1245faf0839eaeeecb6bfaa58203f7fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

The Importance of Robotics to Our Future by John Chamberlain, MS CS ‘ 93
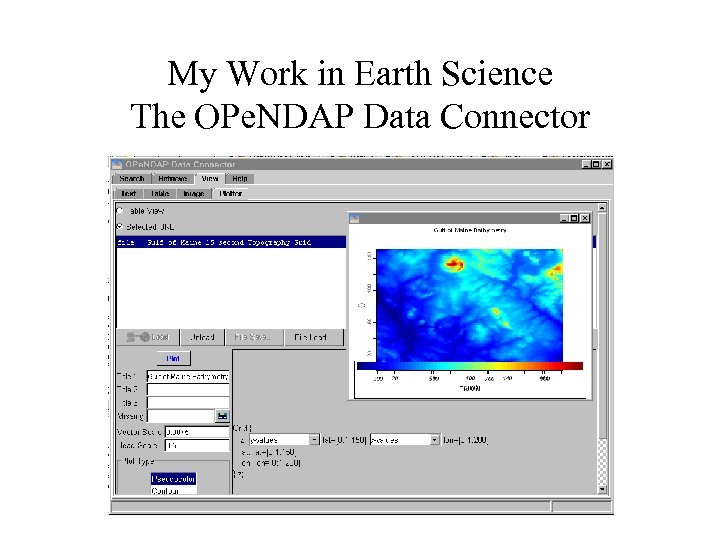
My Work in Earth Science The OPe. NDAP Data Connector

One of my J 2 ME Apps: Handi. Pro
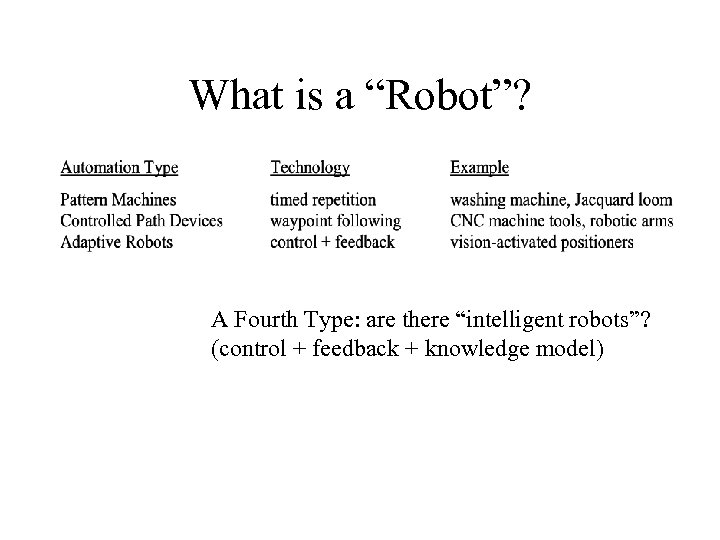
What is a “Robot”? A Fourth Type: are there “intelligent robots”? (control + feedback + knowledge model)

Physical Automation = Currently the single-most important factor in human productivity

The Invisible Revolution • Robotics is the key driver in GDP growth • Robotics is enabling new technologies • Robotics is self-sustaining

Penalty for Not Automating • Non-automated countries are experiencing net decline in per capita GDP • Non-automated countries have accelerating debt loads • Military impotence • Loss of control of local resources
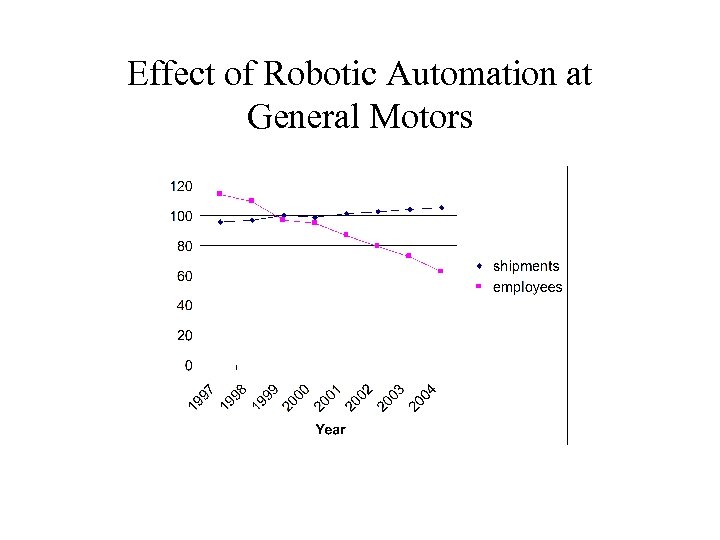
Effect of Robotic Automation at General Motors

The Economy and Automation 1. locate the resources (satellites, probes) 2. gather the resources (farming, mining automation) 3. refine into materials (mill and plant robotics) 4. shape material (tooling) 6. assemble (assemblers, welders, attachment) 7. distribute (packing, palletizing, and transport)
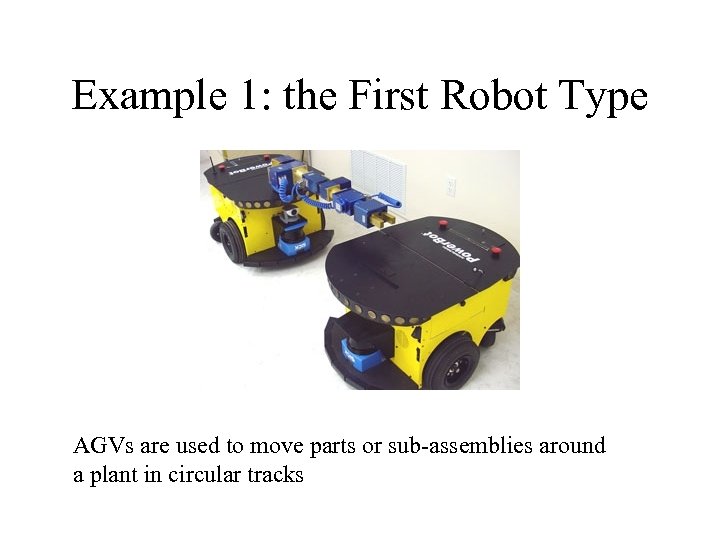
Example 1: the First Robot Type AGVs are used to move parts or sub-assemblies around a plant in circular tracks

Example 2: Gantry Robots 5 -axis gantry robots are commonly used to cut molds
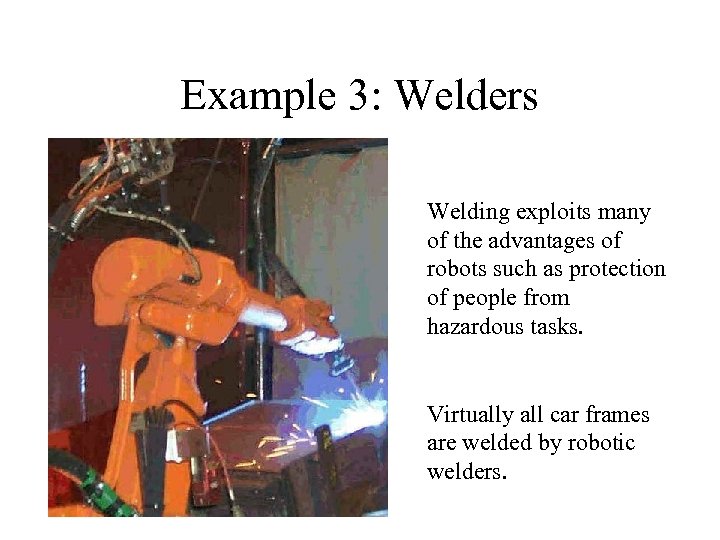
Example 3: Welders Welding exploits many of the advantages of robots such as protection of people from hazardous tasks. Virtually all car frames are welded by robotic welders.

Example 4: Integrated Guidance This John Deere planter uses a GPS guidance system to vary planting depth and other parameters according to field plan created by the farmer on a PC.
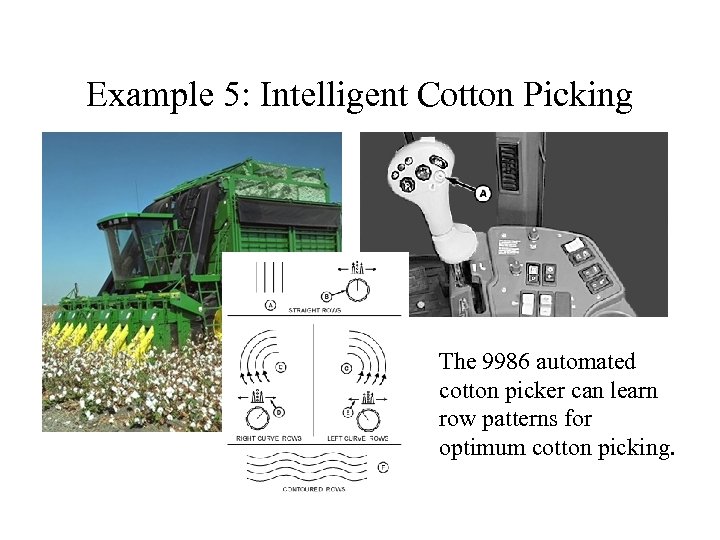
Example 5: Intelligent Cotton Picking The 9986 automated cotton picker can learn row patterns for optimum cotton picking.
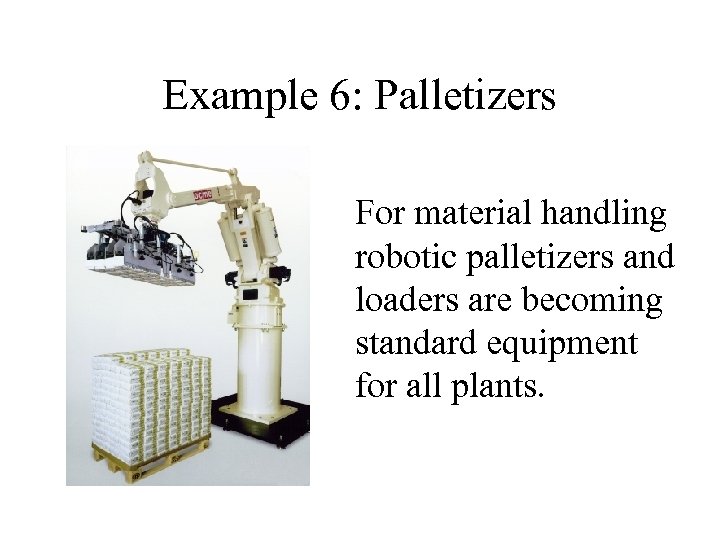
Example 6: Palletizers For material handling robotic palletizers and loaders are becoming standard equipment for all plants.

Example 7: Textile Attachment This robotic hemmer is an example of the future for textiles which could spell radical changes in global trade.

Example 8: Automated Mining This continuous mining machine is on the cutting edge of mineral recovery. Guidance is an important problem.

Key Robotic Technology Areas • • • Servos (feedback controls) Motor drivers and controllers Real-time operating systems Facility management software Robot learning and guidance software
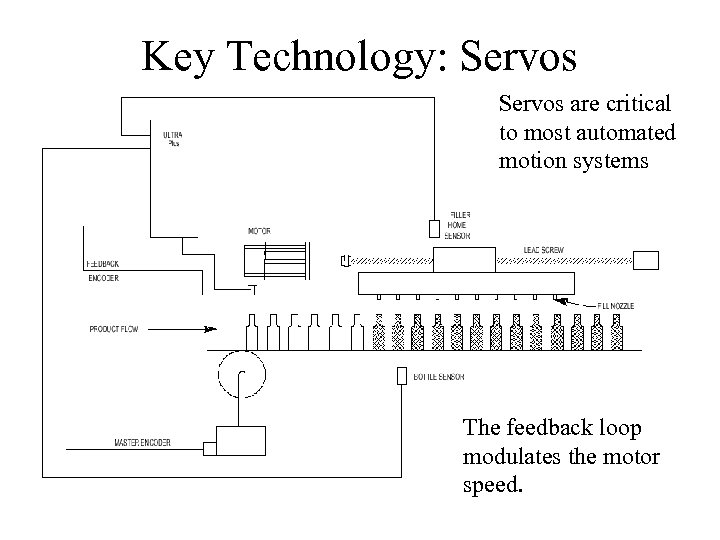
Key Technology: Servos are critical to most automated motion systems The feedback loop modulates the motor speed.
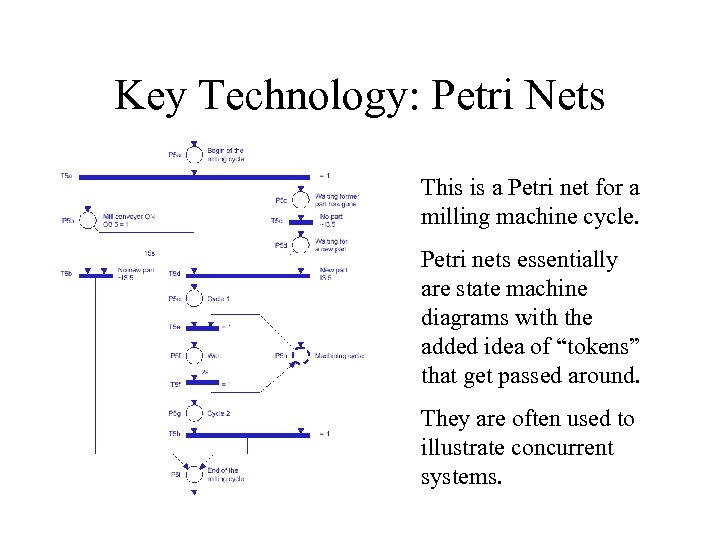
Key Technology: Petri Nets This is a Petri net for a milling machine cycle. Petri nets essentially are state machine diagrams with the added idea of “tokens” that get passed around. They are often used to illustrate concurrent systems.
Key Problems • Real-time motion control (inverse kinematics); “the baseball problem” • Object recognition • Action planning and definition (modeling)

What is the current role for software developers? Answer: not enough.

Ariane-501 June 4, 1996

Reason for Failure? • • • Insufficient Testing Lack of a software backup Running auxiliary tasks on main process Failure to use exception handling Making a downcast

Real Reason for Failure

Improving the Role of Computer Scientists in Robotics • Increase training in key robotics areas such as control systems and basic electronics • Focus the biggest robotics problem of all: behavior description and modeling • Participate in active projects and events such as the upcoming robotics olympics

Oh my goodness! Shut me down. Machines making machines. How perverse! - C 3 PO (Star Wars Episode II: Attack of the Clones)
1245faf0839eaeeecb6bfaa58203f7fa.ppt