00e82809e9be7744fddcff1309c32e67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The Human Immune System
The Human Immune System
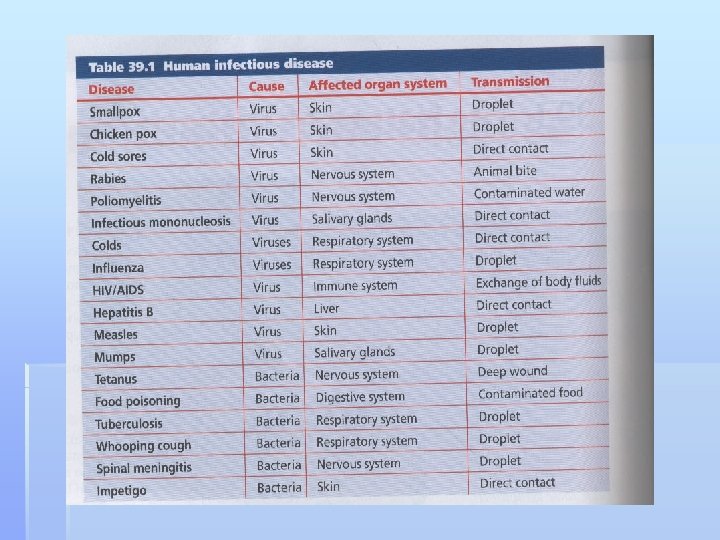
 1. Infectious Diseases A. Definitions 1. Pathogens (germs) a. an organism that causes a disease b. ex. viruses, bacteria, fungi, protista 2. Infectious diseases a. are spread by pathogens b. ex. flu, cold, measles, AIDS c. NOT ex. inherited diseases, most cancers, osteoporosis
1. Infectious Diseases A. Definitions 1. Pathogens (germs) a. an organism that causes a disease b. ex. viruses, bacteria, fungi, protista 2. Infectious diseases a. are spread by pathogens b. ex. flu, cold, measles, AIDS c. NOT ex. inherited diseases, most cancers, osteoporosis
 2. The Body’s Defenses A. Primary Defenses (nonspecific defense) 1. Skin 2. Hair (nose, eyelashes, ears) 3. Mucus, tears, sweat, saliva B. Secondary Defense (nonspecific defense) 1. Inflammatory response- sneezing, watery eyes, cough, fever 2. Caused by histamines 3. Allergies are caused by a hyperactive immune system
2. The Body’s Defenses A. Primary Defenses (nonspecific defense) 1. Skin 2. Hair (nose, eyelashes, ears) 3. Mucus, tears, sweat, saliva B. Secondary Defense (nonspecific defense) 1. Inflammatory response- sneezing, watery eyes, cough, fever 2. Caused by histamines 3. Allergies are caused by a hyperactive immune system
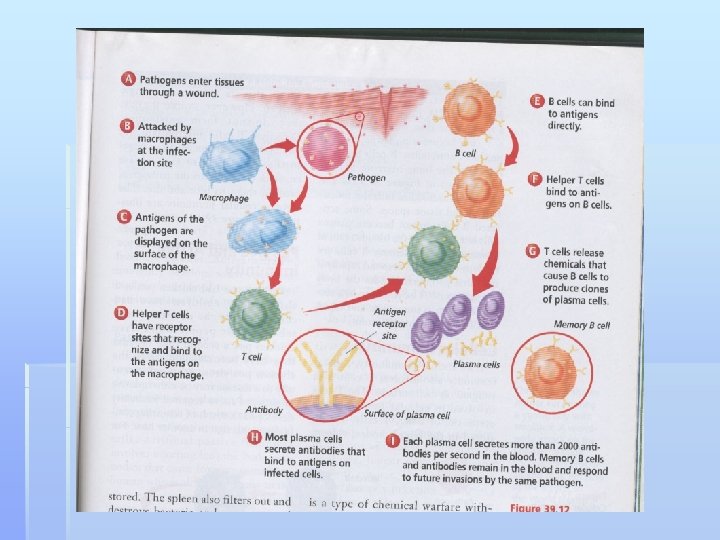
 C. Cellular Immunity (specific defense) 1. Self vs. Non-Self a. Determined by antigens (proteins) on the outside of cells. b. Used to determine foreign substances 2. Macrophages (Security guards) a. white blood cells that read antigens and engulf non-self particles b. Don’t destroy; just hold
C. Cellular Immunity (specific defense) 1. Self vs. Non-Self a. Determined by antigens (proteins) on the outside of cells. b. Used to determine foreign substances 2. Macrophages (Security guards) a. white blood cells that read antigens and engulf non-self particles b. Don’t destroy; just hold
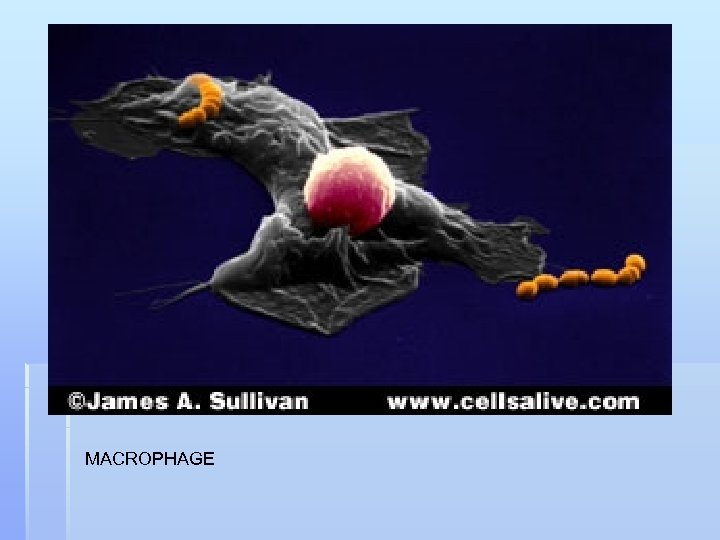 MACROPHAGE
MACROPHAGE
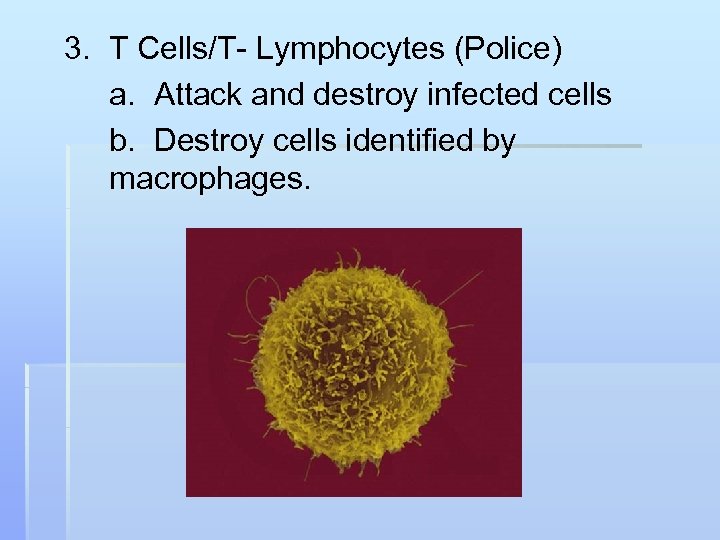 3. T Cells/T- Lymphocytes (Police) a. Attack and destroy infected cells b. Destroy cells identified by macrophages.
3. T Cells/T- Lymphocytes (Police) a. Attack and destroy infected cells b. Destroy cells identified by macrophages.
 Immunity Analogy The old man who lived in the dark house on Peachtree Road had always been a source of neighborhood gossip. Why did he have that big, high wall around his property? Why was the gate always closed and locked? What was he protecting? Did he have a great fortune in gold and jewels? Was he doing secret scientific experiments? One night some kids decided to find out. They gathered all their equipment and made their move. They came through the woods to the back side of the house where erosion had made a hole in the wall. They squeezed through and were able to get inside. But as soon as they stood up, four large dogs came around the corner. The kids tried to run but ended up flat on their backs, held by the barking dogs. By that time the owner had called the police and the intruders were taken away…. without discovering what was in the house.
Immunity Analogy The old man who lived in the dark house on Peachtree Road had always been a source of neighborhood gossip. Why did he have that big, high wall around his property? Why was the gate always closed and locked? What was he protecting? Did he have a great fortune in gold and jewels? Was he doing secret scientific experiments? One night some kids decided to find out. They gathered all their equipment and made their move. They came through the woods to the back side of the house where erosion had made a hole in the wall. They squeezed through and were able to get inside. But as soon as they stood up, four large dogs came around the corner. The kids tried to run but ended up flat on their backs, held by the barking dogs. By that time the owner had called the police and the intruders were taken away…. without discovering what was in the house.
 Homework: § Page 1035: 1 -4
Homework: § Page 1035: 1 -4
 D. Acquired Immunity 1. B-Cells a. Make antibodies to the antigens on pathogens (mug shots) b. How your body remembers how to fight a disease
D. Acquired Immunity 1. B-Cells a. Make antibodies to the antigens on pathogens (mug shots) b. How your body remembers how to fight a disease
 2. Vaccination a. Uses dead pathogens to train the immune system to recognize antigens and fight diseases. b. Polio, tetanus, measles, mumps c. Can’t be used on viruses that change antigens (cold, flu, HIV)
2. Vaccination a. Uses dead pathogens to train the immune system to recognize antigens and fight diseases. b. Polio, tetanus, measles, mumps c. Can’t be used on viruses that change antigens (cold, flu, HIV)
 E. Summary of Defenses 1. Nonspecific Defenses- try to stop everything from entering the body (skin, mucus, inflammatory response) 2. Specific Defenses- try to stop a particular pathogen (macrophages, antibodies, vaccination)
E. Summary of Defenses 1. Nonspecific Defenses- try to stop everything from entering the body (skin, mucus, inflammatory response) 2. Specific Defenses- try to stop a particular pathogen (macrophages, antibodies, vaccination)
 F. Problems in the immune system 1. Autoimmune diseases- when the immune system attacks “self” cells examples: type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis 2. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)- no immune system 3. Rejection of transplanted organs 4. HIV- attacks your immune cells so you can’t fight back and leads to AIDS.
F. Problems in the immune system 1. Autoimmune diseases- when the immune system attacks “self” cells examples: type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis 2. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)- no immune system 3. Rejection of transplanted organs 4. HIV- attacks your immune cells so you can’t fight back and leads to AIDS.
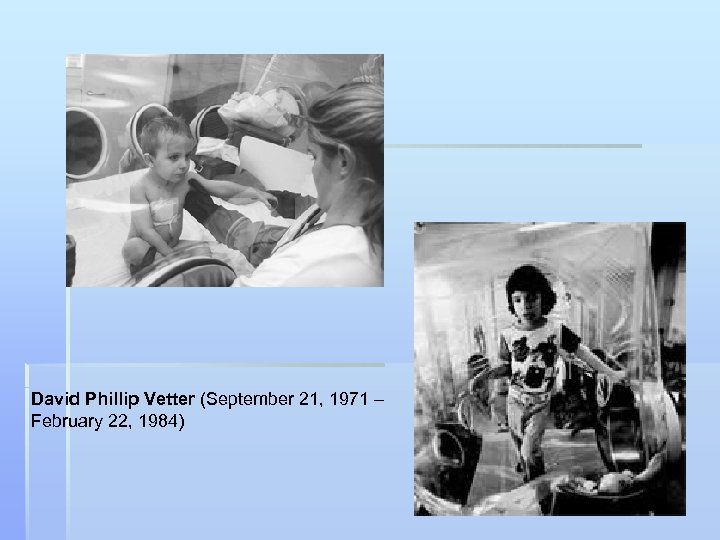 David Phillip Vetter (September 21, 1971 – February 22, 1984)
David Phillip Vetter (September 21, 1971 – February 22, 1984)
 Homework: For each part of the immune system below tell: 1) Is it a molecule or a cell? 2) Write a sentence describing it’s roll in the immune system. a. Antigen d. B-cell b. Antibody e. Macrophage c. Pathogen f. T-cell 3) pg. 1042: 1, 2, 4, 5
Homework: For each part of the immune system below tell: 1) Is it a molecule or a cell? 2) Write a sentence describing it’s roll in the immune system. a. Antigen d. B-cell b. Antibody e. Macrophage c. Pathogen f. T-cell 3) pg. 1042: 1, 2, 4, 5