b6041780f15eb1926ffbddc41fb4b1c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 The Human toll of the Great Depression
The Human toll of the Great Depression
 To Be Discussed • • Timeline of Events People that are effected by the Depression Possible causes of the Depression The Human Toll Impact of Society Psychological Impact on Families The Dust Bowl
To Be Discussed • • Timeline of Events People that are effected by the Depression Possible causes of the Depression The Human Toll Impact of Society Psychological Impact on Families The Dust Bowl
 Timeline of events • We will see & discuss a series of overhead projections with data in regards to the Great Depression – The data will show events as they occurred year after year, which includes: -Bank panics & related problems -The GNP of the U. S Economy -Unemployment Rates -Stock Market Crash
Timeline of events • We will see & discuss a series of overhead projections with data in regards to the Great Depression – The data will show events as they occurred year after year, which includes: -Bank panics & related problems -The GNP of the U. S Economy -Unemployment Rates -Stock Market Crash
 People Effected by The Depression
People Effected by The Depression
 America during the 1920’s • Between 1919 -1929 the economy was booming and people believed that it would never end. • Department stores allowed people to buy appliances and other goods on credit or installment plans which required people to pay an interest rate. • Small time investors were buying shares of stock on margin. -These would be Doctors, Lawyers, & small time businessmen)
America during the 1920’s • Between 1919 -1929 the economy was booming and people believed that it would never end. • Department stores allowed people to buy appliances and other goods on credit or installment plans which required people to pay an interest rate. • Small time investors were buying shares of stock on margin. -These would be Doctors, Lawyers, & small time businessmen)
 Causes of Great Depression • Industries had over produced goods & now needed to scale back on production • Prices in Agriculture had been dropping for years and there was no end in sight in the near future. • Countries all around the world were having economic difficulties as well. • Distribution of the wealth in America was not equal.
Causes of Great Depression • Industries had over produced goods & now needed to scale back on production • Prices in Agriculture had been dropping for years and there was no end in sight in the near future. • Countries all around the world were having economic difficulties as well. • Distribution of the wealth in America was not equal.
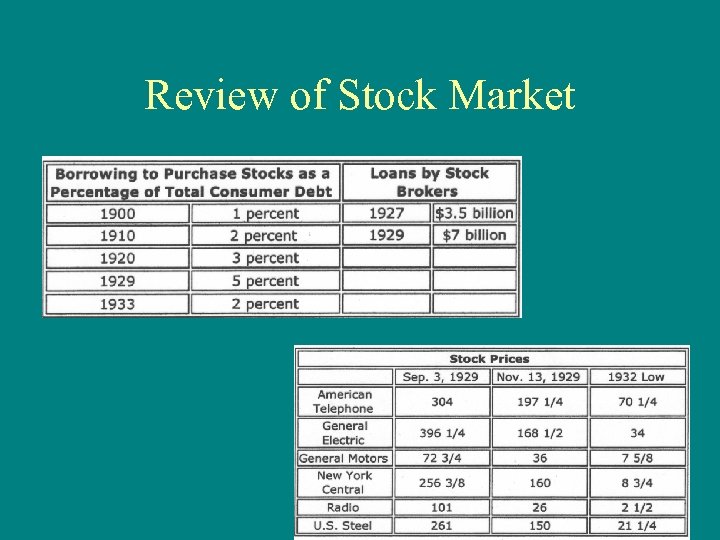
 Crash of the Stock Market • Starting on Oct. 24 th, 1929, the stock market in the U. S began to falter. -Ending on Oct. 29, 1929 with what is now known as “Black Tuesday”. • At the time that the stock market crashed, over 9 million people were investing in stocks. • Historical wise before 1929, the stock market was not a big source for making money. -During 1925 the worth of the stock market was valued at $27 billion. By the summer of 1929, the stock market was valued at $87 billion.
Crash of the Stock Market • Starting on Oct. 24 th, 1929, the stock market in the U. S began to falter. -Ending on Oct. 29, 1929 with what is now known as “Black Tuesday”. • At the time that the stock market crashed, over 9 million people were investing in stocks. • Historical wise before 1929, the stock market was not a big source for making money. -During 1925 the worth of the stock market was valued at $27 billion. By the summer of 1929, the stock market was valued at $87 billion.
 Black Tuesday • The premise behind investing stocks was to buy low, sell high -During the 1920’s, the prices on stocks were very low -Investing in the stock market became known as a way to make lots of many fast and easy. • To purchase stocks people would borrow money from banks & or financiers. -Nearly 75% of all stocks at this time were being purchased on “margin, ” which means an investors paid a small % of the stocks price and borrowed money to pay the rest.
Black Tuesday • The premise behind investing stocks was to buy low, sell high -During the 1920’s, the prices on stocks were very low -Investing in the stock market became known as a way to make lots of many fast and easy. • To purchase stocks people would borrow money from banks & or financiers. -Nearly 75% of all stocks at this time were being purchased on “margin, ” which means an investors paid a small % of the stocks price and borrowed money to pay the rest.
 Black Tuesday cont. . . • The most popular of stocks to buy at the time were for: - Automotive Industry -Radio Manufacturing -Aviation Industry -Oil Industry -Why were these stocks popular?
Black Tuesday cont. . . • The most popular of stocks to buy at the time were for: - Automotive Industry -Radio Manufacturing -Aviation Industry -Oil Industry -Why were these stocks popular?
 Causes cont. . . • During the 1920’s Industries believed that prosperity would never end. -Factories were over producing goods and had finally realized they needed to scale back production. -People believed layoffs would be short, because they believed the market would bounce back and consumers would buy goods again as they had been.
Causes cont. . . • During the 1920’s Industries believed that prosperity would never end. -Factories were over producing goods and had finally realized they needed to scale back production. -People believed layoffs would be short, because they believed the market would bounce back and consumers would buy goods again as they had been.
 Causes cont. . . • Agricultural prices had been dropping for years and farmers were about to be hit even harder. -Since there was an abundant source of food, prices on crops were constantly dropping. -When the Great Depression hit it got worse because now there was still an abundance of food, but nobody could afford to buy it. • To help support farmers, the govt. proposed placing price supports on agricultural sales.
Causes cont. . . • Agricultural prices had been dropping for years and farmers were about to be hit even harder. -Since there was an abundant source of food, prices on crops were constantly dropping. -When the Great Depression hit it got worse because now there was still an abundance of food, but nobody could afford to buy it. • To help support farmers, the govt. proposed placing price supports on agricultural sales.
 Causes cont. . . -These supports would have allowed the govt. to purchase the surplus amount of certain crops at a higher price from farmers. - The govt would then sell the crops on the world market at a cheaper price. -The one problem was that the difference between what the govt. had bought and sold would be made up by raising taxes on domestic food, whereby passing the cost on to consumers.
Causes cont. . . -These supports would have allowed the govt. to purchase the surplus amount of certain crops at a higher price from farmers. - The govt would then sell the crops on the world market at a cheaper price. -The one problem was that the difference between what the govt. had bought and sold would be made up by raising taxes on domestic food, whereby passing the cost on to consumers.
 Causes cont. . . • European countries would also feel the sting of economic hardships. • In many ways each country had a symbiotic relationship as on would suffer so would the other countries around the world. • Such hardships occurred in countries around the world; -In 1931 Austria’s biggest bank failed -Germany imposed currency controls in July -Great Britain went off the gold standard in Sept.
Causes cont. . . • European countries would also feel the sting of economic hardships. • In many ways each country had a symbiotic relationship as on would suffer so would the other countries around the world. • Such hardships occurred in countries around the world; -In 1931 Austria’s biggest bank failed -Germany imposed currency controls in July -Great Britain went off the gold standard in Sept.
 Causes cont. . . • From 1929 -1932, the American economy took its worst hits. -The GNP (Gross National Product) dropped from $104 billion to $59 billion. -Farm prices fell by 60%. The cost of a bushel of wheat dropped from $1. 04 to. 51.
Causes cont. . . • From 1929 -1932, the American economy took its worst hits. -The GNP (Gross National Product) dropped from $104 billion to $59 billion. -Farm prices fell by 60%. The cost of a bushel of wheat dropped from $1. 04 to. 51.
 Causes cont. . . • An even greater problem would be the unequal distribution of wealth during the 1920’s. -During the 1920’s the income for the top 1% of America’s wealthiest people rose 75%, while the rest of the nation’s income rose only 9% -What does this mean, when it comes to surviving the Great Depression? • Many people could not afford to buy the surplus of goods produced by factories. Which meant that people would be out of work for a longer period of time.
Causes cont. . . • An even greater problem would be the unequal distribution of wealth during the 1920’s. -During the 1920’s the income for the top 1% of America’s wealthiest people rose 75%, while the rest of the nation’s income rose only 9% -What does this mean, when it comes to surviving the Great Depression? • Many people could not afford to buy the surplus of goods produced by factories. Which meant that people would be out of work for a longer period of time.
 Causes cont. . . • Because people could not make their payments due to being out of work and the crash of the stock market banks began to fail at a rapid pace. -People were greatly fearing of losing more money so they withdrew their money from banks forcing them to close. -The main reason for people pulling their money out of banks was that their money was not insured, the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) had not been established yet. So if a bank closed you lost your money and could not regain it.
Causes cont. . . • Because people could not make their payments due to being out of work and the crash of the stock market banks began to fail at a rapid pace. -People were greatly fearing of losing more money so they withdrew their money from banks forcing them to close. -The main reason for people pulling their money out of banks was that their money was not insured, the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) had not been established yet. So if a bank closed you lost your money and could not regain it.
 Conclusion • These main points are the reasons why the U. S and the world fell into the Great Depression and why it lasted as long as it did. • Many speculators point to the crash of the stock market as the catalyst. • Others believe that it was the unequal distribution of wealth at stagnated the economy and the nation -What do you think were the main causes of the Great Depression?
Conclusion • These main points are the reasons why the U. S and the world fell into the Great Depression and why it lasted as long as it did. • Many speculators point to the crash of the stock market as the catalyst. • Others believe that it was the unequal distribution of wealth at stagnated the economy and the nation -What do you think were the main causes of the Great Depression?
 Activity for the Lesson • This activity in a normal class setting will take approximately 3 -4 days – Students will be given 1/4 of their yearly salary. – On the second students will be given another 1/4 of their salary with a change in employment or economic status. – On the third and possibly fourth day (pending on student progress to change) students will be given the rest of their yearly income w/changes in the employment or economic status.
Activity for the Lesson • This activity in a normal class setting will take approximately 3 -4 days – Students will be given 1/4 of their yearly salary. – On the second students will be given another 1/4 of their salary with a change in employment or economic status. – On the third and possibly fourth day (pending on student progress to change) students will be given the rest of their yearly income w/changes in the employment or economic status.
 The Great Depression The Human Toll
The Great Depression The Human Toll
 Review of Stock Market
Review of Stock Market
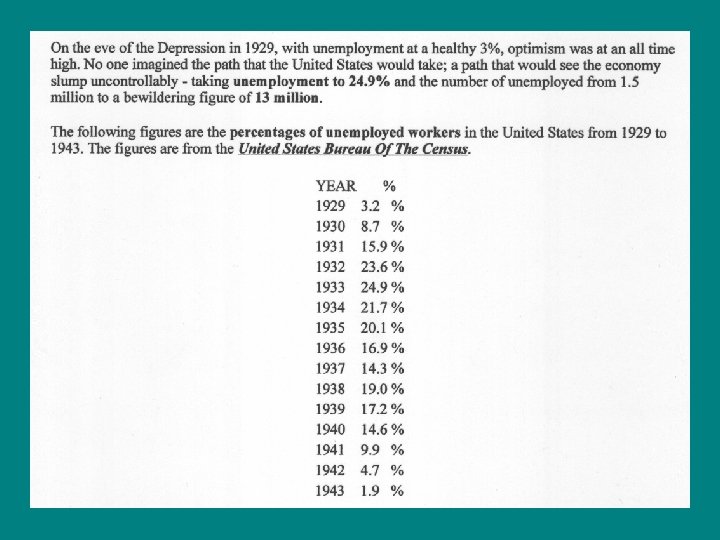
 Unemployment • Before the Great Depression the percentage of the nation that was unemployed was 3. 2%. • By 1933, approximately 25% of the nations population was unemployed, which translates to 13 million people out of jobs. • In the cities -Many people could not make their mortgage or rent payments and ended up being homeless. -Many families would have to scrounge around in garbage cans for food or beg on street corners from the wealthy people that passed by.
Unemployment • Before the Great Depression the percentage of the nation that was unemployed was 3. 2%. • By 1933, approximately 25% of the nations population was unemployed, which translates to 13 million people out of jobs. • In the cities -Many people could not make their mortgage or rent payments and ended up being homeless. -Many families would have to scrounge around in garbage cans for food or beg on street corners from the wealthy people that passed by.
 Impact of Society • There were some places where people could receive free food. -One place was known as a Soup Kitchen, the other was a bread line. • People would try to make homes out of card boxes, rusty car shells, crates, or piece together shacks. -These will become known as shantytowns, these sprang up in empty lots within cities and also just around cities.
Impact of Society • There were some places where people could receive free food. -One place was known as a Soup Kitchen, the other was a bread line. • People would try to make homes out of card boxes, rusty car shells, crates, or piece together shacks. -These will become known as shantytowns, these sprang up in empty lots within cities and also just around cities.


 Social & Psychological Effects • People had become so demoralized by the experience that suicides increased 30% during 19281932. • Many people did not go to see a doctor or a dentist because they didn’t have the money to spare. -People had to make tough decisions as to how to spend their money. In most cases it came down to life and death. • Women who didn’t work before took jobs to help support the family when the man was out of work
Social & Psychological Effects • People had become so demoralized by the experience that suicides increased 30% during 19281932. • Many people did not go to see a doctor or a dentist because they didn’t have the money to spare. -People had to make tough decisions as to how to spend their money. In most cases it came down to life and death. • Women who didn’t work before took jobs to help support the family when the man was out of work

 Social & Psychological effects cont. . . • Men that believed they had to provide for their family, would leave home to find work -In order to do this they would ride the rails across the country in search of jobs and send money back home when they were employed. • Society recognized with various needs of one another and tried to help. -People would give blankets, food and even space in their home for families that were in need.
Social & Psychological effects cont. . . • Men that believed they had to provide for their family, would leave home to find work -In order to do this they would ride the rails across the country in search of jobs and send money back home when they were employed. • Society recognized with various needs of one another and tried to help. -People would give blankets, food and even space in their home for families that were in need.
 Families • During the early years of the Great Depression families stuck together. -To entertain themselves they played board games like Monopoly. • Women tried very had to save money and keep a close eye on the family budget. -Women would go shopping together, buy large amounts of food and split the costs. -Many families would forego buying new clothes, instead they would patch up old clothes and hand them down to younger children.
Families • During the early years of the Great Depression families stuck together. -To entertain themselves they played board games like Monopoly. • Women tried very had to save money and keep a close eye on the family budget. -Women would go shopping together, buy large amounts of food and split the costs. -Many families would forego buying new clothes, instead they would patch up old clothes and hand them down to younger children.
 Closeness in a Time of Need • The Great Depression brought communities back together. -People would go out of their way for others. -The old habits of our nation had returned and would shape a new generation of people that lived through one of America’s hardest times. • The Great Depression would also change people’s lifestyles from spending money freely to saving and thriftiness.
Closeness in a Time of Need • The Great Depression brought communities back together. -People would go out of their way for others. -The old habits of our nation had returned and would shape a new generation of people that lived through one of America’s hardest times. • The Great Depression would also change people’s lifestyles from spending money freely to saving and thriftiness.
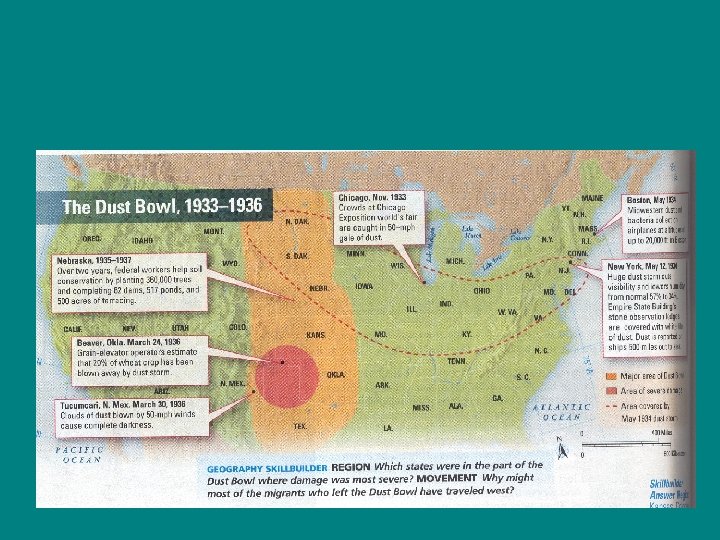
 Economic Conditions get Worse • One of the nations worst natural disaster to hurt American society was the Dust Bowl, which lasted from 1933 -1936. -The regions effected by the Dust Bowl were in the Mid-West region of the U. S -States that were most effected were in -N. Texas -Oklahoma -Missouri -Arkansas • What was the Dust Bowl?
Economic Conditions get Worse • One of the nations worst natural disaster to hurt American society was the Dust Bowl, which lasted from 1933 -1936. -The regions effected by the Dust Bowl were in the Mid-West region of the U. S -States that were most effected were in -N. Texas -Oklahoma -Missouri -Arkansas • What was the Dust Bowl?
 The Dust Bowl • The Dust Bowl was a three period of dry weather coupled with high winds blowing threw the mid-west. -Since there was little to no rain the soil became very dry and unfertile, so growing crops became very hard -The wind would blew away all of the fertile top soil into the air causing massive air pollution. -As described by many inhabitants the days seemed like nights because it was so dark.
The Dust Bowl • The Dust Bowl was a three period of dry weather coupled with high winds blowing threw the mid-west. -Since there was little to no rain the soil became very dry and unfertile, so growing crops became very hard -The wind would blew away all of the fertile top soil into the air causing massive air pollution. -As described by many inhabitants the days seemed like nights because it was so dark.
 Dust Bowl cont…. • The mid-west region however would not be the only region effected by the gusts of wind kicking up the soil. -Many states to the north-east were also effected by the large amounts of dust in the air and would cause breathing problems in various cities. • This would be the catalyst for a great migration movement of people leaving the mid-west to go to the west coast states. -These people were known as Okies.
Dust Bowl cont…. • The mid-west region however would not be the only region effected by the gusts of wind kicking up the soil. -Many states to the north-east were also effected by the large amounts of dust in the air and would cause breathing problems in various cities. • This would be the catalyst for a great migration movement of people leaving the mid-west to go to the west coast states. -These people were known as Okies.