2cf52a2d3c6eb8280bec323977c56d79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The Great Depression: Causes and Effects 6. 3: Explain the causes and consequences of the Great Depression, including the disparities in income and wealth distribution; the collapse of the farm economy and the effects of the Dust Bowl; limited governmental regulation; taxes, investment; and stock market speculation; policies of the federal government and the Federal Reserve System; and the effects of the Great Depression on the people.
The Great Depression: Causes and Effects 6. 3: Explain the causes and consequences of the Great Depression, including the disparities in income and wealth distribution; the collapse of the farm economy and the effects of the Dust Bowl; limited governmental regulation; taxes, investment; and stock market speculation; policies of the federal government and the Federal Reserve System; and the effects of the Great Depression on the people.
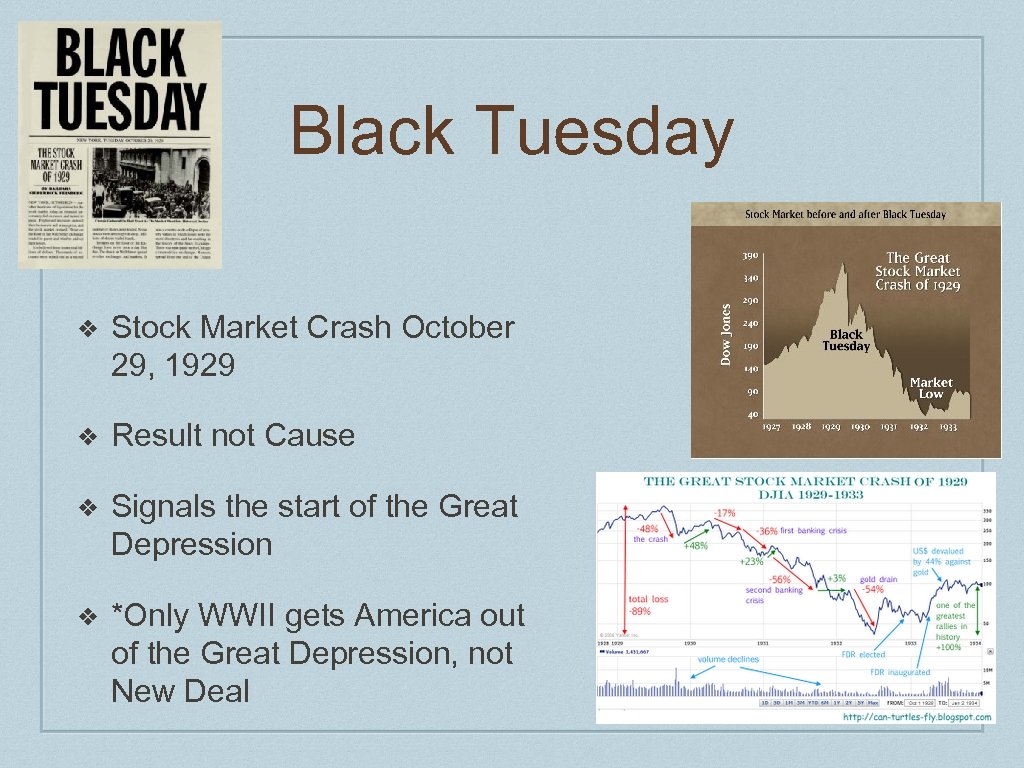 Black Tuesday ❖ Stock Market Crash October 29, 1929 ❖ Result not Cause ❖ Signals the start of the Great Depression ❖ *Only WWII gets America out of the Great Depression, not New Deal
Black Tuesday ❖ Stock Market Crash October 29, 1929 ❖ Result not Cause ❖ Signals the start of the Great Depression ❖ *Only WWII gets America out of the Great Depression, not New Deal
 Causes of the Great Depression ❖ 1. Disparity of Incomes ❖ 2. Buying on Credit ❖ 3. Farm Economy Collapse ❖ 4. laissez-faire policy and the end of Progressivism ❖ 5. Taxes ❖ 6. Stock Market Speculation ❖ 7. Federal Reserve
Causes of the Great Depression ❖ 1. Disparity of Incomes ❖ 2. Buying on Credit ❖ 3. Farm Economy Collapse ❖ 4. laissez-faire policy and the end of Progressivism ❖ 5. Taxes ❖ 6. Stock Market Speculation ❖ 7. Federal Reserve
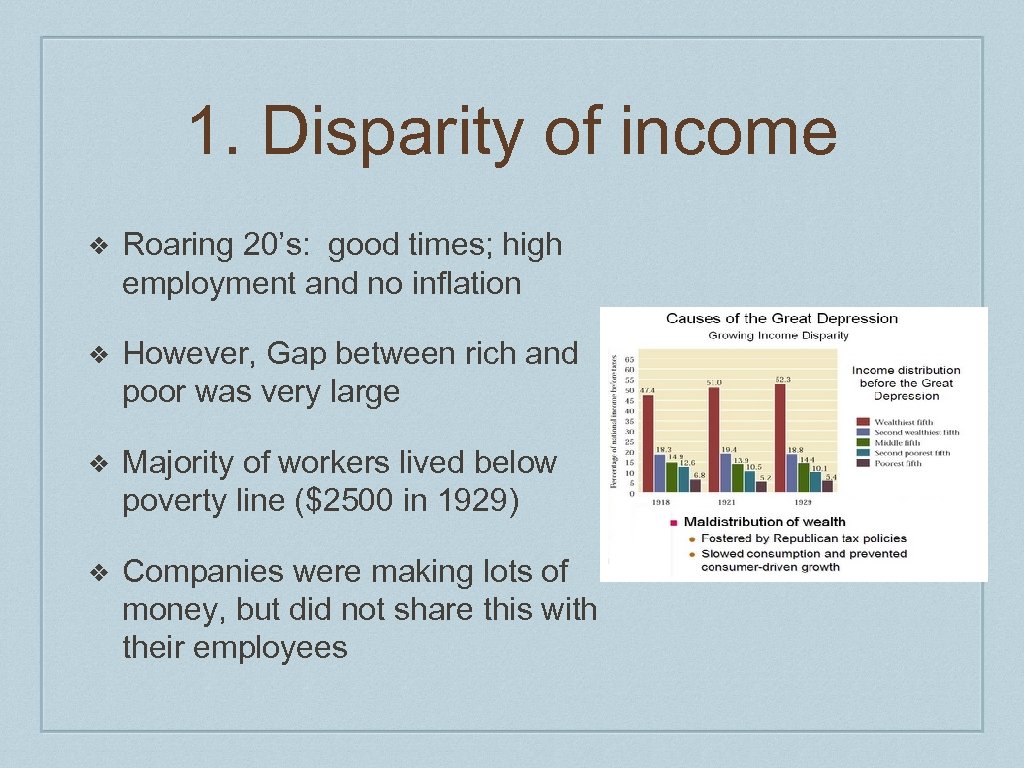 1. Disparity of income ❖ Roaring 20’s: good times; high employment and no inflation ❖ However, Gap between rich and poor was very large ❖ Majority of workers lived below poverty line ($2500 in 1929) ❖ Companies were making lots of money, but did not share this with their employees
1. Disparity of income ❖ Roaring 20’s: good times; high employment and no inflation ❖ However, Gap between rich and poor was very large ❖ Majority of workers lived below poverty line ($2500 in 1929) ❖ Companies were making lots of money, but did not share this with their employees
 2. Buying on Credit ❖ At some point creditors will stop giving people credit ❖ Consumers cannot buy anymore ❖ Drop in consumer spending = lay -offs ❖ Layoffs = less spending, which then = more lay-offs
2. Buying on Credit ❖ At some point creditors will stop giving people credit ❖ Consumers cannot buy anymore ❖ Drop in consumer spending = lay -offs ❖ Layoffs = less spending, which then = more lay-offs
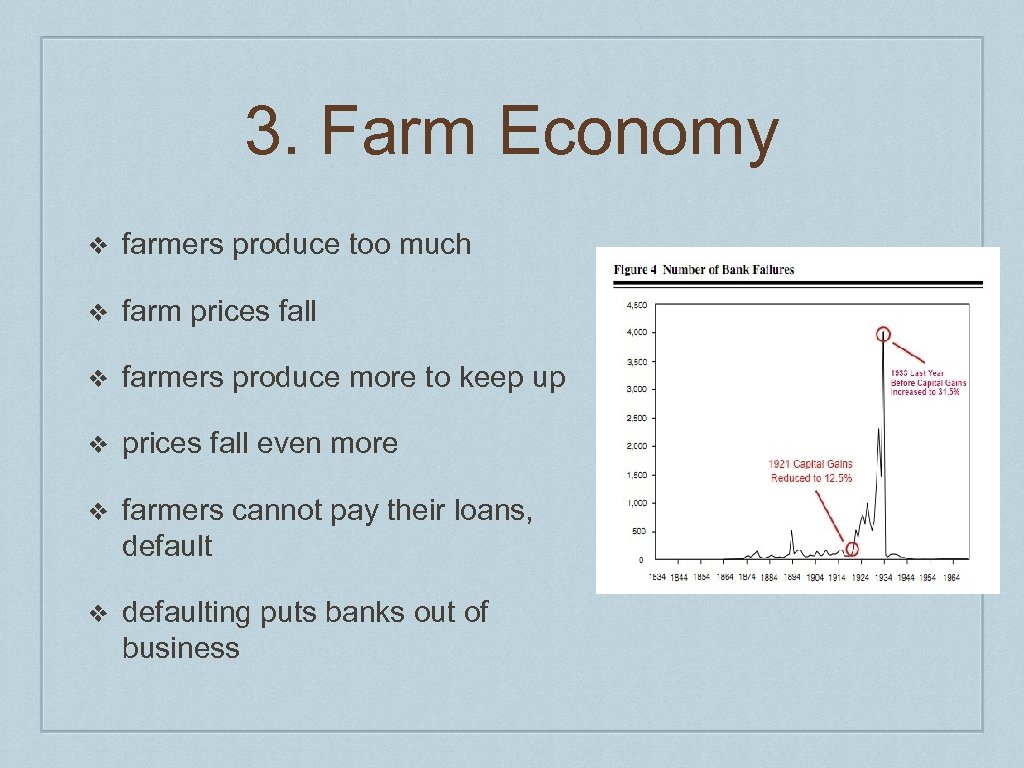 3. Farm Economy ❖ farmers produce too much ❖ farm prices fall ❖ farmers produce more to keep up ❖ prices fall even more ❖ farmers cannot pay their loans, default ❖ defaulting puts banks out of business
3. Farm Economy ❖ farmers produce too much ❖ farm prices fall ❖ farmers produce more to keep up ❖ prices fall even more ❖ farmers cannot pay their loans, default ❖ defaulting puts banks out of business
 4. laissez-faire policy and the End of Progressivism ❖ Big Business allowed to do whatever they want - laissez-faire ❖ ❖ ❖ tariff raised on foreign goods to help protect US industry child labor and minimum wage overturned Is this an end of Progressivism? Who does the tariff hurt?
4. laissez-faire policy and the End of Progressivism ❖ Big Business allowed to do whatever they want - laissez-faire ❖ ❖ ❖ tariff raised on foreign goods to help protect US industry child labor and minimum wage overturned Is this an end of Progressivism? Who does the tariff hurt?
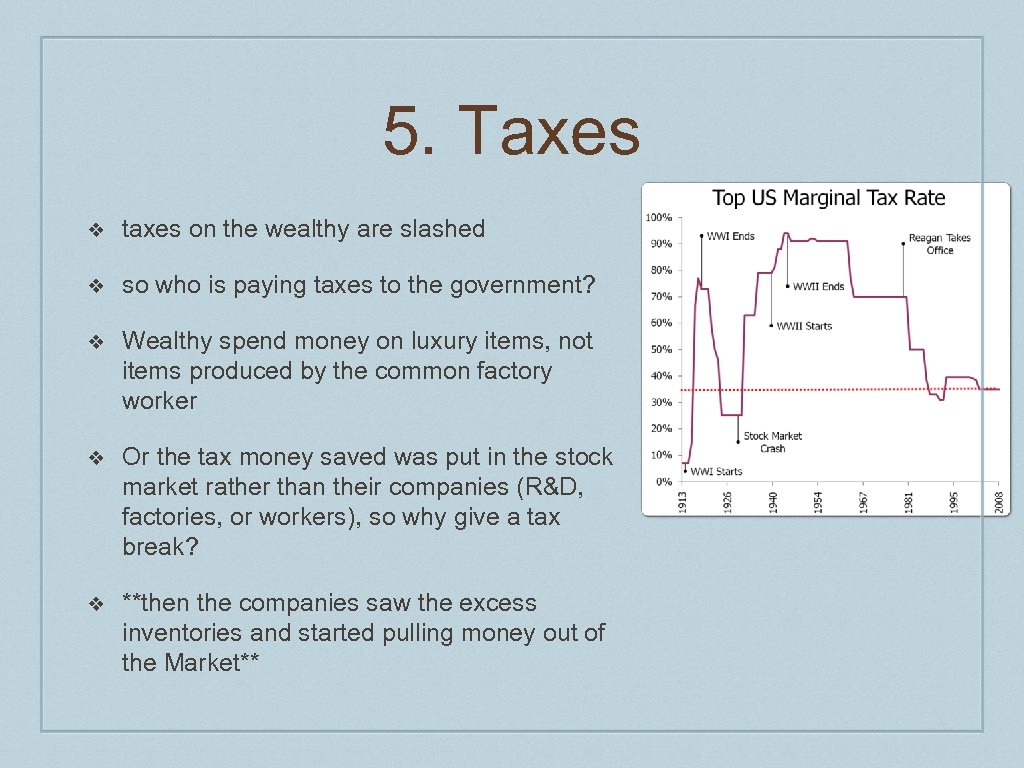 5. Taxes ❖ taxes on the wealthy are slashed ❖ so who is paying taxes to the government? ❖ Wealthy spend money on luxury items, not items produced by the common factory worker ❖ Or the tax money saved was put in the stock market rather than their companies (R&D, factories, or workers), so why give a tax break? ❖ **then the companies saw the excess inventories and started pulling money out of the Market**
5. Taxes ❖ taxes on the wealthy are slashed ❖ so who is paying taxes to the government? ❖ Wealthy spend money on luxury items, not items produced by the common factory worker ❖ Or the tax money saved was put in the stock market rather than their companies (R&D, factories, or workers), so why give a tax break? ❖ **then the companies saw the excess inventories and started pulling money out of the Market**
 6. Stock Market Speculation ❖ “get rich quick” ❖ buy on margin - investor allowed to borrow the money to buy stocks now ❖ People had to sell, which drove the price down even further ❖ Black Tuesday - some wealthy tried to prop up the Stock Market, but to no avail
6. Stock Market Speculation ❖ “get rich quick” ❖ buy on margin - investor allowed to borrow the money to buy stocks now ❖ People had to sell, which drove the price down even further ❖ Black Tuesday - some wealthy tried to prop up the Stock Market, but to no avail
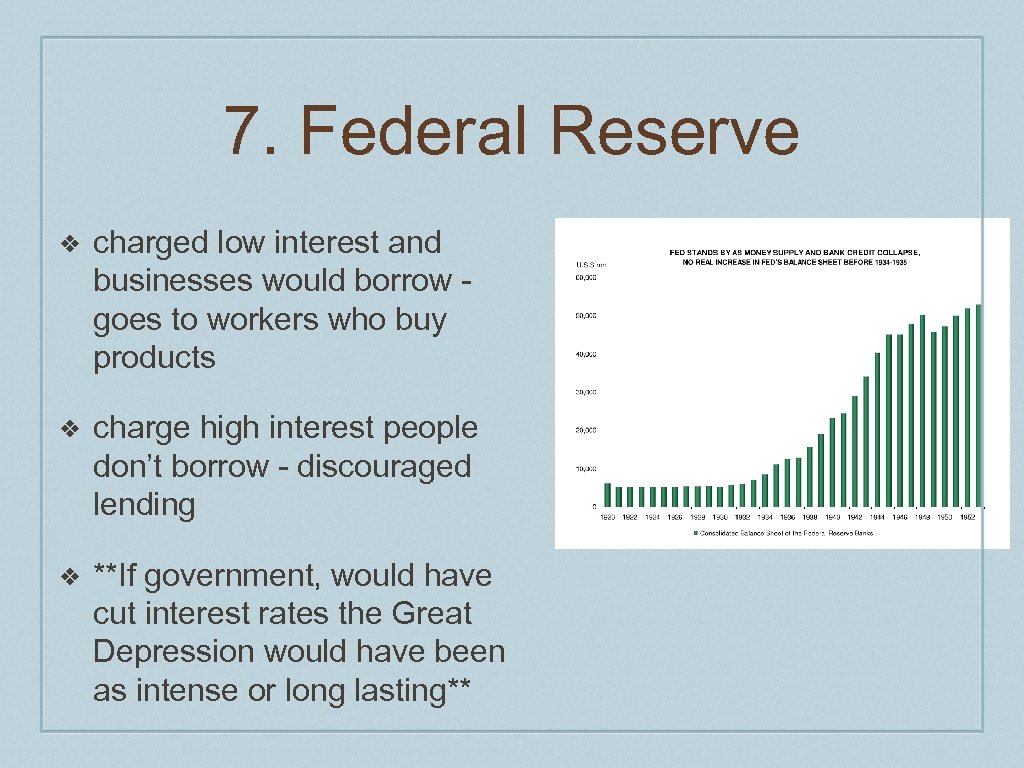 7. Federal Reserve ❖ charged low interest and businesses would borrow goes to workers who buy products ❖ charge high interest people don’t borrow - discouraged lending ❖ **If government, would have cut interest rates the Great Depression would have been as intense or long lasting**
7. Federal Reserve ❖ charged low interest and businesses would borrow goes to workers who buy products ❖ charge high interest people don’t borrow - discouraged lending ❖ **If government, would have cut interest rates the Great Depression would have been as intense or long lasting**
 Government to the aid ❖ 1. because of influence of Big Business the Government issues a tariff - which made goods high ❖ other Countries can’t sell their goods in America and therefore cannot buy American ❖ Also impose their own tariff on American goods ❖ 2. President Hoover urges companies to voluntarily maintain wages and hours - companies do the opposite ❖ 3. Advocates “rugged individualism”
Government to the aid ❖ 1. because of influence of Big Business the Government issues a tariff - which made goods high ❖ other Countries can’t sell their goods in America and therefore cannot buy American ❖ Also impose their own tariff on American goods ❖ 2. President Hoover urges companies to voluntarily maintain wages and hours - companies do the opposite ❖ 3. Advocates “rugged individualism”
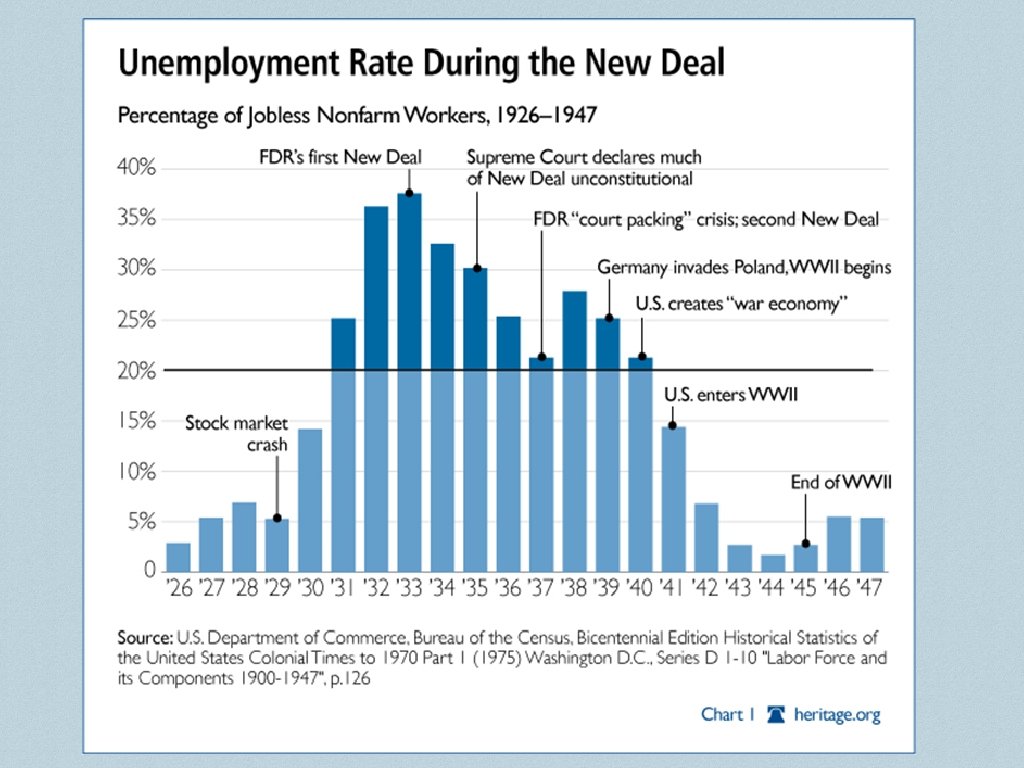
 Impact on the People ❖ 25% Unemployment ❖ People lost their homes - took to the streets ❖ People that still had jobs had their hours and wages cut ❖ People only bought necessities - further led to lay-offs ❖ “Runs” on banks ❖ people fear losing money and take all their money out of banks
Impact on the People ❖ 25% Unemployment ❖ People lost their homes - took to the streets ❖ People that still had jobs had their hours and wages cut ❖ People only bought necessities - further led to lay-offs ❖ “Runs” on banks ❖ people fear losing money and take all their money out of banks
 Images ❖ Soup Kitchens ❖ Bread Lines ❖ Hoovervilles ❖ Dust Bowls ❖ Okies ❖ Bonus Army
Images ❖ Soup Kitchens ❖ Bread Lines ❖ Hoovervilles ❖ Dust Bowls ❖ Okies ❖ Bonus Army
 People ❖ people undernourished ❖ schools closed ❖ Abandonment increases – Men leave families for work or shame ❖ Suicide rate increases sharply ❖ birthrate fell – ❖ Men no longer the head of the household ❖ People for help looked to the government
People ❖ people undernourished ❖ schools closed ❖ Abandonment increases – Men leave families for work or shame ❖ Suicide rate increases sharply ❖ birthrate fell – ❖ Men no longer the head of the household ❖ People for help looked to the government
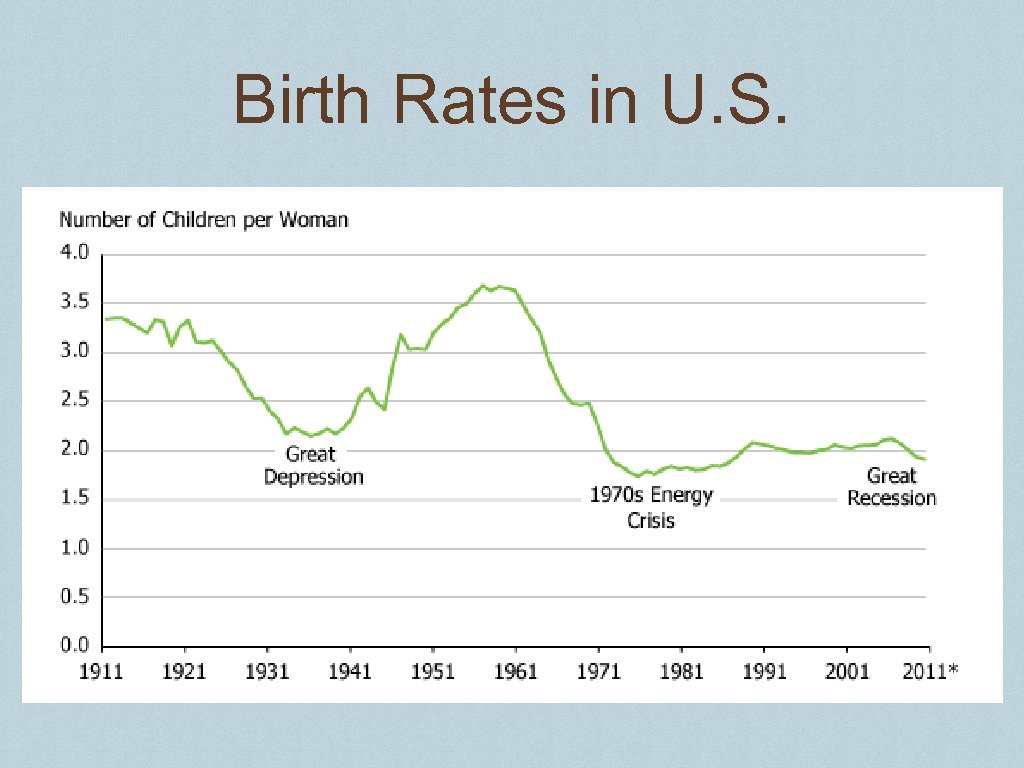 Birth Rates in U. S.
Birth Rates in U. S.


