51fdcbb53784a7538507e72e424b36f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 The Higher Education System in England Wales Peter Hartley University of Birmingham, UK 1
The Higher Education System in England Wales Peter Hartley University of Birmingham, UK 1
 Content ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Higher Education Access to Higher Education The ‘Traditional’ System Degree Progression Quality Assurance Agency Academic Content QAA Framework Academic Achievement QAA Guidelines Structure of Degree Programmes Undergraduate Degrees Module Failure and Progression Level of Degree Student Funding Undergraduate Loans Bologna Compliance 2
Content ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Higher Education Access to Higher Education The ‘Traditional’ System Degree Progression Quality Assurance Agency Academic Content QAA Framework Academic Achievement QAA Guidelines Structure of Degree Programmes Undergraduate Degrees Module Failure and Progression Level of Degree Student Funding Undergraduate Loans Bologna Compliance 2
 Higher Education: Post-18 years Education, ¡ Distinguished from ‘Further Education’ ¡ University education at Degree level ¡ Approximately 1. 5 m Full-time and part-time students ¡ 3
Higher Education: Post-18 years Education, ¡ Distinguished from ‘Further Education’ ¡ University education at Degree level ¡ Approximately 1. 5 m Full-time and part-time students ¡ 3
 Access to Higher Education Normal requirement for UK students ¡ Three passes at A-level ¡ A-level: Advanced level General Certificate of Education ¡ Number and level varies by institution and programme of study ¡ 4
Access to Higher Education Normal requirement for UK students ¡ Three passes at A-level ¡ A-level: Advanced level General Certificate of Education ¡ Number and level varies by institution and programme of study ¡ 4
 The ‘Traditional’ System ¡ Bachelor Degree (BSc, BEd, BEng…) l ¡ Master Degree taught (MSc, MA, MBA…) l ¡ Normally one year Master Degree research (MPhil) l ¡ Normally three years Normally 1. 5 to two years Doctoral Degree (Ph. D, Soc. Sc. D, Ed. D, Eng. D…) l Normally three years 5
The ‘Traditional’ System ¡ Bachelor Degree (BSc, BEd, BEng…) l ¡ Master Degree taught (MSc, MA, MBA…) l ¡ Normally one year Master Degree research (MPhil) l ¡ Normally three years Normally 1. 5 to two years Doctoral Degree (Ph. D, Soc. Sc. D, Ed. D, Eng. D…) l Normally three years 5
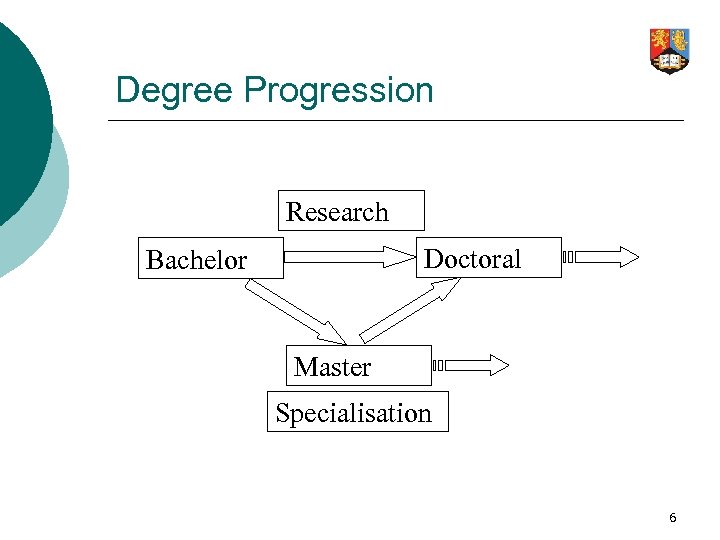 Degree Progression Research Doctoral Bachelor Master Specialisation 6
Degree Progression Research Doctoral Bachelor Master Specialisation 6
 Quality Assurance Agency ¡ QAA – Established in 1997: Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (http: //www. qaa. ac. uk) ¡ Three Important Aspects l l l Sets out a framework of awards for different levels of achievement (2001) Produce subject ‘benchmark’ statements Assesses the quality of the operating procedures supporting academic activities 7
Quality Assurance Agency ¡ QAA – Established in 1997: Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (http: //www. qaa. ac. uk) ¡ Three Important Aspects l l l Sets out a framework of awards for different levels of achievement (2001) Produce subject ‘benchmark’ statements Assesses the quality of the operating procedures supporting academic activities 7
 Academic Content Academic content must be subject to external scrutiny ¡ External Examiner ¡ Professional Accreditation (IMech. E, IMC…, UK-SPEC*) ¡ Programme Review ¡ *http: //www. engc. org. uk/UKSPEC established in 2004 to oversee professional competence in engineering education 8
Academic Content Academic content must be subject to external scrutiny ¡ External Examiner ¡ Professional Accreditation (IMech. E, IMC…, UK-SPEC*) ¡ Programme Review ¡ *http: //www. engc. org. uk/UKSPEC established in 2004 to oversee professional competence in engineering education 8
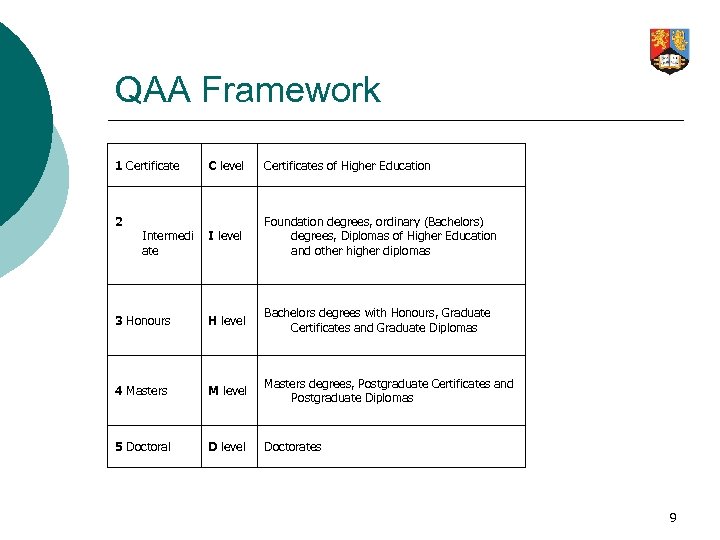 QAA Framework 1 Certificate C level Certificates of Higher Education I level Foundation degrees, ordinary (Bachelors) degrees, Diplomas of Higher Education and other higher diplomas 3 Honours H level Bachelors degrees with Honours, Graduate Certificates and Graduate Diplomas 4 Masters M level Masters degrees, Postgraduate Certificates and Postgraduate Diplomas 5 Doctoral D level Doctorates 2 Intermedi ate 9
QAA Framework 1 Certificate C level Certificates of Higher Education I level Foundation degrees, ordinary (Bachelors) degrees, Diplomas of Higher Education and other higher diplomas 3 Honours H level Bachelors degrees with Honours, Graduate Certificates and Graduate Diplomas 4 Masters M level Masters degrees, Postgraduate Certificates and Postgraduate Diplomas 5 Doctoral D level Doctorates 2 Intermedi ate 9
 Academic Achievement Award of any qualification is based on the achievement of specific skills or ‘learning outcomes’ ¡ Degree programmes must specify expected outcomes at programme and module level ¡ 10
Academic Achievement Award of any qualification is based on the achievement of specific skills or ‘learning outcomes’ ¡ Degree programmes must specify expected outcomes at programme and module level ¡ 10
 QAA Guidelines Honours level An Honours graduate will have developed an understanding of a complex body of knowledge, some of it at the current boundaries of an academic discipline. Through this, the graduate will have developed analytical techniques and problem-solving skills that can be applied in many types of employment. The graduate will be able to evaluate evidence, arguments and assumptions, to reach sound judgements, and to communicate effectively. An Honours graduate should have the qualities needed for employment in situations requiring the exercise of personal responsibility, and decision-making in complex and unpredictable circumstances. ¡ 11
QAA Guidelines Honours level An Honours graduate will have developed an understanding of a complex body of knowledge, some of it at the current boundaries of an academic discipline. Through this, the graduate will have developed analytical techniques and problem-solving skills that can be applied in many types of employment. The graduate will be able to evaluate evidence, arguments and assumptions, to reach sound judgements, and to communicate effectively. An Honours graduate should have the qualities needed for employment in situations requiring the exercise of personal responsibility, and decision-making in complex and unpredictable circumstances. ¡ 11
 Structure of Degree Programmes ¡ Engineering Degrees at Birmingham l l l BEng – 3 year undergraduate degree MEng – 4 year undergraduate degree MSc – one year taught postgraduate degree MPhil/MRes – 1. 5 to 2 year research postgraduate degree Ph. D – 3 year research postgraduate degree Eng. D – 4 year research/industrial postgraduate degree 12
Structure of Degree Programmes ¡ Engineering Degrees at Birmingham l l l BEng – 3 year undergraduate degree MEng – 4 year undergraduate degree MSc – one year taught postgraduate degree MPhil/MRes – 1. 5 to 2 year research postgraduate degree Ph. D – 3 year research postgraduate degree Eng. D – 4 year research/industrial postgraduate degree 12
 Undergraduate Degrees ¡ Each year l l l 12 modules Each module requires 100 hours student-effort 1200 hours student-effort per year 30 -week academic year 10 credits per module (pass: 10 credits, fail: zero credits) 120 credits per year (100 required to progress to next year) 13
Undergraduate Degrees ¡ Each year l l l 12 modules Each module requires 100 hours student-effort 1200 hours student-effort per year 30 -week academic year 10 credits per module (pass: 10 credits, fail: zero credits) 120 credits per year (100 required to progress to next year) 13
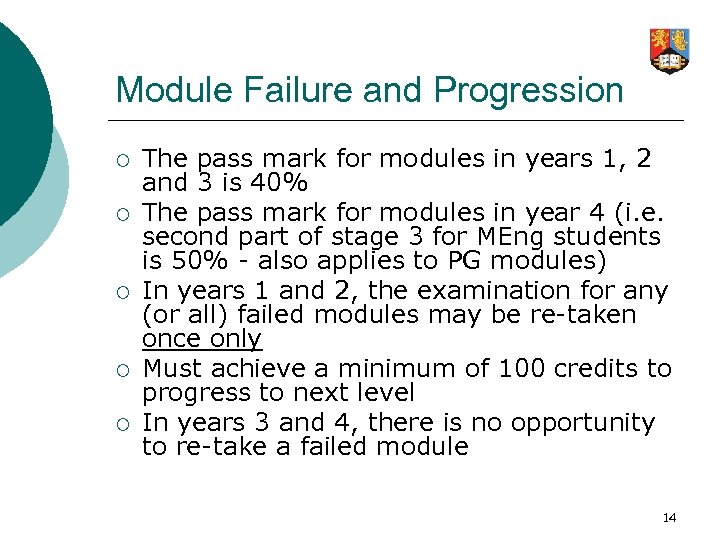 Module Failure and Progression ¡ ¡ ¡ The pass mark for modules in years 1, 2 and 3 is 40% The pass mark for modules in year 4 (i. e. second part of stage 3 for MEng students is 50% - also applies to PG modules) In years 1 and 2, the examination for any (or all) failed modules may be re-taken once only Must achieve a minimum of 100 credits to progress to next level In years 3 and 4, there is no opportunity to re-take a failed module 14
Module Failure and Progression ¡ ¡ ¡ The pass mark for modules in years 1, 2 and 3 is 40% The pass mark for modules in year 4 (i. e. second part of stage 3 for MEng students is 50% - also applies to PG modules) In years 1 and 2, the examination for any (or all) failed modules may be re-taken once only Must achieve a minimum of 100 credits to progress to next level In years 3 and 4, there is no opportunity to re-take a failed module 14
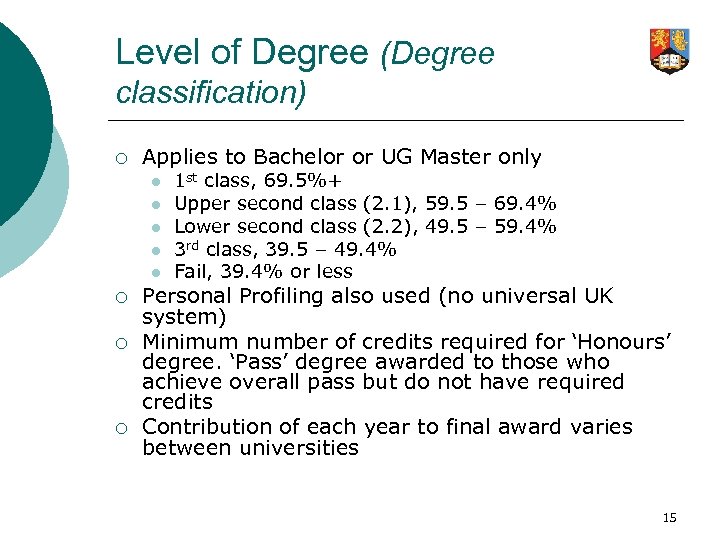 Level of Degree (Degree classification) ¡ Applies to Bachelor or UG Master only l l l ¡ ¡ ¡ 1 st class, 69. 5%+ Upper second class (2. 1), 59. 5 – 69. 4% Lower second class (2. 2), 49. 5 – 59. 4% 3 rd class, 39. 5 – 49. 4% Fail, 39. 4% or less Personal Profiling also used (no universal UK system) Minimum number of credits required for ‘Honours’ degree. ‘Pass’ degree awarded to those who achieve overall pass but do not have required credits Contribution of each year to final award varies between universities 15
Level of Degree (Degree classification) ¡ Applies to Bachelor or UG Master only l l l ¡ ¡ ¡ 1 st class, 69. 5%+ Upper second class (2. 1), 59. 5 – 69. 4% Lower second class (2. 2), 49. 5 – 59. 4% 3 rd class, 39. 5 – 49. 4% Fail, 39. 4% or less Personal Profiling also used (no universal UK system) Minimum number of credits required for ‘Honours’ degree. ‘Pass’ degree awarded to those who achieve overall pass but do not have required credits Contribution of each year to final award varies between universities 15
 Student Funding For UG programmes (BEng, MEng) the UK government provides loans ¡ For Ph. D programmes a grant is provided (£ 15385 pa – non taxable, including fees of £ 3085). Research support (at least in engineering) usually restricted to applied research. No provision for MSc support. ¡ 16
Student Funding For UG programmes (BEng, MEng) the UK government provides loans ¡ For Ph. D programmes a grant is provided (£ 15385 pa – non taxable, including fees of £ 3085). Research support (at least in engineering) usually restricted to applied research. No provision for MSc support. ¡ 16
 Undergraduate Loans ¡ Maintenance loan of up to £ 3300 pa l ¡ Fee support, up to £ 3000 pa l ¡ (Other support available for low income, including non-repayable grants) (From September 2006 Universities may increase their course fee, up to a maximum of £ 3000) Repayment l l From April 6 th after graduation (or if leaving University before completion), if income is more than £ 15000 pa. Interest rate is currently 3. 2% (about one third of Bank loan rate) Loan outstanding is written off after 25 years. 17
Undergraduate Loans ¡ Maintenance loan of up to £ 3300 pa l ¡ Fee support, up to £ 3000 pa l ¡ (Other support available for low income, including non-repayable grants) (From September 2006 Universities may increase their course fee, up to a maximum of £ 3000) Repayment l l From April 6 th after graduation (or if leaving University before completion), if income is more than £ 15000 pa. Interest rate is currently 3. 2% (about one third of Bank loan rate) Loan outstanding is written off after 25 years. 17
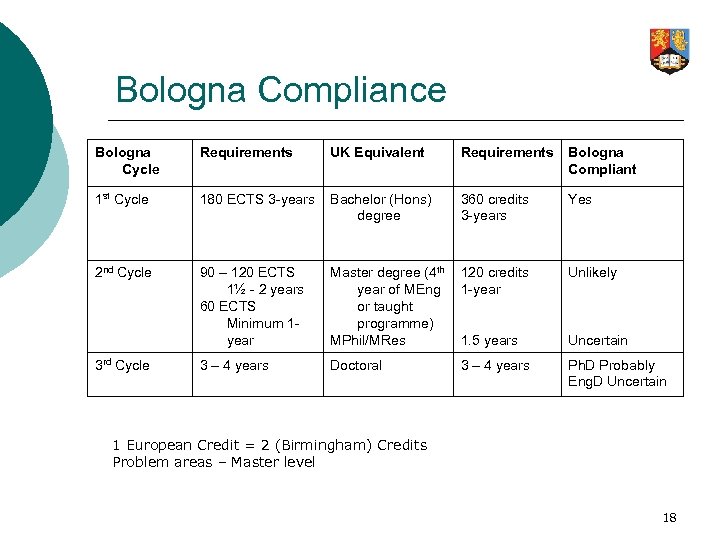 Bologna Compliance Bologna Cycle Requirements UK Equivalent Requirements Bologna Compliant 1 st Cycle 180 ECTS 3 -years Bachelor (Hons) degree 360 credits 3 -years Yes 2 nd Cycle 90 – 120 ECTS 1½ - 2 years 60 ECTS Minimum 1 year Master degree (4 th year of MEng or taught programme) MPhil/MRes 120 credits 1 -year Unlikely 1. 5 years Uncertain 3 – 4 years Doctoral 3 – 4 years Ph. D Probably Eng. D Uncertain 3 rd Cycle 1 European Credit = 2 (Birmingham) Credits Problem areas – Master level 18
Bologna Compliance Bologna Cycle Requirements UK Equivalent Requirements Bologna Compliant 1 st Cycle 180 ECTS 3 -years Bachelor (Hons) degree 360 credits 3 -years Yes 2 nd Cycle 90 – 120 ECTS 1½ - 2 years 60 ECTS Minimum 1 year Master degree (4 th year of MEng or taught programme) MPhil/MRes 120 credits 1 -year Unlikely 1. 5 years Uncertain 3 – 4 years Doctoral 3 – 4 years Ph. D Probably Eng. D Uncertain 3 rd Cycle 1 European Credit = 2 (Birmingham) Credits Problem areas – Master level 18
 Acknowledgements ¡ The invitation and support of the University of Novi-Sad is acknowledged with thanks. 19
Acknowledgements ¡ The invitation and support of the University of Novi-Sad is acknowledged with thanks. 19


