1fed1e444878c858c2ddd30e4e1454e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 The Great War, 1914 -1919
The Great War, 1914 -1919
 Main Points Long term & Short term Origins n Debates over War n Main Events n Casualties of War n Nativism and xenophobia n Legacies n
Main Points Long term & Short term Origins n Debates over War n Main Events n Casualties of War n Nativism and xenophobia n Legacies n
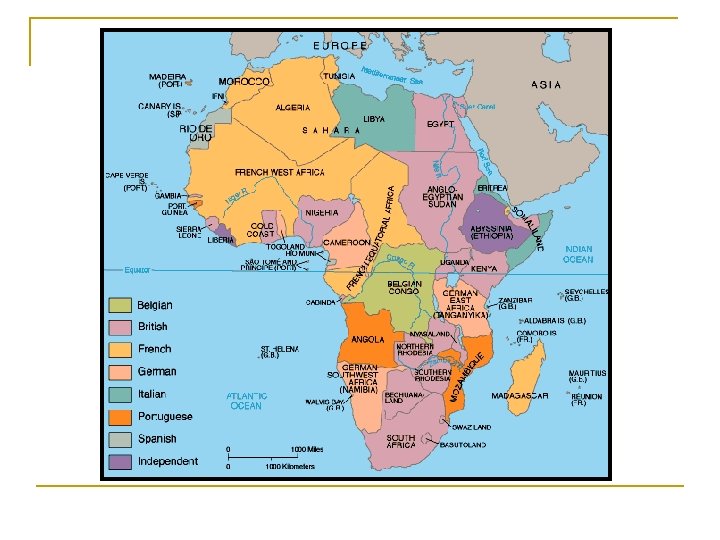
 Long term Origins n n n n European & Russian expansion Geopolitical competition Scramble for Africa, control over Middle East Age of empire and Imperialism International “entangling alliances” American economic interests Alliance with Britain
Long term Origins n n n n European & Russian expansion Geopolitical competition Scramble for Africa, control over Middle East Age of empire and Imperialism International “entangling alliances” American economic interests Alliance with Britain
 Short term Causes n n Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria. Hungary (Central powers) killed by Serbian nationalist (Allied powers), which wanted independence from A-H attacked Serbia, and France defended it British had to back French, and Germans backed A-H, and Russia joined BR & FR Europe fell into war due to empire and alliances
Short term Causes n n Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria. Hungary (Central powers) killed by Serbian nationalist (Allied powers), which wanted independence from A-H attacked Serbia, and France defended it British had to back French, and Germans backed A-H, and Russia joined BR & FR Europe fell into war due to empire and alliances
 War Begins… n Triple Entente q q Britain, France, Russia Serbia Triple Alliance (Central Powers) q q Germany, A-H Ottoman Empire (Turkey)
War Begins… n Triple Entente q q Britain, France, Russia Serbia Triple Alliance (Central Powers) q q Germany, A-H Ottoman Empire (Turkey)
 Modern Warfare and Death n n n Industrial Warfare Poison, tanks, machine guns, bombs Trench Warfare 10 million battle dead 20 million hunger and disease
Modern Warfare and Death n n n Industrial Warfare Poison, tanks, machine guns, bombs Trench Warfare 10 million battle dead 20 million hunger and disease

 End of U. S. Neutrality n n Anti-German & Hungarian views Pro-British views, cultural and racial ties American loans Industrial & economic ties with FR & BR
End of U. S. Neutrality n n Anti-German & Hungarian views Pro-British views, cultural and racial ties American loans Industrial & economic ties with FR & BR

 Entering the War n n n U. S. assisted Britain German U-Boats Lusitania 1915 Zimmerman Telegram to Mexico, 1917 April 2, 1917 War Declaration “Make the World Safe for Democracy”
Entering the War n n n U. S. assisted Britain German U-Boats Lusitania 1915 Zimmerman Telegram to Mexico, 1917 April 2, 1917 War Declaration “Make the World Safe for Democracy”
 War is Good for Business n William J. Bryan, Secretary of State 1914: q n n n “opened the doors of all the weaker countries to an invasion of American capital & enterprise” J. P. Morgan: millions of $ in loans to Britain U. S. Steel made $348 million in profits selling to Britain $100 s of millions in U. S. supplies, weapons, ships, tanks, etc to allies
War is Good for Business n William J. Bryan, Secretary of State 1914: q n n n “opened the doors of all the weaker countries to an invasion of American capital & enterprise” J. P. Morgan: millions of $ in loans to Britain U. S. Steel made $348 million in profits selling to Britain $100 s of millions in U. S. supplies, weapons, ships, tanks, etc to allies
 Peace Responses n n W. E. B. Du. Bois: the war is for “the gold and diamonds of South Africa, the cocoa of Angola and Nigeria, the rubber and ivory of the Congo, the palm oil of the West Coast…” Eugene Debs: “They tell us that we live in a great free republic, that our institutions are democratic; that we are a free and self-governing people. That is too much, even for a joke…Wars throughout history have been waged for conquest and plunder. The master class has always declared the wars; the poor subjects have always fought the battles.
Peace Responses n n W. E. B. Du. Bois: the war is for “the gold and diamonds of South Africa, the cocoa of Angola and Nigeria, the rubber and ivory of the Congo, the palm oil of the West Coast…” Eugene Debs: “They tell us that we live in a great free republic, that our institutions are democratic; that we are a free and self-governing people. That is too much, even for a joke…Wars throughout history have been waged for conquest and plunder. The master class has always declared the wars; the poor subjects have always fought the battles.
 Continued… n n n Many Americans did not see the connection between their security or national interests and what they believed were the imperial rivalries, treaties, and agreements between European powers Only 75, 000 Americans volunteered within the first three months after declaration Sen. Thomas Hardwick (GA): “There was undoubtedly general and widespread opposition on the part of most people…to the enactment of the draft law. Numerous and largely attended mass meetings held in every part of the U. S. protested against it. ”
Continued… n n n Many Americans did not see the connection between their security or national interests and what they believed were the imperial rivalries, treaties, and agreements between European powers Only 75, 000 Americans volunteered within the first three months after declaration Sen. Thomas Hardwick (GA): “There was undoubtedly general and widespread opposition on the part of most people…to the enactment of the draft law. Numerous and largely attended mass meetings held in every part of the U. S. protested against it. ”
 Women and Protest n n n Jeannette Rankin, the first woman elected to the U. S. House: “I want to stand by my country, but I cannot vote for war. I vote NO. ” Kate Richards O’Hare, “the women of the U. S. were nothing more or less than brood sows, to raise children to get into the army and made into fertilizer. ” Women’s Peace Party
Women and Protest n n n Jeannette Rankin, the first woman elected to the U. S. House: “I want to stand by my country, but I cannot vote for war. I vote NO. ” Kate Richards O’Hare, “the women of the U. S. were nothing more or less than brood sows, to raise children to get into the army and made into fertilizer. ” Women’s Peace Party
 War Mobilization n n Federal control over economy Selective Service Act: draft War Industries Board controlled military production and ensured control over profits, distribution, and manufacture War Labor Board broke strikes and enforced labor support for the war
War Mobilization n n Federal control over economy Selective Service Act: draft War Industries Board controlled military production and ensured control over profits, distribution, and manufacture War Labor Board broke strikes and enforced labor support for the war
 Manufacturing Support n n n Tell American that their actions would make the world safe for democracy Self-Determination Committee on Public Information q q Propaganda Racist images Patriotism Fear and force
Manufacturing Support n n n Tell American that their actions would make the world safe for democracy Self-Determination Committee on Public Information q q Propaganda Racist images Patriotism Fear and force
 Continued… n n Nationalism/patriotism to unite poor people, people of color, to believe that their security depends on following capitalists and politicians who tell them to sacrifice for a “way of life. ” Convince them that their problem are NOT associated with internal class warfare or racism, but international dangers Convince them that they are good and righteous people, and that their actions will spread democracy and bring liberty to others. Fighting is American: fight if you want to be accepted and have a part of the American dream
Continued… n n Nationalism/patriotism to unite poor people, people of color, to believe that their security depends on following capitalists and politicians who tell them to sacrifice for a “way of life. ” Convince them that their problem are NOT associated with internal class warfare or racism, but international dangers Convince them that they are good and righteous people, and that their actions will spread democracy and bring liberty to others. Fighting is American: fight if you want to be accepted and have a part of the American dream
 (En)forcing “Patriotism” n n n George Creel (CPI) Banned German language Sauerkraut = Liberty cabbage Frankfurters = hot dogs Immigration restrictions against Germans US War in Iraq q French Fries = Freedom Fries
(En)forcing “Patriotism” n n n George Creel (CPI) Banned German language Sauerkraut = Liberty cabbage Frankfurters = hot dogs Immigration restrictions against Germans US War in Iraq q French Fries = Freedom Fries
 Be A MAN and go to war…REAL MEN fight…
Be A MAN and go to war…REAL MEN fight…
 Support the war, or are you Un-American?
Support the war, or are you Un-American?
 The first casualty of war… n Espionage Act of 1917 q n Sedition Act of 1918 q n Criminalized public gathering and organizing against the war Criminalized written material criticizing the war Schenk v. U. S. (1919) rejected free speech
The first casualty of war… n Espionage Act of 1917 q n Sedition Act of 1918 q n Criminalized public gathering and organizing against the war Criminalized written material criticizing the war Schenk v. U. S. (1919) rejected free speech
 America during the War n n Charles Schenk was arrested for distributing anti-war leaflets, sentenced to prison under the Espionage Act Nearly 1000 arrested, w/o trial, under the Act New York Times , 1917, “More than 100 men enrolled yesterday in the American Vigilante Patrol at the offices of the American Defense Society…the Patrol was formed to put an end to seditious street oratory. ” El Paso, TX: Closed down the border, fears of revolutionaries, anti-Mexican hysteria, Tom Lea
America during the War n n Charles Schenk was arrested for distributing anti-war leaflets, sentenced to prison under the Espionage Act Nearly 1000 arrested, w/o trial, under the Act New York Times , 1917, “More than 100 men enrolled yesterday in the American Vigilante Patrol at the offices of the American Defense Society…the Patrol was formed to put an end to seditious street oratory. ” El Paso, TX: Closed down the border, fears of revolutionaries, anti-Mexican hysteria, Tom Lea
 Continued… n n n Nearly 350, 000 evaded the draft 65, 000 claimed conscientious objector status Soldiers based in Ft. Riley, KS, refusing to fight were tortured University professors fired for vocal opposition 50, 000 American soldiers dead by end of war in November 1918
Continued… n n n Nearly 350, 000 evaded the draft 65, 000 claimed conscientious objector status Soldiers based in Ft. Riley, KS, refusing to fight were tortured University professors fired for vocal opposition 50, 000 American soldiers dead by end of war in November 1918
 The War Ends… n Bolshevik Revolution in Russia, Oct. 1917 q q n Wilson’s Fourteen Points, Jan. 1918 q q n n Vladmir Lenin and others pulled Russia out of war Treaty gave eastern Russia to Germany (Poland, etc) National self-determination Open Diplomacy Free commerce and travel League of Nations Germany accepted defeat, 1919 Treaty of Versailles, June 1919
The War Ends… n Bolshevik Revolution in Russia, Oct. 1917 q q n Wilson’s Fourteen Points, Jan. 1918 q q n n Vladmir Lenin and others pulled Russia out of war Treaty gave eastern Russia to Germany (Poland, etc) National self-determination Open Diplomacy Free commerce and travel League of Nations Germany accepted defeat, 1919 Treaty of Versailles, June 1919
 After the War n n Competing Visions q Socialism & Capitalism Creating nations q n Finland, Lithuania, Poland, Hungary, Czech, Yugoslavia, Romania “The German Question” q q Punishment $, Guilt, Army
After the War n n Competing Visions q Socialism & Capitalism Creating nations q n Finland, Lithuania, Poland, Hungary, Czech, Yugoslavia, Romania “The German Question” q q Punishment $, Guilt, Army
 The Red Scare In the US n n n Bolsheviks=socialists & communists Free speech vs. national security Anti-communist hysteria Labor strikes and protest Conservatives said reformers were socialists and wanted revolution Government stopped political dissent
The Red Scare In the US n n n Bolsheviks=socialists & communists Free speech vs. national security Anti-communist hysteria Labor strikes and protest Conservatives said reformers were socialists and wanted revolution Government stopped political dissent
 Propaganda
Propaganda
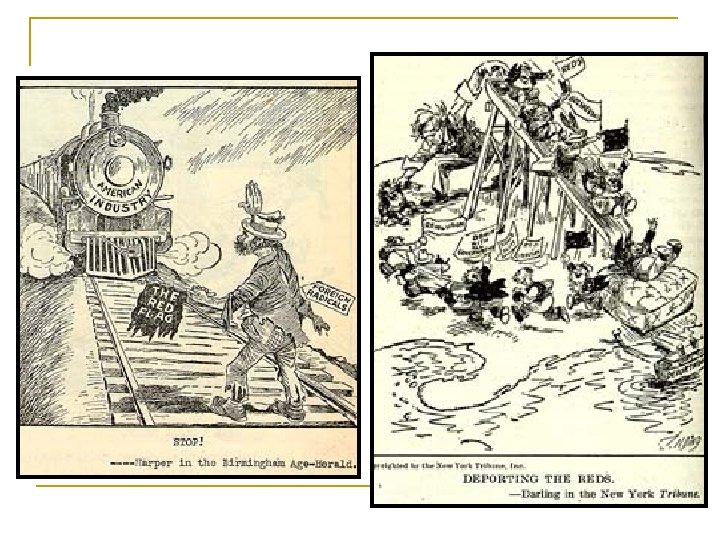
 Anti-Immigrant Propaganda n n n n Anti-radical sentiments merged with Antiimmigrant beliefs Distortion of political views Manufacture a threat, increase fear, focus that fear on a particular group Blame problems on target group Associate patriotism and Americanism with opposition to that group Oppression masked in national security Invasion, end of civilization
Anti-Immigrant Propaganda n n n n Anti-radical sentiments merged with Antiimmigrant beliefs Distortion of political views Manufacture a threat, increase fear, focus that fear on a particular group Blame problems on target group Associate patriotism and Americanism with opposition to that group Oppression masked in national security Invasion, end of civilization
 The Brown Scare…
The Brown Scare…

 Attacks on Civil Rights n n n U. S. AG Mitchell Palmer arrested thousands w/o charges or trial 1919 -22: Hoover deported around 5, 000 foreigners Invaded homes Albert Burlson, U. S. Mail Opened “seditious” mail & refused to mail suspect periodicals
Attacks on Civil Rights n n n U. S. AG Mitchell Palmer arrested thousands w/o charges or trial 1919 -22: Hoover deported around 5, 000 foreigners Invaded homes Albert Burlson, U. S. Mail Opened “seditious” mail & refused to mail suspect periodicals
 n n n The Washington Post "There is no time to waste on hairsplitting over infringement of liberty. " New York Times referred to the injuries to a group of suspects as "souvenirs of the new attitude of aggressiveness which had been assumed by the Federal agents against Reds and suspected Reds. ” Twelve prominent lawyers that included future Supreme Court Justice Felix Frankfurter published "A Report on the Illegal Practices of The United States Department of Justice, " citing violations of the Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, and Eighth Amendments to the Constitution and accusing Palmer of "illegal acts" and "wanton violence. " Palmer then issued a series of warnings that a revolutionary plot to overthrow the government was to be launched on May 1, 1920. Nothing happened.
n n n The Washington Post "There is no time to waste on hairsplitting over infringement of liberty. " New York Times referred to the injuries to a group of suspects as "souvenirs of the new attitude of aggressiveness which had been assumed by the Federal agents against Reds and suspected Reds. ” Twelve prominent lawyers that included future Supreme Court Justice Felix Frankfurter published "A Report on the Illegal Practices of The United States Department of Justice, " citing violations of the Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, and Eighth Amendments to the Constitution and accusing Palmer of "illegal acts" and "wanton violence. " Palmer then issued a series of warnings that a revolutionary plot to overthrow the government was to be launched on May 1, 1920. Nothing happened.
 Conclusions n n n n American economic interests and global politics War profit and support for Britain Manufacturing support for War in a Democracy Xenophobia and the Red Scare Origins of modern anti-immigrant hysteria Many people questioned the alleged “progress” that had been made during the “modern era”
Conclusions n n n n American economic interests and global politics War profit and support for Britain Manufacturing support for War in a Democracy Xenophobia and the Red Scare Origins of modern anti-immigrant hysteria Many people questioned the alleged “progress” that had been made during the “modern era”


