1f9759c3d38c8d2274481a9dfc8eca75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

The Global Positioning System A Worldwide Information Utility February 2001

Overview • • • Policy Applications & Markets Augmentations Sustainment & Modernization International Cooperation

Policy

GPS is a Dual-Use System • Cold War spinoff – Developed in 1970 s-1980 s to support Allied forces – Prominent in Gulf War, Kosovo – After KAL-007, civilians gained free access to Standard Positioning Service • Commercial use now dwarfs military use • GPS policy is managed at a national level by the Interagency GPS Executive Board (IGEB)

Interagency GPS Executive Board Defense Transportation State Commerce Agriculture Interior Joint Chiefs of Staff NASA Justice

United States GPS Policy • Presidential Decision Directive signed in 1996, endorsed by Congress in 1998 • GPS Standard Positioning Service to remain free of direct user fees • U. S. to promote acceptance and use of GPS as a world standard • Selective Availability -- ended May 2000 • IGEB to manage GPS as a national asset

United States GPS Policy, cont’d. • Encourage private sector investment in/use of GPS technologies and services • Promote safety and efficiency in transportation and other fields • Promote international cooperation in using GPS for peaceful purposes • Advance scientific and technical capabilities • Strengthen and maintain national security

Applications & Markets

Worldwide Sales of GPS Goods & Services Will Reach $16 B by 2003

Worldwide GPS Revenues By Market Segment

Car Navigation • • • On-board navigation Fleet management Roadside assistance Stolen vehicle recovery Enhanced services Mass market dominated by Japan • Dataquest: Unit sales of chips for car navigation to reach 11. 3 M in 2001 • $4. 7 B sales by 2003

Consumer/Recreational • Portable receivers for fishermen, hunters, hikers, cyclists, etc. • Recreational facilities -golf courses, ski resorts • Integration of GPS into cellular phones – E-911 requirement • $3. 8 B market by 2003

Surveying/Mapping/GIS • Sub-centimeter accuracy • 100%-300% savings in time, cost, & labor – Control survey point: $10, 000 in 1986; $250 in 1997 • • Rural electrification Telecom tower placement Pipelines Oil, gas, and mineral exploration • Flood plain mapping • $3. 12 B market by 2003

Tracking/Machine Control • Package/cargo delivery • Fleet and asset management • Theft recovery • Public safety and services • Farming, mining, and construction equipment • DGPS/RTK required for many applications • $3 B market by 2003

Public Services • City planning • Transportation infrastructure – Road Billing Network (ROBIN) – Snowplows • Emergency response – – – Law enforcement Fire fighting Search and rescue Paramedics Disaster relief

Aviation • GPS approved for en-route navigation • More efficient flight routing leads to fuel savings • Better tracking of aircraft enhances safety • Closer spacing of planes increases airspace capacity • $710 M market by 2003

Maritime Navigation • GPS-based vessel tracking and traffic management maximizes effectiveness of waterways • Improved safety increases maritime commerce • Maritime DGPS service for enhanced accuracy and safety available in 34 countries • $210 M market by 2003

Original Equipment Manufacturers • • • Chipsets Electronic boards Antennas, components Standalone receivers $690 M market by 2003

Military • GPS is a recognized NATO standard • GPS is required on all U. S. military systems • Precision munitions widely used during Gulf War, Kosovo

Timing • GPS offers an inexpensive alternative to costly, high maintenance timing equipment • Telecommunications network synchronization & management – Phones, pagers, wireless systems – LANs, WANs, Internet • Financial transactions • Electrical power grid management & fault location • Digital signatures for e-commerce • Some estimate the timing market at $40 -100 M

Scientific Research • Monitoring geological change – Glaciers, tectonic plates, earthquakes, volcanoes • Wildlife behavior • Atmospheric modeling – Water vapor content • Oceanic studies – Tidal patterns – Surface mapping • Time transfer

Environmental Management • Forestry • Wetlands management • Natural resource management • Fisheries boundary enforcement • Endangered species and habitat preservation • Hazardous material cleanup – Oil spills, toxic waste

Emerging GPS Applications • Entrepreneurs and scientific researchers invent new applications almost every day • Higher precision is necessary for many cutting-edge applications – – – Differential GPS (DGPS) Relative DGPS Carrier phase positioning Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Post-processing
Precision Agriculture • Maximize use of resources – Optimized plowing of crop rows – Tailored applications of seeds, fertilizer, water, pesticides – Improved management of land, machinery, personnel, time – Greater crop yields – Net benefit: $5 -14 per acre • Minimize environmental impacts – Localized identification and treatment of distressed crops reduces chemical use – Precise leveling of fields prevents fluid runoff

Open Pit Mining • Enhanced management of assets, equipment • Progress tracked in real-time, remotely • Improved machine control saves time, lowers maintenance and fuel consumption, prevents accidents • Rapid surveying for drilling blast holes • Smaller, more empowered workforce

Space Applications • Improved orbit and attitude control for spacecraft, International Space Station • Space Station return vehicle • Advance Land Observing Satellite uses GPS to calibrate high resolution radar maps • Satellite formation flying • Space launch range safety

Construction • Machinery, asset, and personnel management • Rapid surveys for laying foundation piles, etc. • Accident prevention • Remote control of machinery possible – Japanese volcano dam GPS/RTK technology was used in the construction of the Øresund Bridge between Denmark and Sweden

Europe is a Major Player in the GPS Market • Rapid growth projected, especially in car navigation sector • Many European firms already provide GPS goods and services – Scandanavian GNSS Industry Council • European governments are investing in GPS augmentation and reference systems – Maritime DGPS – EGNOS – EUREF Permanent Network

The Market is Wide Open • • Civil signals are freely available, right now Openly published GPS specifications allow anyone to build receivers (no licensing fees) • Hardware is becoming a commodity • Huge potential exists in value-added services – – – Software development Embedded applications Localized GIS databases Internet integration Wireless markets
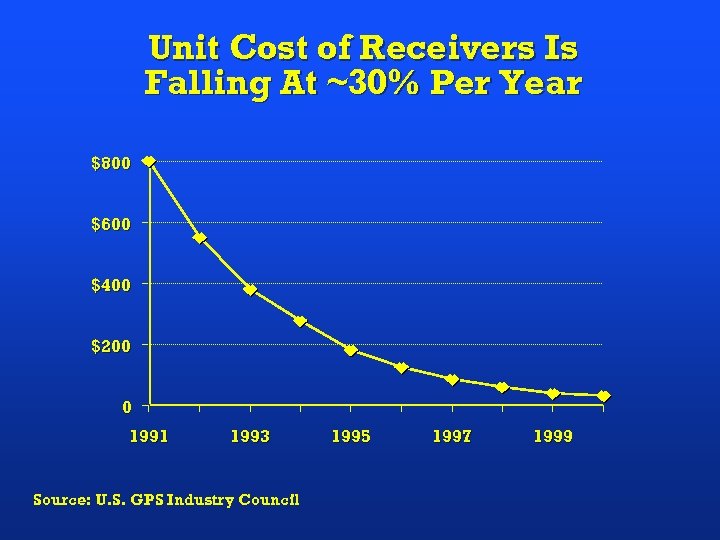
Unit Cost of Receivers Is Falling At ~30% Per Year $800 $600 $400 $200 0 1991 1993 Source: U. S. GPS Industry Council 1995 1997 1999

Projected Relative Market Share
Augmentations

Sustainment & Modernization

Constellation Status • 28 operational satellites – 6 Block IIR satellites on orbit – 23 Block II/IIA operational satellites; • Last launch: January 30, 2001 • Next tentative launch date: August 2001 • Continuously assessing constellation health to determine launch need
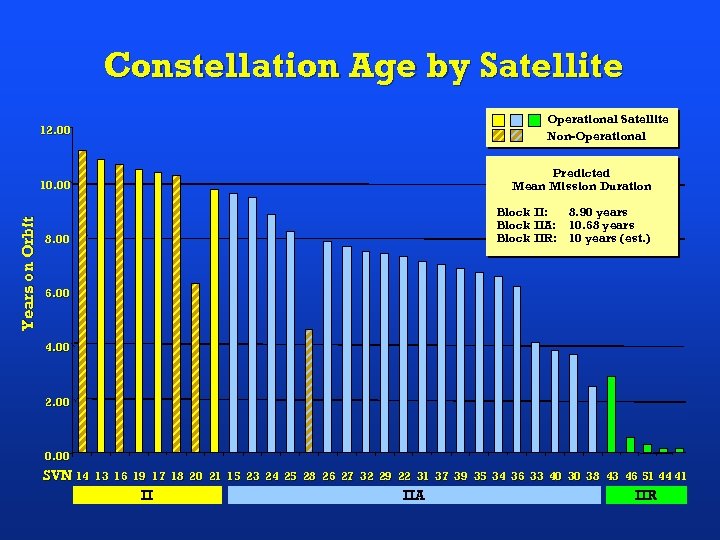
Constellation Age by Satellite 12. 00 Operational Satellite Non-Operational Years on Orbit 10. 00 Predicted Mean Mission Duration 8. 00 Block II: 8. 90 years Block IIA: 10. 68 years Block IIR: 10 years (est. ) 6. 00 4. 00 2. 00 0. 00 SVN 14 13 16 19 17 18 20 21 15 23 24 25 28 26 27 32 29 22 31 37 39 35 34 36 33 40 30 38 43 46 51 44 41 II IIA IIR

GPS Modernization Program • Need for upgrades recognized as GPS entered Full Operational Capability – – – Anti-jam military needs Better, more reliable civilian service Recognized growing importance of GPS to both sectors • 1996 Presidential policy and 1998/1999 Vice Presidential announcements committed U. S. to modernization and improvement path – New signals, better service ( no direct user fees) – Selective Availability (SA) discontinued – Over $1 billion added to future U. S. GPS investment

The End of Selective Availability May 2, 2000
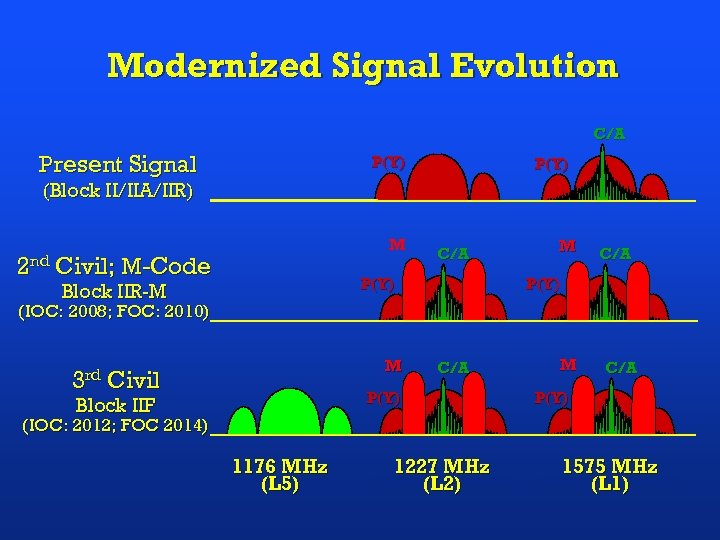
Modernized Signal Evolution C/A Present Signal P(Y) (Block II/IIA/IIR) 2 nd M Civil; M-Code C/A P(Y) Block IIR-M M C/A P(Y) (IOC: 2008; FOC: 2010) 3 rd M Civil C/A P(Y) Block IIF M C/A P(Y) (IOC: 2012; FOC 2014) 1176 MHz (L 5) 1227 MHz (L 2) 1575 MHz (L 1)
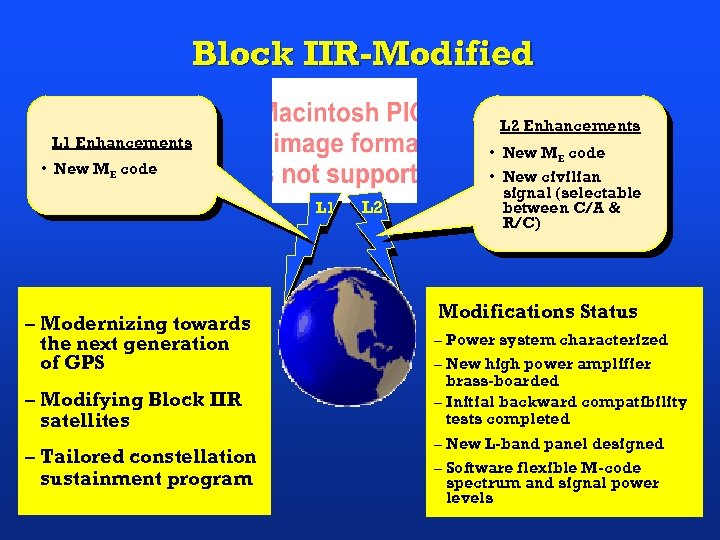
Block IIR-Modified L 2 Enhancements L 1 Enhancements • New ME code L 1 – Modernizing towards the next generation of GPS – Modifying Block IIR satellites – Tailored constellation sustainment program L 2 • New ME code • New civilian signal (selectable between C/A & R/C) Modifications Status – Power system characterized – New high power amplifier brass-boarded – Initial backward compatibility tests completed – New L-band panel designed – Software flexible M-code spectrum and signal power levels
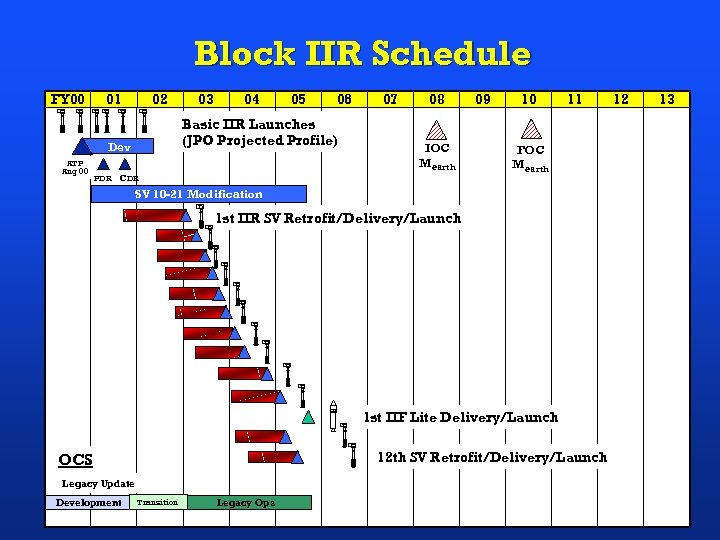
Block IIR Schedule FY 00 USAF 01 USAF 02 USAF PDR 04 05 06 Basic IIR Launches (JPO Projected Profile) Dev ATP Aug 00 03 07 08 09 10 11 USAF IOC Mearth CDR FOC Mearth SV 10 -21 Modification USAF 1 st IIR SV Retrofit/Delivery/Launch USAF USAF USAF 1 st IIF Lite Delivery/Launch USAF 12 th SV Retrofit/Delivery/Launch OCS Legacy Update Development Transition Legacy Ops 12 13
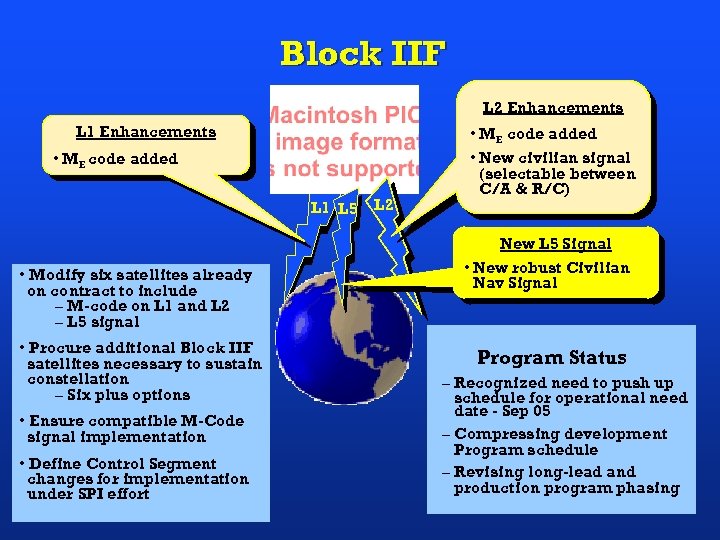
Block IIF L 2 Enhancements L 1 Enhancements • ME code added L 1 L 5 • Modify six satellites already on contract to include – M-code on L 1 and L 2 – L 5 signal • Procure additional Block IIF satellites necessary to sustain constellation – Six plus options • Ensure compatible M-Code signal implementation • Define Control Segment changes for implementation under SPI effort L 2 • ME code added • New civilian signal (selectable between C/A & R/C) New L 5 Signal • New robust Civilian Nav Signal Program Status – Recognized need to push up schedule for operational need date - Sep 05 – Compressing development Program schedule – Revising long-lead and production program phasing
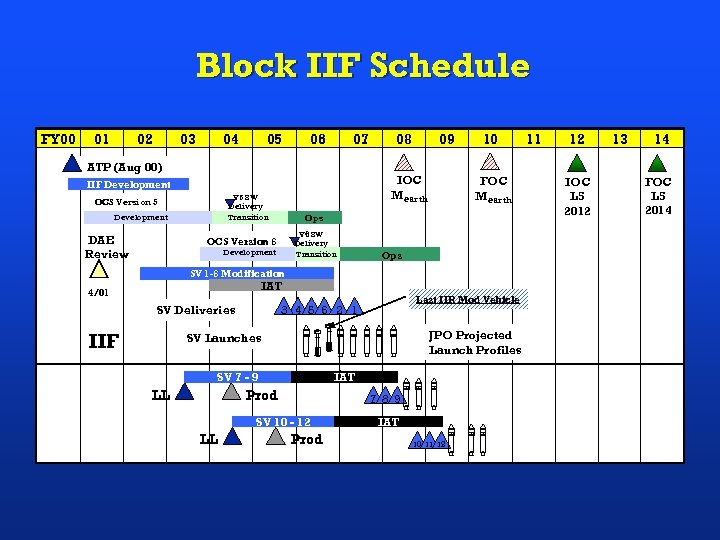
Block IIF Schedule FY 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 ATP (Aug 00) V 5 SW Delivery Transition Development DAE Review 09 IOC Mearth IIF Development OCS Version 5 08 10 FOC Mearth Ops V 6 SW Delivery Transition OCS Version 6 Development Ops SV 1 -6 Modification IAT 4/01 SV Deliveries Last IIR Mod Vehicle 3 4 5 6 2 1 USAF IIF SV Launches SV 7 - 9 LL IAT Prod 7 8 9 SV 10 - 12 LL JPO Projected Launch Profiles USAF Prod IAT 10 11 12 IOC L 5 2012 13 14 FOC L 5 2014
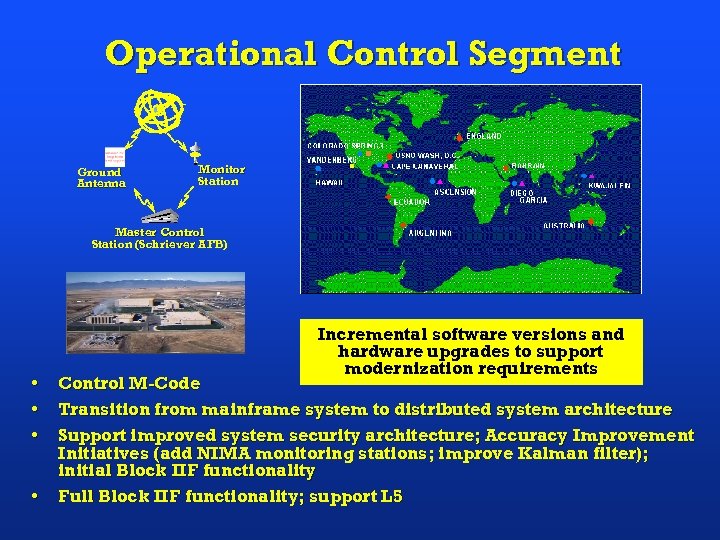
Operational Control Segment Ground Antenna Monitor Station Master Control Station (Schriever AFB) • • Incremental software versions and hardware upgrades to support modernization requirements Control M-Code Transition from mainframe system to distributed system architecture Support improved system security architecture; Accuracy Improvement Initiatives (add NIMA monitoring stations; improve Kalman filter); initial Block IIF functionality Full Block IIF functionality; support L 5
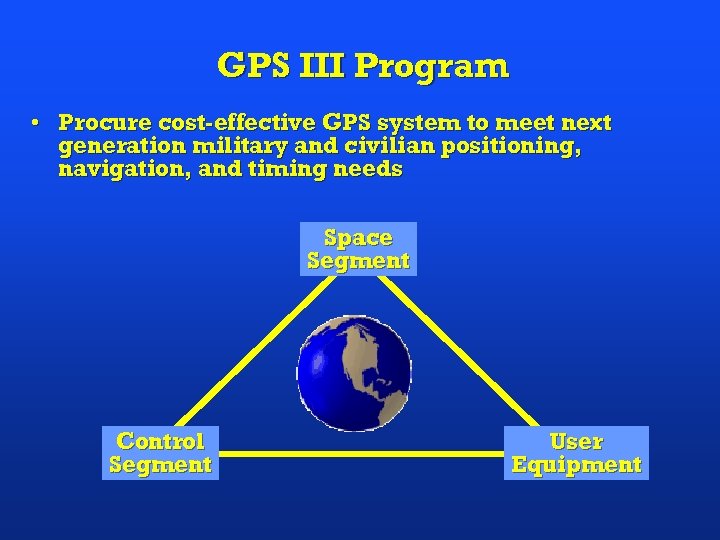
GPS III Program • Procure cost-effective GPS system to meet next generation military and civilian positioning, navigation, and timing needs Space Segment Control Segment User Equipment

The GPS III Opportunity • Assess system-wide architectural alternatives to: – – Achieve current and long term GPS performance goals Reduce long term total ownership costs Capitalize on emerging technologies Provide flexibility and robustness to meet evolving requirements – Discover military and economic value of pushing to higher performance capabilities • Scope – Military and Civil – Possible augmentation opportunities Ensure best GPS system for the next 30 years

GPS III Concept Exploration Phase • 12 -month study between government and industry – – – Two contractors (Lockheed Martin, Boeing) Firm Fixed Price contracts $16 M per contractor Awarded 8 Nov 00 Spectrum Astro (participating on company funds) • Near term goals – – – Build technical requirements set Illustrate requirements through architectural solutions Complete Life Cycle Cost (LCC) and cost benefit assessment

GPS III Study Phase Products • Technical Requirements for Development Milestones • Architectures that support Technical Requirements • Life Cycle Cost estimates for each Architecture • Risk Analysis • Draft System Effectiveness and Performance Metrics • Initial Test and Evaluation Master Plan (TEMP) • Acquisition Strategy • Entry/Exit criteria for Development Milestones • Technology Roadmap

GPS III Architecture Study Status • Successful initial meetings (Nov 00) and Laboratory Days (Jan 01) • Near real-time communication in place (web-based) • Lockheed Martin – Three teams (System Engineering, Architecture, Life Cycle Cost) – Solid initial architectural assessments • Boeing – Five teams (System Concept, User, Ground, Space, Secondary Payloads, Operations and Support) – Focusing on mission and requirements analysis • Spectrum Astro – Signed Memorandum of Agreement (Dec 00) – Program plan, schedule, and team structure near complete – Providing innovative inputs to GPS III, working to improve position for follow-on phases
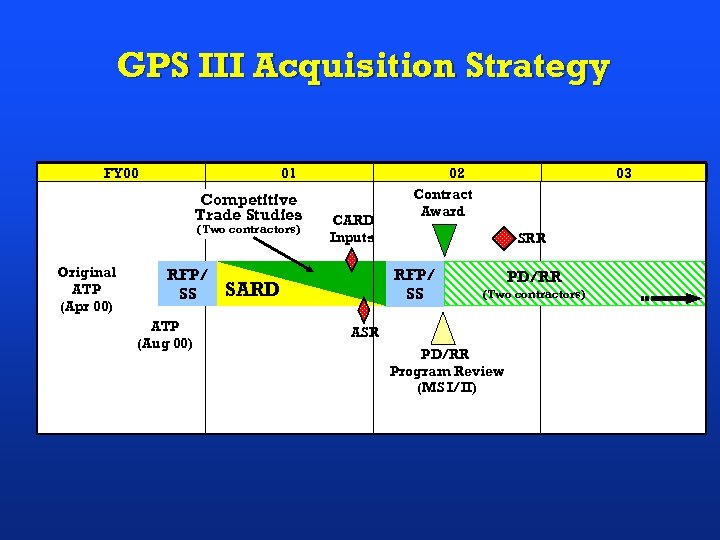
GPS III Acquisition Strategy FY 00 01 Competitive Trade Studies (Two contractors) Original ATP (Apr 00) RFP/ SS ATP (Aug 00) 02 CARD Inputs Contract Award SRR RFP/ SS SARD 03 PD/RR (Two contractors) ASR PD/RR Program Review (MS I/II)
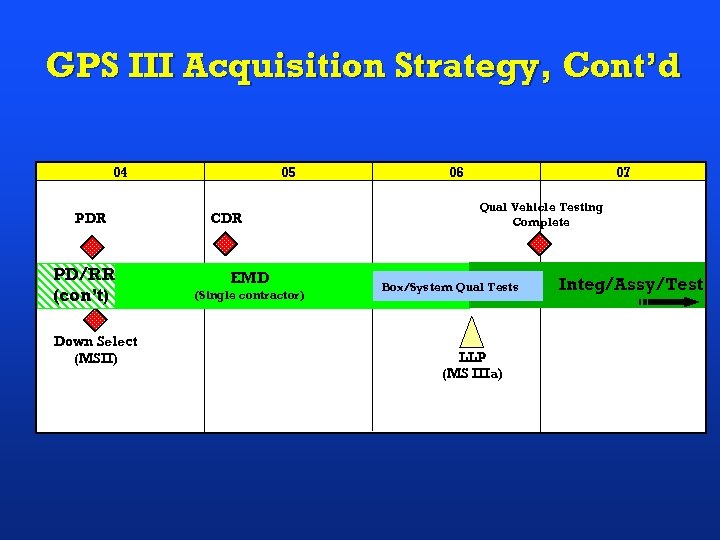
GPS III Acquisition Strategy, Cont’d 04 PDR PD/RR (con’t) Down Select (MSII) 05 CDR EMD (Single contractor) 06 07 Qual Vehicle Testing Complete Box/System Qual Tests LLP (MS IIIa) Integ/Assy/Test

International Cooperation

International Cooperation • Promote acceptance and peaceful use of GPS and its augmentations – International offering of GPS to ICAO and IMO • Service free of direct user charges • Non-proprietary signal standards for civil services – GPS Augmentations -- Worldwide interoperability • Space-based systems (WAAS, MSAS, EGNOS) for aviation • Land-based DGPS technology for maritime and terrestrial uses: already adopted by 35 countries • Global, non-proprietary standards

Principles for Cooperation • No direct user fees for civil and public safety services • Ensure open market driven competition for user equipment and applications • Open signal structure for all civil services to promote equal access for applications development and value added services • Protection of the current radionavigation spectrum from disruption and interference • Use of GPS time, geodesy, and signal structure standards • Seamless, global interoperability of future systems with GPS • Recognition of national and international security issues and protecting against misuse

U. S. - Japan Cooperation • • • September 1998: Joint Statement signed GPS based augmentations Largest commercial market share for products and services • September 1999: Working Groups met in Washington, D. C. – – – Policy Transportation Commercial & Scientific • February 2001: Plenary Meeting, Tokyo

U. S. - Russia Consultation • • May 19 in Washington, D. C. Excellent dialogue – Many common views – Principles of Cooperation • Next meeting in Moscow

U. S. - E. U. Consultations • Use of GPS and its augmentations for commercial products and services incorporating open signal structure • 1998: U. S. presented draft Framework Agreement based on GPS and its augmentations – Consider inclusion of: International Advisory Commission, Intent of Guarantee, Statement of Free Service • 2000: Cooperation concept – Stage 1: Framework Cooperative Agreement based on Principles of Cooperation – Stage 2: Working groups – Stage 3: Follow-on agreement to cover Galileo operations phase

U. S. - E. U. Draft Agreement • Presented to the Commission on October 5 • Embodies GPS Policy & Principles of Cooperation – Government provided satellite signals free of user fees – Interoperability with GPS – Open signals for critical infrastructure and safety-of-life services – Open specifications and markets for civil equipment and services – Users choose which system or combination best meet their needs • • Recognizes efforts of other fora: ICAO, IMO, ITU Accounts for different levels of system maturity Lays foundation for future cooperation Next round of talks scheduled for March 20 -21, 2001

U. S. Questions About Galileo • To be understood: – – Revenue stream generation Future regulatory actions Required use (mandate through standards) Interoperability of free open system with fee-based encrypted system • Safety of life applications – Prevention of misuse – Open specifications and standards for equal worldwide market access – Spectrum use – Security service

Summary • GPS is a key component of the global information infrastructure • U. S. is committed to providing GPS service free of direct user fees to users worldwide • Adherence to U. S. principles has led to GPS standardization and market growth • GPS modernization is under way • U. S. is continuing international outreach to further understanding of GPS, its augmentations, and its applications • U. S. is fostering international dialogue to be responsive to global user needs
1f9759c3d38c8d2274481a9dfc8eca75.ppt