a240c29ab36a740cbdc5edd06e2a688d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 The Incident Command System Charles Stewart MD EMDM
The Incident Command System Charles Stewart MD EMDM
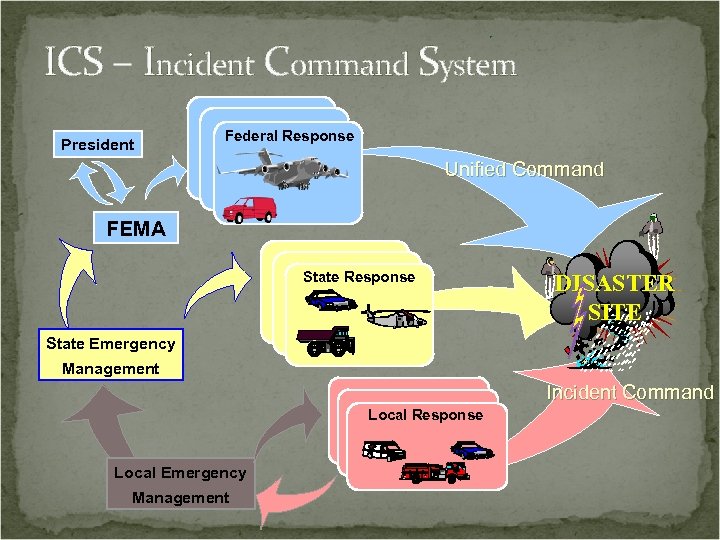 ICS – Incident Command System President Federal Response Unified Command FEMA State Response DISASTER SITE State Emergency Management Incident Command Local Response Local Emergency Management
ICS – Incident Command System President Federal Response Unified Command FEMA State Response DISASTER SITE State Emergency Management Incident Command Local Response Local Emergency Management
 An Organized Response Requires planning Coordinates resources and personnel Find a video that shows an organized response
An Organized Response Requires planning Coordinates resources and personnel Find a video that shows an organized response
 Key Principles of NIMS ICS Span of Control Unity of Command Accountability ? These are basic principles that have been tested in combat and proven to be necessary for successful accomplishment of a mission
Key Principles of NIMS ICS Span of Control Unity of Command Accountability ? These are basic principles that have been tested in combat and proven to be necessary for successful accomplishment of a mission
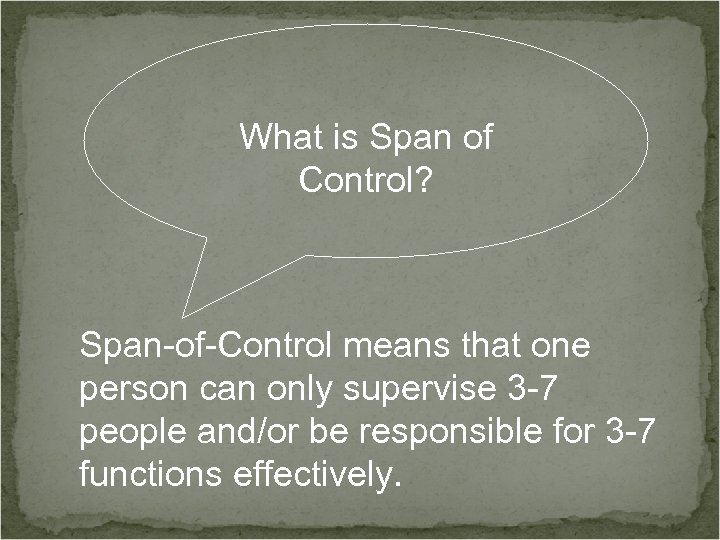 What is Span of Control? Span-of-Control means that one person can only supervise 3 -7 people and/or be responsible for 3 -7 functions effectively.
What is Span of Control? Span-of-Control means that one person can only supervise 3 -7 people and/or be responsible for 3 -7 functions effectively.
 “Span-of-Control” Refers to number of subordinates that one supervisor can manage effectively. Ideal ratio is 5 -to-1 ICS structure can expand or contract to maintain adequate span-of-control by adding/removing sections, branches, divisions, groups, teams. Supervisor 1 2 3 4 5
“Span-of-Control” Refers to number of subordinates that one supervisor can manage effectively. Ideal ratio is 5 -to-1 ICS structure can expand or contract to maintain adequate span-of-control by adding/removing sections, branches, divisions, groups, teams. Supervisor 1 2 3 4 5
 What is Unity of Command? Unity of Command means that you answer to only one person for tasks and assignments.
What is Unity of Command? Unity of Command means that you answer to only one person for tasks and assignments.
 Unity of Command Each person reports to only one individual ICS organizational chart indicates who that is What would you do if someone other than your assigned supervisor asks you to do something other than what you were assigned?
Unity of Command Each person reports to only one individual ICS organizational chart indicates who that is What would you do if someone other than your assigned supervisor asks you to do something other than what you were assigned?
 What does Accountability Mean? There are two types of Accountability: • You know who is on-scene/site, where they are, what they are assigned to do and if they are safe. • Each person does what they were expected to do.
What does Accountability Mean? There are two types of Accountability: • You know who is on-scene/site, where they are, what they are assigned to do and if they are safe. • Each person does what they were expected to do.
 Accountability: People It is the responsibility of the incident commander to know who is on-scene, to make sure they are doing what is needed and “No one is left behind” Check In No freelancing Report to supervisor Check Out/Demobilize
Accountability: People It is the responsibility of the incident commander to know who is on-scene, to make sure they are doing what is needed and “No one is left behind” Check In No freelancing Report to supervisor Check Out/Demobilize
 Responder Etiquette Report to a staging area, not the disaster site
Responder Etiquette Report to a staging area, not the disaster site
 Accountability: Task Give clear assignments Ensure assignment is understood Provide adequate resources Task Completion
Accountability: Task Give clear assignments Ensure assignment is understood Provide adequate resources Task Completion
 Report to Staging Area Sign in when you arrive; Sign out when you leave Bring ID, credentials Find your designated supervisor Follow directions If asked to leave or provide care elsewhere – do so Medical volunteers at staging area
Report to Staging Area Sign in when you arrive; Sign out when you leave Bring ID, credentials Find your designated supervisor Follow directions If asked to leave or provide care elsewhere – do so Medical volunteers at staging area
 Incident Command System Used to organize multiple groups/agencies into one cohesive team Responses and responders may vary, but the organizational principles of ICS remain the same
Incident Command System Used to organize multiple groups/agencies into one cohesive team Responses and responders may vary, but the organizational principles of ICS remain the same
 Initiating ICS When an event occurs, initial actions should include: Scene size up – safety Assume/Announce Command (Even if you are the only person on scene) Initially organizing the response – Assign Tasks Notifying affected agencies (hospitals, LE, Fire/EMS) Maintain Command role until Command is transferred
Initiating ICS When an event occurs, initial actions should include: Scene size up – safety Assume/Announce Command (Even if you are the only person on scene) Initially organizing the response – Assign Tasks Notifying affected agencies (hospitals, LE, Fire/EMS) Maintain Command role until Command is transferred
 ICS Characteristics Critical Characteristics of ICS (7 of 14) Common Terminology Management by Objective Chain of Command/Unity of Command Resource Management Integrated Communications Manageable Span of Control Accountability of personnel and resources
ICS Characteristics Critical Characteristics of ICS (7 of 14) Common Terminology Management by Objective Chain of Command/Unity of Command Resource Management Integrated Communications Manageable Span of Control Accountability of personnel and resources
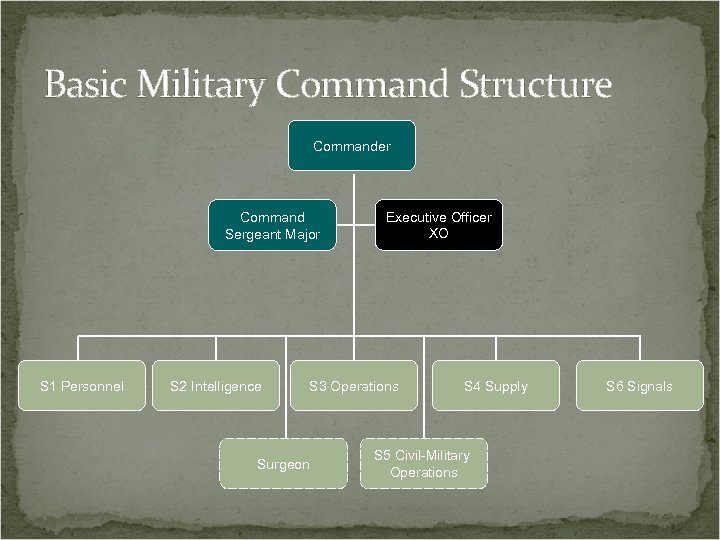 Basic Military Command Structure Commander Command Sergeant Major S 1 Personnel S 2 Intelligence Executive Officer XO S 3 Operations Surgeon S 4 Supply S 5 Civil-Military Operations S 6 Signals
Basic Military Command Structure Commander Command Sergeant Major S 1 Personnel S 2 Intelligence Executive Officer XO S 3 Operations Surgeon S 4 Supply S 5 Civil-Military Operations S 6 Signals
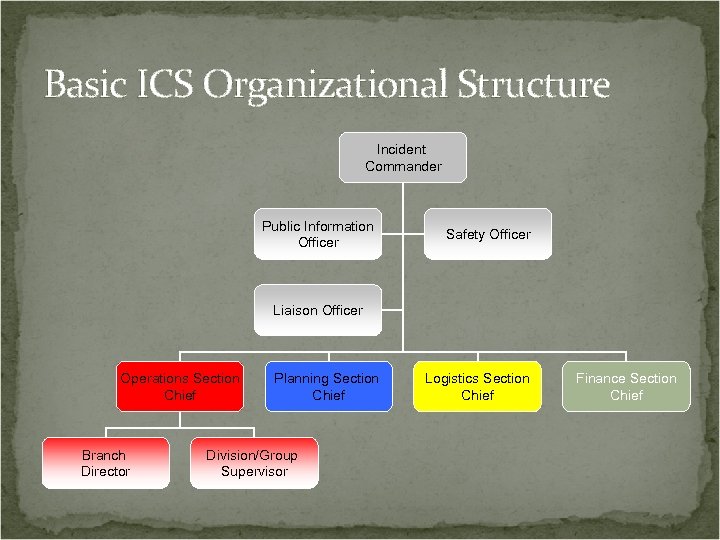 Basic ICS Organizational Structure Incident Commander Public Information Officer Safety Officer Liaison Officer Operations Section Chief Branch Director Planning Section Chief Division/Group Supervisor Logistics Section Chief Finance Section Chief
Basic ICS Organizational Structure Incident Commander Public Information Officer Safety Officer Liaison Officer Operations Section Chief Branch Director Planning Section Chief Division/Group Supervisor Logistics Section Chief Finance Section Chief
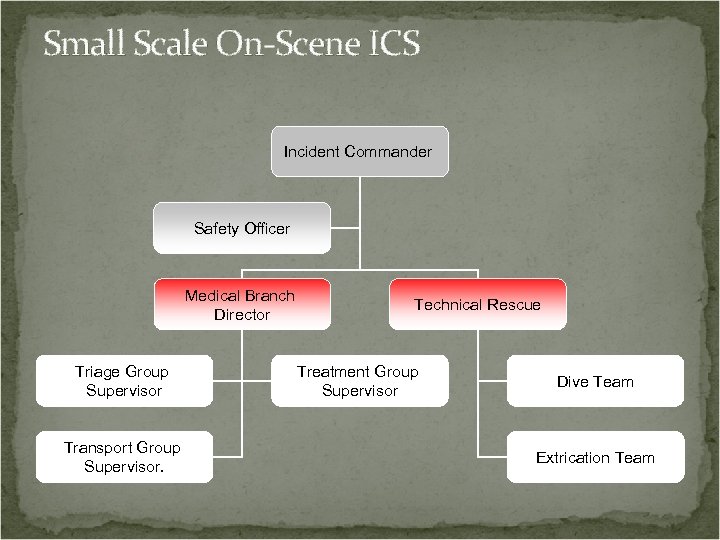 Small Scale On-Scene ICS Incident Commander Safety Officer Medical Branch Director Triage Group Supervisor Transport Group Supervisor. Technical Rescue Treatment Group Supervisor Dive Team Extrication Team
Small Scale On-Scene ICS Incident Commander Safety Officer Medical Branch Director Triage Group Supervisor Transport Group Supervisor. Technical Rescue Treatment Group Supervisor Dive Team Extrication Team
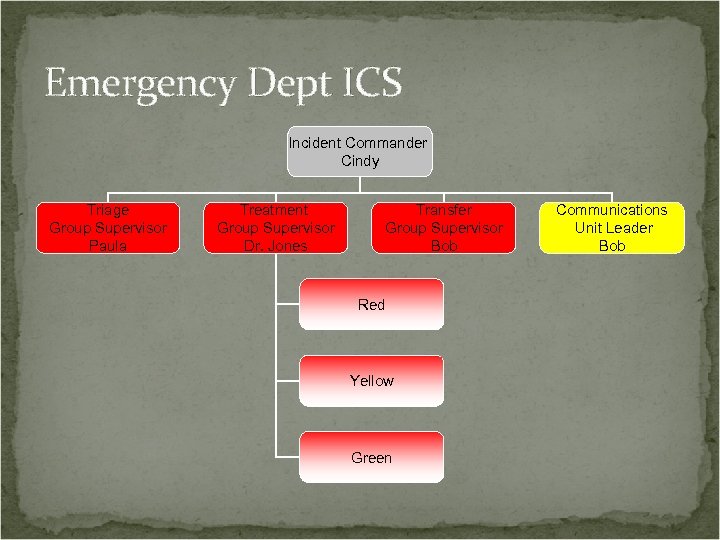 Emergency Dept ICS Incident Commander Cindy Triage Group Supervisor Paula Treatment Group Supervisor Dr. Jones Transfer Group Supervisor Bob Red Yellow Green Communications Unit Leader Bob
Emergency Dept ICS Incident Commander Cindy Triage Group Supervisor Paula Treatment Group Supervisor Dr. Jones Transfer Group Supervisor Bob Red Yellow Green Communications Unit Leader Bob
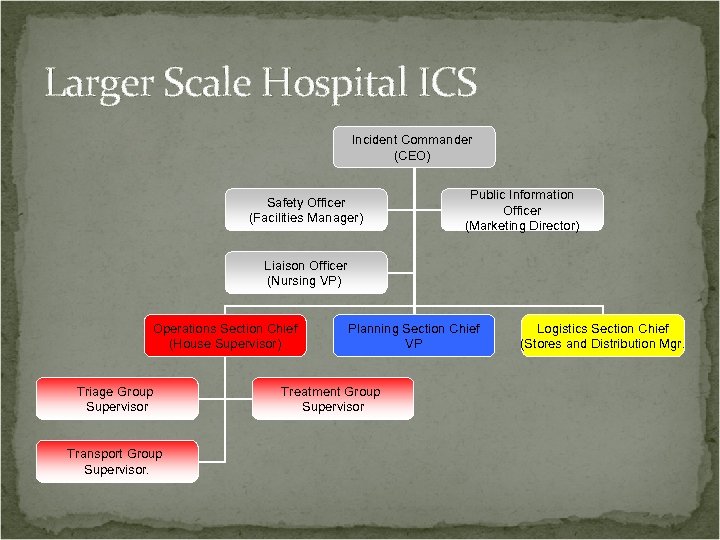 Larger Scale Hospital ICS Incident Commander (CEO) Safety Officer (Facilities Manager) Public Information Officer (Marketing Director) Liaison Officer (Nursing VP) Operations Section Chief (House Supervisor) Triage Group Supervisor Transport Group Supervisor. Planning Section Chief VP Treatment Group Supervisor Logistics Section Chief (Stores and Distribution Mgr.
Larger Scale Hospital ICS Incident Commander (CEO) Safety Officer (Facilities Manager) Public Information Officer (Marketing Director) Liaison Officer (Nursing VP) Operations Section Chief (House Supervisor) Triage Group Supervisor Transport Group Supervisor. Planning Section Chief VP Treatment Group Supervisor Logistics Section Chief (Stores and Distribution Mgr.
 Mobilization of Resources What resources are available to my community during an MCI?
Mobilization of Resources What resources are available to my community during an MCI?
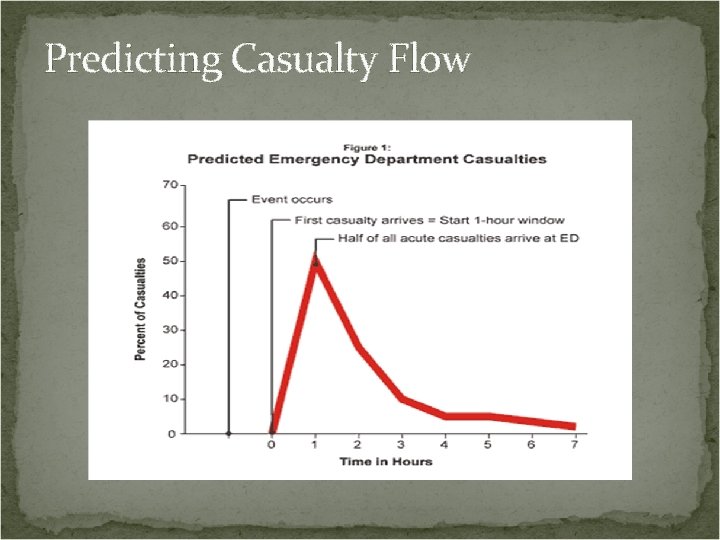 Predicting Casualty Flow
Predicting Casualty Flow
 Local Resources Ground Ambulances EMTs Air Ambulances Flight Crews Fire/Rescue Vehicles Firefighters ED beds MDs, RNs Hospital beds RNs, CNAs Operating Rooms Surgeons, OR Crews Blood Supply Blood Bank Staff Imaging/Lab Capacity Imaging/Lab Staff Ventilators Resp Therapists
Local Resources Ground Ambulances EMTs Air Ambulances Flight Crews Fire/Rescue Vehicles Firefighters ED beds MDs, RNs Hospital beds RNs, CNAs Operating Rooms Surgeons, OR Crews Blood Supply Blood Bank Staff Imaging/Lab Capacity Imaging/Lab Staff Ventilators Resp Therapists
 External Resources Refer to the “External Resources” handout in your packet: Regional (Chem. Paks, Antibiotics, Antivirals) State (MCI trailers in Helena, MHMAS ) Federal (DMAT, SNS, FEMA)
External Resources Refer to the “External Resources” handout in your packet: Regional (Chem. Paks, Antibiotics, Antivirals) State (MCI trailers in Helena, MHMAS ) Federal (DMAT, SNS, FEMA)
 ICS/MCI Roles & Responsibilities Every incident must have an Incident Commander. In the next few slides we will describe the positions/functions within the Incident Command System critical to managing multiple casualty incidents.
ICS/MCI Roles & Responsibilities Every incident must have an Incident Commander. In the next few slides we will describe the positions/functions within the Incident Command System critical to managing multiple casualty incidents.
 Key ICS Roles in a MCI IC – Every incident must have an IC Medical Branch Director – Only if the incident is big enough and you have the resources to fill the position. Triage Group Supervisor Treatment Group Supervisor Transport/Transfer Group Supervisor Rescue or Decon Group Supervisor
Key ICS Roles in a MCI IC – Every incident must have an IC Medical Branch Director – Only if the incident is big enough and you have the resources to fill the position. Triage Group Supervisor Treatment Group Supervisor Transport/Transfer Group Supervisor Rescue or Decon Group Supervisor
 The Incident Commander Role: Assumes and announces command Leads response effort
The Incident Commander Role: Assumes and announces command Leads response effort
 IC Responsibilities: Assess incident and communicate an Incident Action Plan (IAP) Ensure the safety of responders Request additional resources Develop organizational structure that effectively manages incident (Assign, Delegate) Develop plans that stay ahead of the need for resources Maintain Command until Command is transferred.
IC Responsibilities: Assess incident and communicate an Incident Action Plan (IAP) Ensure the safety of responders Request additional resources Develop organizational structure that effectively manages incident (Assign, Delegate) Develop plans that stay ahead of the need for resources Maintain Command until Command is transferred.
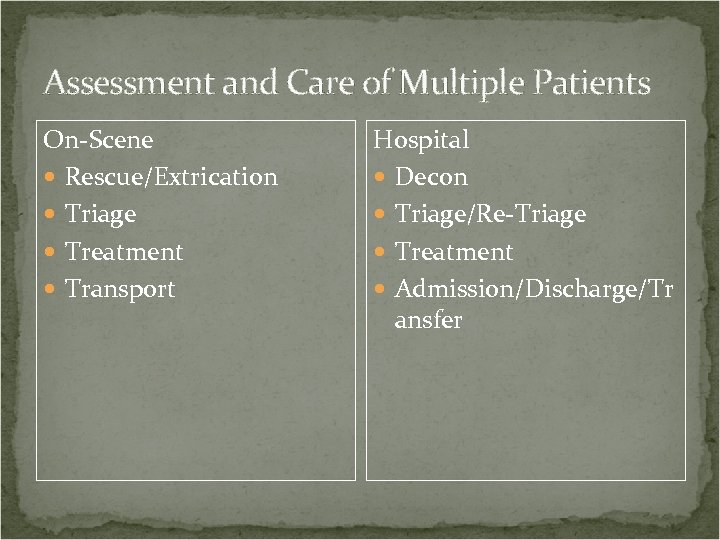 Assessment and Care of Multiple Patients On-Scene Rescue/Extrication Triage Treatment Transport Hospital Decon Triage/Re-Triage Treatment Admission/Discharge/Tr ansfer
Assessment and Care of Multiple Patients On-Scene Rescue/Extrication Triage Treatment Transport Hospital Decon Triage/Re-Triage Treatment Admission/Discharge/Tr ansfer
 Medical Branch Director Responsibilities Takes the medical burden off the IC or Operations Section Chief The Medical Branch Director assigns and supervises the triage, treatment and transfer group supervisors The Medical Branch Director reports to the Operations Section Chief or the IC
Medical Branch Director Responsibilities Takes the medical burden off the IC or Operations Section Chief The Medical Branch Director assigns and supervises the triage, treatment and transfer group supervisors The Medical Branch Director reports to the Operations Section Chief or the IC
 Rescue Group(s) This and triage are happening simultaneously – in concert with each other. Extrication Technical Rescue Dive Teams Haz. Mat Decon Patient Movement (out of hazard zone to patient collection area/treatment tarps)
Rescue Group(s) This and triage are happening simultaneously – in concert with each other. Extrication Technical Rescue Dive Teams Haz. Mat Decon Patient Movement (out of hazard zone to patient collection area/treatment tarps)
 On-Scene Triage Responsibilities: Size up number and acuity of patients See each patient rapidly and categorize using a standard triage system Document the triage category assigned Communicate (with who) the order of treatment (who needs help first? )
On-Scene Triage Responsibilities: Size up number and acuity of patients See each patient rapidly and categorize using a standard triage system Document the triage category assigned Communicate (with who) the order of treatment (who needs help first? )
 Hospital Triage Responsibilities: • Identify the location(s) where triage will occur • Ensure safe access and egress • Anticipate self transporting patients • Implement hospital MCI triage protocol* • Communicate / document triage decisions to Treatment Group
Hospital Triage Responsibilities: • Identify the location(s) where triage will occur • Ensure safe access and egress • Anticipate self transporting patients • Implement hospital MCI triage protocol* • Communicate / document triage decisions to Treatment Group
 Scene Treatment Responsibilities: Locate a suitable treatment area and report that location to Triage Group Supervisor and Command. Evaluate resources required for patient treatment, and report those needs to Command Provide suitable “immediate” and “delayed” treatment areas. Assign, direct, supervise, and coordinate personnel within your group. Allocate resources. Provide lifesaving basic life support before advanced life support. Match patient needs with provider skills Report progress to Command
Scene Treatment Responsibilities: Locate a suitable treatment area and report that location to Triage Group Supervisor and Command. Evaluate resources required for patient treatment, and report those needs to Command Provide suitable “immediate” and “delayed” treatment areas. Assign, direct, supervise, and coordinate personnel within your group. Allocate resources. Provide lifesaving basic life support before advanced life support. Match patient needs with provider skills Report progress to Command
 Hospital Treatment Responsibilities • Provide definitive care: identify and fix the problem • Provide lifesaving basic life support before advanced life support. • Organize care providers into efficient teams – use ICS principles to maintain control. • Match patient needs with provider skills. • Use available resources, making decisions about resource allocation at each step. • Use tools to document and aid organization • Transport/Transfer/Admit them to the place where these needs can be met.
Hospital Treatment Responsibilities • Provide definitive care: identify and fix the problem • Provide lifesaving basic life support before advanced life support. • Organize care providers into efficient teams – use ICS principles to maintain control. • Match patient needs with provider skills. • Use available resources, making decisions about resource allocation at each step. • Use tools to document and aid organization • Transport/Transfer/Admit them to the place where these needs can be met.
 Scene Transport Responsibilities: Establish/communicate location of ambulance staging (if Command has not already done so) and patient loading areas. Report resource requirements to Command Establish/manage a helicopter landing site if warranted Communicate with Command Hospitals to obtain medical facility status and treatment capabilities. Supervise assigned personnel Coordinate with other divisions/groups Efficiently and safely move patients to the next location in the continuum of care while providing for their medical needs enroute. Report progress to Command
Scene Transport Responsibilities: Establish/communicate location of ambulance staging (if Command has not already done so) and patient loading areas. Report resource requirements to Command Establish/manage a helicopter landing site if warranted Communicate with Command Hospitals to obtain medical facility status and treatment capabilities. Supervise assigned personnel Coordinate with other divisions/groups Efficiently and safely move patients to the next location in the continuum of care while providing for their medical needs enroute. Report progress to Command
 Hospital Transfer Responsibilities • Communicate with treatment group supervisor for information about patients who need transfer to other facilities • Determine the number and type of transportation resources needed and available. • Arrange transport to referral centers (stage resources early? ) • Stage resources until needed • Efficiently and safely move patients to the next location in the continuum of care while providing for their medical needs enroute. • Communicate with receiving facilities to determine capacity and provide advance information
Hospital Transfer Responsibilities • Communicate with treatment group supervisor for information about patients who need transfer to other facilities • Determine the number and type of transportation resources needed and available. • Arrange transport to referral centers (stage resources early? ) • Stage resources until needed • Efficiently and safely move patients to the next location in the continuum of care while providing for their medical needs enroute. • Communicate with receiving facilities to determine capacity and provide advance information
 Staying Organized Organizational Tools Plans Protocols Forms Job Action Sheets
Staying Organized Organizational Tools Plans Protocols Forms Job Action Sheets
 Break
Break


