THE HISTOLOGY OF THE FIBROUSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE The

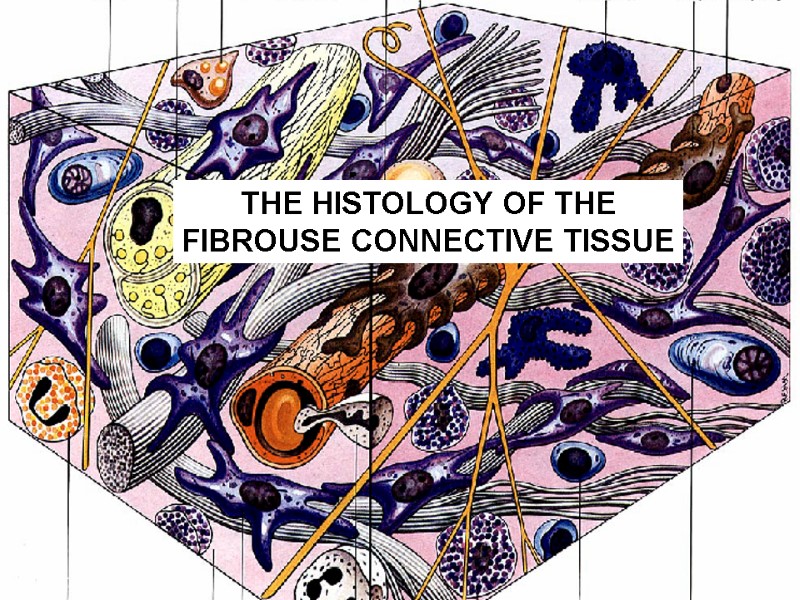
THE HISTOLOGY OF THE FIBROUSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE

The plan of the lecture The general features of the fibrouse connective tissue. Classification and the specific features of each one. Micro- and submicroscopic organisation, histochemical features and the functions of the loose irregular connective tissue. Dense connective tissue, it’s histological features and localization at the human organism.
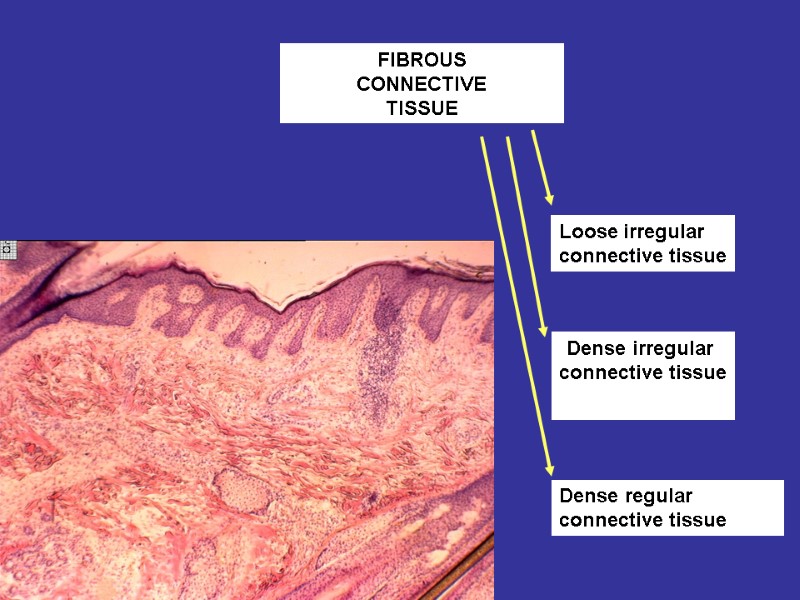
FIBROUS CONNECTIVE TISSUE Loose irregular connective tissue Dense irregular connective tissue Dense regular connective tissue

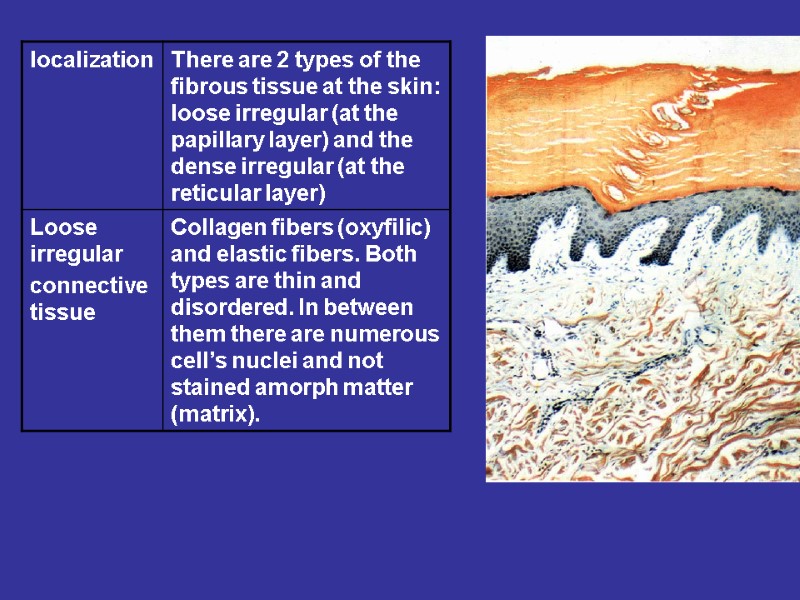
Loose irregular connective tissue Features: too many cells, small volume of the ground substance and small number of the fibers. The fibers are disordered Localization: walls of internal organs, the vascular adventitia, the proper connective tissue plate of the mucous coats, submucous tela.
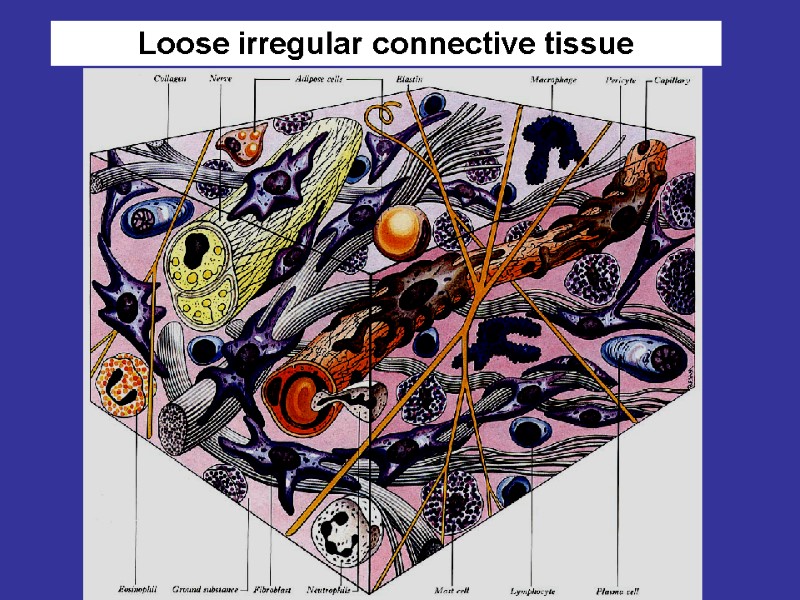
Рыхлая волокнистая неоформленная Loose irregular connective tissue
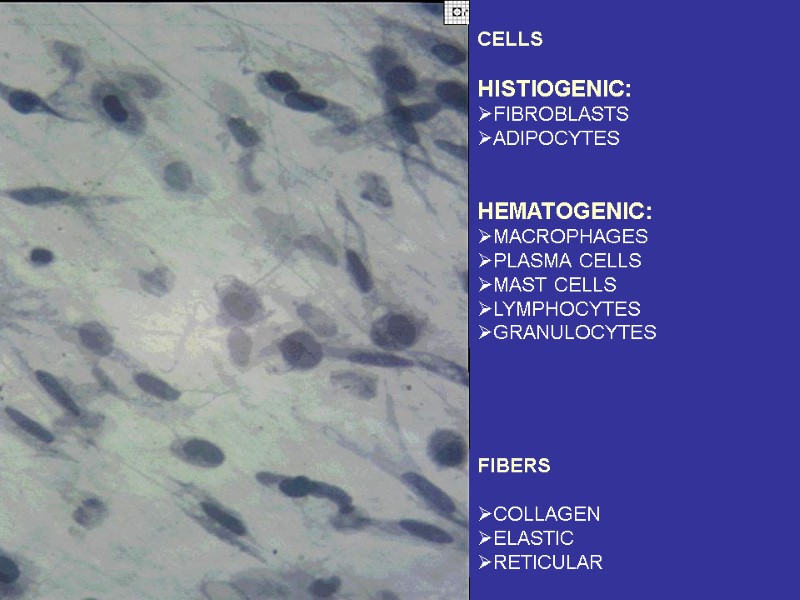
CELLS HISTIOGENIC: FIBROBLASTS ADIPOCYTES HEMATOGENIC: MACROPHAGES PLASMA CELLS MAST CELLS LYMPHOCYTES GRANULOCYTES FIBERS COLLAGEN ELASTIC RETICULAR
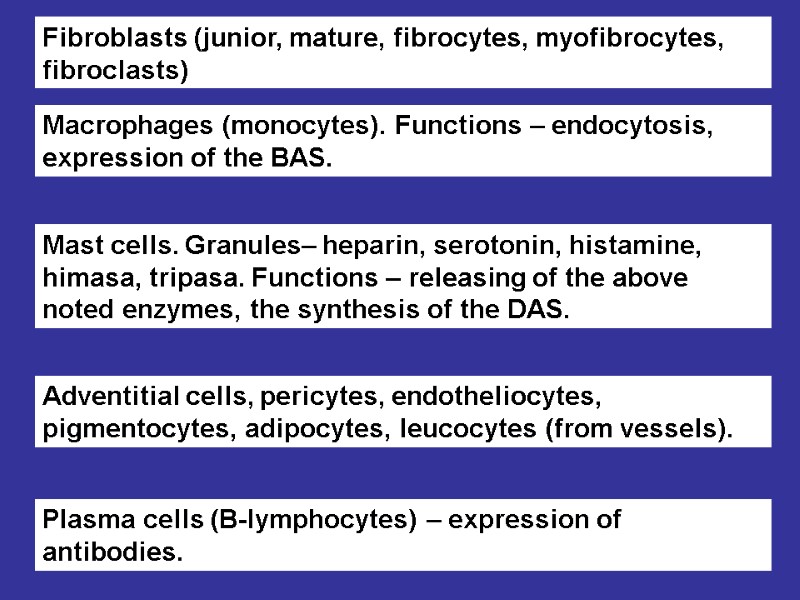
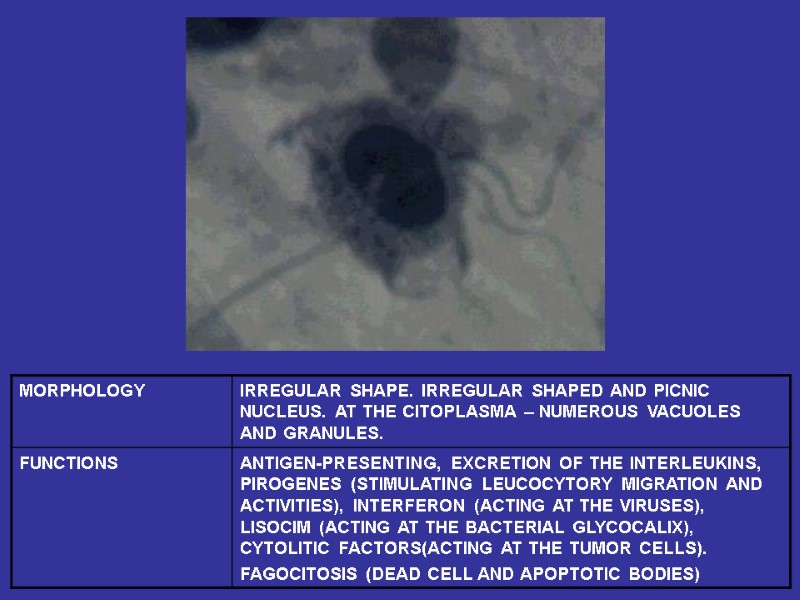
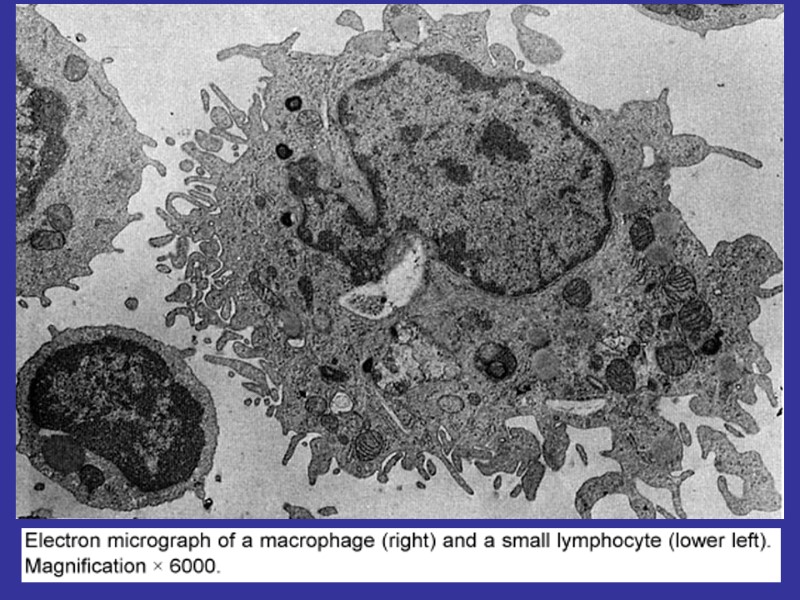
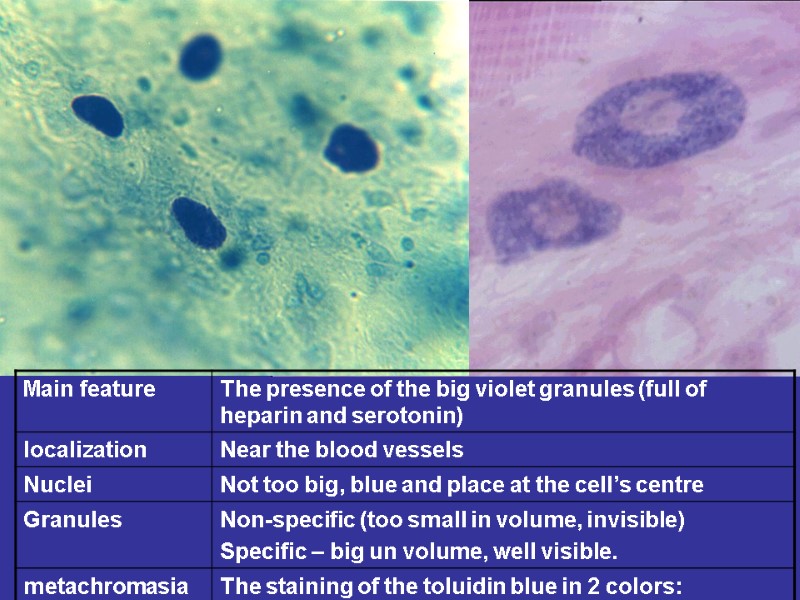
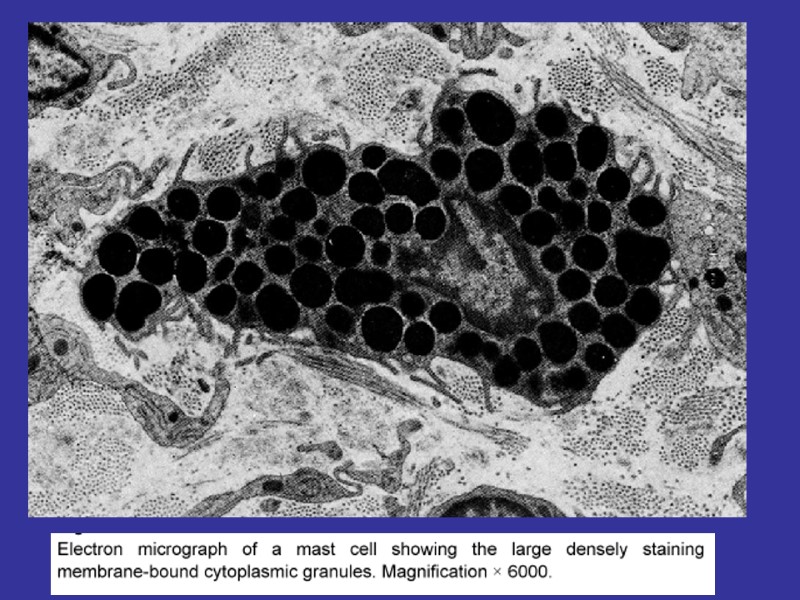
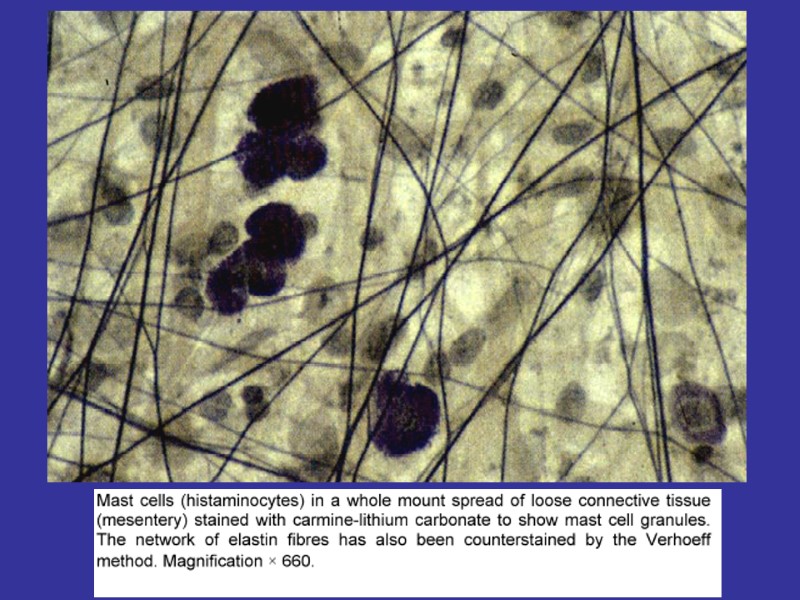
Fibroblasts (junior, mature, fibrocytes, myofibrocytes, fibroclasts) Macrophages (monocytes). Functions – endocytosis, expression of the BAS. Mast cells. Granules– heparin, serotonin, histamine, himasa, tripasa. Functions – releasing of the above noted enzymes, the synthesis of the DAS. Adventitial cells, pericytes, endotheliocytes, pigmentocytes, adipocytes, leucocytes (from vessels). Plasma cells (В-lymphocytes) – expression of antibodies.
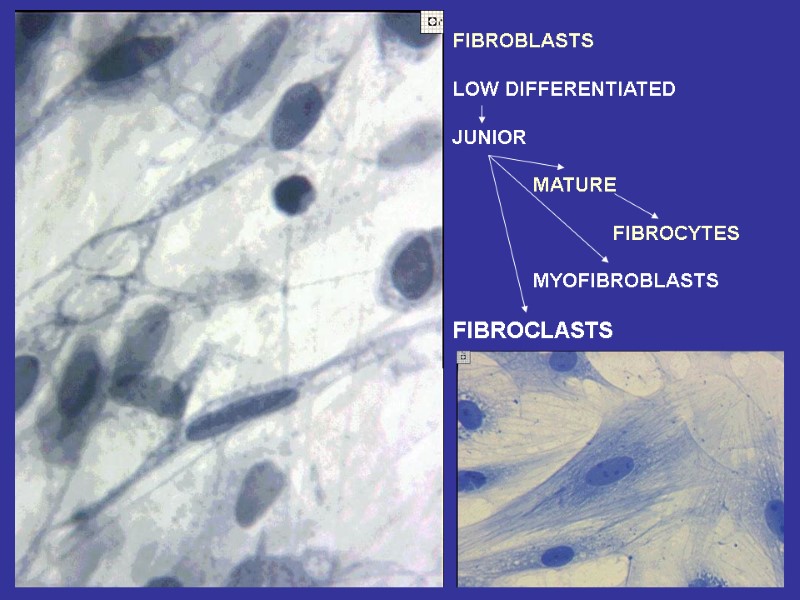
FIBROBLASTS LOW DIFFERENTIATED JUNIOR MATURE FIBROCYTES MYOFIBROBLASTS FIBROCLASTS

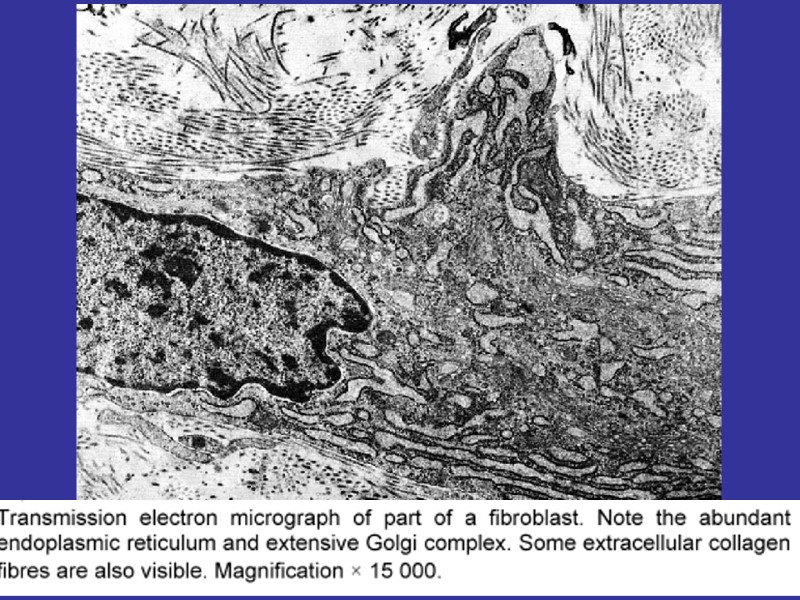
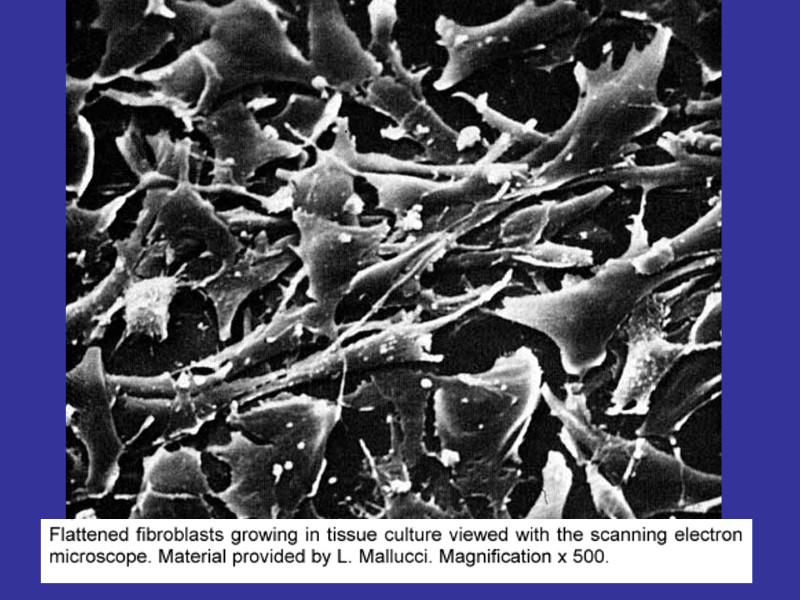

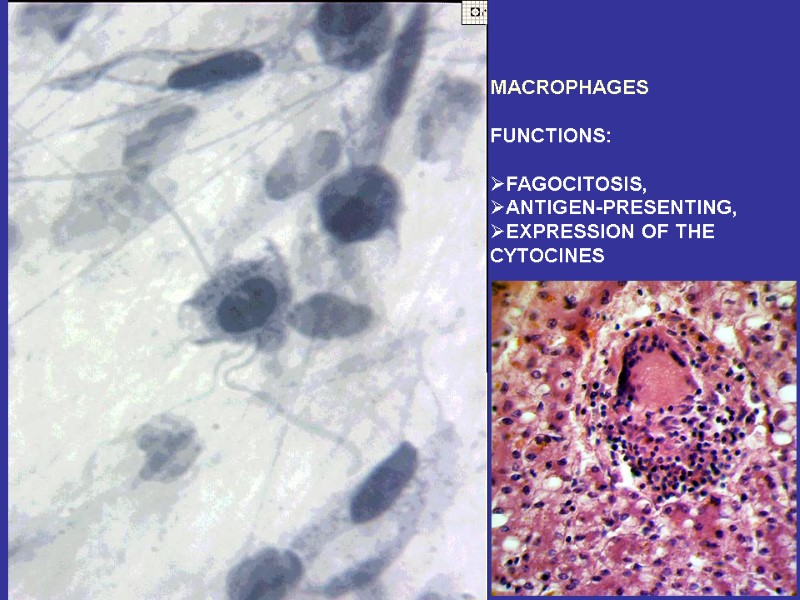
MACROPHAGES FUNCTIONS: FAGOCITOSIS, ANTIGEN-PRESENTING, EXPRESSION OF THE CYTOCINES

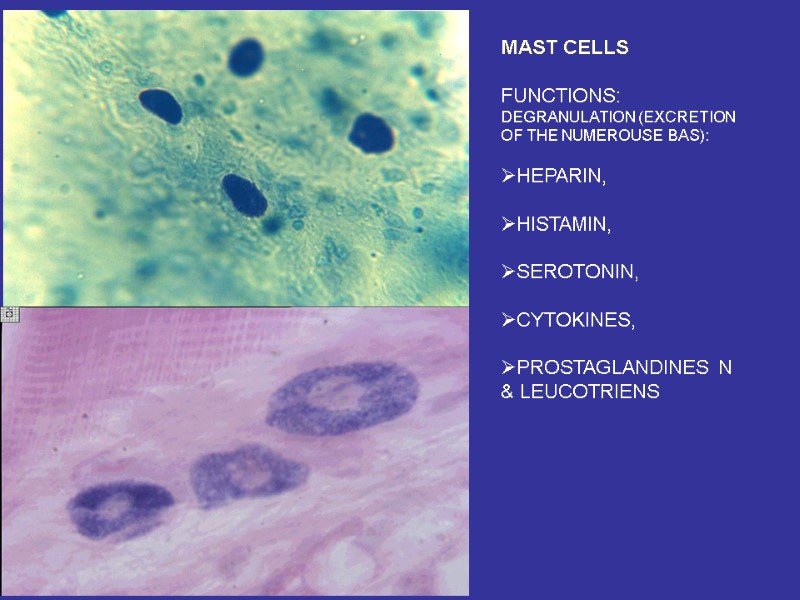
MAST CELLS FUNCTIONS: DEGRANULATION (EXCRETION OF THE NUMEROUSE BAS): HEPARIN, HISTAMIN, SEROTONIN, CYTOKINES, PROSTAGLANDINES N & LEUCOTRIENS
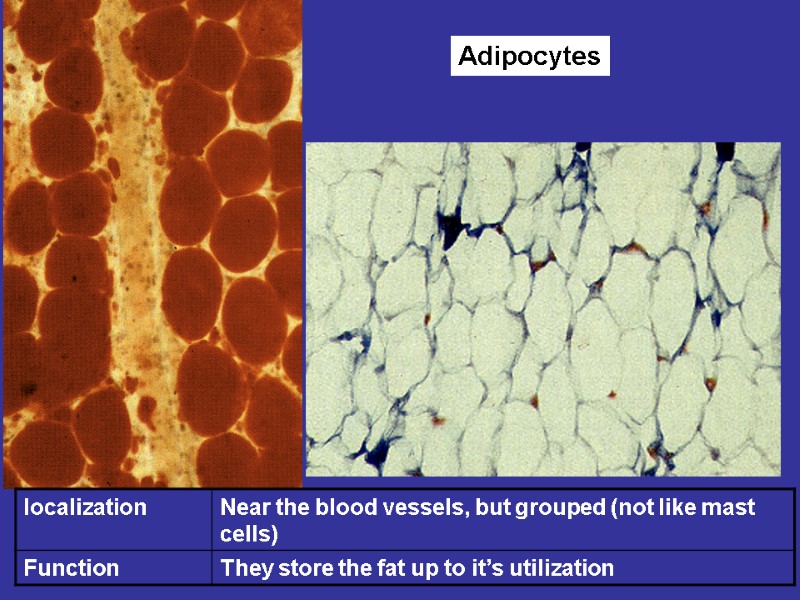
Adipocytes
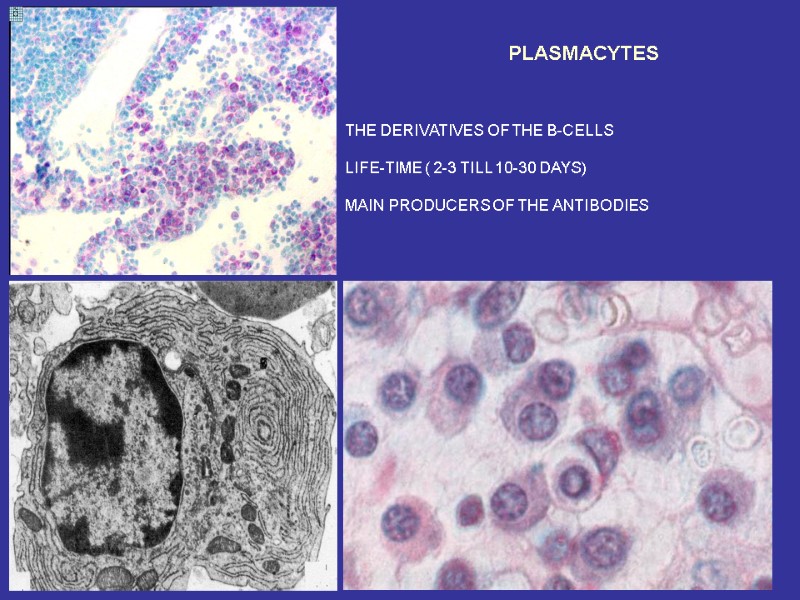
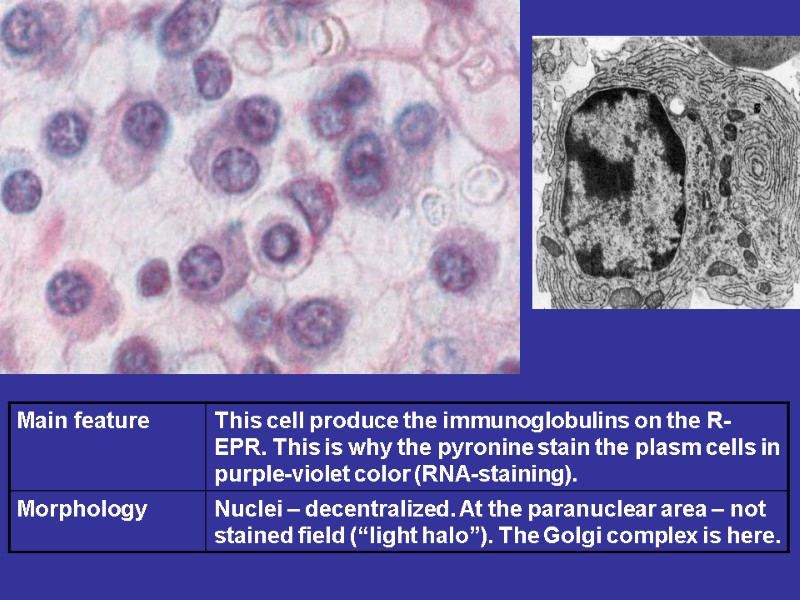
PLASMACYTES THE DERIVATIVES OF THE B-CELLS LIFE-TIME ( 2-3 TILL 10-30 DAYS) MAIN PRODUCERS OF THE ANTIBODIES

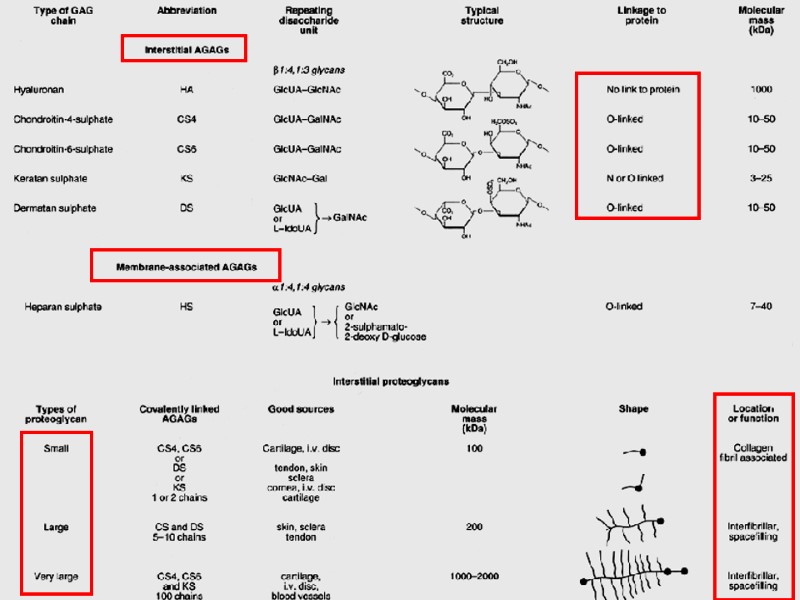
GRAUND SUBSTANCE FIBERS AMORPH SUBSTANCE (MATRIX) FIBRILLAR PROTEINS ADHESIVE PRONEINS GLICOSAMINEGLICANES FIBRONECTIN, LAMININ HEPARIN, HYALURON ACID, HONDROITINCULPHATES, DERMATANSULPHATES, CERATANSULPHATES
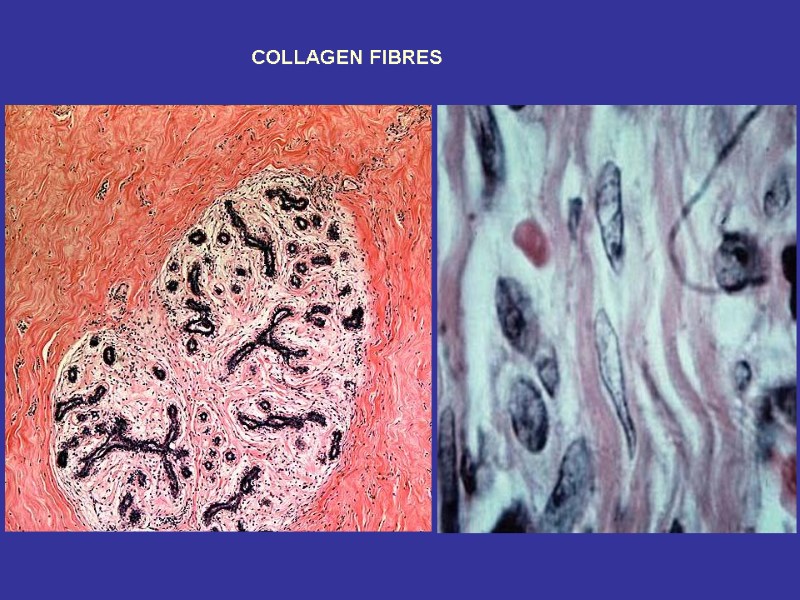
COLLAGEN FIBRES
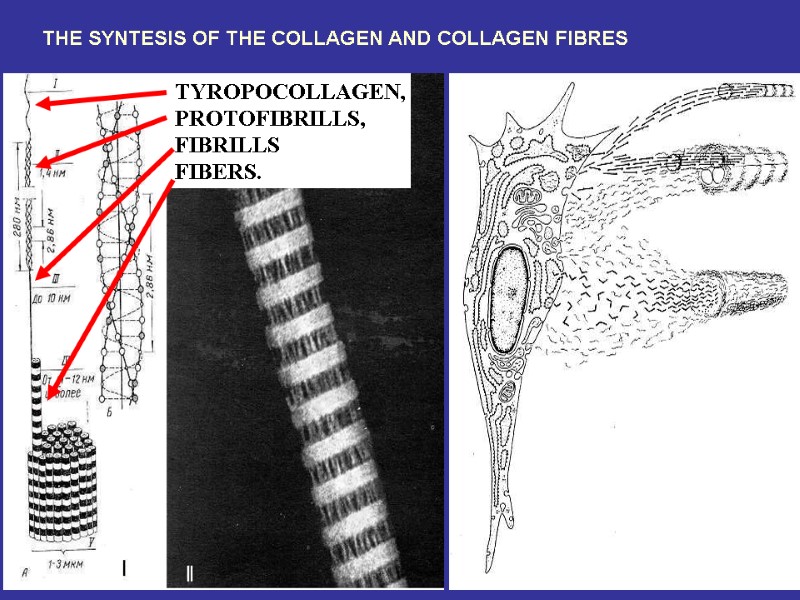
THE SYNTESIS OF THE COLLAGEN AND COLLAGEN FIBRES TYROPOCOLLAGEN, PROTOFIBRILLS, FIBRILLS FIBERS.
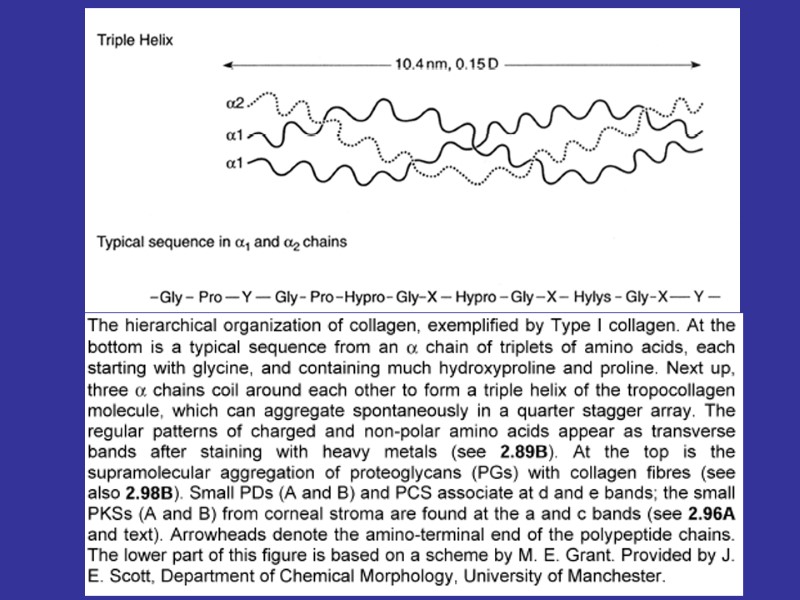
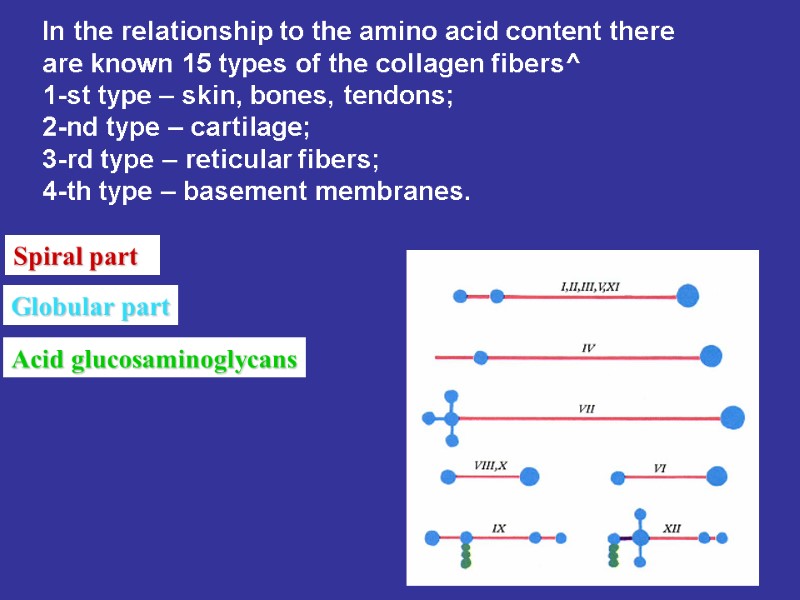
Spiral part Globular part Acid glucosaminoglycans In the relationship to the amino acid content there are known 15 types of the collagen fibers^ 1-st type – skin, bones, tendons; 2-nd type – cartilage; 3-rd type – reticular fibers; 4-th type – basement membranes.
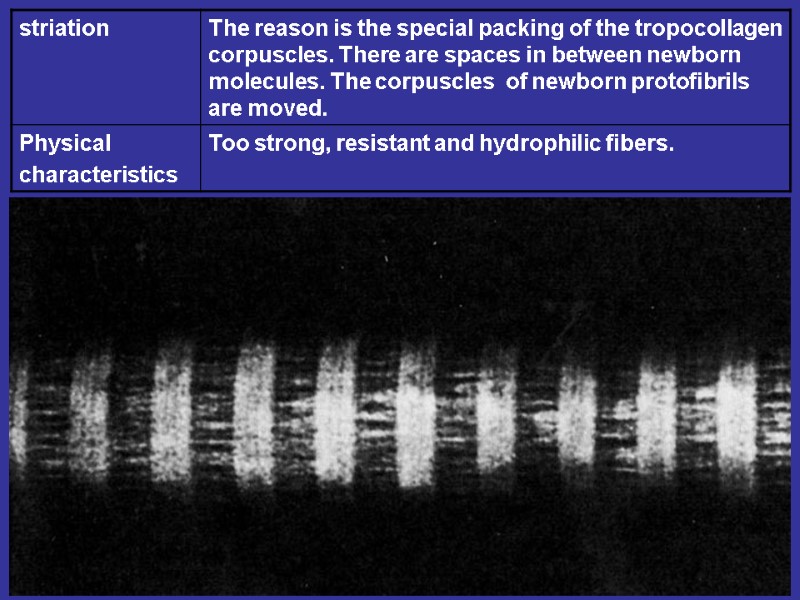
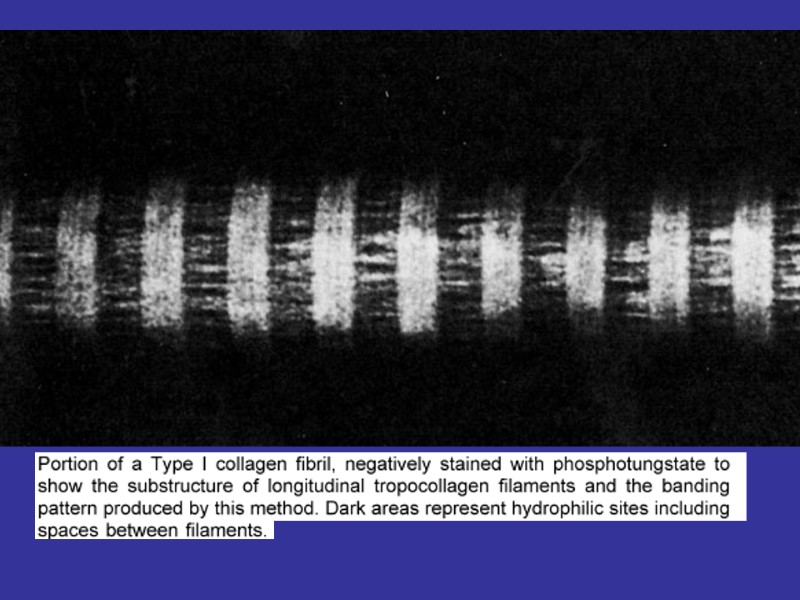
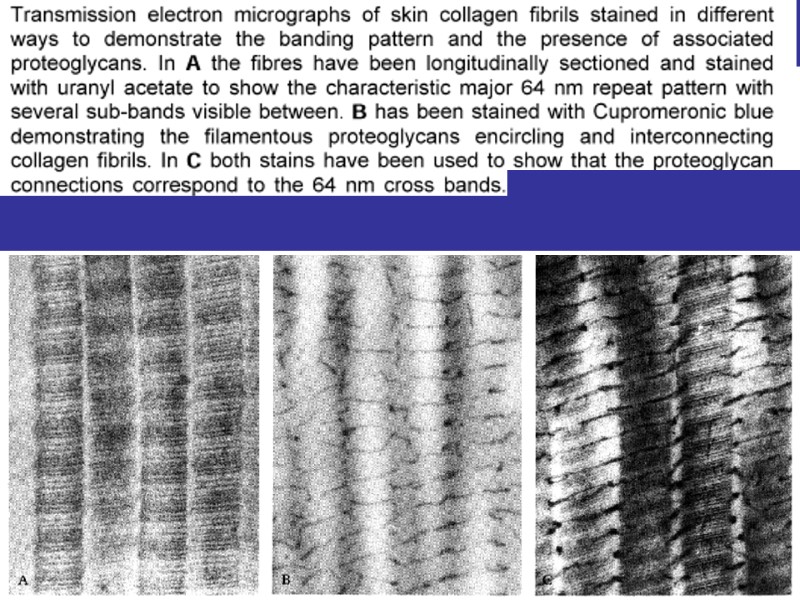
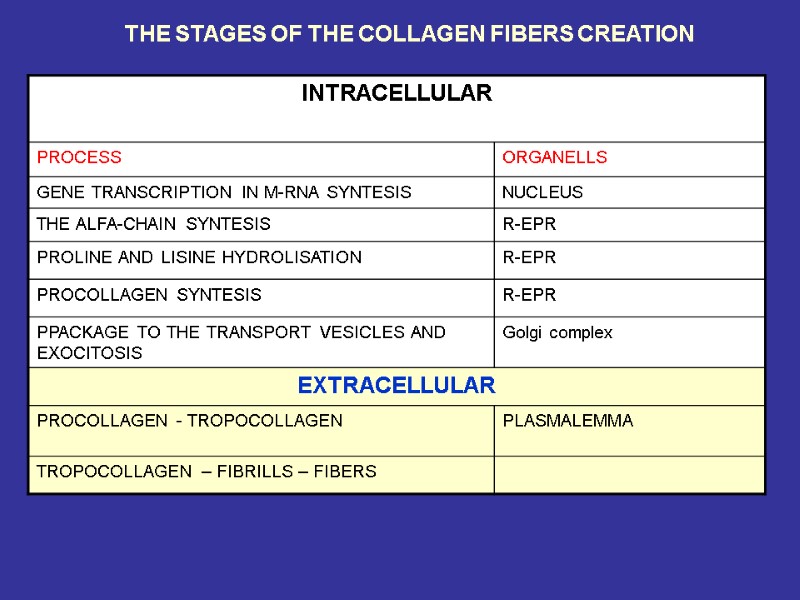
THE STAGES OF THE COLLAGEN FIBERS CREATION
Ground substance : glucosaminoglycans (interstitial and membrane assotiated). Proteoglycans: AGAG+protein Glicoproteins – fibronectin, laminin. Proteins, coming from the blood (60% of all albumins + globulins + ions). The consistence of the ground substance – jell. The degree of polymerization.
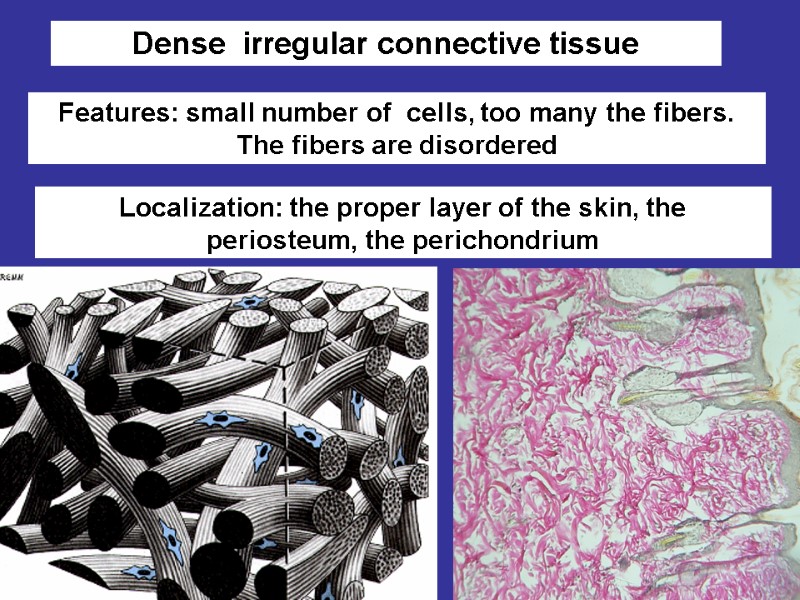
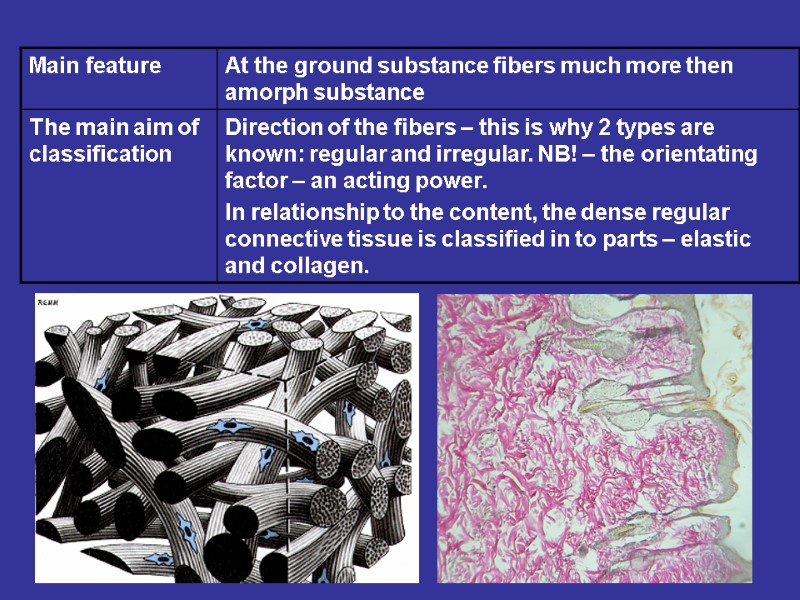
Плотная волокнистая неоформленная Features: small number of cells, too many the fibers. The fibers are disordered Dense irregular connective tissue Localization: the proper layer of the skin, the periosteum, the perichondrium


Dense regular connective tissue Features: small number of cells, too many the fibers. The fibers are well ordered (grouped at bundles) Localization: the tendo, articular capsule, ligaments, fascia.
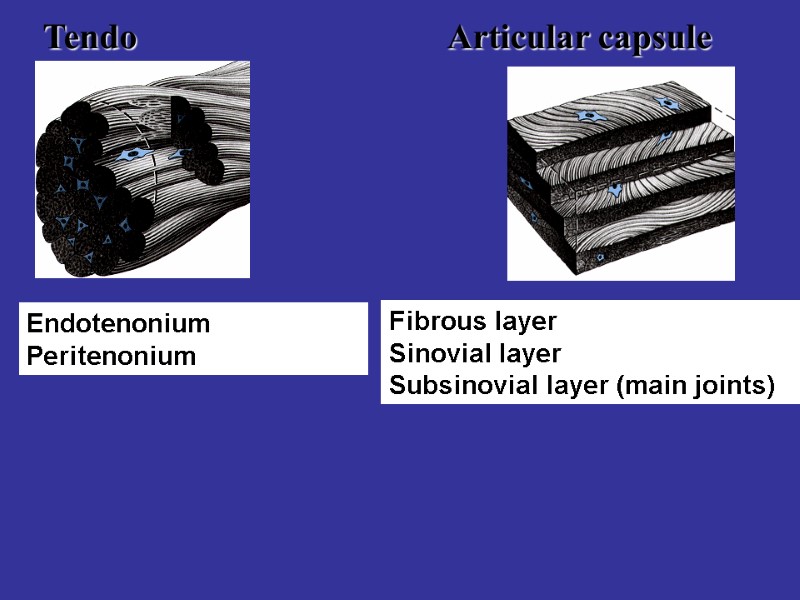
Tendo Articular capsule Endotenonium Peritenonium Fibrous layer Sinovial layer Subsinovial layer (main joints)
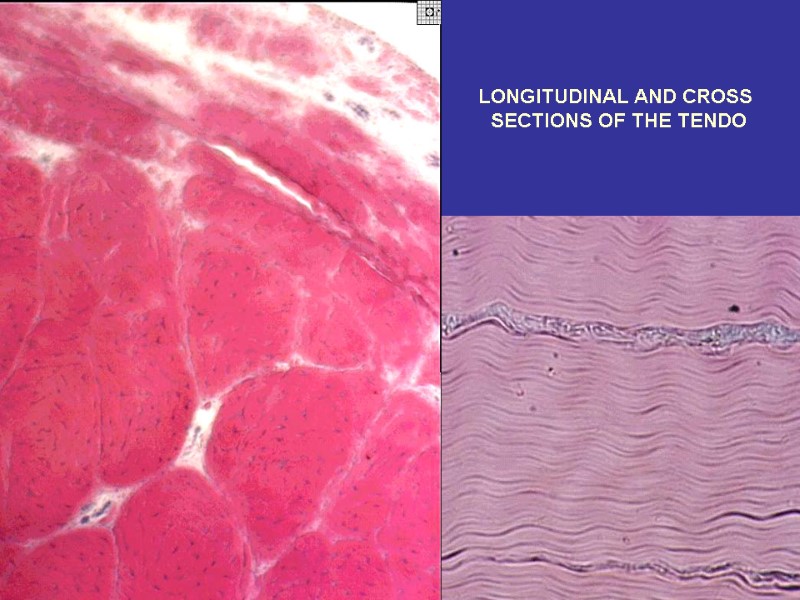
LONGITUDINAL AND CROSS SECTIONS OF THE TENDO
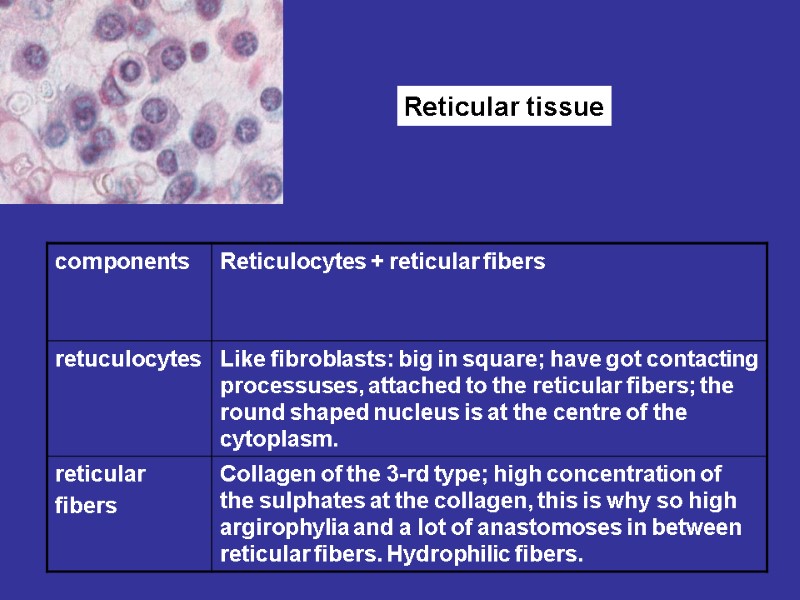
Reticular tissue
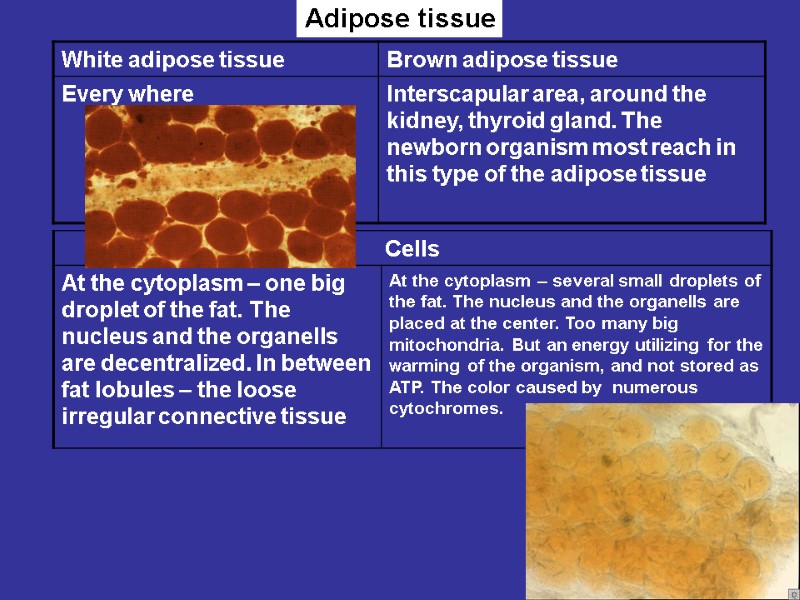
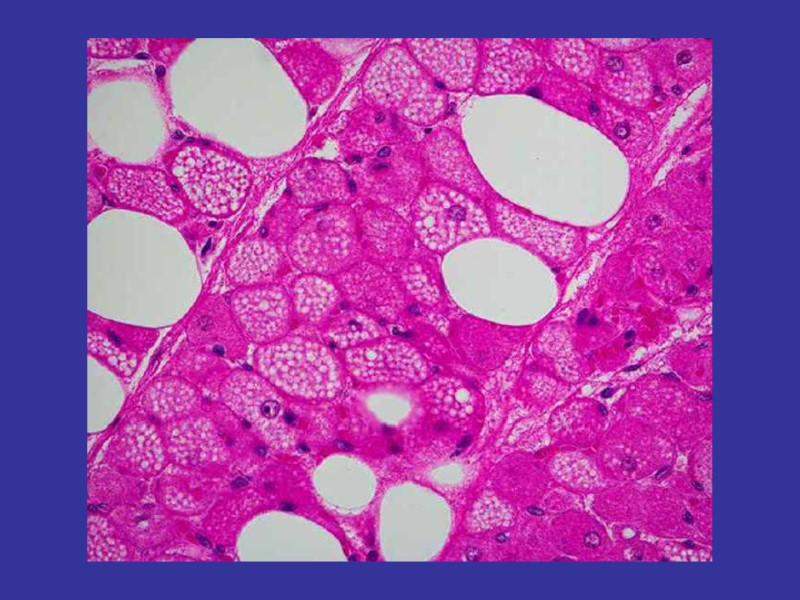
Adipose tissue
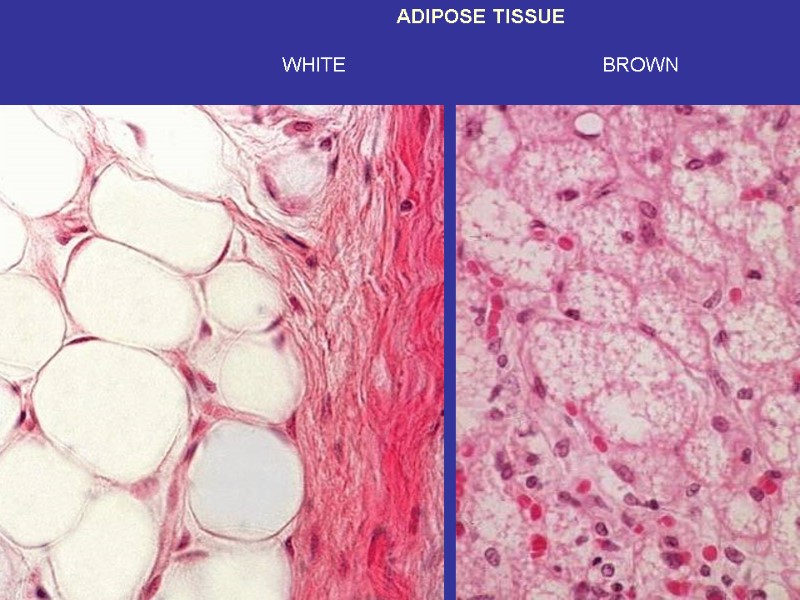
ADIPOSE TISSUE WHITE BROWN
13554-fibrous_connective_tissue.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

