564f87f633d93593ad3bc5bf80b770d7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

The Information Systems Revolution Transforming Business and Management

Class Activity • Break into groups of four and – Introduce yourself to the members of your group and describe yourself to the members of your group – Information technology can help companies to… – Identify five knowledge- and informationintense products

VW Mexico and the Internet • SAP’s ERP system integrated with the web to reduce part ordering time from 10 to 5 days – Enabled dealer to use a browser and get order information through an intranet on the worldwide web

VW Mexico and the Internet • SAP’s ERP system integrated with the web to reduce part ordering time from 10 to 5 days – Enabled dealer to use a browser and get order information through an intranet on the worldwide web

Information Systems… Can help companies to: – Extend their reach to faraway locations – Offer new products and services – Reshape jobs and work flows, and perhaps profoundly change the way they conduct business

Three Powerful Worldwide Changes 1. Globalization 2. Transformation of industrial economies to knowledge and information-based economies 3. Transformation of the enterprise

Globalization • Management & Control In A Global Marketplace • Competition In World Markets • Global Work Groups • Global Delivery Systems * 1. 5

Globalization • Information systems are a powerful ally enabling businesses to – Communicate with distributors, suppliers, and customers worldwide – Operate 24/7 – Serve local and international reporting needs – Compete globally by bringing your products and services to a global market

Transformation of Industrial Economies… • To knowledge- and information-based service economies. – Increase need for white-collar workers – Manufacturing has moved to low-wage countries – Knew knowledge- and information-intense products

Transformation of Industrial Economies… • To knowledge- and information-based service economies. – Increase need for white-collar workers – Manufacturing has moved to low-wage countries. – Knew knowledge- and information-intense products

Transformation of Industrial Economies… • To knowledge- and information-based service economies. – Increase need for white-collar workers – Manufacturing has moved to low-wage countries. For how long? – Knew knowledge- and information-intense products
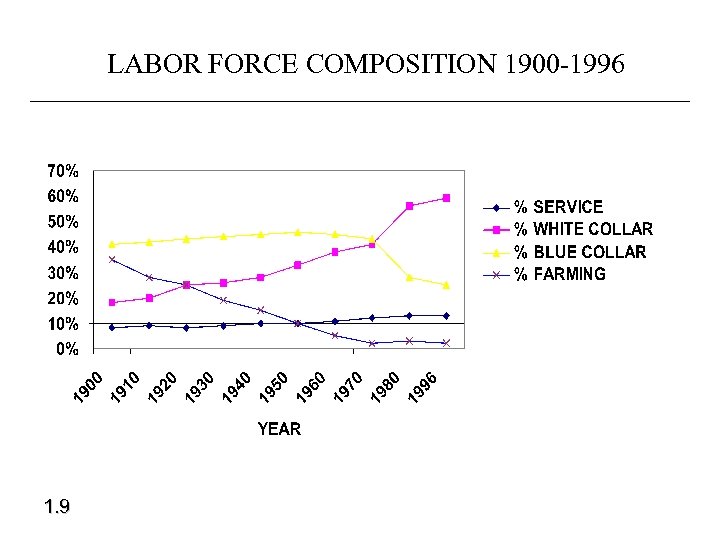
LABOR FORCE COMPOSITION 1900 -1996 1. 9

Economic Transformation • • 1. 6 Knowledge-based Economies Productivity New Products & Services Knowledge As An Asset Time-based Competition Shorter Product Life Turbulent Environment Limited Employee Knowledge Base *

Knowledge- and Information. Intense Products • Credit cards • Overnight package delivery • Worldwide reservation systems
Transformation Of The Enterprise • • Flattening Decentralization Flexibility Location Independence Low Transaction Costs Empowerment Collaborative Work * 1. 7
What is an Information System • A set of interrelated components that – Collects data - INPUT – Transforms data - PROCESS – Disseminates information - OUTPUT
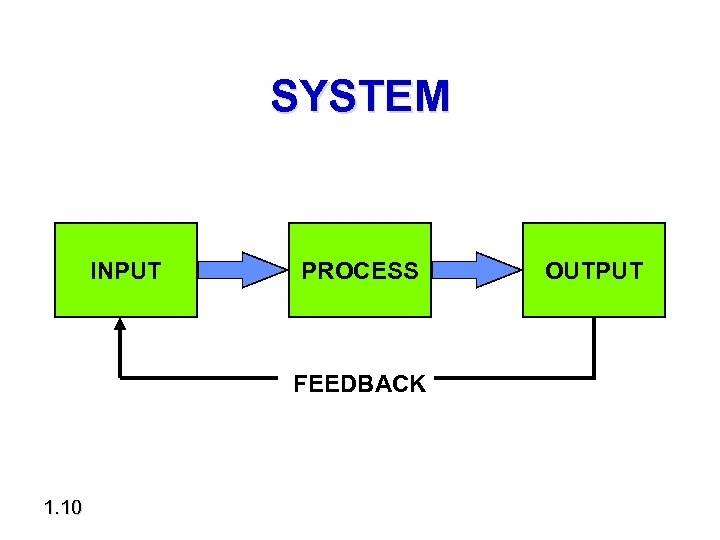
SYSTEM INPUT PROCESS FEEDBACK 1. 10 OUTPUT
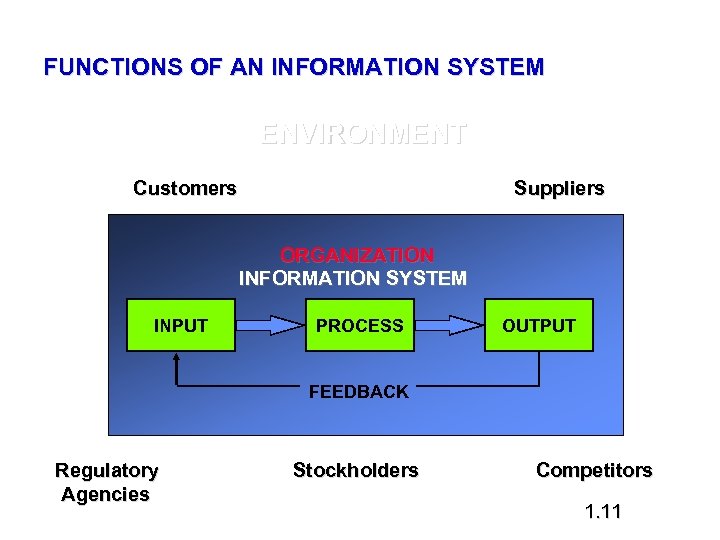
FUNCTIONS OF AN INFORMATION SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT Customers Suppliers ORGANIZATION INFORMATION SYSTEM INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT FEEDBACK Regulatory Agencies Stockholders Competitors 1. 11

What is an information system? • An organizational and management solution, based on information technology, to a challenge posed by the environment.
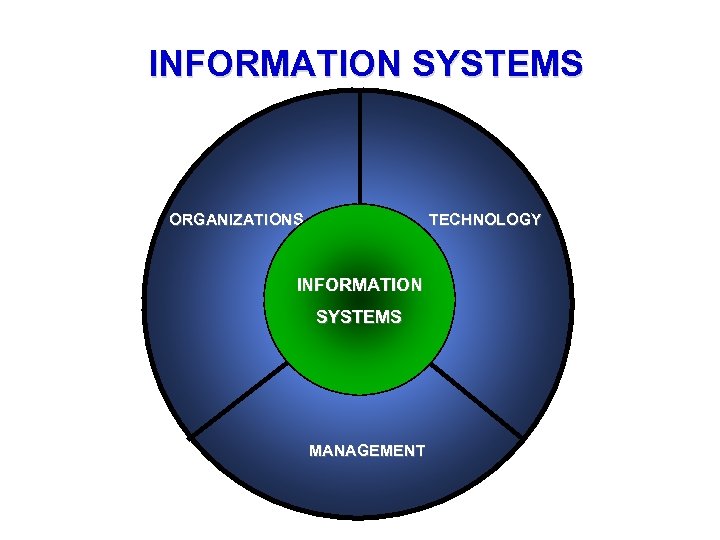
INFORMATION SYSTEMS ORGANIZATIONS TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT

The Key Elements of an Organization • • People Structure and operating procedures Politics Culture

People 1. Knowledge workers – Product or service designers and knowledge creators 2. Data workers – The paper-pushers 3. Production or service workers – Producers/service providers

Structure • • • Sales and Marketing Manufacturing Finance Accounting Human Resources

SOCIOTECHNICAL PERSPECTIVE Information systems are sociotechnical systems. Though they are composed of machines devices, and “hard” physical technology, they require substantial social, organizational, and intellectual investment to make them work properly *
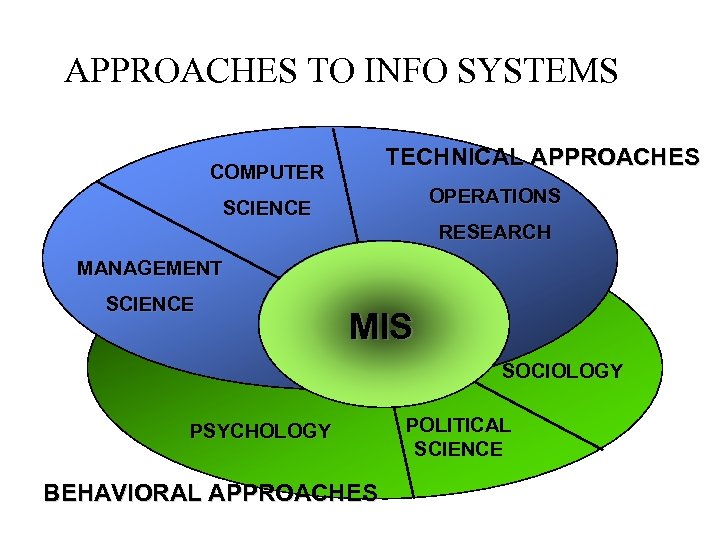
APPROACHES TO INFO SYSTEMS TECHNICAL APPROACHES COMPUTER OPERATIONS SCIENCE RESEARCH MANAGEMENT SCIENCE MIS SOCIOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY BEHAVIORAL APPROACHES POLITICAL SCIENCE

Behavioral Approach • Focuses on strategic business integration, design, implementation, and utilization • Focuses on changes in – Attitude – Management and organizational policy – Behavior
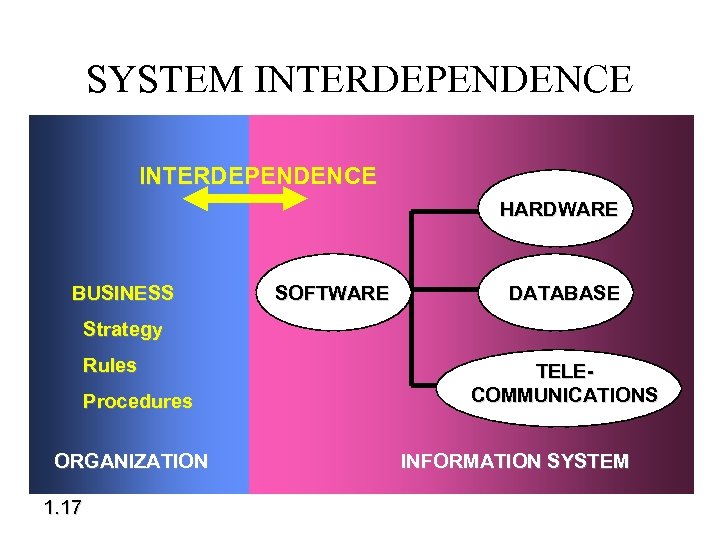
SYSTEM INTERDEPENDENCE HARDWARE BUSINESS SOFTWARE DATABASE Strategy Rules Procedures ORGANIZATION 1. 17 TELECOMMUNICATIONS INFORMATION SYSTEM

Information System Impacts • What a business would like to do in five years is often dependent on what its systems will be able to do – Becoming the high-quality or low-cost producer – Developing new products – Increasing employee productivity
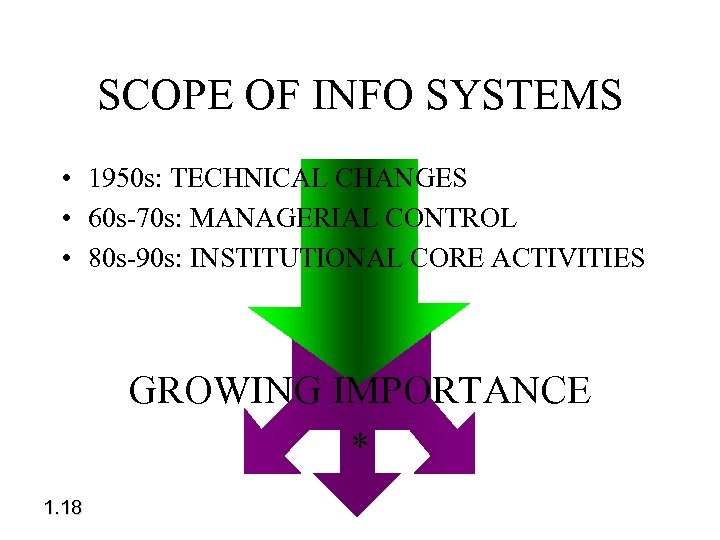
SCOPE OF INFO SYSTEMS • 1950 s: TECHNICAL CHANGES • 60 s-70 s: MANAGERIAL CONTROL • 80 s-90 s: INSTITUTIONAL CORE ACTIVITIES GROWING IMPORTANCE * 1. 18

Computing Power • Doubling every 18 months • The performance of the microprocessors have improved 25, 000 times since their invention 25 years ago • Soaring power has spawned powerful communications networks the largest of which is…
What You Can Do On The Internet • Communicate & Collaborate – e-mail • Access Information – Databases • Discussions – Chats • Obtain Information – FTP • Entertainment – Play…, view…, read…, animate… • Business Transactions 1. 19 – Advertise, sell, and purchase *

The Number of Internet Users • Greater than 250 million today!

New Options For Organizational Design • • • 1. 20 Flattening Organizations Separating Work From Location Increasing Flexibility Refining Organizational Boundaries Reorganizing Work Flows *

The Changing Management Process • Enterprise Resource Planning • Electronic Commerce • Electronic Business * 1. 21

Enterprise Resource Planning Software Integrates All Facets: • Planning, Manufacturing, Inventory, Sales, Finance, Accounting • Transactions Alert All Involved Factors • Updates Files, Speeds Action, Cuts Cost * 1. 22

Electronic Commerce • Internet Links Buyers, Sellers • Lowers Transaction Costs • Goods & Services Advertised, Bought, Exchanged Worldwide • B 2 B Transactions Increasing * 1. 23

Electronic Business • Intranet: Business Builds Private, Secure Network • E-mail, Web Documents, Group Software Extends Effective Communication & Control • Virtual Organization * 1. 24
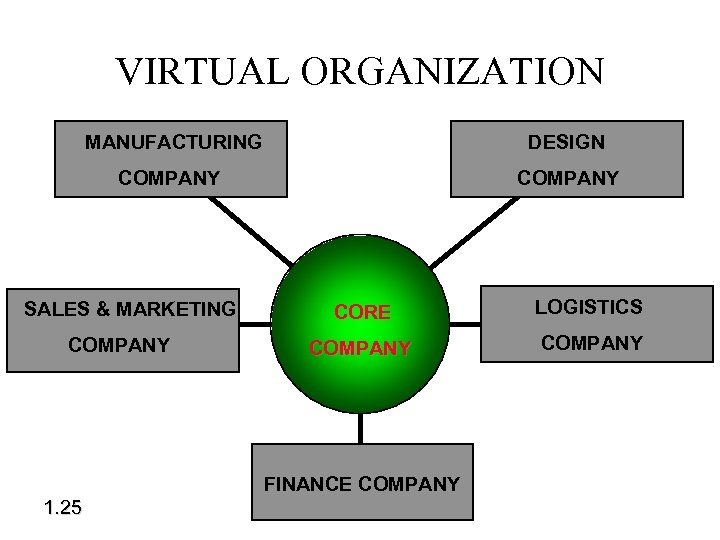
VIRTUAL ORGANIZATION MANUFACTURING DESIGN COMPANY SALES & MARKETING COMPANY CORE LOGISTICS COMPANY FINANCE COMPANY 1. 25

CHALLENGE OF INFO SYSTEMS • STRATEGIC: Maintaining a competitive edge • GLOBALIZATION: Integrated systems • INFO ARCHITECTURE: Development • INVESTMENT: What is the value? • RESPONSIBILITY & CONTROL: Ethics * 1. 26
564f87f633d93593ad3bc5bf80b770d7.ppt