6dfdd9b0b440884a2b93b43b42b91af3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 The Great Depression
The Great Depression
![Main Causes: 1) Overproduction 2) Tariffs 3) Debt 4) Stock Market Crash [Black Tuesday] Main Causes: 1) Overproduction 2) Tariffs 3) Debt 4) Stock Market Crash [Black Tuesday]](https://present5.com/presentation/6dfdd9b0b440884a2b93b43b42b91af3/image-2.jpg) Main Causes: 1) Overproduction 2) Tariffs 3) Debt 4) Stock Market Crash [Black Tuesday]
Main Causes: 1) Overproduction 2) Tariffs 3) Debt 4) Stock Market Crash [Black Tuesday]
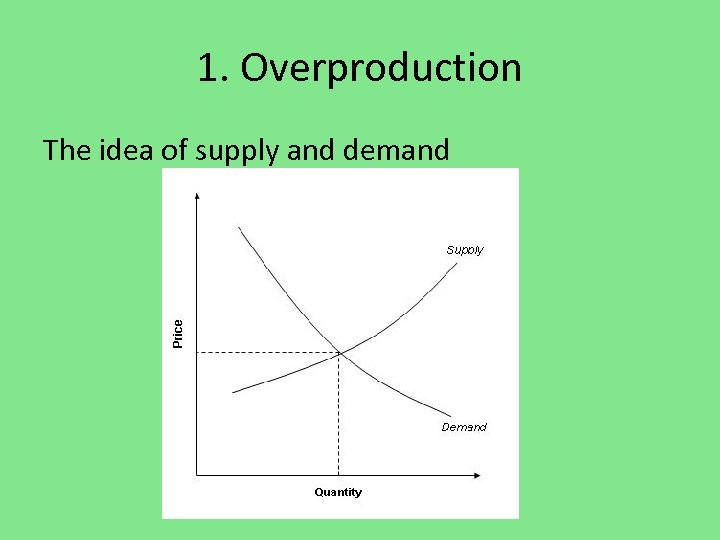 1. Overproduction The idea of supply and demand
1. Overproduction The idea of supply and demand
 Both industry and agriculture produced more goods than consumers could buy. Result? Surplus of goods. Prices decline dramatically. Causes less production and job loss Closure of many factories and farms Cycle repeats itself over and over again.
Both industry and agriculture produced more goods than consumers could buy. Result? Surplus of goods. Prices decline dramatically. Causes less production and job loss Closure of many factories and farms Cycle repeats itself over and over again.
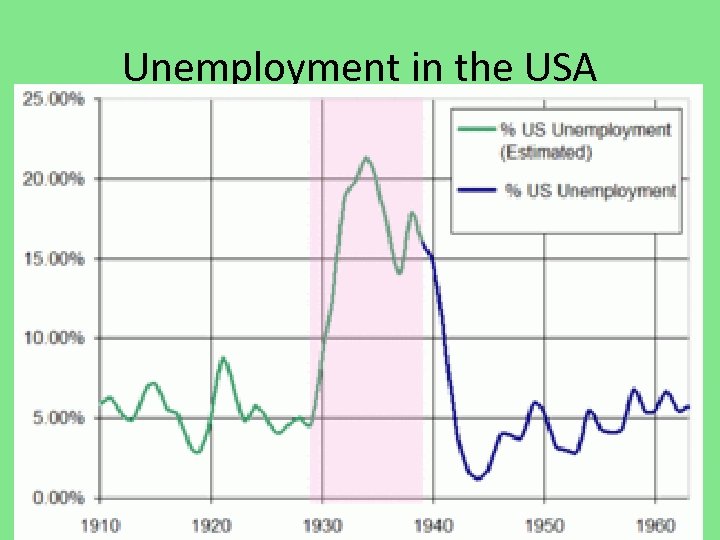 Unemployment in the USA
Unemployment in the USA
 2. Tariffs America maintained high tariffs throughout the 1920 s. This slowed down foreign trade. Countries responded with their own tariffs. Because of increasingly connected economies, if trade declined, all countries were affected.
2. Tariffs America maintained high tariffs throughout the 1920 s. This slowed down foreign trade. Countries responded with their own tariffs. Because of increasingly connected economies, if trade declined, all countries were affected.
 3. Debt USA lent money after WWI to help countries out of debt Those countries relied on selling their products to the USA to get money to re-pay the loans. Because of protectionism in the USA trade reduces, which causes economies of those re-building countries to decline. Because economies are connected, if problems affect one country, they will affect many.
3. Debt USA lent money after WWI to help countries out of debt Those countries relied on selling their products to the USA to get money to re-pay the loans. Because of protectionism in the USA trade reduces, which causes economies of those re-building countries to decline. Because economies are connected, if problems affect one country, they will affect many.
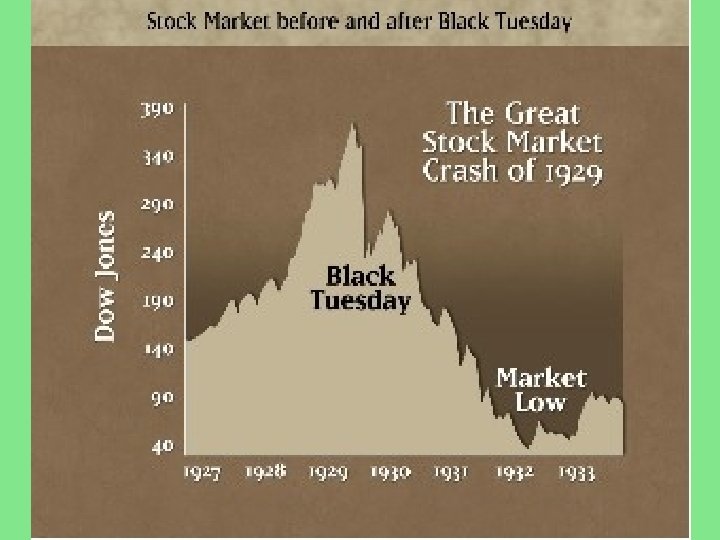
 4. Stock Market Crash • October 1929: Black Tuesday • When the stock market rises sharply it is an easy way to make money. • People had borrowed money and spent their savings in the stock market (speculation)
4. Stock Market Crash • October 1929: Black Tuesday • When the stock market rises sharply it is an easy way to make money. • People had borrowed money and spent their savings in the stock market (speculation)
 Companies were becoming less profitable (because of overproduction) A sell off happened while prices were high Soon as more shares were on the market, prices dropped very suddenly This caused panic and everyone sold as fast as possible and soon the stocks were worthless.
Companies were becoming less profitable (because of overproduction) A sell off happened while prices were high Soon as more shares were on the market, prices dropped very suddenly This caused panic and everyone sold as fast as possible and soon the stocks were worthless.
 Effects of the Great Depression Unemployment rates highest in the twentieth century. – Example: In 1933 it was 25%; (the highest since 1940 has been 9. 7%) Bank Failures because of such a significant loss of money (individuals and/or Stock Market) Some Europeans countries rejected democracy and instead turned to other forms of government (Dictatorships…)
Effects of the Great Depression Unemployment rates highest in the twentieth century. – Example: In 1933 it was 25%; (the highest since 1940 has been 9. 7%) Bank Failures because of such a significant loss of money (individuals and/or Stock Market) Some Europeans countries rejected democracy and instead turned to other forms of government (Dictatorships…)
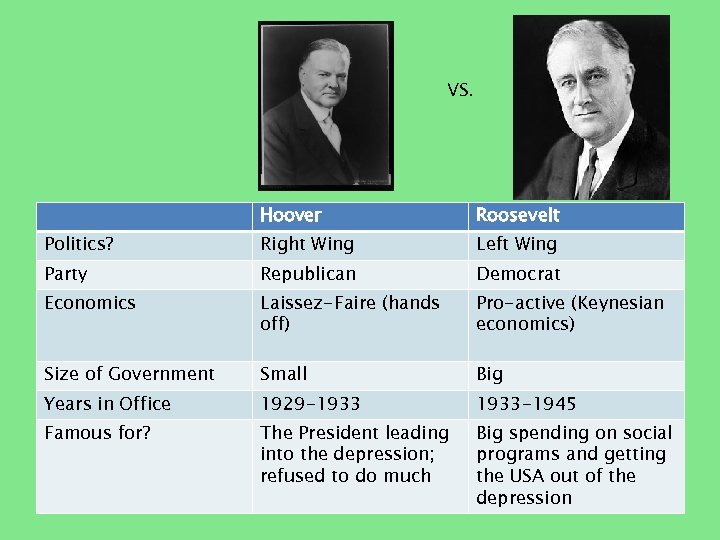 VS. Hoover Roosevelt Politics? Right Wing Left Wing Party Republican Democrat Economics Laissez-Faire (hands off) Pro-active (Keynesian economics) Size of Government Small Big Years in Office 1929 -1933 -1945 Famous for? The President leading into the depression; refused to do much Big spending on social programs and getting the USA out of the depression
VS. Hoover Roosevelt Politics? Right Wing Left Wing Party Republican Democrat Economics Laissez-Faire (hands off) Pro-active (Keynesian economics) Size of Government Small Big Years in Office 1929 -1933 -1945 Famous for? The President leading into the depression; refused to do much Big spending on social programs and getting the USA out of the depression
 Roosevelt to Power… • "So first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself. "
Roosevelt to Power… • "So first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself. "
 FDR – First 100 Days Government spending to create jobs Promised Americans ‘A New Deal’ First actions: Immediate Problems – Emergency Banking Act – Shut down banks and only reopened stable ones. – Federal Emergency Relief Act - $500 million of aid to unemployed and hungry Americans. – Economy Act – Cut wages of government workers – Abolished prohibition “Fireside Chats” – Talks on radio to the Americans explaining his actions.
FDR – First 100 Days Government spending to create jobs Promised Americans ‘A New Deal’ First actions: Immediate Problems – Emergency Banking Act – Shut down banks and only reopened stable ones. – Federal Emergency Relief Act - $500 million of aid to unemployed and hungry Americans. – Economy Act – Cut wages of government workers – Abolished prohibition “Fireside Chats” – Talks on radio to the Americans explaining his actions.
 First New Deal Goal: Create work for the unemployed Belief in “deficit financing” Many “Alphabet Agencies” created
First New Deal Goal: Create work for the unemployed Belief in “deficit financing” Many “Alphabet Agencies” created
 Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC): – Youth in agricultural areas – Jobs: Tree planting, reforesting, etc. – 2. 5 million young men participated in the organization
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC): – Youth in agricultural areas – Jobs: Tree planting, reforesting, etc. – 2. 5 million young men participated in the organization
 Works Progress Administration (WPA) Built schools, dams, bridges, roads.
Works Progress Administration (WPA) Built schools, dams, bridges, roads.
 Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) • Gave farmers money to produce less food. • Income of farmers increased as prices went up • Why would this plan be controversial?
Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) • Gave farmers money to produce less food. • Income of farmers increased as prices went up • Why would this plan be controversial?
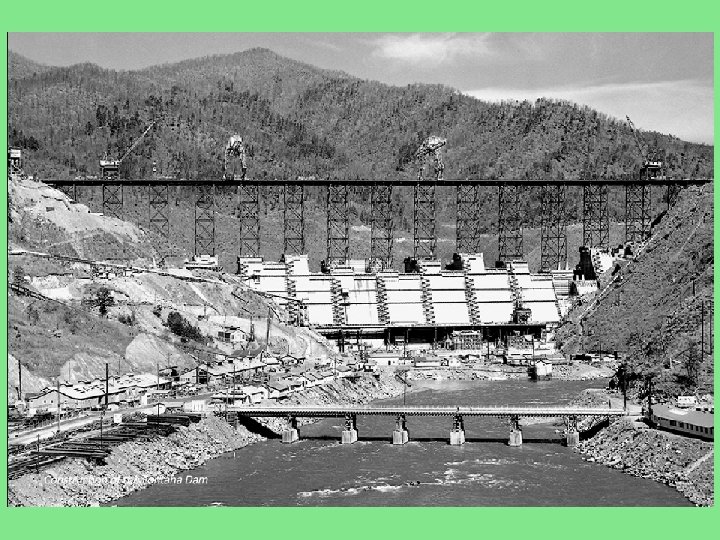 Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) • Dam construction • Reasons? – Stop flooding – Generate electricity – Modern the poor farms of the area – Create work!
Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) • Dam construction • Reasons? – Stop flooding – Generate electricity – Modern the poor farms of the area – Create work!
 Second New Deal 1935 – Continued to help the poor and unemployed Social Security Act – Pensions for old people Wagner Act – Gave legal rights to trade unions to negotiate for wages National Housing Act – Reduced rents, built homes Did Roosevelt fix the Great Depression? No. He stabilized things, but WWII ended it.
Second New Deal 1935 – Continued to help the poor and unemployed Social Security Act – Pensions for old people Wagner Act – Gave legal rights to trade unions to negotiate for wages National Housing Act – Reduced rents, built homes Did Roosevelt fix the Great Depression? No. He stabilized things, but WWII ended it.
 Opponents of FDR Wealthy businessmen and owners. What didn’t they like? Big government spending and size of government. They wanted freedom to operate without regulations. What was FDR accused of? Being a socialist/communist
Opponents of FDR Wealthy businessmen and owners. What didn’t they like? Big government spending and size of government. They wanted freedom to operate without regulations. What was FDR accused of? Being a socialist/communist
 How did it affect other countries? Any country that produced raw materials was hurt by the decrease in global trade. In many countries political instability led to dictatorships (Italy, Germany, parts of South America) Others developed more socialized programs and a welfare state (Canada, US, Scandinavian countries)
How did it affect other countries? Any country that produced raw materials was hurt by the decrease in global trade. In many countries political instability led to dictatorships (Italy, Germany, parts of South America) Others developed more socialized programs and a welfare state (Canada, US, Scandinavian countries)
 Worldwide stats International trade plunged 2/3 Cities dependent on industry were hit hard Crop prices dropped 60% Most countries underwent government run relief reforms Most countries moved politically to the right or left in search of a better structure (FDR, Hitler, Stalin, etc. )
Worldwide stats International trade plunged 2/3 Cities dependent on industry were hit hard Crop prices dropped 60% Most countries underwent government run relief reforms Most countries moved politically to the right or left in search of a better structure (FDR, Hitler, Stalin, etc. )
 Europe Economic decline had been coming for awhile, but the stock market crash was the final catalyst as many wealthy Europeans had invested in it Several countries turned to leaders that promised better times and a change, even if their ideas were radical Suffered low wages, unemployment, growing dependence on military production (Germany) Forced colonies to buy only European products ½ German population lived in poverty
Europe Economic decline had been coming for awhile, but the stock market crash was the final catalyst as many wealthy Europeans had invested in it Several countries turned to leaders that promised better times and a change, even if their ideas were radical Suffered low wages, unemployment, growing dependence on military production (Germany) Forced colonies to buy only European products ½ German population lived in poverty
 Latin America Had a strong economic tie to the U. S. According to a League of Nations report at the time, Chile, Peru, and Bolivia were the hardest hit countries in the world Fascist governments rose in popularity as a result, particularly in Brazil Industrialization began finally in Brazil only Many colonial areas depended on the sale of their agricultural exports to afford industrial imports, but couldn’t any longer Results: greater state planning in economy, new political ideas imitating dictatorships in Europe
Latin America Had a strong economic tie to the U. S. According to a League of Nations report at the time, Chile, Peru, and Bolivia were the hardest hit countries in the world Fascist governments rose in popularity as a result, particularly in Brazil Industrialization began finally in Brazil only Many colonial areas depended on the sale of their agricultural exports to afford industrial imports, but couldn’t any longer Results: greater state planning in economy, new political ideas imitating dictatorships in Europe
 Asia Depended on rubber and tin trade with the West (automobile industry) Companies in Asia had much less profit because of lack of sales Japanese exports dropped 50% Bad harvests and unemployment Results: suspicion of West increased, Japan tried to seek more Asian markets
Asia Depended on rubber and tin trade with the West (automobile industry) Companies in Asia had much less profit because of lack of sales Japanese exports dropped 50% Bad harvests and unemployment Results: suspicion of West increased, Japan tried to seek more Asian markets


