Aim over the last 60 years: "to promote quality assurance and quality control of pharmaceuticals" 9 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 What is the WHO Expert Committee? l Official Advisory Body to Director-General of WHO l Governed through rules and procedures (Ref. WHO Manual) l Participation to Expert Committee (EC) meetings: – Voting members ("Experts") selected from WHO Panel of Experts – Technical advisers – Observers: - international organizations, - NGOs, - professional associations… 10 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
What is the WHO Expert Committee? l Official Advisory Body to Director-General of WHO l Governed through rules and procedures (Ref. WHO Manual) l Participation to Expert Committee (EC) meetings: – Voting members ("Experts") selected from WHO Panel of Experts – Technical advisers – Observers: - international organizations, - NGOs, - professional associations… 10 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Outcome of the WHO Expert Committee? l Report of this WHO Expert Committee • Summarizes discussion • Gives recommendations to WHO + Member States • Includes newly adopted guidelines; • Is presented to WHO Governing Bodies for final comments, endorsement and implementation by Member States l constitutes WHO technical guidance 11 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Outcome of the WHO Expert Committee? l Report of this WHO Expert Committee • Summarizes discussion • Gives recommendations to WHO + Member States • Includes newly adopted guidelines; • Is presented to WHO Governing Bodies for final comments, endorsement and implementation by Member States l constitutes WHO technical guidance 11 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO does the work … with Partners (1) l National/Regional regulatory authorities and quality control laboratories l Regional/Interregional regulatory groups (ASEAN, ICH. . . ) l International organizations (UNAIDS, UNICEF, World Bank…) l International professional and other associations, NGOs (incl. industry, consumer associations: IFPMA-IGPA-WSMI, IPEC, FIP, WMA, MSF…) 12 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO does the work … with Partners (1) l National/Regional regulatory authorities and quality control laboratories l Regional/Interregional regulatory groups (ASEAN, ICH. . . ) l International organizations (UNAIDS, UNICEF, World Bank…) l International professional and other associations, NGOs (incl. industry, consumer associations: IFPMA-IGPA-WSMI, IPEC, FIP, WMA, MSF…) 12 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO does the work … with Partners (2) l Pharmacopoeia Commissions and Secretariats (e. g. Brazilian, BP, IP, JP, Ph. Eur, Ch. P, USP, and PDG ) l WHO Expert Panel on The International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations (official nomination process) l WHO Collaborating Centres (official nomination process) l Specialists from all areas (regulatory, university, industry…) 13 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO does the work … with Partners (2) l Pharmacopoeia Commissions and Secretariats (e. g. Brazilian, BP, IP, JP, Ph. Eur, Ch. P, USP, and PDG ) l WHO Expert Panel on The International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations (official nomination process) l WHO Collaborating Centres (official nomination process) l Specialists from all areas (regulatory, university, industry…) 13 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO Consultative procedure l This process is designed to ensure wide consultation and transparency during monograph development and to make the adopted texts available in a timely manner. 14 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO Consultative procedure l This process is designed to ensure wide consultation and transparency during monograph development and to make the adopted texts available in a timely manner. 14 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (1) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 1: Identification of specific pharmaceutical products for which Quality Control (QC) specifications need to be developed, confirmation by all WHO parties concerned (including Department of Essential Medicines and Pharmaceutical Policies (EMP) specific disease programmes and the Prequalification Programme) l Step 2*: Provision of contact details from manufacturers of the above products in collaboration with all parties concerned l Step 3*: Contact manufacturers for provision of QC specifications and samples l Step 4: Identify and contact QC laboratories for collaboration in the project (2 -3 laboratories depending on how many pharmaceutical products have been identified in step 1), Contract for laboratory work 15 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (1) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 1: Identification of specific pharmaceutical products for which Quality Control (QC) specifications need to be developed, confirmation by all WHO parties concerned (including Department of Essential Medicines and Pharmaceutical Policies (EMP) specific disease programmes and the Prequalification Programme) l Step 2*: Provision of contact details from manufacturers of the above products in collaboration with all parties concerned l Step 3*: Contact manufacturers for provision of QC specifications and samples l Step 4: Identify and contact QC laboratories for collaboration in the project (2 -3 laboratories depending on how many pharmaceutical products have been identified in step 1), Contract for laboratory work 15 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (2) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 5: Prepare the contract for drafting the specifications and undertaking the necessary laboratory work l Step 6: Search for information on QC specifications available in the public domain l Step 7: Laboratory testing, development and validation of QC Specifications l Step 8: Support WHO Collaborating Centre in the establishment of International Chemical Reference Substances l Step 9: Follow the consultative process, mailing of draft specifications to Expert Panel and specialists 16 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (2) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 5: Prepare the contract for drafting the specifications and undertaking the necessary laboratory work l Step 6: Search for information on QC specifications available in the public domain l Step 7: Laboratory testing, development and validation of QC Specifications l Step 8: Support WHO Collaborating Centre in the establishment of International Chemical Reference Substances l Step 9: Follow the consultative process, mailing of draft specifications to Expert Panel and specialists 16 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (3) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 10: Discussion of comments with contract laboratories, WHO Collaborating Centres, additional laboratory testing to verify and/or validate specifications l Step 11: Consultation to discuss the comments and test results received as feedback l Step 12: recirculation for comments l Step 13: as step 10 l Step 14: Present the drafts to the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations for possible formal adoption, … if not adopted repetition of steps 11 to 13 as often as necessary 17 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (3) …. . or why it takes so long…. l Step 10: Discussion of comments with contract laboratories, WHO Collaborating Centres, additional laboratory testing to verify and/or validate specifications l Step 11: Consultation to discuss the comments and test results received as feedback l Step 12: recirculation for comments l Step 13: as step 10 l Step 14: Present the drafts to the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations for possible formal adoption, … if not adopted repetition of steps 11 to 13 as often as necessary 17 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (4) …. . or why it takes so long…. … If adopted proceed to step 15 l Step 15: Incorporate all changes agreed during the discussion leading to adoption together with any editorial points. Where necessary, also take account of any further comments that may still be received due to comment deadlines for recirculated texts (Step 12 and beyond) falling shortly after the meeting. l Step 16: In all cases, confirm the amended text by correspondence with the relevant experts and/or contract laboratory before making it available on the WHO Medicines website. l Step 17: Make "final texts" available on the Medicines website to provide users such as PQ assessors and manufacturers with the approved specifications in advance of the next publication date. 18 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO Procedure for the preparation of drug Quality Control specifications (4) …. . or why it takes so long…. … If adopted proceed to step 15 l Step 15: Incorporate all changes agreed during the discussion leading to adoption together with any editorial points. Where necessary, also take account of any further comments that may still be received due to comment deadlines for recirculated texts (Step 12 and beyond) falling shortly after the meeting. l Step 16: In all cases, confirm the amended text by correspondence with the relevant experts and/or contract laboratory before making it available on the WHO Medicines website. l Step 17: Make "final texts" available on the Medicines website to provide users such as PQ assessors and manufacturers with the approved specifications in advance of the next publication date. 18 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Manufacturer's involvement Dialogue from the early stages of development of the draft monograph to the final text… l Samples, Reference material l Documentation l Discussion on analytical issues when relevant l Comments on draft(s) 19 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Manufacturer's involvement Dialogue from the early stages of development of the draft monograph to the final text… l Samples, Reference material l Documentation l Discussion on analytical issues when relevant l Comments on draft(s) 19 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
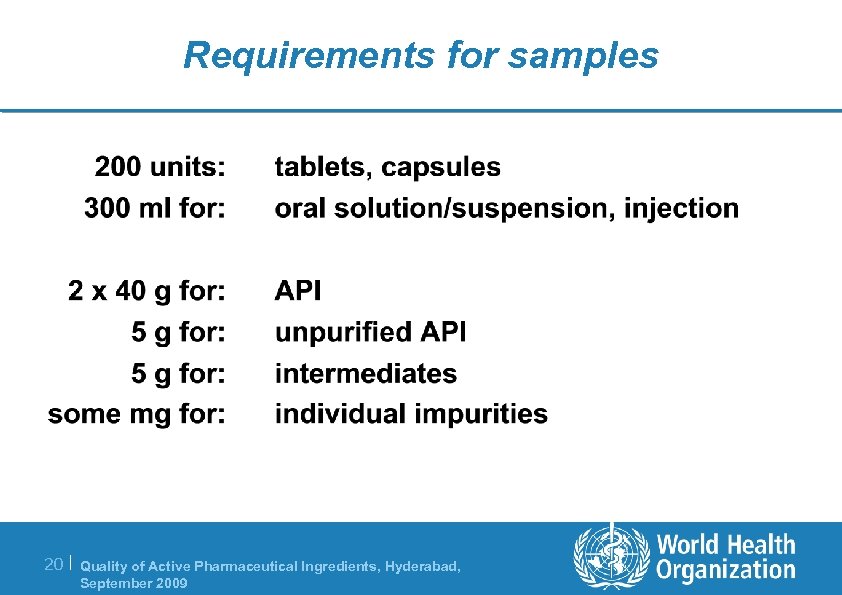 Requirements for samples 20 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Requirements for samples 20 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Requirements for specifications (1) Manufacturer's documentation is kept confidential l Description, Chemistry, Solubility, Storage, Labelling l Definition, with information on polymorphism if relevant l Identification l Assay l Specific tests (sulfated ash, optical rotation, loss on drying…) l Related substances 21 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Requirements for specifications (1) Manufacturer's documentation is kept confidential l Description, Chemistry, Solubility, Storage, Labelling l Definition, with information on polymorphism if relevant l Identification l Assay l Specific tests (sulfated ash, optical rotation, loss on drying…) l Related substances 21 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
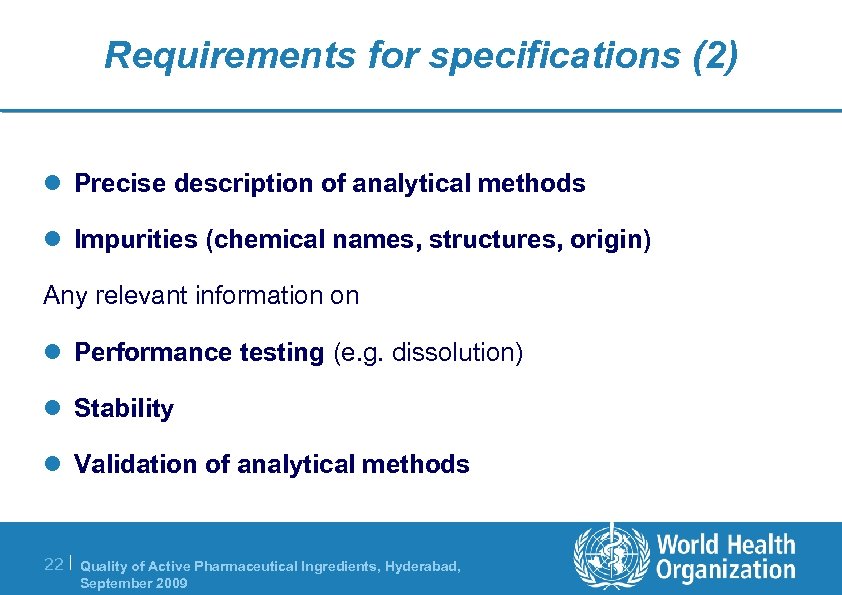 Requirements for specifications (2) l Precise description of analytical methods l Impurities (chemical names, structures, origin) Any relevant information on l Performance testing (e. g. dissolution) l Stability l Validation of analytical methods 22 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Requirements for specifications (2) l Precise description of analytical methods l Impurities (chemical names, structures, origin) Any relevant information on l Performance testing (e. g. dissolution) l Stability l Validation of analytical methods 22 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Comments on drafts Different possible channels to communicate with the Secretariat as comments may be received l directly from the manufacturers l via the international manufacturers associations (opportunity is then given to other manufacturers to comment on drafts) ex: list of impurities, Manufacture section… 23 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Comments on drafts Different possible channels to communicate with the Secretariat as comments may be received l directly from the manufacturers l via the international manufacturers associations (opportunity is then given to other manufacturers to comment on drafts) ex: list of impurities, Manufacture section… 23 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 24 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
24 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia ®current: 4 th Edition + 1 st Supplement ® Consolidated in : 2 Volumes - Vol. 1: pharmaceutical substances (A-O) - Vol. 2: pharmaceutical substances (P-X) + dosage forms + radiopharmaceuticals + methods of analysis + reagents 1 st Supplement - new requirements and revisions Available in Publication, CD-ROM and Online http: //www. who. int/medicines/publications/pharmacopoeia/overview/ 25 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia ®current: 4 th Edition + 1 st Supplement ® Consolidated in : 2 Volumes - Vol. 1: pharmaceutical substances (A-O) - Vol. 2: pharmaceutical substances (P-X) + dosage forms + radiopharmaceuticals + methods of analysis + reagents 1 st Supplement - new requirements and revisions Available in Publication, CD-ROM and Online http: //www. who. int/medicines/publications/pharmacopoeia/overview/ 25 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 4 th Edition – (1) 4 th Edition ®Monographs on antiretrovirals (ARVs) ®Revision of existing monographs ®Improved presentation ®Improved cross-referencing to general methods ®Improved search functions for CD-ROM and online version ®New notice on "manufacture" ®New notice on impurities ®New list of impurities shown to be controlled by tests 26 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
4 th Edition – (1) 4 th Edition ®Monographs on antiretrovirals (ARVs) ®Revision of existing monographs ®Improved presentation ®Improved cross-referencing to general methods ®Improved search functions for CD-ROM and online version ®New notice on "manufacture" ®New notice on impurities ®New list of impurities shown to be controlled by tests 26 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 4 th Edition (2) First Supplement ®About 30 new monographs for medicines for HIV/AIDS, TB and Malaria, including some for children ®Revisions, 125 IR reference spectra, supplementary info 27 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
4 th Edition (2) First Supplement ®About 30 new monographs for medicines for HIV/AIDS, TB and Malaria, including some for children ®Revisions, 125 IR reference spectra, supplementary info 27 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
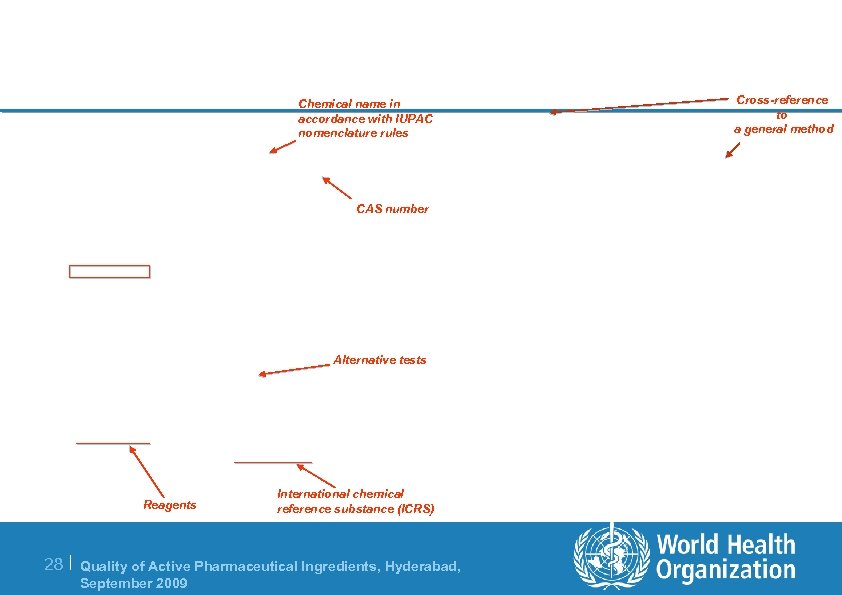 Chemical name in accordance with IUPAC nomenclature rules CAS number Alternative tests Reagents International chemical reference substance (ICRS) 28 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 Cross-reference to a general method
Chemical name in accordance with IUPAC nomenclature rules CAS number Alternative tests Reagents International chemical reference substance (ICRS) 28 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 Cross-reference to a general method
 List of known and potential impurities that have been shown to be controlled by this monograph 29 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
List of known and potential impurities that have been shown to be controlled by this monograph 29 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
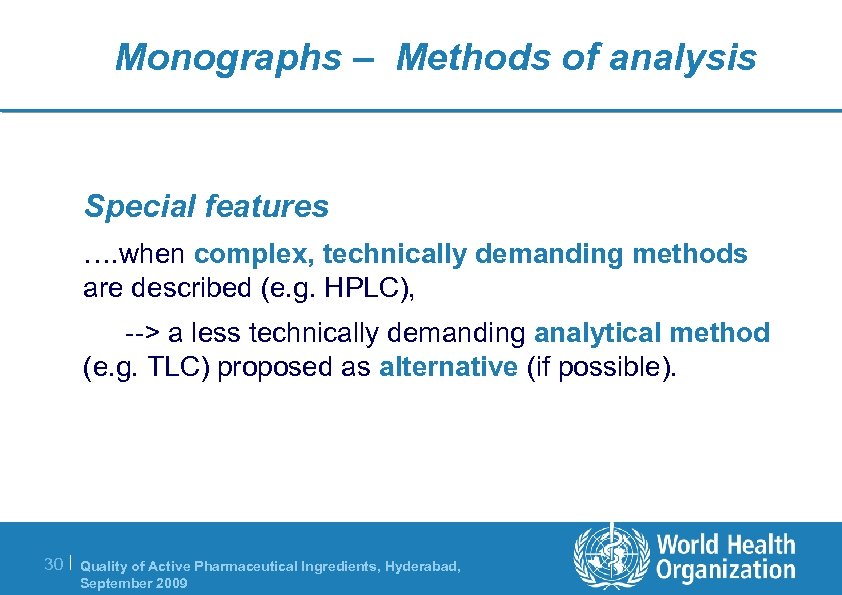 Monographs – Methods of analysis Special features …. when complex, technically demanding methods are described (e. g. HPLC), --> a less technically demanding analytical method (e. g. TLC) proposed as alternative (if possible). 30 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Monographs – Methods of analysis Special features …. when complex, technically demanding methods are described (e. g. HPLC), --> a less technically demanding analytical method (e. g. TLC) proposed as alternative (if possible). 30 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
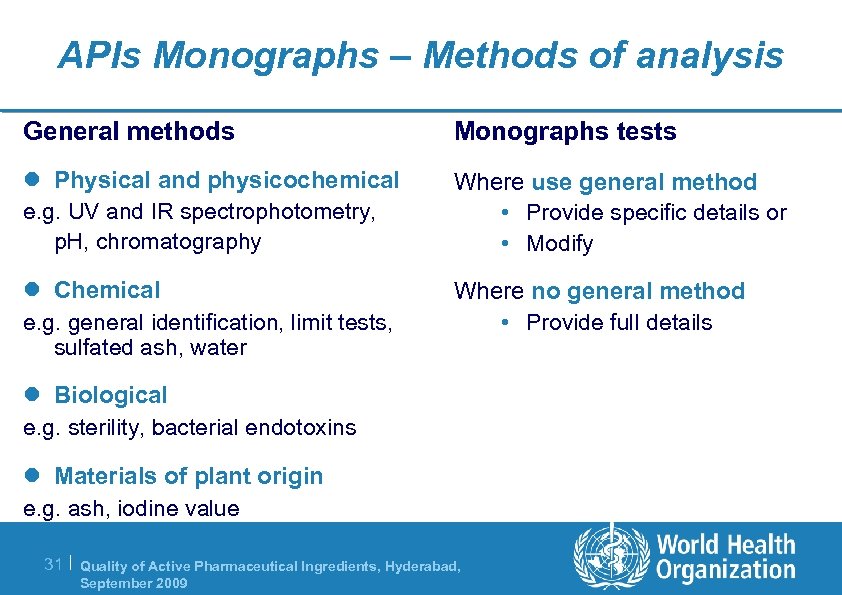 APIs Monographs – Methods of analysis General methods Monographs tests l Physical and physicochemical Where use general method • Provide specific details or • Modify e. g. UV and IR spectrophotometry, p. H, chromatography l Chemical e. g. general identification, limit tests, sulfated ash, water Where no general method • Provide full details l Biological e. g. sterility, bacterial endotoxins l Materials of plant origin e. g. ash, iodine value 31 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Methods of analysis General methods Monographs tests l Physical and physicochemical Where use general method • Provide specific details or • Modify e. g. UV and IR spectrophotometry, p. H, chromatography l Chemical e. g. general identification, limit tests, sulfated ash, water Where no general method • Provide full details l Biological e. g. sterility, bacterial endotoxins l Materials of plant origin e. g. ash, iodine value 31 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
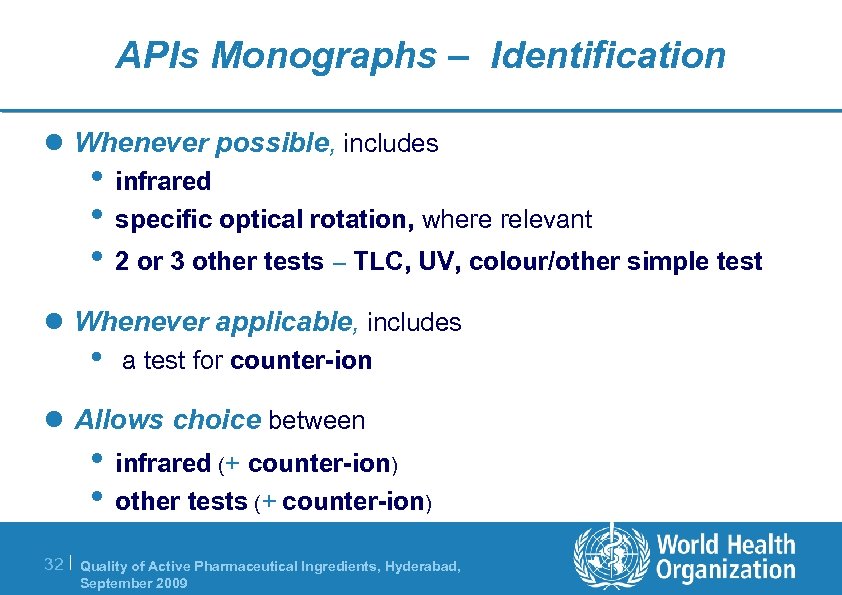 APIs Monographs – Identification l Whenever possible, includes • infrared • specific optical rotation, where relevant • 2 or 3 other tests – TLC, UV, colour/other simple test l Whenever applicable, includes • a test for counter-ion l Allows choice between • infrared (+ counter-ion) • other tests (+ counter-ion) 32 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Identification l Whenever possible, includes • infrared • specific optical rotation, where relevant • 2 or 3 other tests – TLC, UV, colour/other simple test l Whenever applicable, includes • a test for counter-ion l Allows choice between • infrared (+ counter-ion) • other tests (+ counter-ion) 32 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 APIs Monographs – Manufacture Statements under the heading "Manufacture" l serve to alert users and may include • requirements/mandatory instructions to manufacturers • guidance – when clear from wording l deal with aspects of quality not controlled within the body of the monograph 33 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Manufacture Statements under the heading "Manufacture" l serve to alert users and may include • requirements/mandatory instructions to manufacturers • guidance – when clear from wording l deal with aspects of quality not controlled within the body of the monograph 33 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
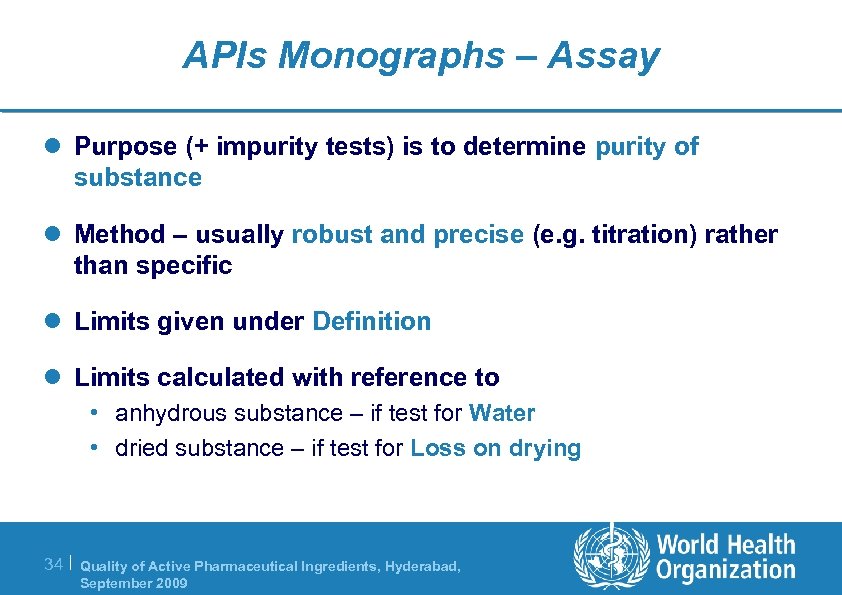 APIs Monographs – Assay l Purpose (+ impurity tests) is to determine purity of substance l Method – usually robust and precise (e. g. titration) rather than specific l Limits given under Definition l Limits calculated with reference to • anhydrous substance – if test for Water • dried substance – if test for Loss on drying 34 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Assay l Purpose (+ impurity tests) is to determine purity of substance l Method – usually robust and precise (e. g. titration) rather than specific l Limits given under Definition l Limits calculated with reference to • anhydrous substance – if test for Water • dried substance – if test for Loss on drying 34 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
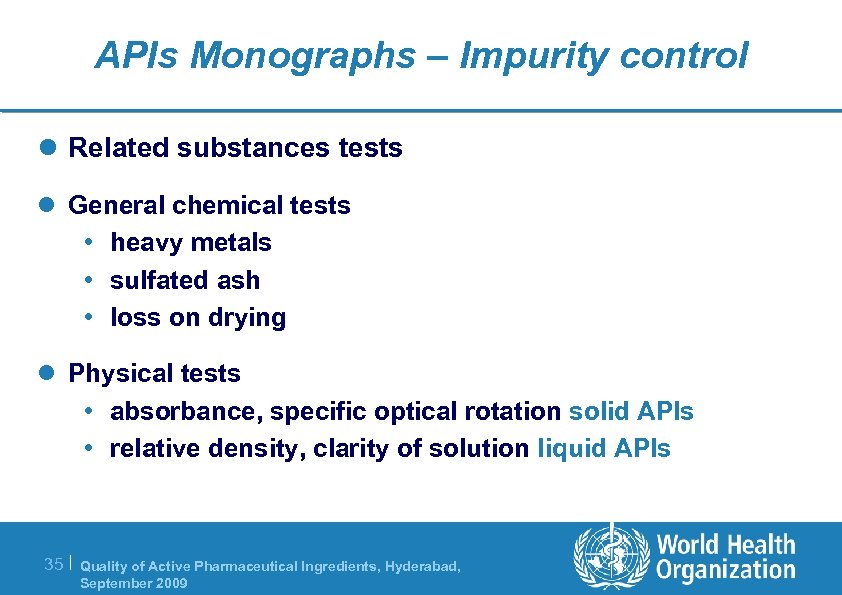 APIs Monographs – Impurity control l Related substances tests l General chemical tests • heavy metals • sulfated ash • loss on drying l Physical tests • absorbance, specific optical rotation solid APIs • relative density, clarity of solution liquid APIs 35 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Impurity control l Related substances tests l General chemical tests • heavy metals • sulfated ash • loss on drying l Physical tests • absorbance, specific optical rotation solid APIs • relative density, clarity of solution liquid APIs 35 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 APIs Monographs – Related substances General considerations l Test methods - usually HPLC or TLC l Acceptance criteria - comparison of peak areas or spot intensities l A test may control known and unknown impurities l Known impurities may be named or unnamed within the test 36 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Related substances General considerations l Test methods - usually HPLC or TLC l Acceptance criteria - comparison of peak areas or spot intensities l A test may control known and unknown impurities l Known impurities may be named or unnamed within the test 36 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 APIs Monographs – Related substances General considerations l Any list of impurities provided at the end of monograph • is not part of the requirements • is given for information • includes likely and potential impurities that have been shown to be controlled by the requirements of the monograph l Other impurities may also be controlled • list may be extended 37 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
APIs Monographs – Related substances General considerations l Any list of impurities provided at the end of monograph • is not part of the requirements • is given for information • includes likely and potential impurities that have been shown to be controlled by the requirements of the monograph l Other impurities may also be controlled • list may be extended 37 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 International Chemical Reference Substances (ICRS) ® More than 200 ICRS + melting point reference substances ® Established by WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR CHEMICAL REFERENCE SUBSTANCES ® Primary reference standard ® Linked to Ph. Int ® Includes: - Directions for use - Certificate of analysis ® Monitoring and on-going stability testing ® Can be used for tests and analysis not included in Ph. Int 38 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
International Chemical Reference Substances (ICRS) ® More than 200 ICRS + melting point reference substances ® Established by WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR CHEMICAL REFERENCE SUBSTANCES ® Primary reference standard ® Linked to Ph. Int ® Includes: - Directions for use - Certificate of analysis ® Monitoring and on-going stability testing ® Can be used for tests and analysis not included in Ph. Int 38 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
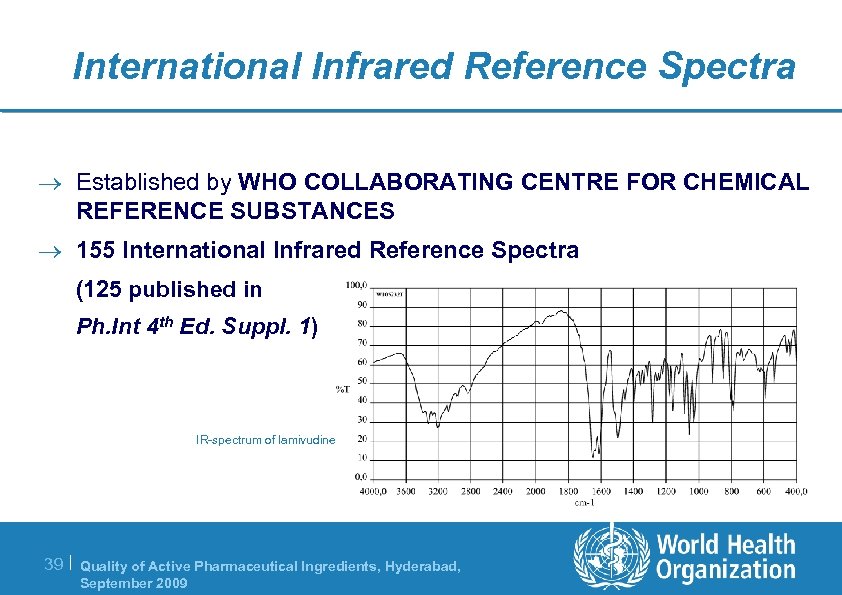 International Infrared Reference Spectra ® Established by WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR CHEMICAL REFERENCE SUBSTANCES ® 155 International Infrared Reference Spectra (125 published in Ph. Int 4 th Ed. Suppl. 1) IR-spectrum of lamivudine 39 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
International Infrared Reference Spectra ® Established by WHO COLLABORATING CENTRE FOR CHEMICAL REFERENCE SUBSTANCES ® 155 International Infrared Reference Spectra (125 published in Ph. Int 4 th Ed. Suppl. 1) IR-spectrum of lamivudine 39 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Newly adopted monographs 42 nd WHO Expert Committee • • Lumefantrine Artemether and lumefantrine tablets • • • Rifampicin, isoniazid and ethambutol tablets Rifampicin and isoniazid dispersible tablets Rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide dispersible tablets 40 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • • Zinc sulfate tablets, paediatric Zinc sulfate oral solution, paediatric • Magnesium sulfate injection
Newly adopted monographs 42 nd WHO Expert Committee • • Lumefantrine Artemether and lumefantrine tablets • • • Rifampicin, isoniazid and ethambutol tablets Rifampicin and isoniazid dispersible tablets Rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide dispersible tablets 40 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • • Zinc sulfate tablets, paediatric Zinc sulfate oral solution, paediatric • Magnesium sulfate injection
 Newly adopted monographs 43 rd WHO Expert Committee (1) • • • Artemether and Lumefantrine oral suspension Chloroquine sulfate oral solution Quinine sulfate tablets • • • Cycloserine capsules Ethambutol hydrochloride tablets • • • Mebendazole Oseltamivir phosphate Chewable Mebendazole tablets 41 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • Efavirenz capsules Efavirenz oral solution Emtricitabine Nevirapine oral suspension Nevirapine tablets Zidovudine, Lamivudine and Nevirapine tablets
Newly adopted monographs 43 rd WHO Expert Committee (1) • • • Artemether and Lumefantrine oral suspension Chloroquine sulfate oral solution Quinine sulfate tablets • • • Cycloserine capsules Ethambutol hydrochloride tablets • • • Mebendazole Oseltamivir phosphate Chewable Mebendazole tablets 41 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • Efavirenz capsules Efavirenz oral solution Emtricitabine Nevirapine oral suspension Nevirapine tablets Zidovudine, Lamivudine and Nevirapine tablets
 Newly adopted monographs 43 rd WHO Expert Committee (2) • • • Fludeoxyglucose (18 F) injection Gallium citrate (67 Ga) injection Thallous chloride (201 Tl) injection Iobenguane (123 I) injection Technetium (99 m. Tc) pentetate complex injection 42 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • Sodium iodide (131 I) injection Sodium iodide (131 I) solution Sodium pertechnetate (99 m. Tc) injection (fission) Sodium pertechnetate (99 m. Tc) injection (non-fission)
Newly adopted monographs 43 rd WHO Expert Committee (2) • • • Fludeoxyglucose (18 F) injection Gallium citrate (67 Ga) injection Thallous chloride (201 Tl) injection Iobenguane (123 I) injection Technetium (99 m. Tc) pentetate complex injection 42 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 • • Sodium iodide (131 I) injection Sodium iodide (131 I) solution Sodium pertechnetate (99 m. Tc) injection (fission) Sodium pertechnetate (99 m. Tc) injection (non-fission)
 Work programme l Entire Work Plan 2009 accessible on The Ph. Int website http: //www. who. int/medicines/publications/pharmacopoeia/Workplan 2009. pdf l Updated after Expert Committee Meetings new focus on anti-infectives) l Adopted monographs available on specific pages + drafts texts in future 43 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 (e. g.
Work programme l Entire Work Plan 2009 accessible on The Ph. Int website http: //www. who. int/medicines/publications/pharmacopoeia/Workplan 2009. pdf l Updated after Expert Committee Meetings new focus on anti-infectives) l Adopted monographs available on specific pages + drafts texts in future 43 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009 (e. g.
 WHO’s strategy for quality control ® Step-wise approach: l l Basic tests (identification) Screening tests (TLC) The International Pharmacopoeia International reference materials (ICRS and IR reference spectra) 44 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
WHO’s strategy for quality control ® Step-wise approach: l l Basic tests (identification) Screening tests (TLC) The International Pharmacopoeia International reference materials (ICRS and IR reference spectra) 44 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia's advantages (1) l 1. Specifications validated internationally, through an independent scientific process l 2. Input from WHO Collaborating Centres, national Drug Quality Control laboratories l 3. Collaboration with manufacturers around the world, especially for new projects l 4. Development considering the costs of analysis, i. e. using as few ICRS as possible 45 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia's advantages (1) l 1. Specifications validated internationally, through an independent scientific process l 2. Input from WHO Collaborating Centres, national Drug Quality Control laboratories l 3. Collaboration with manufacturers around the world, especially for new projects l 4. Development considering the costs of analysis, i. e. using as few ICRS as possible 45 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 The International Pharmacopoeia's advantages (2) l 5. Collaboration with standard-setting organizations and parties, including regional and national pharmacopoeias l 6. Networking and close collaboration with WHO Member States, Drug Regulatory Authorities l 7. Links with other WHO activities l 8. FREE FOR USE by all Member States 46 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
The International Pharmacopoeia's advantages (2) l 5. Collaboration with standard-setting organizations and parties, including regional and national pharmacopoeias l 6. Networking and close collaboration with WHO Member States, Drug Regulatory Authorities l 7. Links with other WHO activities l 8. FREE FOR USE by all Member States 46 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
 Thank you ! 47 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009
Thank you ! 47 | Quality of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Hyderabad, September 2009


