55299db421c9ff8994c243bde3b6d5c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 THE GREENING OF REGISTERED APPRENTICESHIP: An Environmental Scan of the Impact of Green Jobs on Registered Apprenticeship and Implications for Workforce Development
THE GREENING OF REGISTERED APPRENTICESHIP: An Environmental Scan of the Impact of Green Jobs on Registered Apprenticeship and Implications for Workforce Development
 Agenda § § § § Introduction Goals & Objectives Stakeholders Interviewed Stakeholder Industry Assessment Training & Education Impacts Strategic Partnerships & Collaboration Conclusion Next Steps
Agenda § § § § Introduction Goals & Objectives Stakeholders Interviewed Stakeholder Industry Assessment Training & Education Impacts Strategic Partnerships & Collaboration Conclusion Next Steps
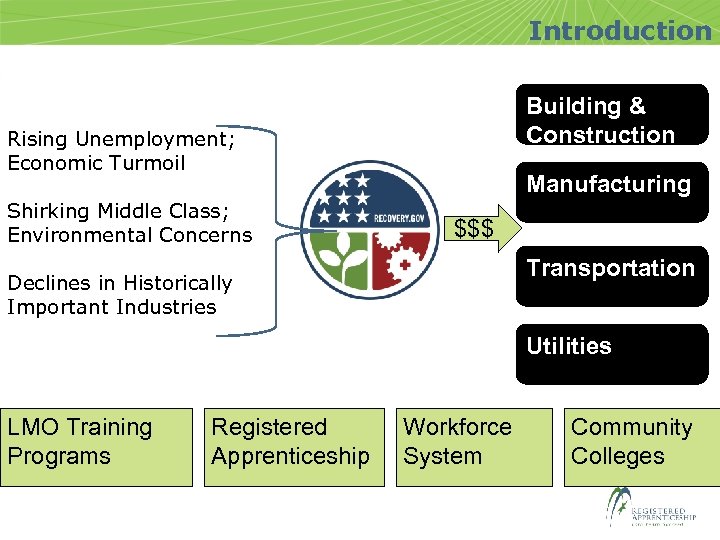 Introduction Building & Construction Rising Unemployment; Economic Turmoil Shirking Middle Class; Environmental Concerns Manufacturing $$$ Transportation Declines in Historically Important Industries Utilities LMO Training Programs Registered Apprenticeship Workforce System Community Colleges
Introduction Building & Construction Rising Unemployment; Economic Turmoil Shirking Middle Class; Environmental Concerns Manufacturing $$$ Transportation Declines in Historically Important Industries Utilities LMO Training Programs Registered Apprenticeship Workforce System Community Colleges
 Introduction Rising Unemployment; Economic Turmoil ; Shirking Middle Class; Environmental Concerns; Declines in Historically Important Industries • Registered Apprenticeship Building & Construction • Workforce System Manufacturing Transportation Energy/Utilities • Community Colleges • LMO Training Programs
Introduction Rising Unemployment; Economic Turmoil ; Shirking Middle Class; Environmental Concerns; Declines in Historically Important Industries • Registered Apprenticeship Building & Construction • Workforce System Manufacturing Transportation Energy/Utilities • Community Colleges • LMO Training Programs
 Goals and Objectives § Impact of green on select industries § Role of apprenticeship in “green jobs” § How have RA stakeholders modified training to meet new green needs? § Partnering successes between RA, workforce system, education & others in the green economy. § Best practices in pre-apprenticeship & activities to train dislocated workers § Not a comprehensive review of green.
Goals and Objectives § Impact of green on select industries § Role of apprenticeship in “green jobs” § How have RA stakeholders modified training to meet new green needs? § Partnering successes between RA, workforce system, education & others in the green economy. § Best practices in pre-apprenticeship & activities to train dislocated workers § Not a comprehensive review of green.
 Stakeholders Interviewed Represent leadership from range of industries likely to be impacted by green including: building and construction; transportation; advanced manufacturing; building services; and electrical utilities § § § § ABC HBI/NAHB IEC IBEW/NJATC IUOE LIUNA-AGC NIMS § § § § Seafarers SEIU SMWIA UA UBC UPS UWUA
Stakeholders Interviewed Represent leadership from range of industries likely to be impacted by green including: building and construction; transportation; advanced manufacturing; building services; and electrical utilities § § § § ABC HBI/NAHB IEC IBEW/NJATC IUOE LIUNA-AGC NIMS § § § § Seafarers SEIU SMWIA UA UBC UPS UWUA
 ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF GREEN IN SELECT INDUSTRIES
ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF GREEN IN SELECT INDUSTRIES
 Stakeholder Industry Assessment § Industries continue to meet the demands of the green economy by implementing changes to processes, materials & technologies How are green technologies, processes § Key relationships with vendors, manufacturers, and materials impacting colleges & research selected industries? institutions keep industries on the cutting-edge. § Organizations communicate social benefits of green to new and existing members
Stakeholder Industry Assessment § Industries continue to meet the demands of the green economy by implementing changes to processes, materials & technologies How are green technologies, processes § Key relationships with vendors, manufacturers, and materials impacting colleges & research selected industries? institutions keep industries on the cutting-edge. § Organizations communicate social benefits of green to new and existing members
 Industry Spotlight § HVAC and plumbing have shifted the industry to gray water systems, low-flow fixtures, solar heating systems and other new technologies and products. § Fundamental skills remain relatively unchanged. § Relationships with vendors critical § Partnership with Washtenaw Community College allows apprentices to earn college degrees § Transforms public and potential recruits’ view of critical industry
Industry Spotlight § HVAC and plumbing have shifted the industry to gray water systems, low-flow fixtures, solar heating systems and other new technologies and products. § Fundamental skills remain relatively unchanged. § Relationships with vendors critical § Partnership with Washtenaw Community College allows apprentices to earn college degrees § Transforms public and potential recruits’ view of critical industry
 Stakeholder Industry Assessment § Future employment growth but minimal impact on existing occupational structures; How is green changing occupations and occupational structures in these select industries? § Entry opportunities in green jobs should lead to longterm, sustainable careers.
Stakeholder Industry Assessment § Future employment growth but minimal impact on existing occupational structures; How is green changing occupations and occupational structures in these select industries? § Entry opportunities in green jobs should lead to longterm, sustainable careers.
 Industry Spotlight “Most of the residential construction trades will be impacted. The skills of carpenters, electricians, plumbers, HVAC, brick masonry will all change in some way and how they interact and affect each other will need to be coordinated… Builders need to know green building practices in order to stay competitive. It’s about looking at what makes a house work more efficiently and applying new technologies. ” Fred Humphreys, NAHB/HBI
Industry Spotlight “Most of the residential construction trades will be impacted. The skills of carpenters, electricians, plumbers, HVAC, brick masonry will all change in some way and how they interact and affect each other will need to be coordinated… Builders need to know green building practices in order to stay competitive. It’s about looking at what makes a house work more efficiently and applying new technologies. ” Fred Humphreys, NAHB/HBI
 Industry Spotlight § ““While I can’t say that creating a new occupation won’t happen; due to licensing requirements, I really don’t see the electrical work being done as part of a new occupation. Therefore, there would be little impact to IEC member contractors other than an expansion of their workload to include the electrical and mechanical aspects of alternative energy installations. At the same time, training requirements for electricians will be expanded to include whatever new technologies are introduced. ” Robert Baird
Industry Spotlight § ““While I can’t say that creating a new occupation won’t happen; due to licensing requirements, I really don’t see the electrical work being done as part of a new occupation. Therefore, there would be little impact to IEC member contractors other than an expansion of their workload to include the electrical and mechanical aspects of alternative energy installations. At the same time, training requirements for electricians will be expanded to include whatever new technologies are introduced. ” Robert Baird
 Industry Spotlight § HBI/NAHB, UBC emphasized that skills required for solar panel installation should be incorporated into existing construction trades rather than evolving into a separate occupation.
Industry Spotlight § HBI/NAHB, UBC emphasized that skills required for solar panel installation should be incorporated into existing construction trades rather than evolving into a separate occupation.
 Industry Spotlight § IUOE has identified hybrid and diesel mechanics and jobs related to windmill farm work as well as GPS programmers, installers and maintenance providers on heavy equipment as possible new occupations that may result from the emphasis on green job creation.
Industry Spotlight § IUOE has identified hybrid and diesel mechanics and jobs related to windmill farm work as well as GPS programmers, installers and maintenance providers on heavy equipment as possible new occupations that may result from the emphasis on green job creation.
 Stakeholder Industry Assessment What are the key green opportunities for occupational growth? § Industries prepping for occupational growth are focused on the need for materials & technologies (manufacturing) as well as energy transmission (utilities). § Anticipated occupational growth will be driven by specific green trends and will vary geographically, leading to targeted sector strategies;
Stakeholder Industry Assessment What are the key green opportunities for occupational growth? § Industries prepping for occupational growth are focused on the need for materials & technologies (manufacturing) as well as energy transmission (utilities). § Anticipated occupational growth will be driven by specific green trends and will vary geographically, leading to targeted sector strategies;
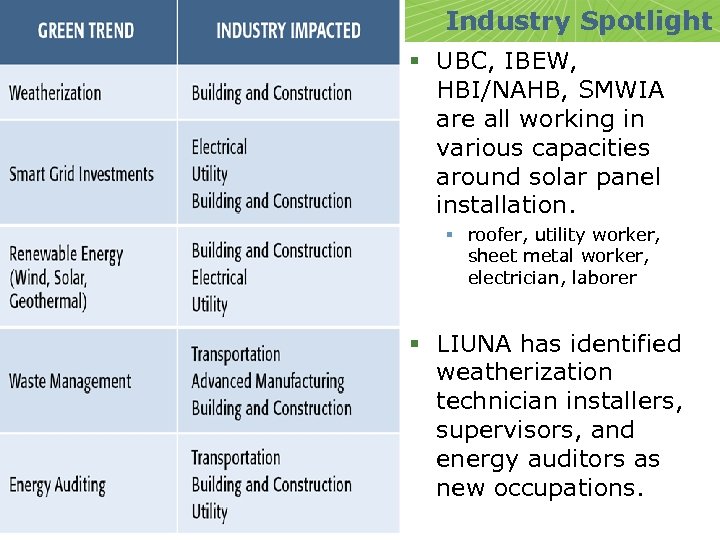 Industry Spotlight § UBC, IBEW, HBI/NAHB, SMWIA are all working in various capacities around solar panel installation. § roofer, utility worker, sheet metal worker, electrician, laborer § LIUNA has identified weatherization technician installers, supervisors, and energy auditors as new occupations.
Industry Spotlight § UBC, IBEW, HBI/NAHB, SMWIA are all working in various capacities around solar panel installation. § roofer, utility worker, sheet metal worker, electrician, laborer § LIUNA has identified weatherization technician installers, supervisors, and energy auditors as new occupations.
 THE IMPACT OF GREEN ON TRAINING AND EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS:
THE IMPACT OF GREEN ON TRAINING AND EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS:
 Training and Education Requirements How are organizations modifying training and education activities in relation to green jobs and green technologies? § Seamless approach to training their future workforce & updating skills of existing workers to meet the market demand. • Stakeholders engage vendors, academic institutions & Federal agencies to contribute to the training and R&D efforts.
Training and Education Requirements How are organizations modifying training and education activities in relation to green jobs and green technologies? § Seamless approach to training their future workforce & updating skills of existing workers to meet the market demand. • Stakeholders engage vendors, academic institutions & Federal agencies to contribute to the training and R&D efforts.
 Industry Spotlight § UPS is up-skilling its existing mechanic workforce to handle lower-emission vehicles and incorporating green concepts and green principles into its training programs.
Industry Spotlight § UPS is up-skilling its existing mechanic workforce to handle lower-emission vehicles and incorporating green concepts and green principles into its training programs.
 Industry Spotlight § NECA/IBEW/NJATC has developed renewable energy curriculum and updated both journeyworker upgrade and apprenticeship training materials, primarily in the solar and wind areas.
Industry Spotlight § NECA/IBEW/NJATC has developed renewable energy curriculum and updated both journeyworker upgrade and apprenticeship training materials, primarily in the solar and wind areas.
 Training and Education Requirements § Primary training vehicle for green-collar job opportunities for these select industries. What role will apprenticeship play in preparing skilled workers for green-collar jobs? § Programs have the opportunity to conduct outreach & recruit sociallyconscience new workers (often youth)
Training and Education Requirements § Primary training vehicle for green-collar job opportunities for these select industries. What role will apprenticeship play in preparing skilled workers for green-collar jobs? § Programs have the opportunity to conduct outreach & recruit sociallyconscience new workers (often youth)
 Industry Spotlight § For UA to raise awareness about green to its existing and potential workforce as it relates to HVAC and plumbing, they sponsor a green training trailer known as the HVAC Mobile Green Classroom that provides information on the latest green technology and handson training opportunities.
Industry Spotlight § For UA to raise awareness about green to its existing and potential workforce as it relates to HVAC and plumbing, they sponsor a green training trailer known as the HVAC Mobile Green Classroom that provides information on the latest green technology and handson training opportunities.
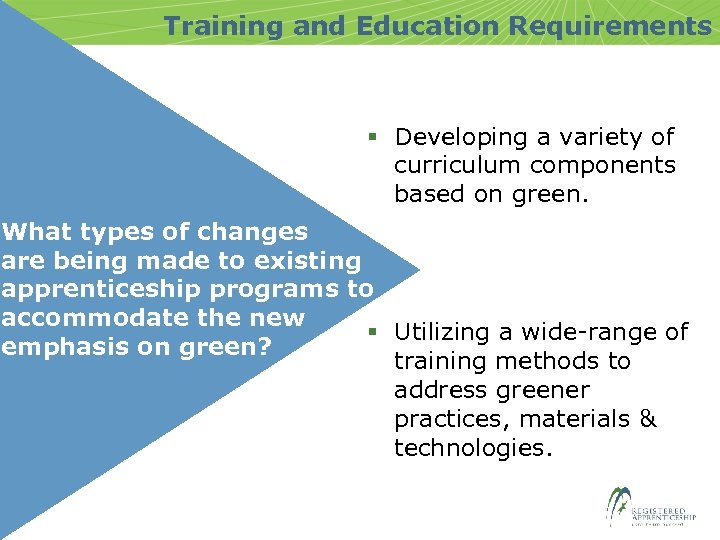 Training and Education Requirements § Developing a variety of curriculum components based on green. What types of changes are being made to existing apprenticeship programs to accommodate the new § Utilizing a wide-range of emphasis on green? training methods to address greener practices, materials & technologies.
Training and Education Requirements § Developing a variety of curriculum components based on green. What types of changes are being made to existing apprenticeship programs to accommodate the new § Utilizing a wide-range of emphasis on green? training methods to address greener practices, materials & technologies.
 Industry Spotlight § ABC added a 15 - hour module to its apprenticeship curriculum focusing on identifying green practices & increasing worker awareness of green concepts. § module covers green products, waste management and the basics of the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Green Building Rating System™
Industry Spotlight § ABC added a 15 - hour module to its apprenticeship curriculum focusing on identifying green practices & increasing worker awareness of green concepts. § module covers green products, waste management and the basics of the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Green Building Rating System™
 Industry Spotlight § The Seafarers have developed self-paced, online distance learning programs & offer certificates for the completion of Hazardous Material Control & Management and Environmental Awareness courses.
Industry Spotlight § The Seafarers have developed self-paced, online distance learning programs & offer certificates for the completion of Hazardous Material Control & Management and Environmental Awareness courses.
 Industry Spotlight § SEIU has developed green building classes that cover energy usage, water conservation, green cleaning and maintenance, and a variety of other topics.
Industry Spotlight § SEIU has developed green building classes that cover energy usage, water conservation, green cleaning and maintenance, and a variety of other topics.
 Industry Spotlight § LIUNA has created a comprehensive weatherization training program. Courses teach: § skills for weatherization technician, energy auditor or supervisor. § Other courses cover general construction, safety and environmental hazards, and life and employability skills.
Industry Spotlight § LIUNA has created a comprehensive weatherization training program. Courses teach: § skills for weatherization technician, energy auditor or supervisor. § Other courses cover general construction, safety and environmental hazards, and life and employability skills.
 Training and Education Requirements § Provide a sustainable pathway out of poverty. § Need to further link preapprenticeship and What is the role and scope of pre-apprenticeship. in preparing the next generation of workers § Emerging need for multifor a green disciplinary preeconomy? apprenticeship programs to address commonalities around green.
Training and Education Requirements § Provide a sustainable pathway out of poverty. § Need to further link preapprenticeship and What is the role and scope of pre-apprenticeship. in preparing the next generation of workers § Emerging need for multifor a green disciplinary preeconomy? apprenticeship programs to address commonalities around green.
 Industry Spotlight § UWUA has two preapprenticeship programs in California and Massachusetts entitled “Intro to the Utility Industry. ” § The program includes leadership development & diversity components and is comprised of mostly women and minorities.
Industry Spotlight § UWUA has two preapprenticeship programs in California and Massachusetts entitled “Intro to the Utility Industry. ” § The program includes leadership development & diversity components and is comprised of mostly women and minorities.
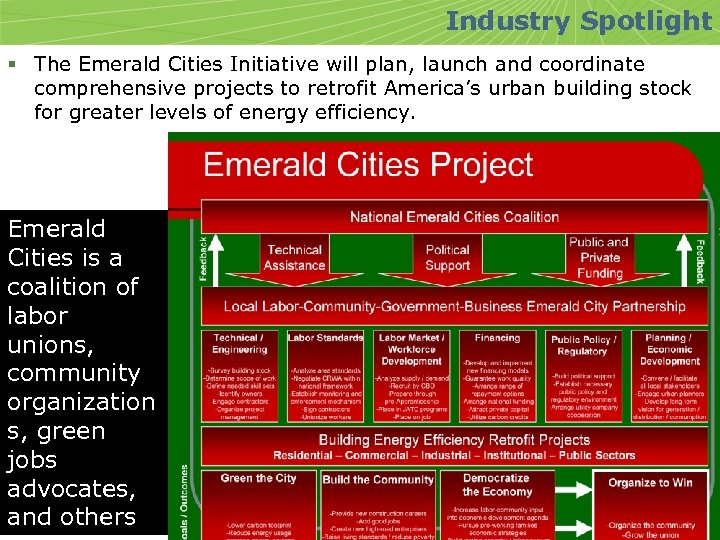 Industry Spotlight § The Emerald Cities Initiative will plan, launch and coordinate comprehensive projects to retrofit America’s urban building stock for greater levels of energy efficiency. Emerald Cities is a coalition of labor unions, community organization s, green jobs advocates, and others
Industry Spotlight § The Emerald Cities Initiative will plan, launch and coordinate comprehensive projects to retrofit America’s urban building stock for greater levels of energy efficiency. Emerald Cities is a coalition of labor unions, community organization s, green jobs advocates, and others
 Industry Spotlight § NECA/IBEW/NJATC (in partnership with other LMOs) is developing a multi-disciplinary preapprenticeship program that will teach skills such as: § safety, math, blueprint reading and allow students to explore occupations and ultimately enter into desired apprenticeship programs.
Industry Spotlight § NECA/IBEW/NJATC (in partnership with other LMOs) is developing a multi-disciplinary preapprenticeship program that will teach skills such as: § safety, math, blueprint reading and allow students to explore occupations and ultimately enter into desired apprenticeship programs.
 STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS AND COLLABORATIONS TO MEET “GREEN” CHALLENGES
STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIPS AND COLLABORATIONS TO MEET “GREEN” CHALLENGES
 Partnerships and Collaborations § Partnering with: What kind of partnerships are developing around green jobs and technologies? § national organizations and Federal agencies to address diverse but shared policy interests. § With start-ups and R&D hubs at universities to stay on cutting-edge § Advocacy groups & community-based organizations
Partnerships and Collaborations § Partnering with: What kind of partnerships are developing around green jobs and technologies? § national organizations and Federal agencies to address diverse but shared policy interests. § With start-ups and R&D hubs at universities to stay on cutting-edge § Advocacy groups & community-based organizations
 Industry Spotlight § NIMS has over 350 active partnerships to ensure training meets industry demand “We are engaged nationwide. We have over 350 Metalworking Technical Committees with at least three manufacturing companies on each; some with 12 -18 companies. Our stakeholders have over 6, 000 companies. ” NIMS Executive Director Stephen Mandes :
Industry Spotlight § NIMS has over 350 active partnerships to ensure training meets industry demand “We are engaged nationwide. We have over 350 Metalworking Technical Committees with at least three manufacturing companies on each; some with 12 -18 companies. Our stakeholders have over 6, 000 companies. ” NIMS Executive Director Stephen Mandes :
 Industry Spotlight § The crafts that the UA represents have always been at the forefront of education and training as it relates to environmental friendly applications and systems. As such, we work with many organizations on training initiatives that enhance the skills of our workforce so they can compete for quality jobs in the HVAC and plumbing industries. ” § - Michael Arndt, UA director of training
Industry Spotlight § The crafts that the UA represents have always been at the forefront of education and training as it relates to environmental friendly applications and systems. As such, we work with many organizations on training initiatives that enhance the skills of our workforce so they can compete for quality jobs in the HVAC and plumbing industries. ” § - Michael Arndt, UA director of training
 Partnerships and Collaborations How & to what extent are preapprenticeship efforts & collaborations being used to increase the pipeline of workers for green jobs? § Localized preapprenticeship training partnerships are crucial to preparing applicants for RA programs. § Showcase the many green elements that exist in these occupations § prefer a structure for preapprenticeship that would establish direct linkages with RA programs.
Partnerships and Collaborations How & to what extent are preapprenticeship efforts & collaborations being used to increase the pipeline of workers for green jobs? § Localized preapprenticeship training partnerships are crucial to preparing applicants for RA programs. § Showcase the many green elements that exist in these occupations § prefer a structure for preapprenticeship that would establish direct linkages with RA programs.
 Industry Spotlight § SMWIA’s Local 18 in the Milwaukee/Racine area of Wisconsin works with the Partnership for Working families
Industry Spotlight § SMWIA’s Local 18 in the Milwaukee/Racine area of Wisconsin works with the Partnership for Working families
 § HBI/NAHB associations in St. Louis, Jacksonville, Fla. , and Lexington, Ky. , have relationships with local corporations, community colleges, the workforce system and high schools to develop apprenticeship programs that result in credit toward associate and bachelor’s degrees. § Moving forward, green building practices and interim credentials will be incorporated into program curricula. Industry Spotlight
§ HBI/NAHB associations in St. Louis, Jacksonville, Fla. , and Lexington, Ky. , have relationships with local corporations, community colleges, the workforce system and high schools to develop apprenticeship programs that result in credit toward associate and bachelor’s degrees. § Moving forward, green building practices and interim credentials will be incorporated into program curricula. Industry Spotlight
 Partnerships and Collaborations § While most stakeholders are focused on the reemployment of their existing members, there are isolated examples of What types of activities re-employment efforts are occurring to an effort to that could be expanded. retrain dislocated workers from other § Many stakeholders are industries? engaged in veteran reemployment activities.
Partnerships and Collaborations § While most stakeholders are focused on the reemployment of their existing members, there are isolated examples of What types of activities re-employment efforts are occurring to an effort to that could be expanded. retrain dislocated workers from other § Many stakeholders are industries? engaged in veteran reemployment activities.
 Industry Spotlight § UBC sees significant opportunities for reemployment in solar panel installation, an occupation that requires a great deal of welding. Consequently, UBC is actively recruiting dislocated welders from other industries and preparing them for job opportunities.
Industry Spotlight § UBC sees significant opportunities for reemployment in solar panel installation, an occupation that requires a great deal of welding. Consequently, UBC is actively recruiting dislocated welders from other industries and preparing them for job opportunities.
 § UWUA is working to transition dislocated workers from the auto and aerospace industries into various jobs including auditor, cable splicer, overhead lineman, and weatherization technician positions. § SEIU’s Public Services Division is developing plans to re-employ dislocated park service employees in landscaping, roofing, and water management jobs in public buildings. Industry Spotlight
§ UWUA is working to transition dislocated workers from the auto and aerospace industries into various jobs including auditor, cable splicer, overhead lineman, and weatherization technician positions. § SEIU’s Public Services Division is developing plans to re-employ dislocated park service employees in landscaping, roofing, and water management jobs in public buildings. Industry Spotlight
 CONCLUSIONS
CONCLUSIONS
 Conclusions 1 Green Already Has And Continues To Have A Significant, Positive And Evolving/Adapting Impact On These Key Industries And Their Related Occupations; § Green is rapidly changing existing industries & occupations. § Skill enhancements are currently being deployed to apprentices and journeyworkers alike. § Organizations are partnering with start-ups, manufacturers, university R&D laboratories, business incubators, etc. to stay on the cutting edge. § Industries recognize that their involvement in “green” has created an opportunity to appeal to a new set of socially conscious workers – mainly youth.
Conclusions 1 Green Already Has And Continues To Have A Significant, Positive And Evolving/Adapting Impact On These Key Industries And Their Related Occupations; § Green is rapidly changing existing industries & occupations. § Skill enhancements are currently being deployed to apprentices and journeyworkers alike. § Organizations are partnering with start-ups, manufacturers, university R&D laboratories, business incubators, etc. to stay on the cutting edge. § Industries recognize that their involvement in “green” has created an opportunity to appeal to a new set of socially conscious workers – mainly youth.
 Conclusions 2 Polices and Investments in green jobs should lead to longterm sustainable careers with emphasis on rebuilding America’s middle class § Ensure that opportunities have long-term career potential & pathways out of poverty. § Pathways must include training, education and workplace opportunities beyond immediate needs & lead to life-long careers with competitive wages. § Stakeholders would like to see investments that focus on supporting sustainable careers (carpenter, electrician, etc. ), rather than short-term skills (weatherization, wind generator technician).
Conclusions 2 Polices and Investments in green jobs should lead to longterm sustainable careers with emphasis on rebuilding America’s middle class § Ensure that opportunities have long-term career potential & pathways out of poverty. § Pathways must include training, education and workplace opportunities beyond immediate needs & lead to life-long careers with competitive wages. § Stakeholders would like to see investments that focus on supporting sustainable careers (carpenter, electrician, etc. ), rather than short-term skills (weatherization, wind generator technician).
 Conclusions 3 Registered Apprenticeship is at the nexus of the green economy. § Primary entry into crucial occupations in the green economy. § green building occupations; utility workers; renewable energy installers and technicians (solar, wind); hybrid mechanics, etc. § Continually updates to training and the delivery of training. § Established process that engages employers, educators, manufacturers & others to ensure curriculum and training meets current $ future workforce needs.
Conclusions 3 Registered Apprenticeship is at the nexus of the green economy. § Primary entry into crucial occupations in the green economy. § green building occupations; utility workers; renewable energy installers and technicians (solar, wind); hybrid mechanics, etc. § Continually updates to training and the delivery of training. § Established process that engages employers, educators, manufacturers & others to ensure curriculum and training meets current $ future workforce needs.
 Conclusions 4 In order to meet rapidly changing market demands, Registered Apprenticeship stakeholders are taking advantage of newer, more flexible training approaches. § RA programs deliver just-in-time training to meet the adult learning styles. § include interim certifications, distance learning, electronic media and various hybrid/combination training. § Enhanced delivery of curriculum allows for adaptability of course material & for more efficiency accommodating new trends & innovations in an industry. § Many stakeholders have already developed modules, curriculum and interim certifications around green materials, products and technologies.
Conclusions 4 In order to meet rapidly changing market demands, Registered Apprenticeship stakeholders are taking advantage of newer, more flexible training approaches. § RA programs deliver just-in-time training to meet the adult learning styles. § include interim certifications, distance learning, electronic media and various hybrid/combination training. § Enhanced delivery of curriculum allows for adaptability of course material & for more efficiency accommodating new trends & innovations in an industry. § Many stakeholders have already developed modules, curriculum and interim certifications around green materials, products and technologies.
 Conclusions 5 Pre-apprenticeship programs and clearly defined occupational career ladders can provide pathways out of poverty and further engage traditionally hard-to-reach populations in the green-collar economy. § RA programs require applicants to have foundation-level skills § Pre-apprenticeship programs that directly connect to apprenticeship positions can provide gateways for hard- to-serve populations § multi-disciplinary pre-apprenticeship approach around green could have several benefits. § exposing a worker to a variety of industries prior to long-term commitment; § addressing skills & materials that are specific to green; and § further ensuring that pathways out of poverty are sustainable.
Conclusions 5 Pre-apprenticeship programs and clearly defined occupational career ladders can provide pathways out of poverty and further engage traditionally hard-to-reach populations in the green-collar economy. § RA programs require applicants to have foundation-level skills § Pre-apprenticeship programs that directly connect to apprenticeship positions can provide gateways for hard- to-serve populations § multi-disciplinary pre-apprenticeship approach around green could have several benefits. § exposing a worker to a variety of industries prior to long-term commitment; § addressing skills & materials that are specific to green; and § further ensuring that pathways out of poverty are sustainable.
 Conclusions 6 New and innovative partnership models have evolved in order to embrace the changing needs of our global and green economy. § RA programs are finding shared goals & interests with advocacy groups, Federal agencies, universities, community-based organizations & others § Partnerships are developed around: § multi-disciplinary training partnerships, industry standards, innovation, economic and workforce development, business incubation & policy. § Openness to exploring new collaborations that aid in rebuilding America’s middle class. § Some have begun to look at ways to partner with organizations around re-employment activities.
Conclusions 6 New and innovative partnership models have evolved in order to embrace the changing needs of our global and green economy. § RA programs are finding shared goals & interests with advocacy groups, Federal agencies, universities, community-based organizations & others § Partnerships are developed around: § multi-disciplinary training partnerships, industry standards, innovation, economic and workforce development, business incubation & policy. § Openness to exploring new collaborations that aid in rebuilding America’s middle class. § Some have begun to look at ways to partner with organizations around re-employment activities.
 Conclusions 7 Great opportunities exist for widespread, systemic partnerships between Registered Apprenticeship and the education and public workforce system. § Partnering is a natural and inherent element to Registered Apprenticeship. § Opportunity exists for further collaboration around preapprenticeship between workforce system and RA § Bridging the gap could address the critical need to provide pathways out of poverty and career ladders that lead to middle class wages § Partnership efforts that support transitioning dislocated workers and veterans could be expanded.
Conclusions 7 Great opportunities exist for widespread, systemic partnerships between Registered Apprenticeship and the education and public workforce system. § Partnering is a natural and inherent element to Registered Apprenticeship. § Opportunity exists for further collaboration around preapprenticeship between workforce system and RA § Bridging the gap could address the critical need to provide pathways out of poverty and career ladders that lead to middle class wages § Partnership efforts that support transitioning dislocated workers and veterans could be expanded.
 QUESTIONS/COMMENTS? www. doleta. gov/OA Ladd. John@dol. gov
QUESTIONS/COMMENTS? www. doleta. gov/OA Ladd. John@dol. gov


