0e7a4bdb310261cbe5b1b6d2d65d8023.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 The IEA Response System for Oil Supply Emergencies Aad van Bohemen Head, Emergency Policy Division International Energy Agency For 38 th Meeting of the APEC Energy Working Group, Bali, Indonesia, 16 -20 November 2009 © OECD/IEA - 2009
The IEA Response System for Oil Supply Emergencies Aad van Bohemen Head, Emergency Policy Division International Energy Agency For 38 th Meeting of the APEC Energy Working Group, Bali, Indonesia, 16 -20 November 2009 © OECD/IEA - 2009
 The International Energy Agency 28 member countries Poland ENERGY SUPPLY Australia Austria Belgium Canada Czech Republic Denmark Japan Finland France Korea Greece Germany New Zealand Hungary Ireland United States Italy Luxembourg Norway The Netherlands Portugal Switzerland Slovakia Spain Turkey Sweden United Kingdom © OECD/IEA - 2009
The International Energy Agency 28 member countries Poland ENERGY SUPPLY Australia Austria Belgium Canada Czech Republic Denmark Japan Finland France Korea Greece Germany New Zealand Hungary Ireland United States Italy Luxembourg Norway The Netherlands Portugal Switzerland Slovakia Spain Turkey Sweden United Kingdom © OECD/IEA - 2009
 APEC – IEA cooperation ENERGY SUPPLY Energy Security Initiative (ESI) l JODI ØTo promote market transparency l Real-time Sharing System ØCoordination of contingency plans l Emergency responses; oil stocks ØCooperation with the IEA ØMembers report arrangements on a voluntary basis 3 © OECD/IEA - 2009
APEC – IEA cooperation ENERGY SUPPLY Energy Security Initiative (ESI) l JODI ØTo promote market transparency l Real-time Sharing System ØCoordination of contingency plans l Emergency responses; oil stocks ØCooperation with the IEA ØMembers report arrangements on a voluntary basis 3 © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Impetus to establish the IEA 1973/74 oil crisis ENERGY SUPPLY l Avoid competition for limited supplies Ø“Go-it-alone”, uncoordinated policy ineffective l Coordinated action Ømechanism for response l Safety net Øemergency reserves ≥ 90 days of net oil imports ØDemand restraint measures (7 -10%) 4 © OECD/IEA - 2009
Impetus to establish the IEA 1973/74 oil crisis ENERGY SUPPLY l Avoid competition for limited supplies Ø“Go-it-alone”, uncoordinated policy ineffective l Coordinated action Ømechanism for response l Safety net Øemergency reserves ≥ 90 days of net oil imports ØDemand restraint measures (7 -10%) 4 © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Member Government Responsibilities l Legislation ENERGY SUPPLY to ensure participation in IEA decisions with appropriate emergency measures l Emergency response team (NESO) ØCo-ordinate emergency operations ØInterface with domestic oil industry ØInterface with IEA emergency operations l Data collection ØMonthly Oil Statistics ØEmergency questionnaire © OECD/IEA - 2009
Member Government Responsibilities l Legislation ENERGY SUPPLY to ensure participation in IEA decisions with appropriate emergency measures l Emergency response team (NESO) ØCo-ordinate emergency operations ØInterface with domestic oil industry ØInterface with IEA emergency operations l Data collection ØMonthly Oil Statistics ØEmergency questionnaire © OECD/IEA - 2009
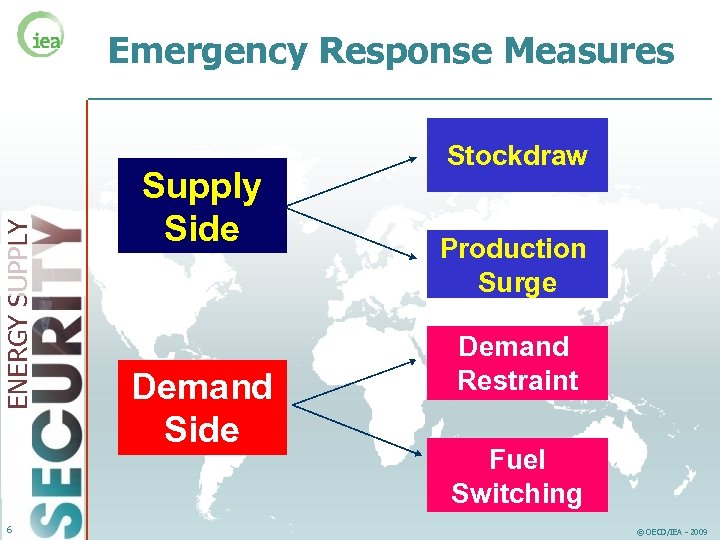 ENERGY SUPPLY Emergency Response Measures 6 Supply Side Demand Side Stockdraw Production Surge Demand Restraint Fuel Switching © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY Emergency Response Measures 6 Supply Side Demand Side Stockdraw Production Surge Demand Restraint Fuel Switching © OECD/IEA - 2009
 IEA Stockholding Obligation l Total oil reserves cover at least 90 days ENERGY SUPPLY Ø Net-imports of previous year Ø Crude and refined product 7 l The calculation Ø excludes marine bunkers and naphtha Ø deducts 10% for unavailable stocks l Main types of stocks excluded: Ø oil not yet produced Ø stocks held in pipelines, tankers at sea, in service stations, retail stores, military stocks © OECD/IEA - 2009
IEA Stockholding Obligation l Total oil reserves cover at least 90 days ENERGY SUPPLY Ø Net-imports of previous year Ø Crude and refined product 7 l The calculation Ø excludes marine bunkers and naphtha Ø deducts 10% for unavailable stocks l Main types of stocks excluded: Ø oil not yet produced Ø stocks held in pipelines, tankers at sea, in service stations, retail stores, military stocks © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Stockholding Options l Industry stocks ENERGY SUPPLY Compulsory stocks and commercial stocks held by companies l Public stocks Ø Government stocks Financed with central government budget, Held exclusively for emergency purposes or Ø Agency stocks Maintained for emergency purposes Held/controlled by public bodies or agencies 8 © OECD/IEA - 2009
Stockholding Options l Industry stocks ENERGY SUPPLY Compulsory stocks and commercial stocks held by companies l Public stocks Ø Government stocks Financed with central government budget, Held exclusively for emergency purposes or Ø Agency stocks Maintained for emergency purposes Held/controlled by public bodies or agencies 8 © OECD/IEA - 2009
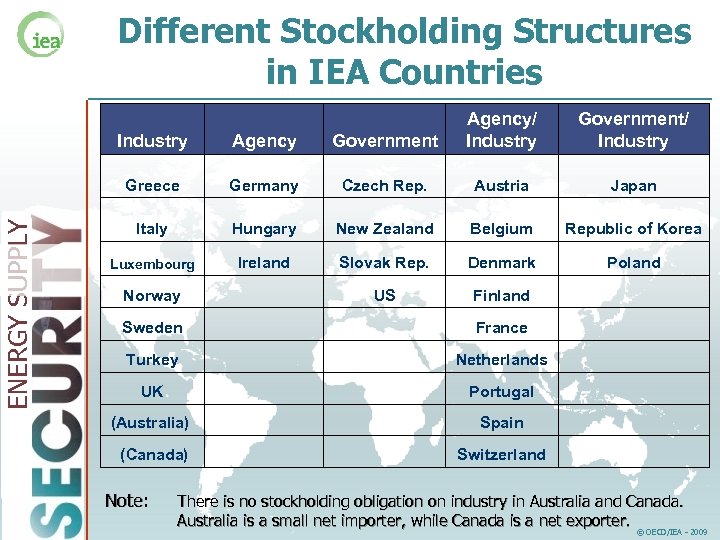 Different Stockholding Structures in IEA Countries Agency Government Greece ENERGY SUPPLY Industry Agency/ Industry Germany Czech Rep. Austria Japan Italy Hungary New Zealand Belgium Republic of Korea Luxembourg Ireland Slovak Rep. Denmark Poland US Finland Norway Sweden Government/ Industry France UK Netherlands Portugal Turkey (Australia) Spain (Canada) Switzerland Note: There is no stockholding obligation on industry in Australia and Canada. Australia is a small net importer, while Canada is a net exporter. © OECD/IEA - 2009
Different Stockholding Structures in IEA Countries Agency Government Greece ENERGY SUPPLY Industry Agency/ Industry Germany Czech Rep. Austria Japan Italy Hungary New Zealand Belgium Republic of Korea Luxembourg Ireland Slovak Rep. Denmark Poland US Finland Norway Sweden Government/ Industry France UK Netherlands Portugal Turkey (Australia) Spain (Canada) Switzerland Note: There is no stockholding obligation on industry in Australia and Canada. Australia is a small net importer, while Canada is a net exporter. © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Financing Mechanisms l Government/Agency Stocks ENERGY SUPPLY A variety of financing methods Ø Initial set-up/capital costs v Financed from central government budget v Bank loans also used Ø Running costs of stockholding agencies v Financed from central government budget v Through a fee (levy) charged on product sales v Through a fee charged to industry l Compulsory Industry Stocks Ø Relevant costs are included in consumer prices and borne directly by consumers © OECD/IEA - 2009
Financing Mechanisms l Government/Agency Stocks ENERGY SUPPLY A variety of financing methods Ø Initial set-up/capital costs v Financed from central government budget v Bank loans also used Ø Running costs of stockholding agencies v Financed from central government budget v Through a fee (levy) charged on product sales v Through a fee charged to industry l Compulsory Industry Stocks Ø Relevant costs are included in consumer prices and borne directly by consumers © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Public Stockholding - Choices l What to hold? ENERGY SUPPLY Ø Crude vs. Product l How to hold it? Ø Own storage / rented Ø Co-mingled / segregated l How to release it? Ø Loans, tender, sales Whatever the means for releasing public stocks, the process should be clear for all and regularly tested © OECD/IEA - 2009
Public Stockholding - Choices l What to hold? ENERGY SUPPLY Ø Crude vs. Product l How to hold it? Ø Own storage / rented Ø Co-mingled / segregated l How to release it? Ø Loans, tender, sales Whatever the means for releasing public stocks, the process should be clear for all and regularly tested © OECD/IEA - 2009
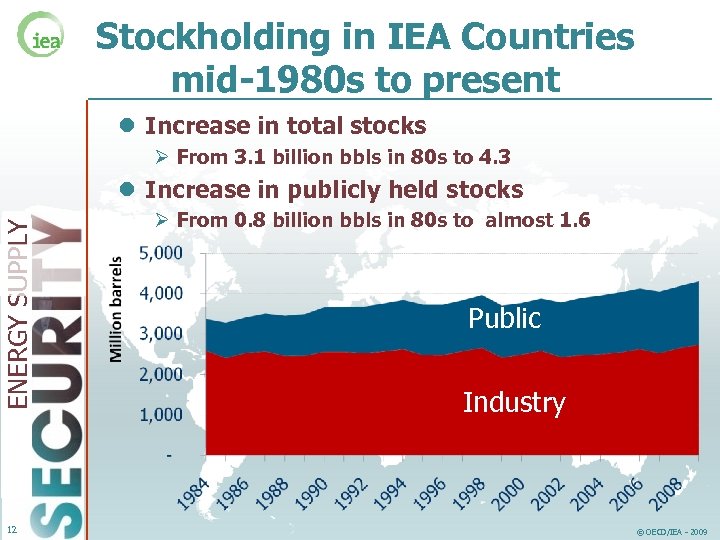 Stockholding in IEA Countries mid-1980 s to present l Increase in total stocks Ø From 3. 1 billion bbls in 80 s to 4. 3 ENERGY SUPPLY l Increase in publicly held stocks 12 Ø From 0. 8 billion bbls in 80 s to almost 1. 6 Public Industry © OECD/IEA - 2009
Stockholding in IEA Countries mid-1980 s to present l Increase in total stocks Ø From 3. 1 billion bbls in 80 s to 4. 3 ENERGY SUPPLY l Increase in publicly held stocks 12 Ø From 0. 8 billion bbls in 80 s to almost 1. 6 Public Industry © OECD/IEA - 2009
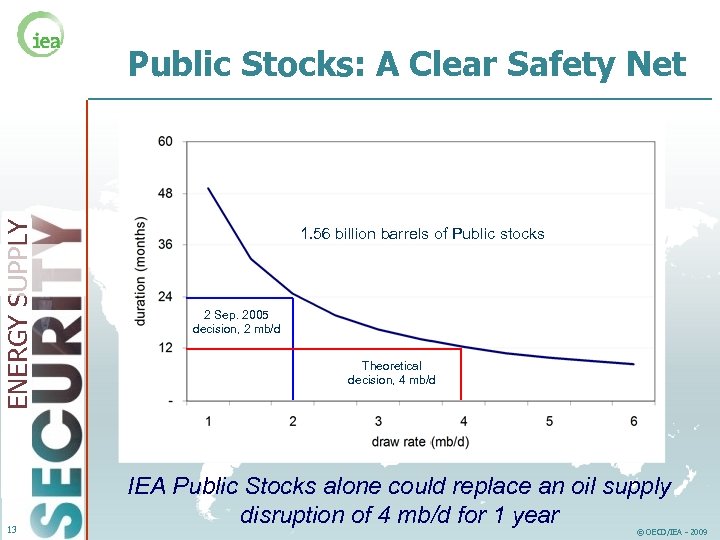 ENERGY SUPPLY Public Stocks: A Clear Safety Net 13 1. 56 billion barrels of Public stocks 2 Sep. 2005 decision, 2 mb/d Theoretical decision, 4 mb/d IEA Public Stocks alone could replace an oil supply disruption of 4 mb/d for 1 year © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY Public Stocks: A Clear Safety Net 13 1. 56 billion barrels of Public stocks 2 Sep. 2005 decision, 2 mb/d Theoretical decision, 4 mb/d IEA Public Stocks alone could replace an oil supply disruption of 4 mb/d for 1 year © OECD/IEA - 2009
 New Emergency Response System ENERGY SUPPLY l 2002 - Initial Contingency Response Plan (ICRP) Ø Standing procedure for § § Prompt, first reaction for 30 days Provides time to consider follow-up action Broad consultation Unanimous decision Ø Executive Director can take initiative § GB members decide § No meeting required Ø Attributes country shares of total response, based on normal oil consumption 14 © OECD/IEA - 2009
New Emergency Response System ENERGY SUPPLY l 2002 - Initial Contingency Response Plan (ICRP) Ø Standing procedure for § § Prompt, first reaction for 30 days Provides time to consider follow-up action Broad consultation Unanimous decision Ø Executive Director can take initiative § GB members decide § No meeting required Ø Attributes country shares of total response, based on normal oil consumption 14 © OECD/IEA - 2009
 IEA Emergency Oil Stock Policy ENERGY SUPPLY The emergency oil stocks l are not for price management 15 Ø ineffective over time Ø masks important price signals l are for short-term oil supply disruptions Ø when market mechanisms break down temporarily Ø provide liquidity for markets to recover Strategic oil stocks cannot effectively replace market mechanisms, only mitigate short-term supply disruptions © OECD/IEA - 2009
IEA Emergency Oil Stock Policy ENERGY SUPPLY The emergency oil stocks l are not for price management 15 Ø ineffective over time Ø masks important price signals l are for short-term oil supply disruptions Ø when market mechanisms break down temporarily Ø provide liquidity for markets to recover Strategic oil stocks cannot effectively replace market mechanisms, only mitigate short-term supply disruptions © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Every disruption is different: Making the assessment ENERGY SUPPLY l What is the full extent of the outage? Ø Will global supply be affected? Ø How long will supply be off line? Ø Are crude, products or both affected? Ø Will there be a direct impact on consumption? l Will spare capacity act as an offset? Ø OPEC dialogue very important Ø Does crude quality match lost supplies? l What will be the market impact of intervention? l Is a regional response necessary? Ø Global market - outages rarely affect only one region © OECD/IEA - 2009
Every disruption is different: Making the assessment ENERGY SUPPLY l What is the full extent of the outage? Ø Will global supply be affected? Ø How long will supply be off line? Ø Are crude, products or both affected? Ø Will there be a direct impact on consumption? l Will spare capacity act as an offset? Ø OPEC dialogue very important Ø Does crude quality match lost supplies? l What will be the market impact of intervention? l Is a regional response necessary? Ø Global market - outages rarely affect only one region © OECD/IEA - 2009
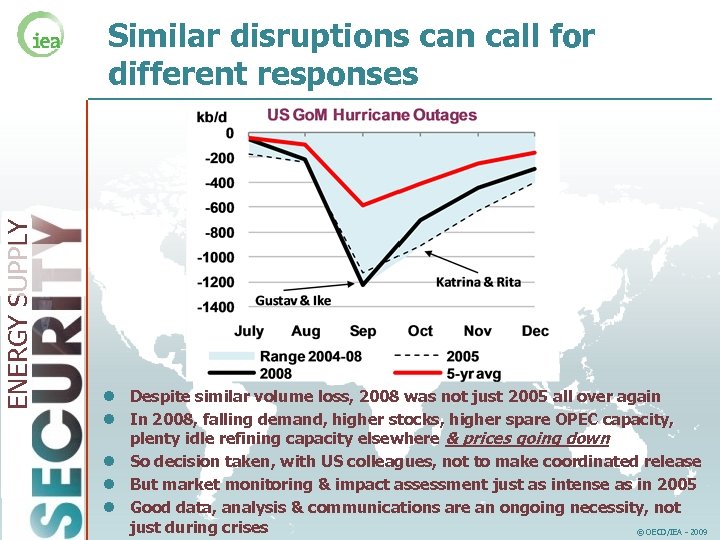 ENERGY SUPPLY Similar disruptions can call for different responses l Despite similar volume loss, 2008 was not just 2005 all over again l In 2008, falling demand, higher stocks, higher spare OPEC capacity, plenty idle refining capacity elsewhere & prices going down l So decision taken, with US colleagues, not to make coordinated release l But market monitoring & impact assessment just as intense as in 2005 l Good data, analysis & communications are an ongoing necessity, not just during crises © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY Similar disruptions can call for different responses l Despite similar volume loss, 2008 was not just 2005 all over again l In 2008, falling demand, higher stocks, higher spare OPEC capacity, plenty idle refining capacity elsewhere & prices going down l So decision taken, with US colleagues, not to make coordinated release l But market monitoring & impact assessment just as intense as in 2005 l Good data, analysis & communications are an ongoing necessity, not just during crises © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Strengthening Emergency Response Systems ENERGY SUPPLY l Emergency Response Reviews (ERR) Ø Country peer reviews on emergency preparedness Ø Checks procedures and institutional arrangements Ø Contributes to identify and improve the weak points of response system l Emergency Response Exercises (ERE) Ø Test the processes for: decision making, communicating, hypothetical release 18 © OECD/IEA - 2009
Strengthening Emergency Response Systems ENERGY SUPPLY l Emergency Response Reviews (ERR) Ø Country peer reviews on emergency preparedness Ø Checks procedures and institutional arrangements Ø Contributes to identify and improve the weak points of response system l Emergency Response Exercises (ERE) Ø Test the processes for: decision making, communicating, hypothetical release 18 © OECD/IEA - 2009
 ENERGY SUPPLY New Approach forward for ERE l Biannual exercises continued (ERE 5 in Paris scheduled in Nov. 2010) l Specific workshops for new or complex issues/policy l Rollout of ERE to key NMCs © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY New Approach forward for ERE l Biannual exercises continued (ERE 5 in Paris scheduled in Nov. 2010) l Specific workshops for new or complex issues/policy l Rollout of ERE to key NMCs © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Thailand-IEA Joint ERE (18 -19 May, 2009 in Bangkok) ENERGY SUPPLY l First time outside Paris, & with a non-member country l Training Session (120 people) Simulation Exercise (60 people) l Structure Ø CNN-style videos Ø Facilitator, game books l Exercise was well tailor-made for Thailand l Many lessons learnt to help Thailand enhance its energy security © OECD/IEA - 2009
Thailand-IEA Joint ERE (18 -19 May, 2009 in Bangkok) ENERGY SUPPLY l First time outside Paris, & with a non-member country l Training Session (120 people) Simulation Exercise (60 people) l Structure Ø CNN-style videos Ø Facilitator, game books l Exercise was well tailor-made for Thailand l Many lessons learnt to help Thailand enhance its energy security © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Outreach is one of IEA core activities: Recent activities with ASEAN in energy security ENERGY SUPPLY Sep. 2007: IEA/Mo. EN Workshop for ASEAN on “Oil Security and National Emergency Preparedness” (BKK) Feb. 2008: IEA-ASEAN Training Course on Oil Emergency Preparedness and Statistics (Paris) June 2008: ERE 4 (Paris) Ø All 10 ASEAN countries, ACE, ASCOPE participated © OECD/IEA - 2009
Outreach is one of IEA core activities: Recent activities with ASEAN in energy security ENERGY SUPPLY Sep. 2007: IEA/Mo. EN Workshop for ASEAN on “Oil Security and National Emergency Preparedness” (BKK) Feb. 2008: IEA-ASEAN Training Course on Oil Emergency Preparedness and Statistics (Paris) June 2008: ERE 4 (Paris) Ø All 10 ASEAN countries, ACE, ASCOPE participated © OECD/IEA - 2009
 ENERGY SUPPLY IEA Publications l “Oil Supply Security 2007”; chapters on ASEAN, China and India l Translation of Brochure on “IEA Response System for Oil Supply Emergencies” into Chinese, Indonesian, Russian, Spanish & Thai l “ Energy Policy Review of Indonesia ” l “ World Energy Outlook 2007 ”; China & India l “ World Energy Outlook 2009 ”; Southeast Asia © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY IEA Publications l “Oil Supply Security 2007”; chapters on ASEAN, China and India l Translation of Brochure on “IEA Response System for Oil Supply Emergencies” into Chinese, Indonesian, Russian, Spanish & Thai l “ Energy Policy Review of Indonesia ” l “ World Energy Outlook 2007 ”; China & India l “ World Energy Outlook 2009 ”; Southeast Asia © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Outreach to APEC will take off ENERGY SUPPLY Communiqué of IEA Ministerial Meeting (Oct. 14 -15, 2009) l IEA Member Countries Ministers asked IEA to Øto expand the training and workshops it offers to partner countries in order to bolster their capacity to formulate sound energy policy. l. Enhanced coordination with regional bodies, such as APEC and the African Union would be fruitful. © OECD/IEA - 2009
Outreach to APEC will take off ENERGY SUPPLY Communiqué of IEA Ministerial Meeting (Oct. 14 -15, 2009) l IEA Member Countries Ministers asked IEA to Øto expand the training and workshops it offers to partner countries in order to bolster their capacity to formulate sound energy policy. l. Enhanced coordination with regional bodies, such as APEC and the African Union would be fruitful. © OECD/IEA - 2009
 The Energy Training and Capacity-Building Programme l 2 year pilot programme, 2010 -2011 ENERGY SUPPLY l Flexible & Tailor-made Activities Ø Seminars, workshops, training sessions of several days to a week Ø To be held at Paris HQ or in host countries Ø Secondments & internships l Topics to be covered Ø Energy policy development Ø Emergency response capability Ø Energy statistics, etc. © OECD/IEA - 2009
The Energy Training and Capacity-Building Programme l 2 year pilot programme, 2010 -2011 ENERGY SUPPLY l Flexible & Tailor-made Activities Ø Seminars, workshops, training sessions of several days to a week Ø To be held at Paris HQ or in host countries Ø Secondments & internships l Topics to be covered Ø Energy policy development Ø Emergency response capability Ø Energy statistics, etc. © OECD/IEA - 2009
 Concluding Remarks: ENERGY SUPPLY Cooperation to be explored: 25 l Workshops l Training l Information sharing during disruptions l Emergency contact points l Emergency Response Exercises l Emergency Response Reviews l Coordination of use of measures during global disruptions © OECD/IEA - 2009
Concluding Remarks: ENERGY SUPPLY Cooperation to be explored: 25 l Workshops l Training l Information sharing during disruptions l Emergency contact points l Emergency Response Exercises l Emergency Response Reviews l Coordination of use of measures during global disruptions © OECD/IEA - 2009
 ENERGY SUPPLY Thank you 26 Contact details: aad. van. bohemen@iea. org epd@iea. org Web site: www. iea. org © OECD/IEA - 2009
ENERGY SUPPLY Thank you 26 Contact details: aad. van. bohemen@iea. org epd@iea. org Web site: www. iea. org © OECD/IEA - 2009


