7591d7a58992cd3dc54c9f36c2509acb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
The Human Visual System • Background on Vision • Human vision – the best system around • Deep network models
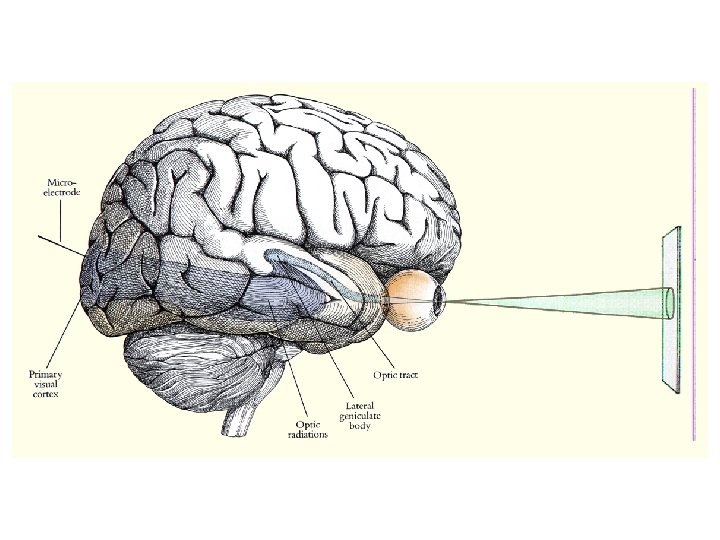
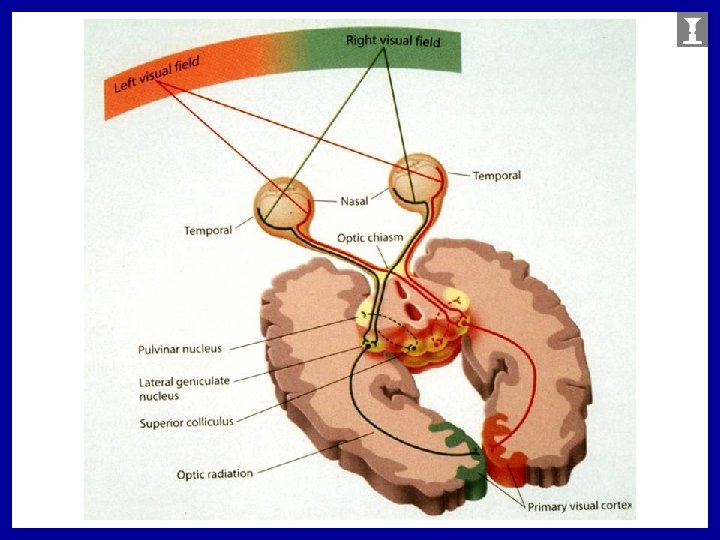

Hemifield neglect
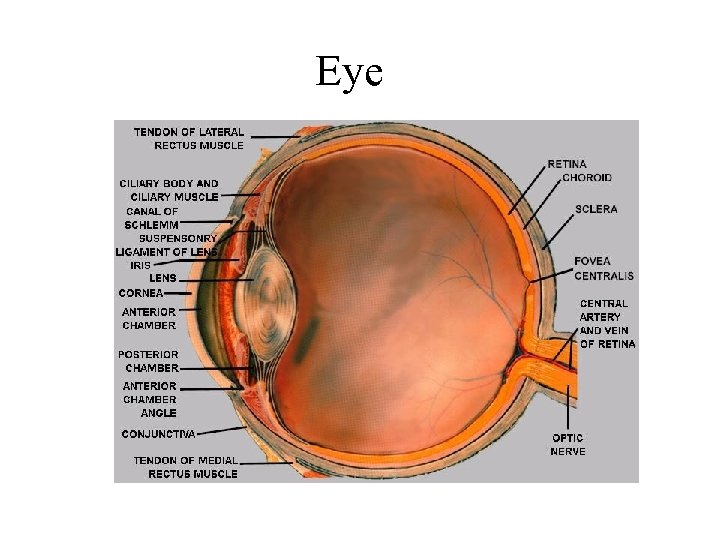
Eye
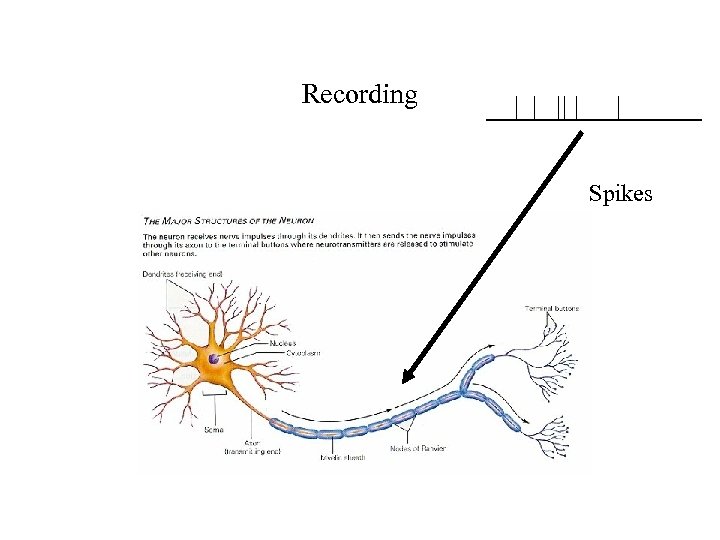
Recording Spikes
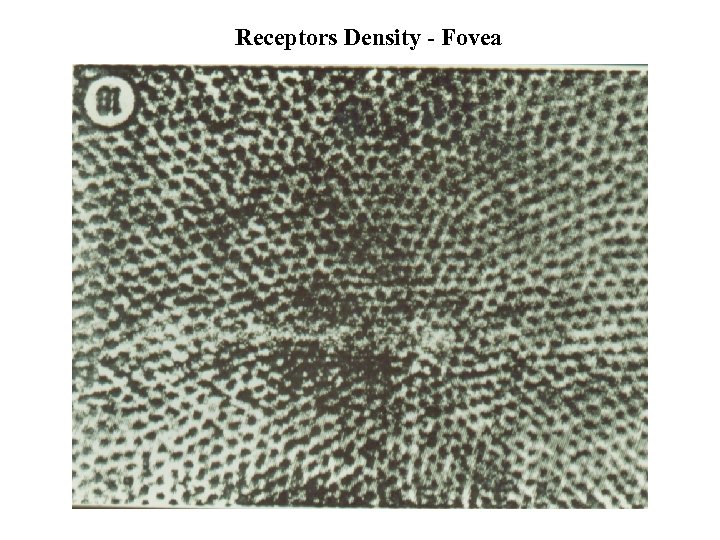
Receptors Density - Fovea

Image Capture • • • Huge dynamic range 10 -8 – 10+6 μW/cm 2 Photons: poisson process. Noisy at low levels For low light: large receptors, slow integration Rods/cones, local adaptation, change of amplitude and time constant, motion deblur

Poisson Distribution
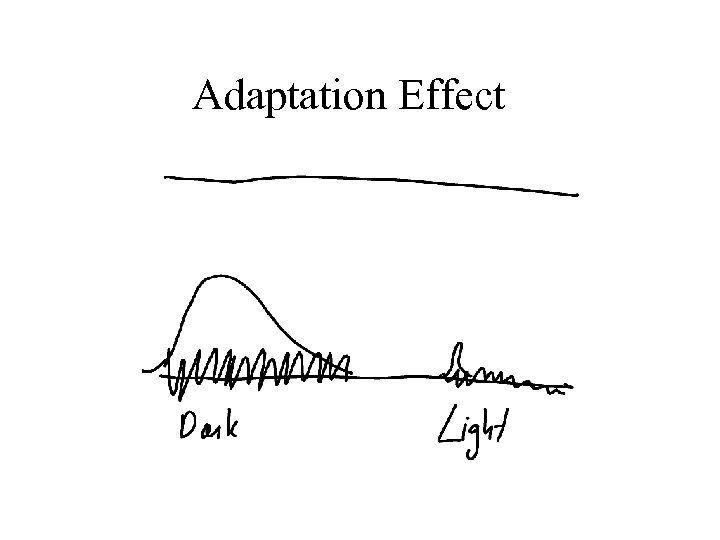
Adaptation Effect

Dynamic Range
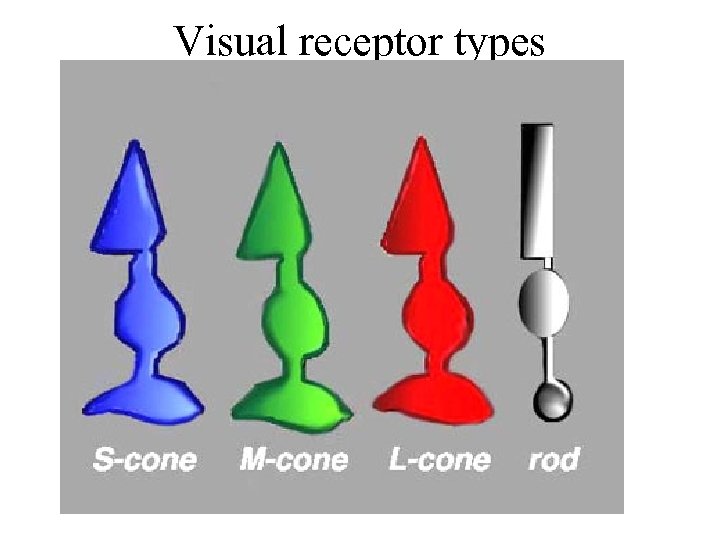
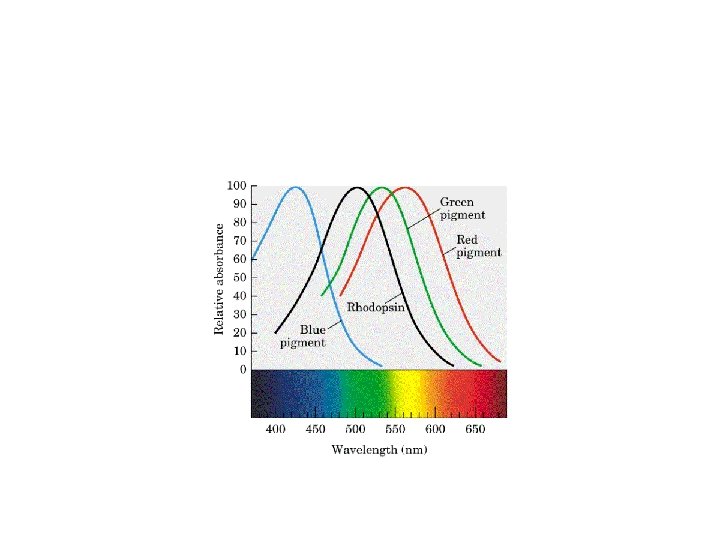
Visual receptor types
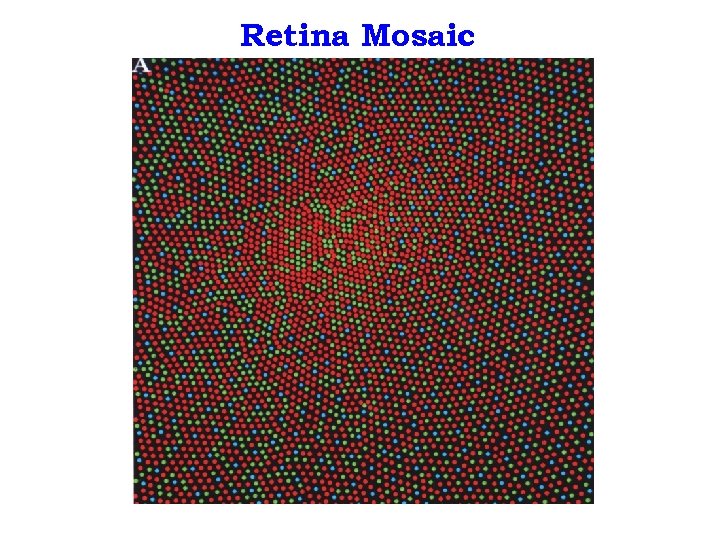
Retina Mosaic
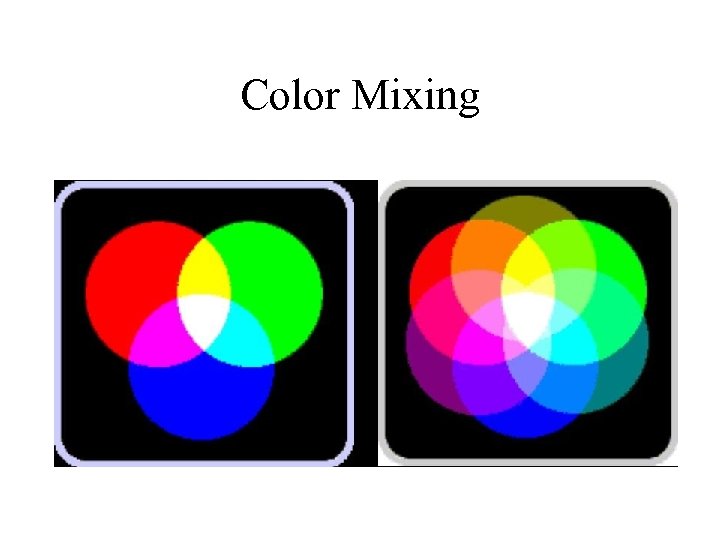
Color Mixing
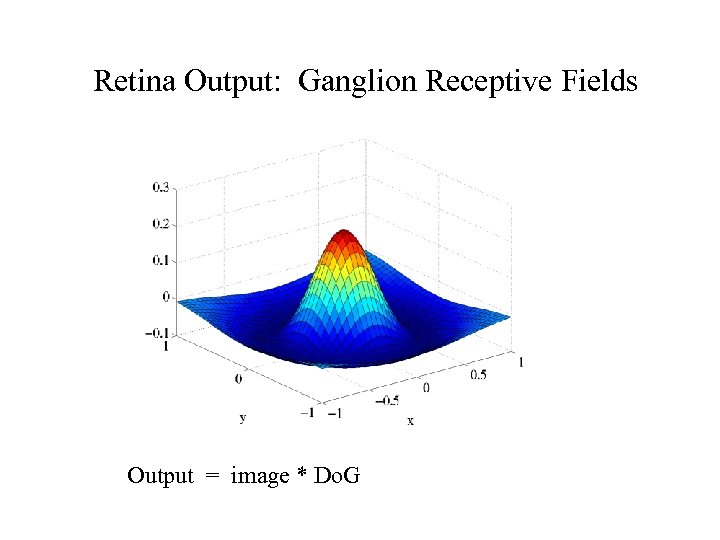
Retina Output: Ganglion Receptive Fields Output = image * Do. G

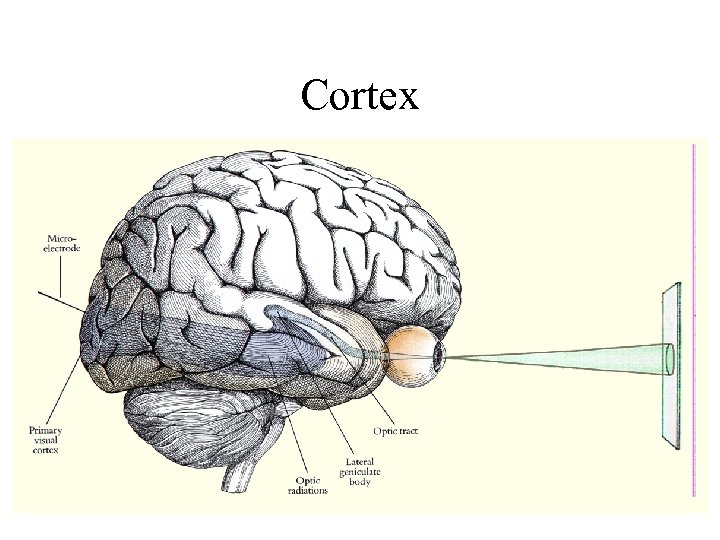
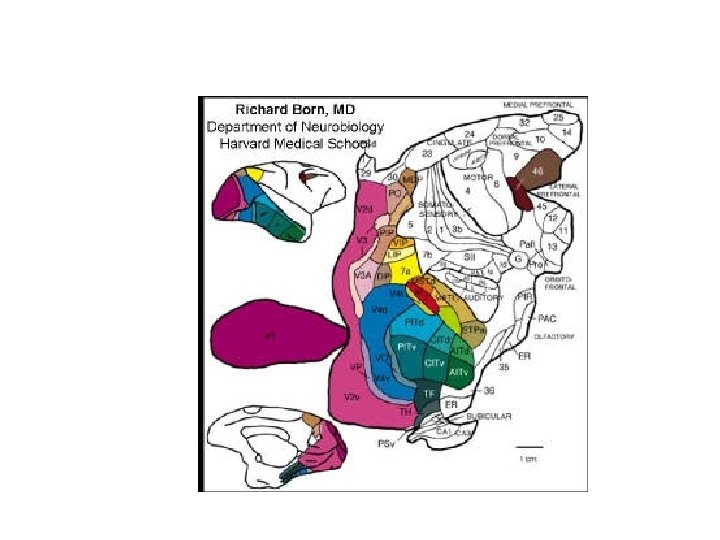
Cortex
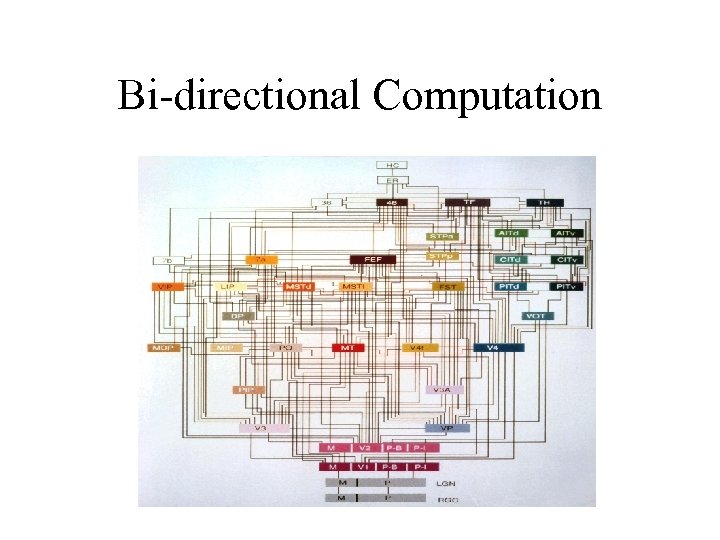
Bi-directional Computation
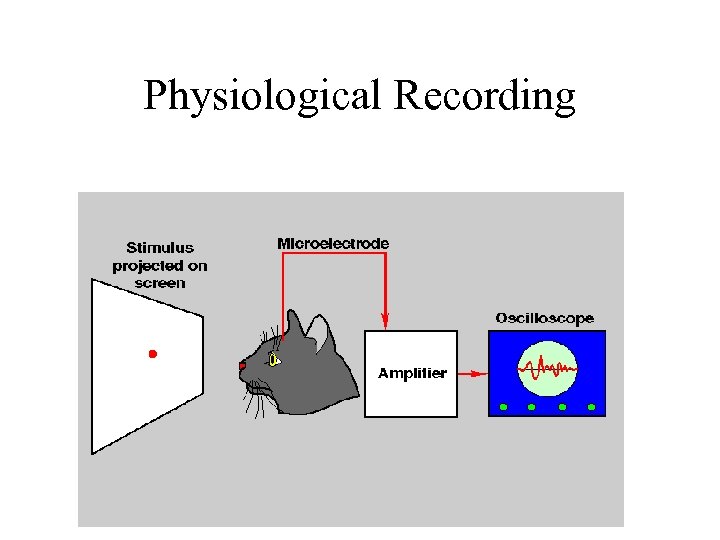
Physiological Recording
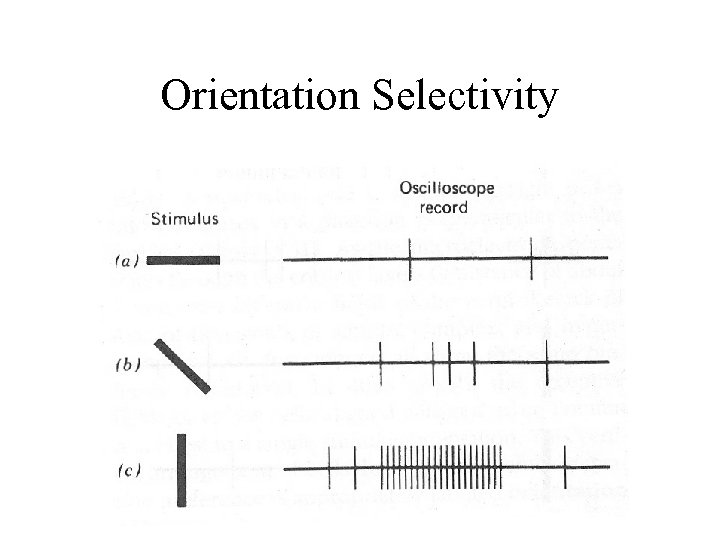
Orientation Selectivity
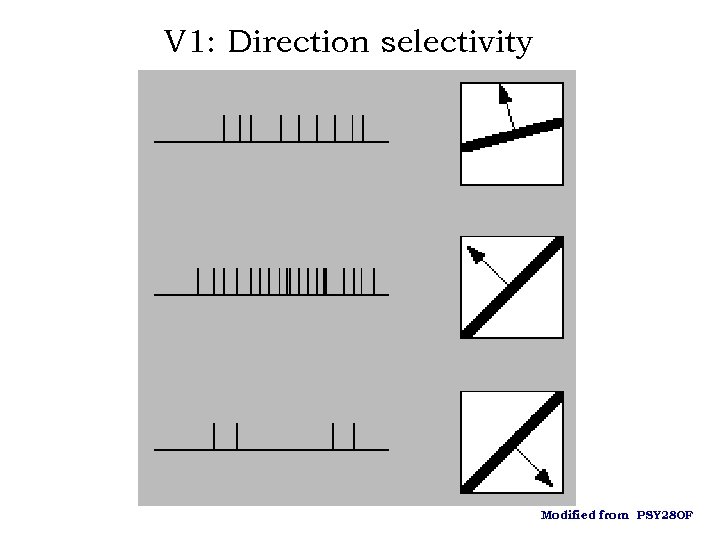
V 1: Direction selectivity Modified from PSY 280 F

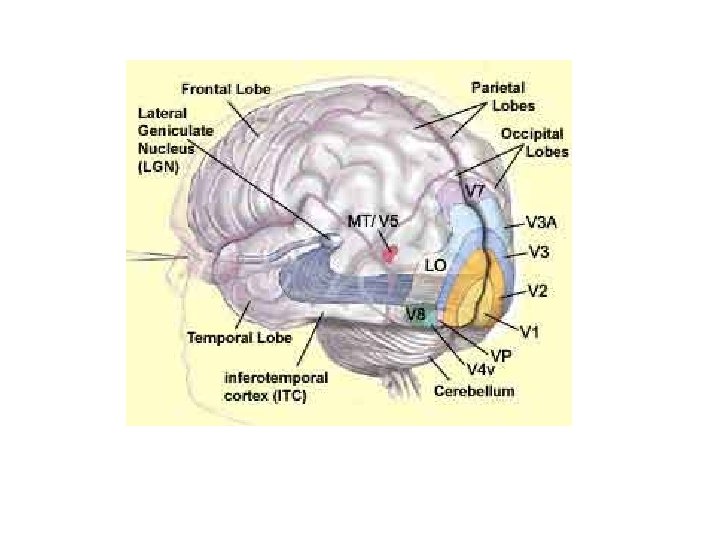
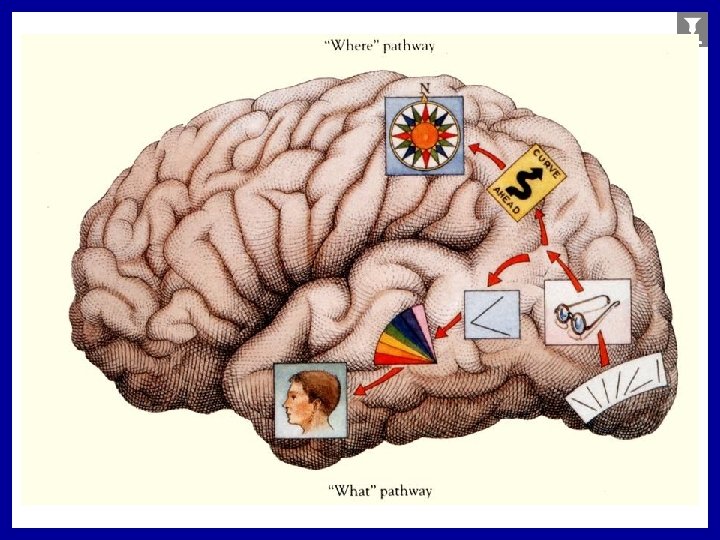
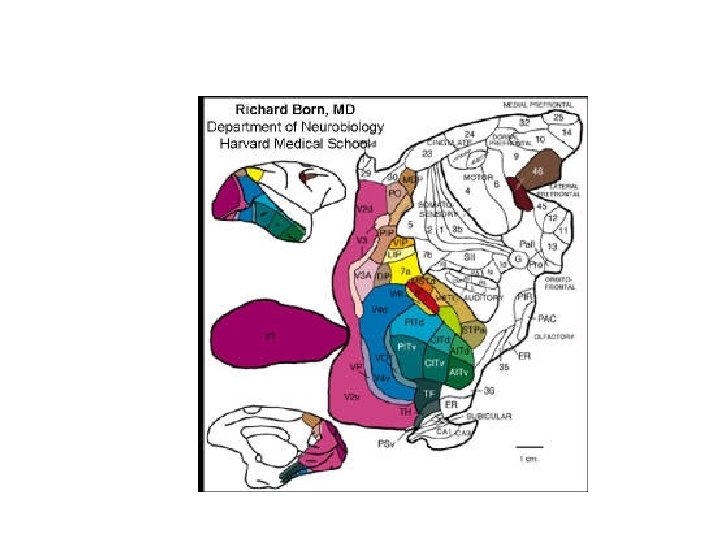
Visual Areas
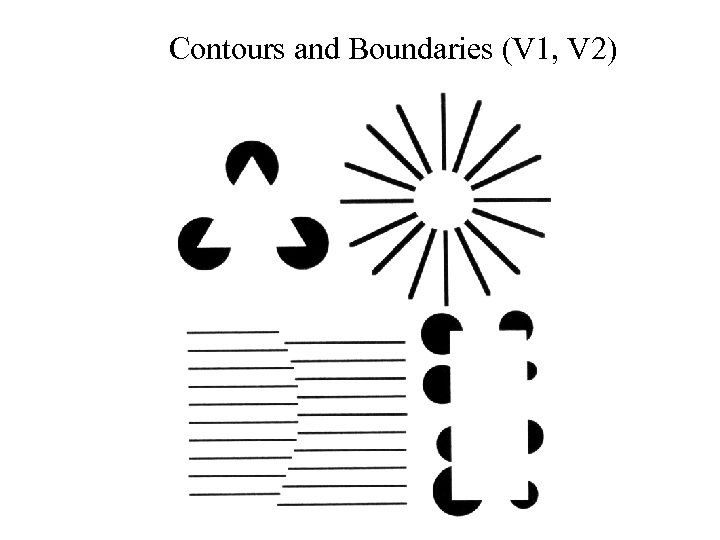
Contours and Boundaries (V 1, V 2)

Stimuli tested in V 2, V 4

Neuronal Responses, V 2
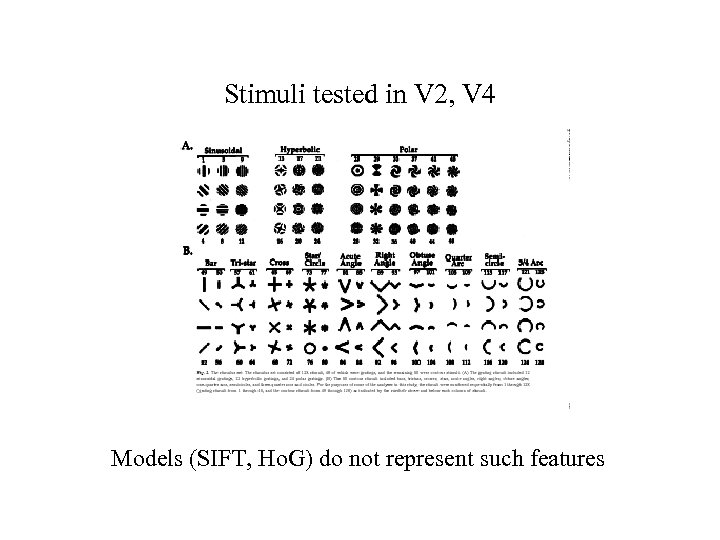
Stimuli tested in V 2, V 4 Models (SIFT, Ho. G) do not represent such features

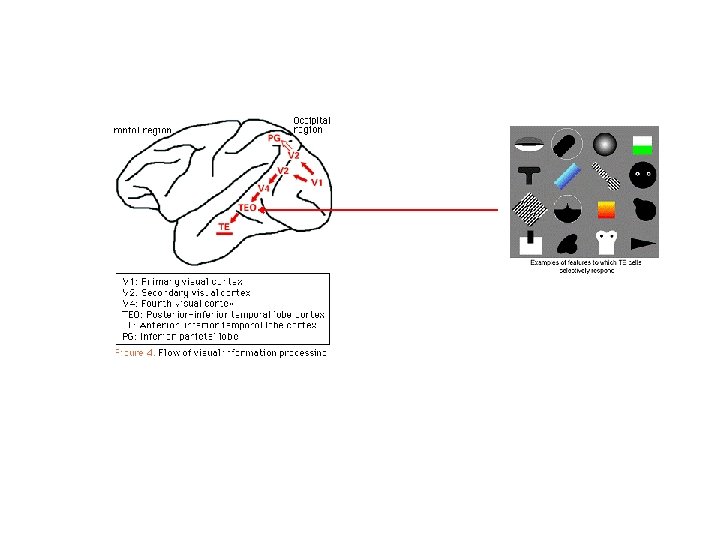
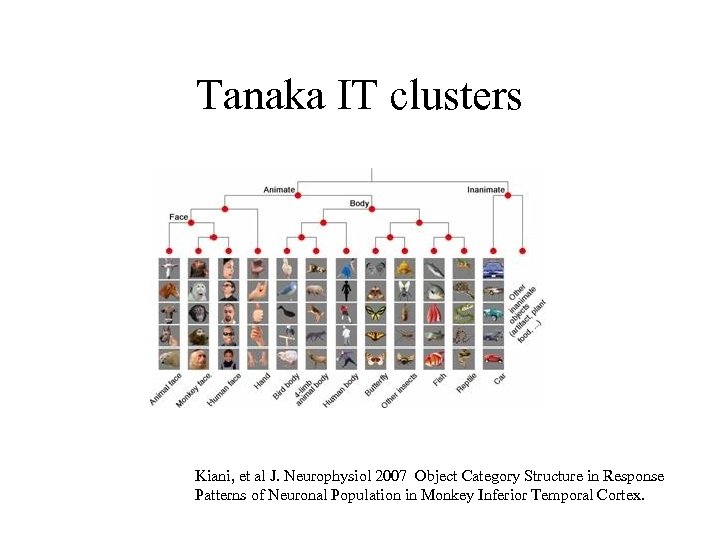
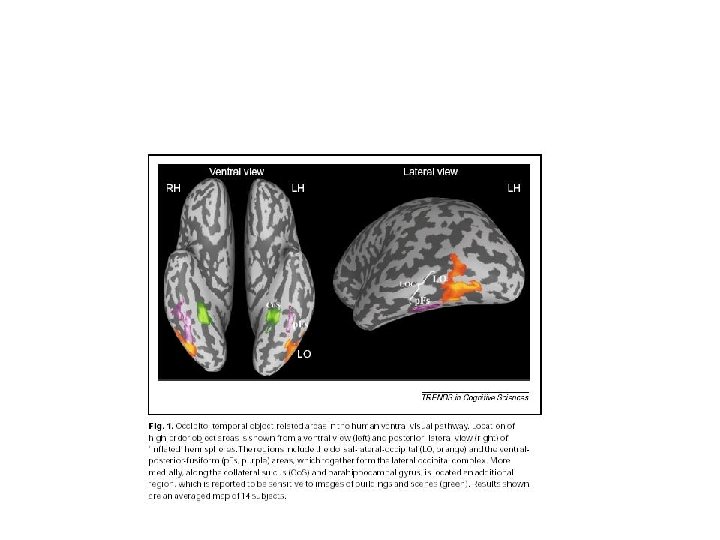
Tanaka IT clusters Kiani, et al J. Neurophysiol 2007 Object Category Structure in Response Patterns of Neuronal Population in Monkey Inferior Temporal Cortex.

f. MRI Magnet
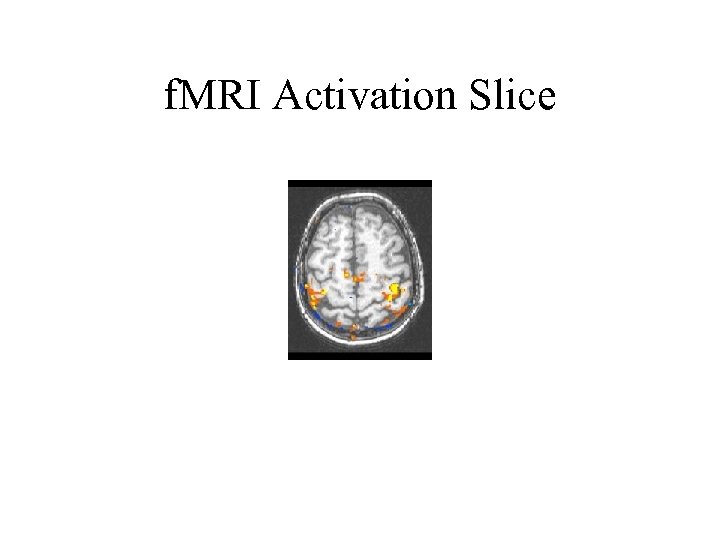
f. MRI Activation Slice
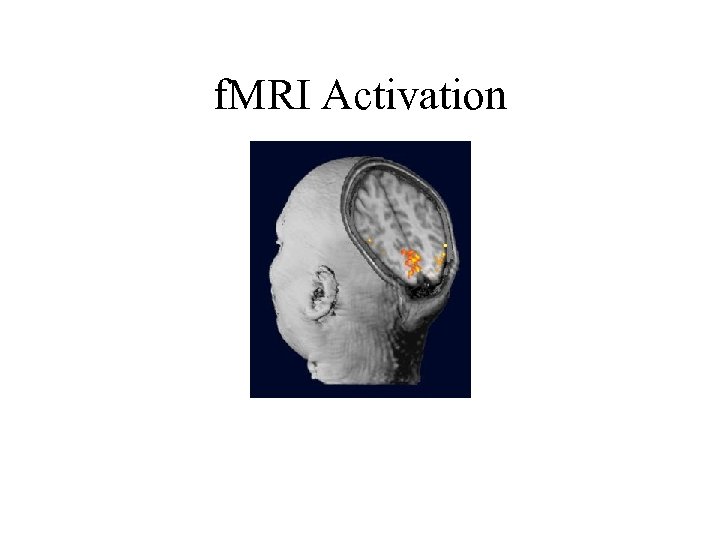
f. MRI Activation
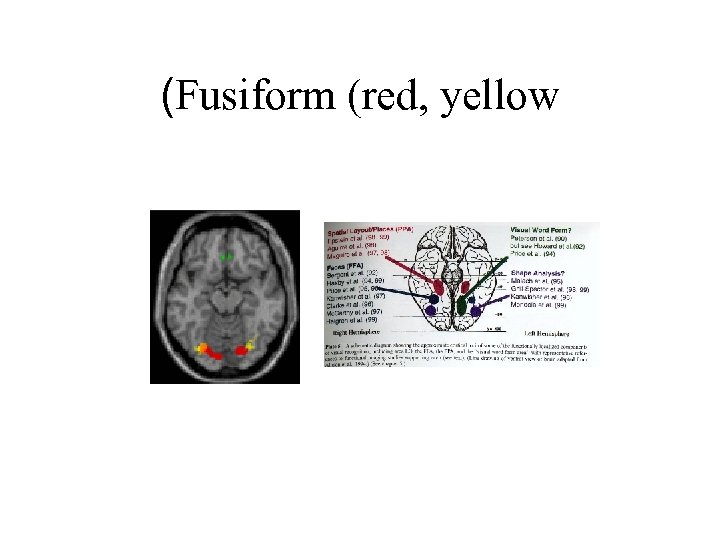
(Fusiform (red, yellow
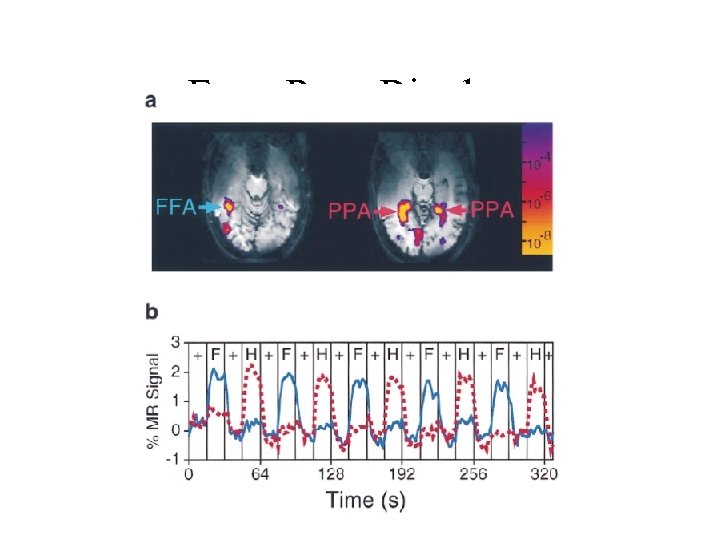
Face-Pace Rivalry
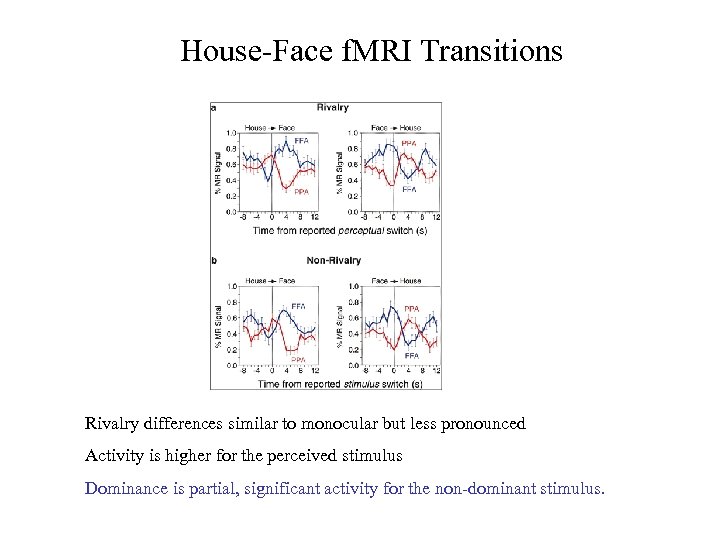
House-Face f. MRI Transitions Rivalry differences similar to monocular but less pronounced Activity is higher for the perceived stimulus Dominance is partial, significant activity for the non-dominant stimulus.
7591d7a58992cd3dc54c9f36c2509acb.ppt