7c27f5d3326c2ffb9ad0c63bb020a4c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 The Industrial City
The Industrial City
 Key Terms H H Frank Sprague Dumbbell tenements Bennett Law Chinese Exclusion Act 1882 H Tongs H Padroni H landsmanshafts
Key Terms H H Frank Sprague Dumbbell tenements Bennett Law Chinese Exclusion Act 1882 H Tongs H Padroni H landsmanshafts
 Growth of the Cities H NYC: 942 k 1870; 3. 4 mil 1900 H CHI: 298 k 1870; 1. 7 mil 1900 H PHI: 674 k 1870; 1 mil 1900 H WASH: 109 k 1870; 278 k 1900 H ATL: 21 k 1870; 90 k 1900 H Cities: a mixed vision
Growth of the Cities H NYC: 942 k 1870; 3. 4 mil 1900 H CHI: 298 k 1870; 1. 7 mil 1900 H PHI: 674 k 1870; 1 mil 1900 H WASH: 109 k 1870; 278 k 1900 H ATL: 21 k 1870; 90 k 1900 H Cities: a mixed vision
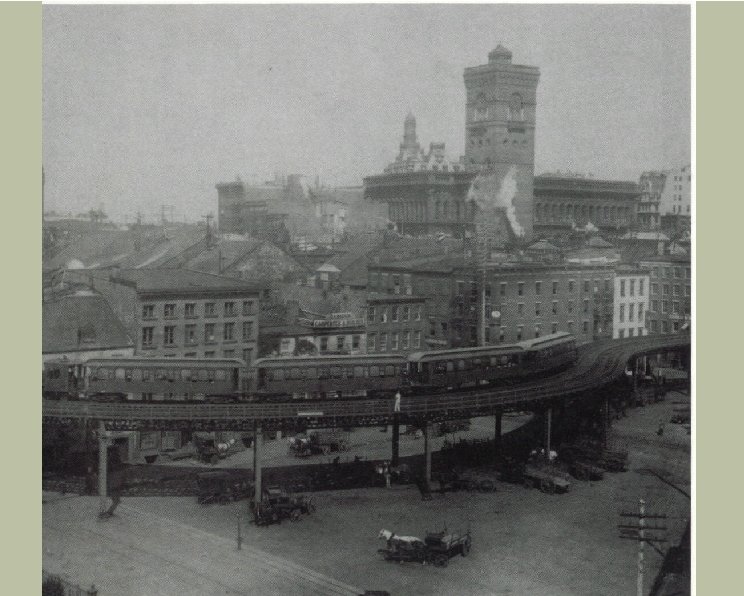
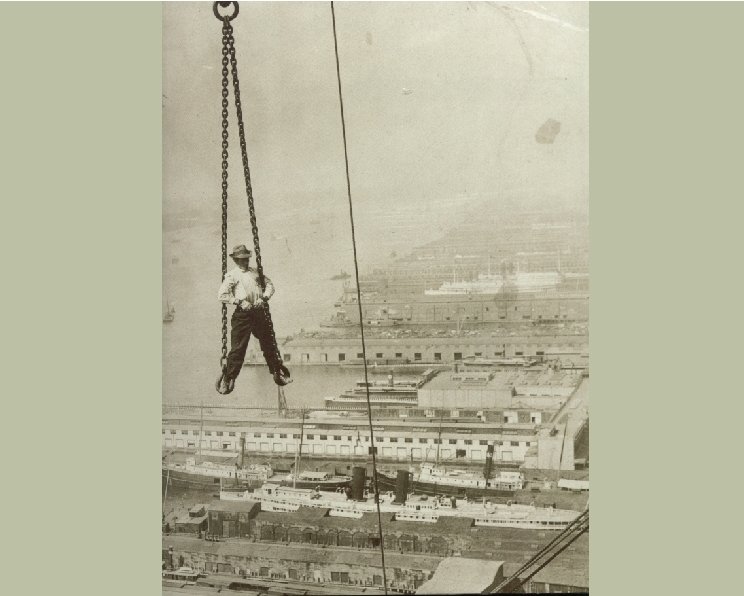
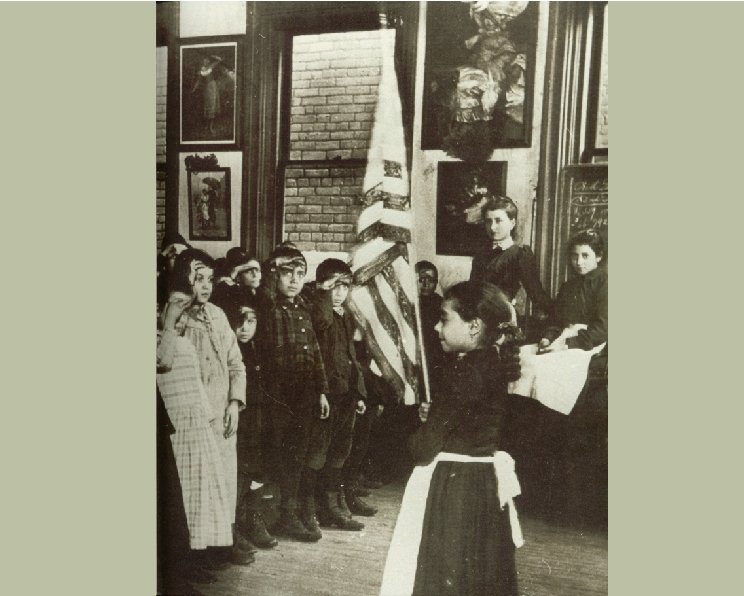
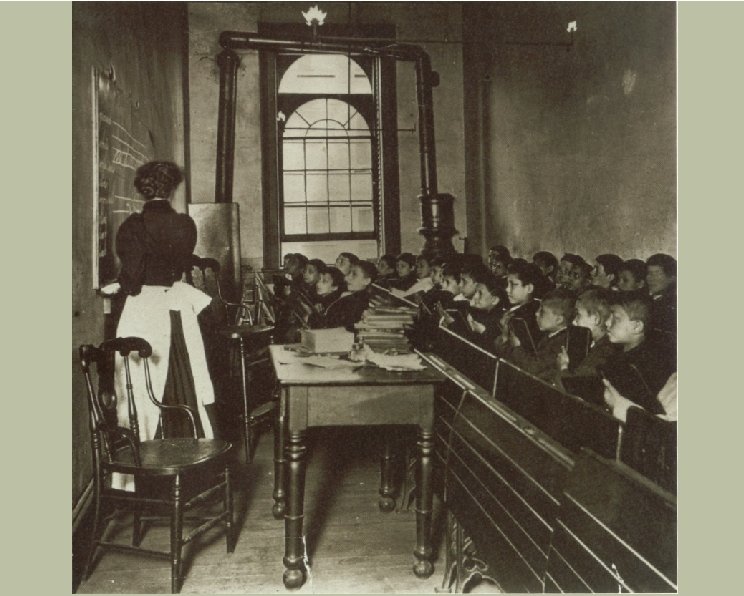








 Technology and Urbanization H Transportation: H H H H H The end of the “walking city” Horse-drawn mass transit Frank Sprague; electric trolley Subways Exodus to the suburbs Construction methods Streets Water Electricity The pocket watch
Technology and Urbanization H Transportation: H H H H H The end of the “walking city” Horse-drawn mass transit Frank Sprague; electric trolley Subways Exodus to the suburbs Construction methods Streets Water Electricity The pocket watch
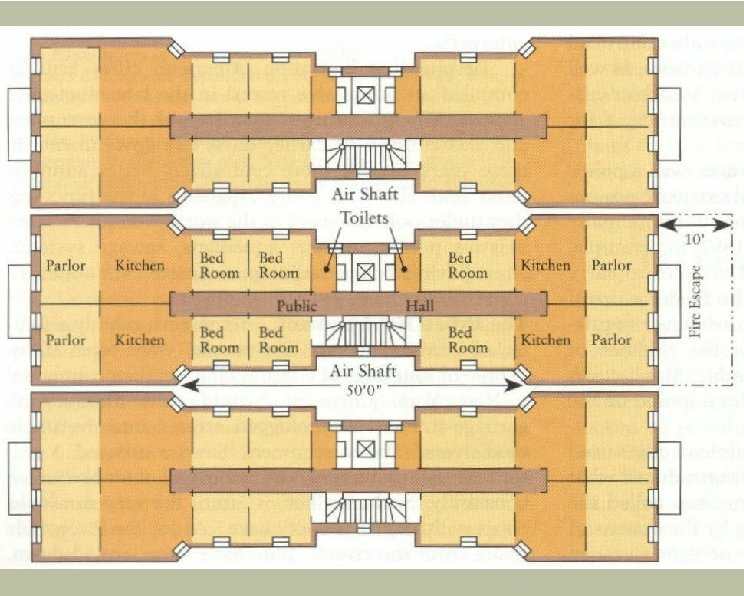
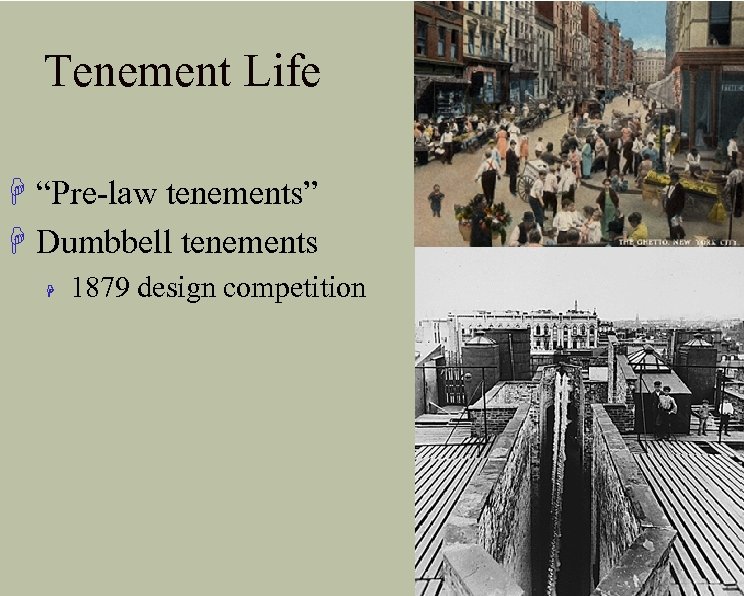 Tenement Life H “Pre-law tenements” H Dumbbell tenements H 1879 design competition
Tenement Life H “Pre-law tenements” H Dumbbell tenements H 1879 design competition
 Urban Problems H Related problems: H H Alcoholism Crime Filth/health issues Labor/working conditions H Safety, child, women labor laws H H Pure food & drugs Disease/mortality rate H Chicago: 3 of 5 babies die before age 5
Urban Problems H Related problems: H H Alcoholism Crime Filth/health issues Labor/working conditions H Safety, child, women labor laws H H Pure food & drugs Disease/mortality rate H Chicago: 3 of 5 babies die before age 5
 The Germans H Contrast with Irish: H H H 1830 -1880 Germans are at least 25% of US immigrants 1900, 26% (Irish 15%) Germans 3 religious groups: Protestant, Catholic, Jewish Urban and agricultural Family migration
The Germans H Contrast with Irish: H H H 1830 -1880 Germans are at least 25% of US immigrants 1900, 26% (Irish 15%) Germans 3 religious groups: Protestant, Catholic, Jewish Urban and agricultural Family migration
 The Germans H German settlement: H 1860 -1890, 40% urban, 60% rural H Different cities from Irish: H Milwaukee, St. Louis, Buffalo, Chicago, Toledo, Detroit -- Midwest H Labor: H Skilled trades, beer, butcher, tailor, etc.
The Germans H German settlement: H 1860 -1890, 40% urban, 60% rural H Different cities from Irish: H Milwaukee, St. Louis, Buffalo, Chicago, Toledo, Detroit -- Midwest H Labor: H Skilled trades, beer, butcher, tailor, etc.
 The German Saloon
The German Saloon
 Language and Religion H Bennett Law, Wisconsin 1890 H Post World War I, hysteria
Language and Religion H Bennett Law, Wisconsin 1890 H Post World War I, hysteria
 The Chinese H (1848 -1882) 300, 000 Chinese to US H “Pushes”: H H War, rebellion, violence Economic conditions Natural disasters Starvation H “Pulls”: H The lure of the “Gold Mountain”
The Chinese H (1848 -1882) 300, 000 Chinese to US H “Pushes”: H H War, rebellion, violence Economic conditions Natural disasters Starvation H “Pulls”: H The lure of the “Gold Mountain”
 The Chinese H Labor: H Early gold miners, “’ 49 ers”
The Chinese H Labor: H Early gold miners, “’ 49 ers”
 The Chinese H Labor: H Central Pacific Railroad
The Chinese H Labor: H Central Pacific Railroad
 The Chinese H Labor: H After the railroad H Few industries - boot and shoe, woolens, cigar and tobacco, sewing H Agriculture H Laundry
The Chinese H Labor: H After the railroad H Few industries - boot and shoe, woolens, cigar and tobacco, sewing H Agriculture H Laundry
 The Chinese H Confronting racism H Naturalization Act, 1870 H Chinese Exclusion Act, 1882 H Violence
The Chinese H Confronting racism H Naturalization Act, 1870 H Chinese Exclusion Act, 1882 H Violence

 The Chinese H Very few women: H H H Prostitutes The Page Law, 1875 Wives H Men: the bachelor society H H Tongs The American Dream denied
The Chinese H Very few women: H H H Prostitutes The Page Law, 1875 Wives H Men: the bachelor society H H Tongs The American Dream denied
 “New Immigrants” H 1880 s new groups H H H Italians Eastern Europeans Jews H 1901 -1910, 1. 5 mil from Ireland, Germany, England H 1901 -1910, 6. 5 mil rest of Europe, 2 mil Italians
“New Immigrants” H 1880 s new groups H H H Italians Eastern Europeans Jews H 1901 -1910, 1. 5 mil from Ireland, Germany, England H 1901 -1910, 6. 5 mil rest of Europe, 2 mil Italians
 “New Immigrants” H Kinship networks H “Middlemen” H Quest for greater production H Unskilled labor H The decline of skilled labor H The family economy H “Cooperate and survive”
“New Immigrants” H Kinship networks H “Middlemen” H Quest for greater production H Unskilled labor H The decline of skilled labor H The family economy H “Cooperate and survive”
 Italians H 1880 -1920, 4. 1 mil Italians H ritornati 30 -50% H Before the 1880 s H intellectuals, artists, musicians H 1880 s, 300, 000 H Settlement: H H H Male: female = 3: 1 97% through New York City East coast, a few elsewhere
Italians H 1880 -1920, 4. 1 mil Italians H ritornati 30 -50% H Before the 1880 s H intellectuals, artists, musicians H 1880 s, 300, 000 H Settlement: H H H Male: female = 3: 1 97% through New York City East coast, a few elsewhere
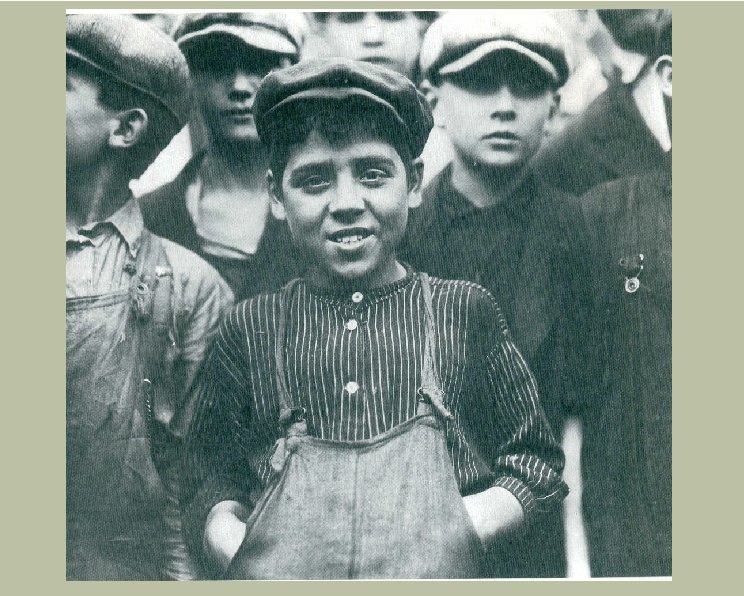
 Italians H Labor: H H H Manual labor padroni Children work young
Italians H Labor: H H H Manual labor padroni Children work young

 Italians H Interests: H H Few organizations Catholic, but not fanatical H Crime H 1910: est. of 100, 000 people, H 527 Italians involved in org. crime H 727 English H Today, only 4% of org. crime = Italian
Italians H Interests: H H Few organizations Catholic, but not fanatical H Crime H 1910: est. of 100, 000 people, H 527 Italians involved in org. crime H 727 English H Today, only 4% of org. crime = Italian
 Italians and politics H Radical political movements H Sacco and Vanzetti
Italians and politics H Radical political movements H Sacco and Vanzetti
 The Polish H “Pushes”: H “They came for bread” H 1850 -1915, 2. 5 mil Polish immigrate H 1/3 return H “Rust belt” H Labor: H Lowest jobs
The Polish H “Pushes”: H “They came for bread” H 1850 -1915, 2. 5 mil Polish immigrate H 1/3 return H “Rust belt” H Labor: H Lowest jobs
 Russian Jews H 1880 - 250, 000 Jews in US H 1924 - 4 mil. Jews in US H “Pushes”: H H H Poor economy The Pale of Settlement Religious persecution H Population increase H Economic rationale H Church & government, pogroms
Russian Jews H 1880 - 250, 000 Jews in US H 1924 - 4 mil. Jews in US H “Pushes”: H H H Poor economy The Pale of Settlement Religious persecution H Population increase H Economic rationale H Church & government, pogroms
 Russian Jews H Difficult migration H Facts: H H Jews younger (14 -40 yrs. ) Industrial skills Literate VERY likely to stay in US H Settlement: H H New York City and east coast Poor, dumbbell tenements
Russian Jews H Difficult migration H Facts: H H Jews younger (14 -40 yrs. ) Industrial skills Literate VERY likely to stay in US H Settlement: H H New York City and east coast Poor, dumbbell tenements
 Russian Jews H Network of employment H Labor: H H Garment industry Entrepreneurial spirit
Russian Jews H Network of employment H Labor: H H Garment industry Entrepreneurial spirit
 Russian Jews H Labor: H H H Peddlers Women in the garment industry Strikes H Landsmanshafts
Russian Jews H Labor: H H H Peddlers Women in the garment industry Strikes H Landsmanshafts
 Ideology, 1865 -1900 H Conflicting themes: H H Growth, wealth Masses who don’t benefit
Ideology, 1865 -1900 H Conflicting themes: H H Growth, wealth Masses who don’t benefit
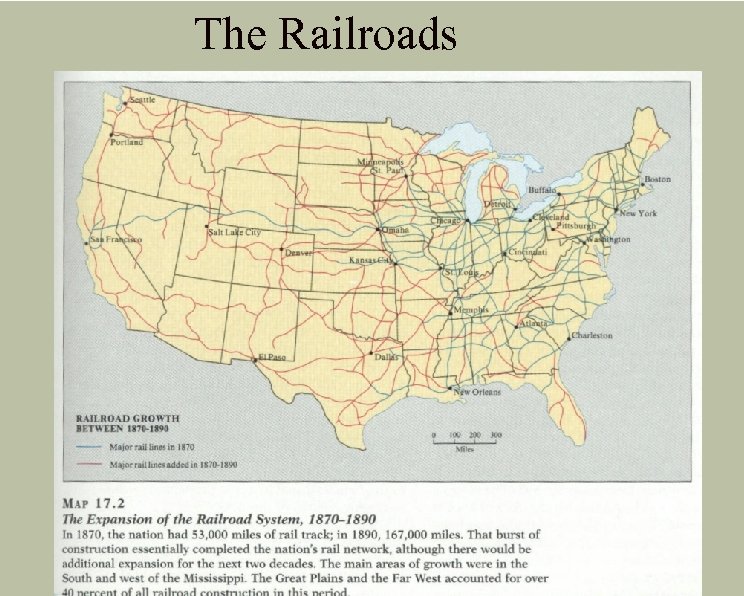 The Railroads
The Railroads
 The Railroads H Government support H 1862 Pacific RR Act H Provided $$ and land H Technology H H H Steel Steam engine Crocker
The Railroads H Government support H 1862 Pacific RR Act H Provided $$ and land H Technology H H H Steel Steam engine Crocker
 The Railroads H Immigration H H 1853 - 12 Chinese immigrants 1854 - 13, 000 H Business tactics H Competition H Collis P. Huntington H Southern Pacific RR H Combination H Pools (cartels) H Trusts H Holding companies
The Railroads H Immigration H H 1853 - 12 Chinese immigrants 1854 - 13, 000 H Business tactics H Competition H Collis P. Huntington H Southern Pacific RR H Combination H Pools (cartels) H Trusts H Holding companies
 Other Businesses H Oil (John D. Rockefeller) H H Standard Oil “Gospel of wealth” H Steel (Andrew Carnegie) H Vertical combination
Other Businesses H Oil (John D. Rockefeller) H H Standard Oil “Gospel of wealth” H Steel (Andrew Carnegie) H Vertical combination
 Organized Labor H Working conditions H H Coal mines Breaker boys
Organized Labor H Working conditions H H Coal mines Breaker boys

 Organized Labor H Unions H H H National Labor Union, 1866 Colored National Labor Union, 1869 Knights of Labor, 1869 H H H Uriah S. Stephens Women & blacks welcome Terrence Powderly 8 -hr. work day, child labor Opposed to strikes 1886 peak, 700, 000
Organized Labor H Unions H H H National Labor Union, 1866 Colored National Labor Union, 1869 Knights of Labor, 1869 H H H Uriah S. Stephens Women & blacks welcome Terrence Powderly 8 -hr. work day, child labor Opposed to strikes 1886 peak, 700, 000
 Organized Labor H Unions H American Federation of Labor, 1881 H Samuel Gompers H More focused: H H Only trade unions Hours, wages, working conditions Strikes 1886 - 140, 000; 1900 - 1 million
Organized Labor H Unions H American Federation of Labor, 1881 H Samuel Gompers H More focused: H H Only trade unions Hours, wages, working conditions Strikes 1886 - 140, 000; 1900 - 1 million
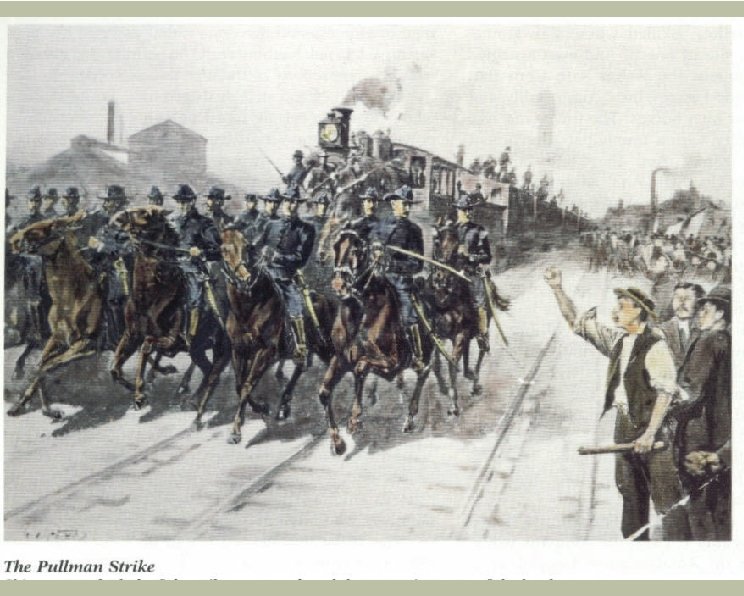
 Organized Labor H Haymarket Riot H H May, 1886 Chicago Used against labor - KOL decline H Homestead Strike H H 1892, Homestead, PA Henry Clay Frick H Pullman Strike, 1894 H Big business favored over labor H Ethnic diversity
Organized Labor H Haymarket Riot H H May, 1886 Chicago Used against labor - KOL decline H Homestead Strike H H 1892, Homestead, PA Henry Clay Frick H Pullman Strike, 1894 H Big business favored over labor H Ethnic diversity

 The West Organizes H Life on the frontier H 1862 Homestead Act H 160 acres H The Grange H Populism H Demands: H Govt. to store surplus crops H “free & unlimited coinage of silver” H Govt. control transportation H Govt. no give land to RR H Coxey’s Army, 1894
The West Organizes H Life on the frontier H 1862 Homestead Act H 160 acres H The Grange H Populism H Demands: H Govt. to store surplus crops H “free & unlimited coinage of silver” H Govt. control transportation H Govt. no give land to RR H Coxey’s Army, 1894
 The Progressive Era H Ideology: H Social Darwinism H Herbert Spencer H “Root hog, or die” H Reform Darwinism H Social Gospel (“WWJD”)
The Progressive Era H Ideology: H Social Darwinism H Herbert Spencer H “Root hog, or die” H Reform Darwinism H Social Gospel (“WWJD”)
 The Progressive Era H Publicity: H “Muckrakers” H The Jungle, Sinclair H Maggie, Crane H How the Other Half Lives, Riis
The Progressive Era H Publicity: H “Muckrakers” H The Jungle, Sinclair H Maggie, Crane H How the Other Half Lives, Riis
 Progressive Era Reforms H “Active government on behalf of the public interest” H Local: Settlement Houses H Jane Addams, Hull House H Parks and playgrounds
Progressive Era Reforms H “Active government on behalf of the public interest” H Local: Settlement Houses H Jane Addams, Hull House H Parks and playgrounds
 Progressive Era Reforms H State: “Wisconsin idea” H H Robert La. Follette Efficiency Experts Direct primary H Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
Progressive Era Reforms H State: “Wisconsin idea” H H Robert La. Follette Efficiency Experts Direct primary H Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
 Progressive Era Reforms H Federal: Teddy Roosevelt H H H Trust-busting Pure food and drugs Conservation H Woodrow Wilson H H H Lower tariffs Federal reserve Anti-trust laws H Shortcomings of the Progressive movement
Progressive Era Reforms H Federal: Teddy Roosevelt H H H Trust-busting Pure food and drugs Conservation H Woodrow Wilson H H H Lower tariffs Federal reserve Anti-trust laws H Shortcomings of the Progressive movement


