4dd0f6c76eb56bccdf41ef81f3918f6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 The GEO 600 Detector Andreas Freise for the GEO 600 Team Max-Planck-Institute for Gravitational Physics University of Hannover May 20, 2002 3/18/2018
The GEO 600 Detector Andreas Freise for the GEO 600 Team Max-Planck-Institute for Gravitational Physics University of Hannover May 20, 2002 3/18/2018
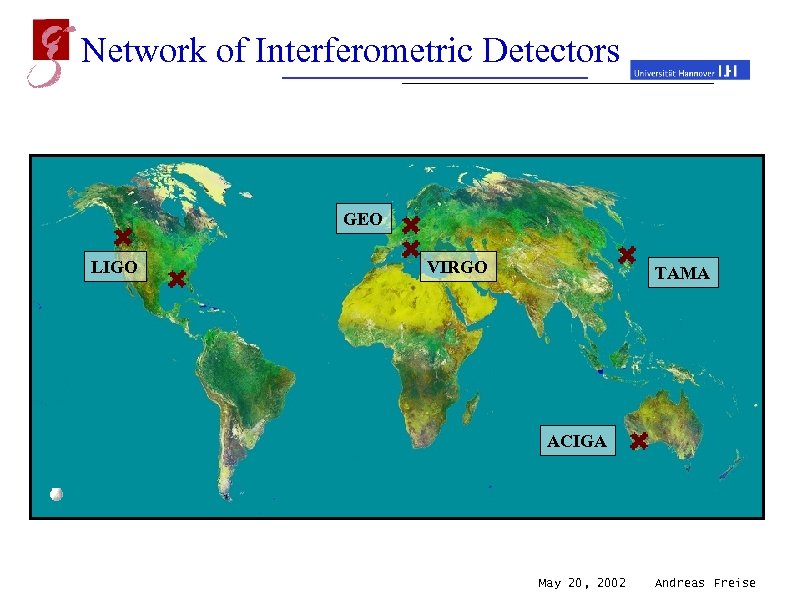 Network of Interferometric Detectors GEO LIGO VIRGO TAMA ACIGA May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Network of Interferometric Detectors GEO LIGO VIRGO TAMA ACIGA May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
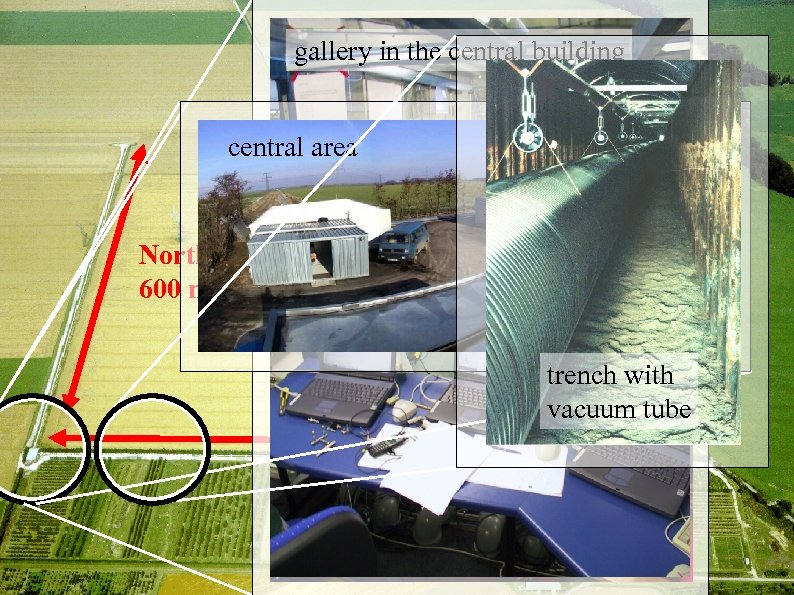 gallery in the central building clean room central area North Arm 600 m East Arm 600 m 3/18/2018 trench with vacuum tube
gallery in the central building clean room central area North Arm 600 m East Arm 600 m 3/18/2018 trench with vacuum tube
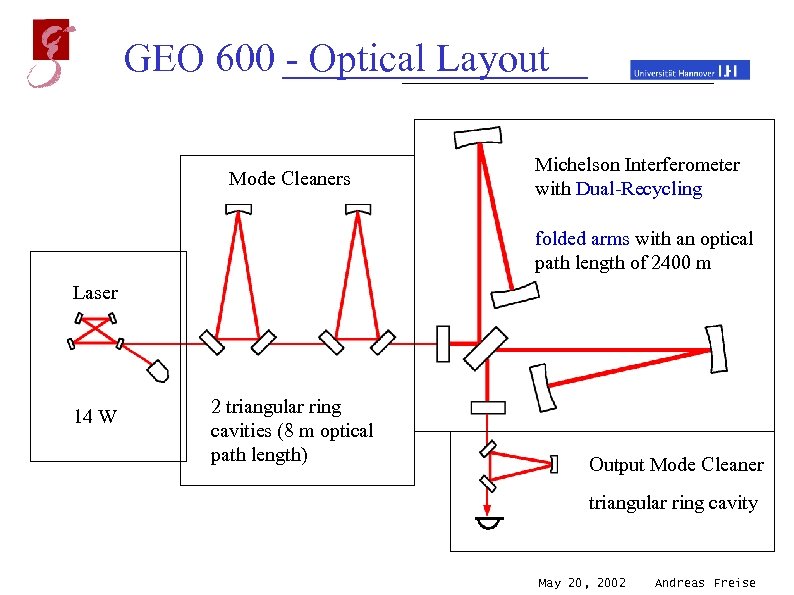 GEO 600 - Optical Layout Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer with Dual-Recycling folded arms with an optical path length of 2400 m Laser 14 W 2 triangular ring cavities (8 m optical path length) Output Mode Cleaner triangular ring cavity May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
GEO 600 - Optical Layout Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer with Dual-Recycling folded arms with an optical path length of 2400 m Laser 14 W 2 triangular ring cavities (8 m optical path length) Output Mode Cleaner triangular ring cavity May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
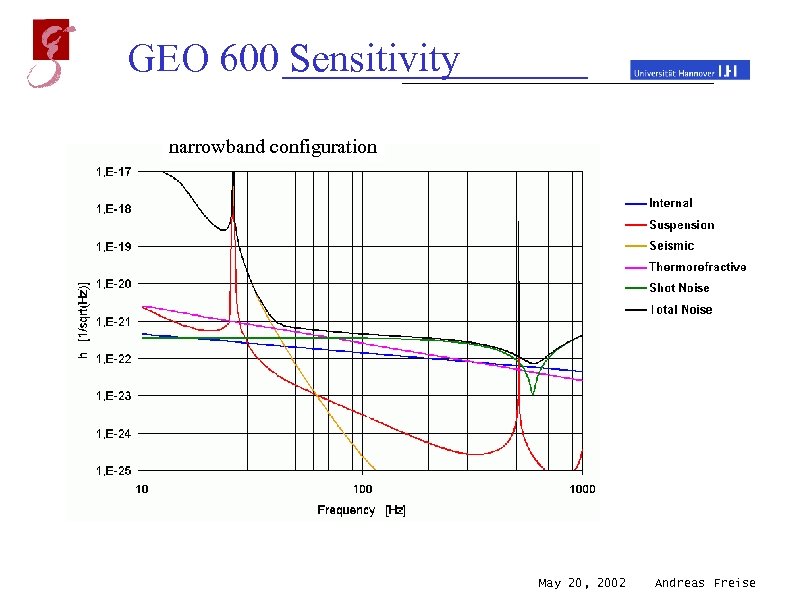 GEO 600 Sensitivity narrowband configuration broadband configuration May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
GEO 600 Sensitivity narrowband configuration broadband configuration May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
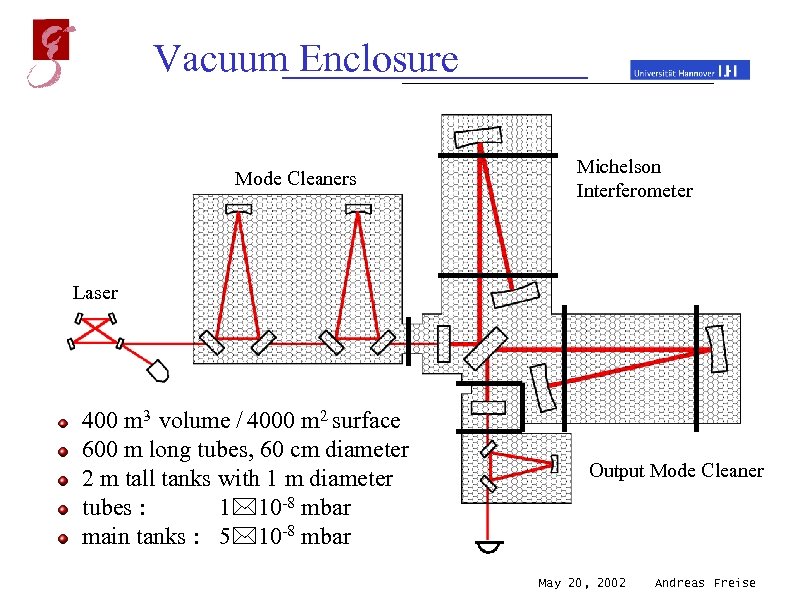 Vacuum Enclosure Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer Laser 400 m 3 volume / 4000 m 2 surface 600 m long tubes, 60 cm diameter 2 m tall tanks with 1 m diameter tubes : 1 10 -8 mbar main tanks : 5 10 -8 mbar Output Mode Cleaner May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Vacuum Enclosure Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer Laser 400 m 3 volume / 4000 m 2 surface 600 m long tubes, 60 cm diameter 2 m tall tanks with 1 m diameter tubes : 1 10 -8 mbar main tanks : 5 10 -8 mbar Output Mode Cleaner May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
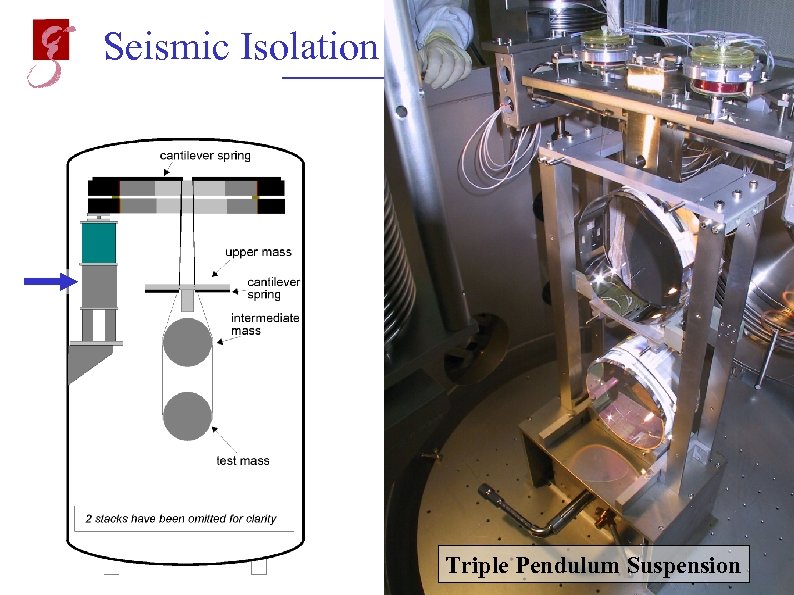 Seismic Isolation The mechanical structure inside each vacuum tank is mounted on three Stacks: Triple Pendulum Suspension May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Seismic Isolation The mechanical structure inside each vacuum tank is mounted on three Stacks: Triple Pendulum Suspension May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
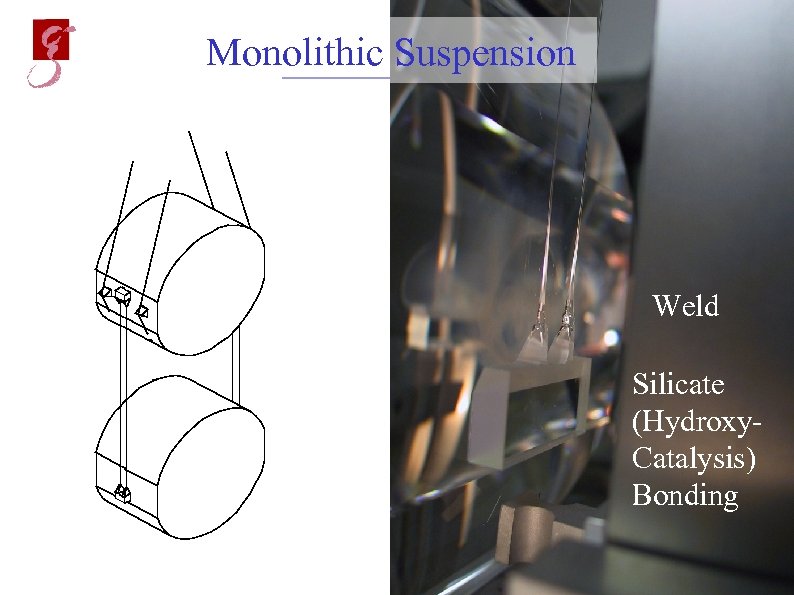 Monolithic Suspension Weld Silicate (Hydroxy. Catalysis) Bonding May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Monolithic Suspension Weld Silicate (Hydroxy. Catalysis) Bonding May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
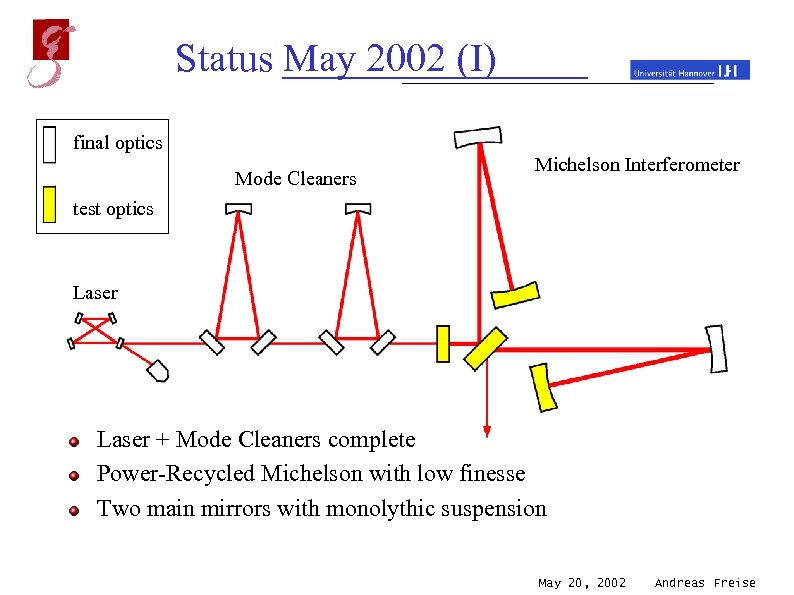 Status May 2002 (I) final optics Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer test optics Laser + Mode Cleaners complete Power-Recycled Michelson with low finesse Two main mirrors with monolythic suspension May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Status May 2002 (I) final optics Mode Cleaners Michelson Interferometer test optics Laser + Mode Cleaners complete Power-Recycled Michelson with low finesse Two main mirrors with monolythic suspension May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
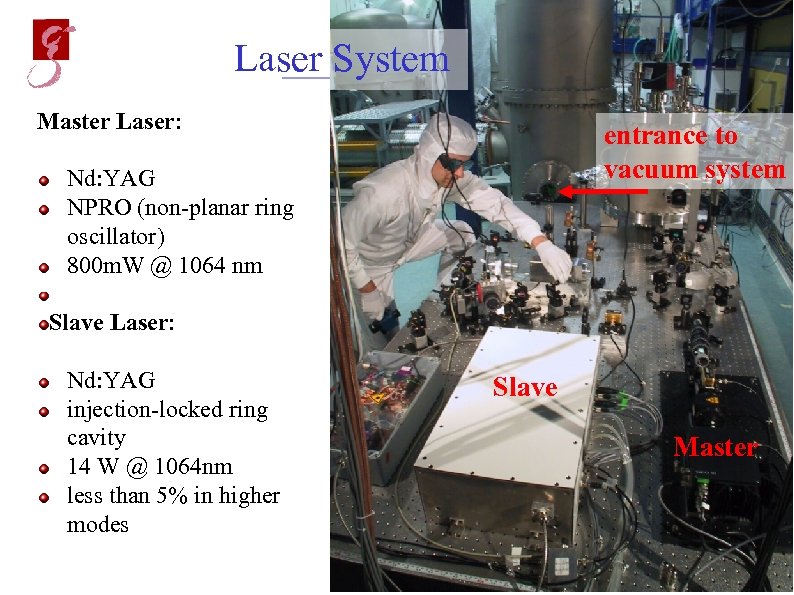 Laser System Master Laser: entrance to vacuum system Nd: YAG NPRO (non-planar ring oscillator) 800 m. W @ 1064 nm Slave Laser: Nd: YAG injection-locked ring Master cavity 14 W @ 1064 nm less than 5% in higher modes Slave Master May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Laser System Master Laser: entrance to vacuum system Nd: YAG NPRO (non-planar ring oscillator) 800 m. W @ 1064 nm Slave Laser: Nd: YAG injection-locked ring Master cavity 14 W @ 1064 nm less than 5% in higher modes Slave Master May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
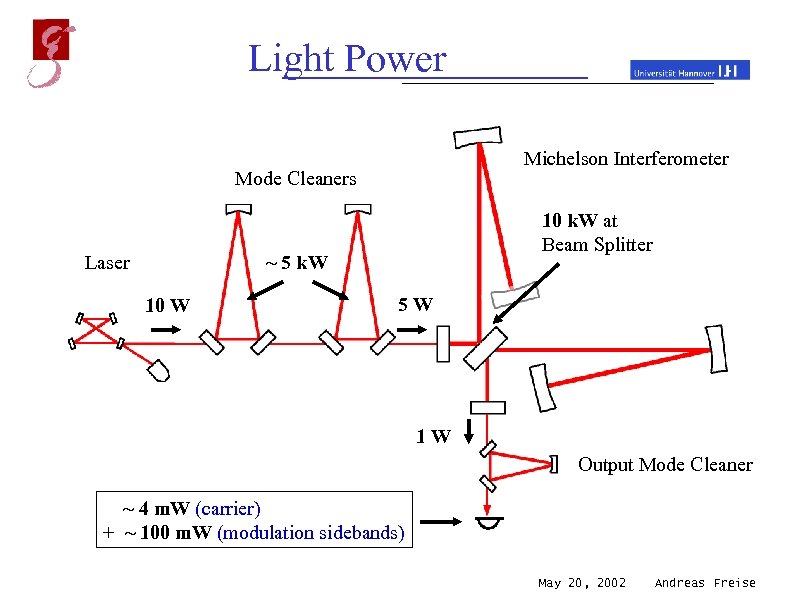 Light Power Michelson Interferometer Mode Cleaners Laser 10 k. W at Beam Splitter ~ 5 k. W 10 W 5 W 1 W Output Mode Cleaner ~ 4 m. W (carrier) + ~ 100 m. W (modulation sidebands) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Light Power Michelson Interferometer Mode Cleaners Laser 10 k. W at Beam Splitter ~ 5 k. W 10 W 5 W 1 W Output Mode Cleaner ~ 4 m. W (carrier) + ~ 100 m. W (modulation sidebands) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
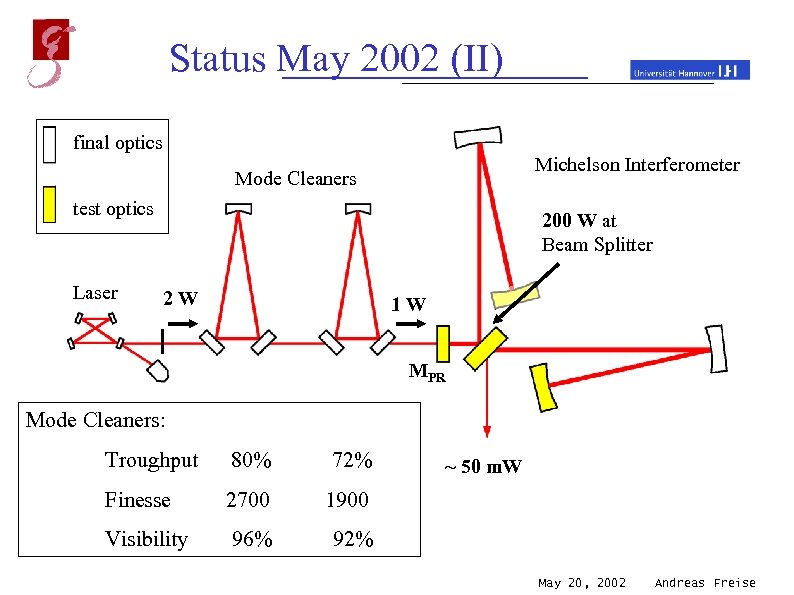 Status May 2002 (II) final optics Michelson Interferometer Mode Cleaners test optics Laser 200 W at Beam Splitter 2 W 1 W MPR Mode Cleaners: Troughput 80% 72% Finesse 2700 1900 Visibility 96% 92% ~ 50 m. W May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Status May 2002 (II) final optics Michelson Interferometer Mode Cleaners test optics Laser 200 W at Beam Splitter 2 W 1 W MPR Mode Cleaners: Troughput 80% 72% Finesse 2700 1900 Visibility 96% 92% ~ 50 m. W May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
 Automated Control control loops made of analog electronics supervised by digital electronics controlled by distributed virtual instruments (Lab. View) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Automated Control control loops made of analog electronics supervised by digital electronics controlled by distributed virtual instruments (Lab. View) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
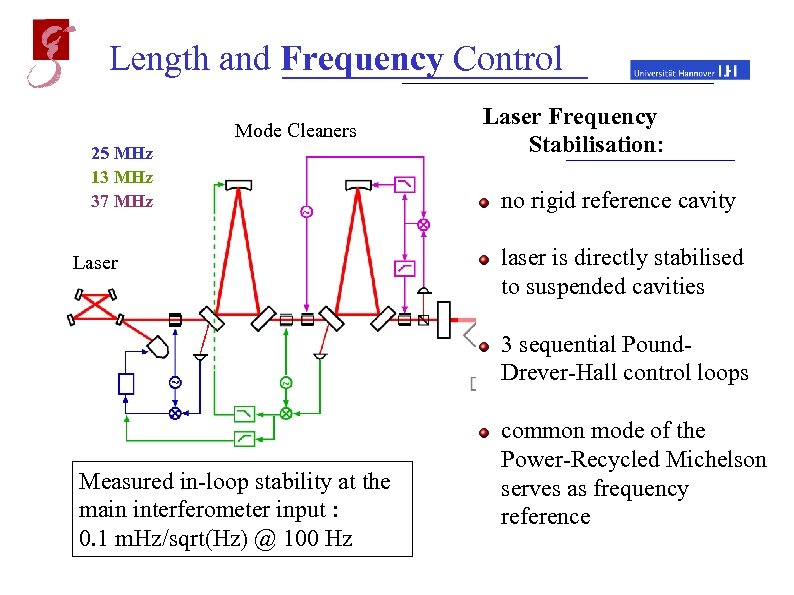 Length and Frequency Control Mode Cleaners 25 MHz 13 MHz 37 MHz Laser Frequency Stabilisation: Michelson Interferometer no rigid reference cavity laser is directly stabilised to suspended cavities 3 sequential Pound. Drever-Hall control loops Measured in-loop stability at the main interferometer input : 0. 1 m. Hz/sqrt(Hz) @ 100 Hz common mode of the Power-Recycled Michelson Output Mode Cleaner serves as frequency reference May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Length and Frequency Control Mode Cleaners 25 MHz 13 MHz 37 MHz Laser Frequency Stabilisation: Michelson Interferometer no rigid reference cavity laser is directly stabilised to suspended cavities 3 sequential Pound. Drever-Hall control loops Measured in-loop stability at the main interferometer input : 0. 1 m. Hz/sqrt(Hz) @ 100 Hz common mode of the Power-Recycled Michelson Output Mode Cleaner serves as frequency reference May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
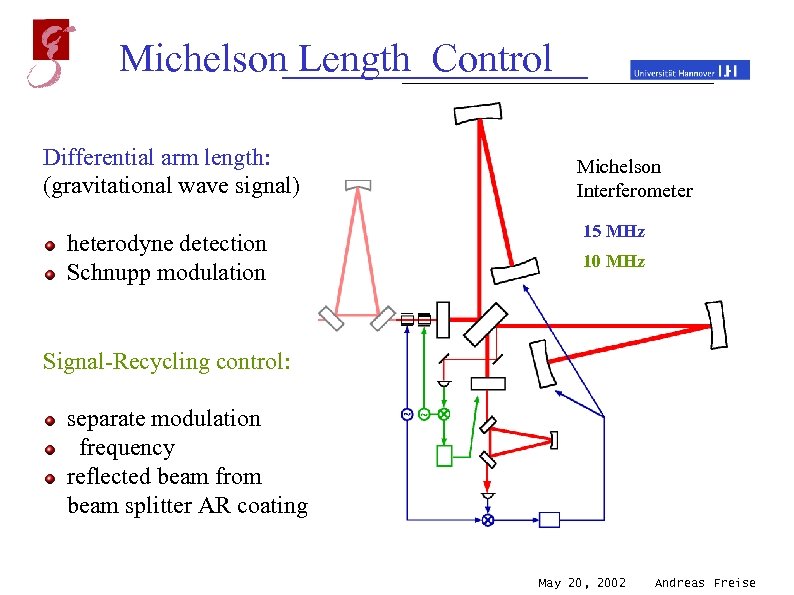 Michelson Length Control Mode Cleaners Differential arm length: (gravitational wave signal) heterodyne detection Laser Schnupp modulation Michelson Interferometer 15 MHz 10 MHz Signal-Recycling control: separate modulation frequency reflected beam from beam splitter AR coating Output Mode Cleaner May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Michelson Length Control Mode Cleaners Differential arm length: (gravitational wave signal) heterodyne detection Laser Schnupp modulation Michelson Interferometer 15 MHz 10 MHz Signal-Recycling control: separate modulation frequency reflected beam from beam splitter AR coating Output Mode Cleaner May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
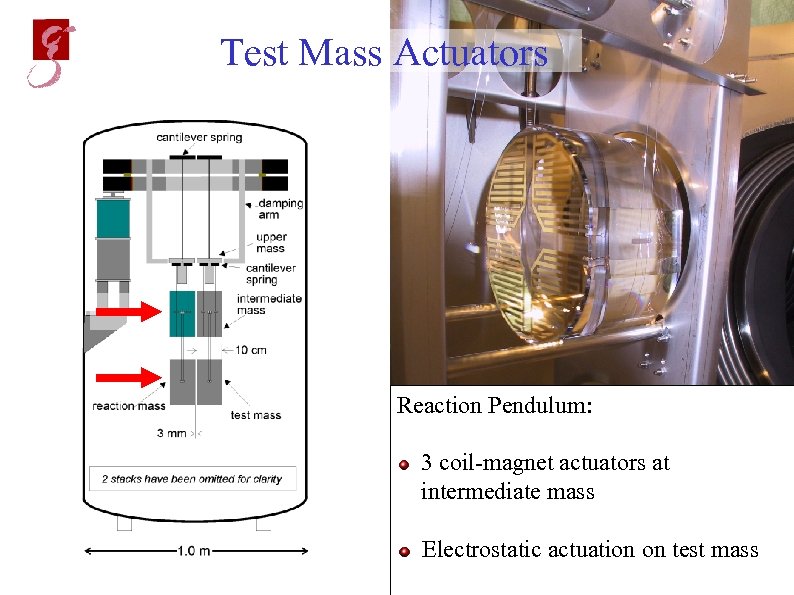 Test Mass Actuators Reaction Pendulum: 3 coil-magnet actuators at intermediate mass Electrostatic actuation on test mass May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Test Mass Actuators Reaction Pendulum: 3 coil-magnet actuators at intermediate mass Electrostatic actuation on test mass May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
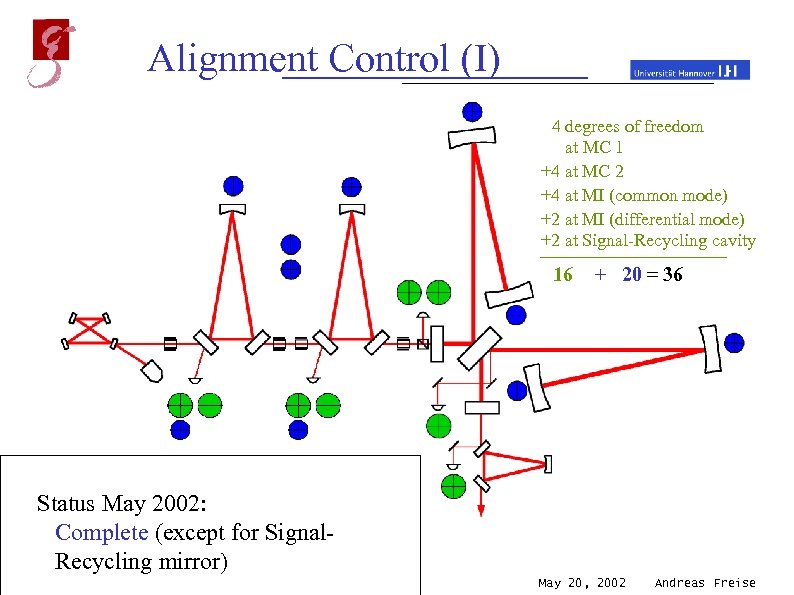 Alignment Control (I) 4 degrees of freedom at MC 1 +4 at MC 2 +4 at MI (common mode) +2 at MI (differential mode) +2 at Signal-Recycling cavity 16 + 20 = 36 differential wave-front sensing Status May 2002: spot position control Complete (except for Signal. Recycling mirror) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Alignment Control (I) 4 degrees of freedom at MC 1 +4 at MC 2 +4 at MI (common mode) +2 at MI (differential mode) +2 at Signal-Recycling cavity 16 + 20 = 36 differential wave-front sensing Status May 2002: spot position control Complete (except for Signal. Recycling mirror) May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
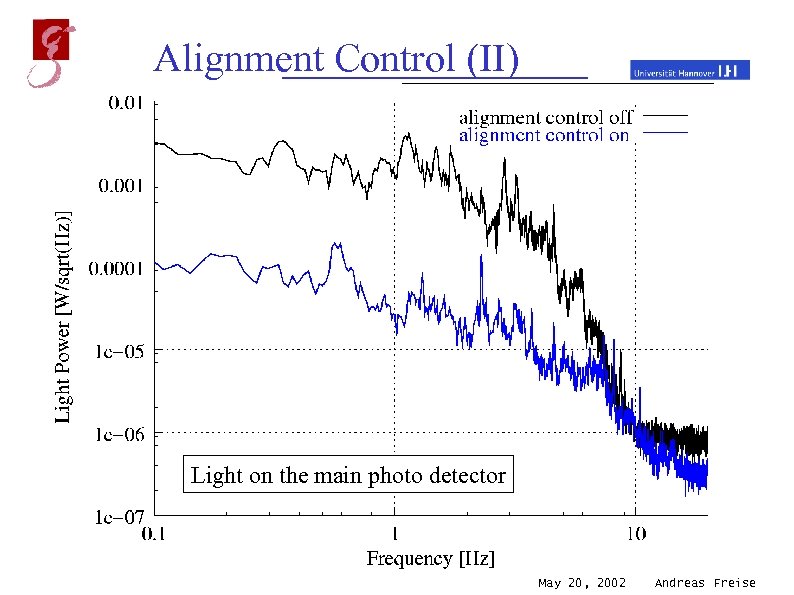 Alignment Control (II) Light on the main photo detector May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Alignment Control (II) Light on the main photo detector May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
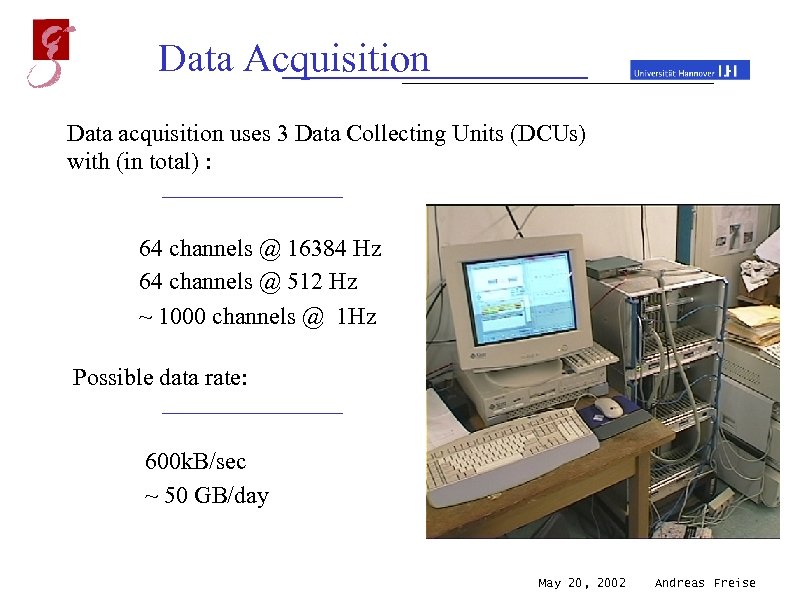 Data Acquisition Data acquisition uses 3 Data Collecting Units (DCUs) with (in total) : 64 channels @ 16384 Hz 64 channels @ 512 Hz ~ 1000 channels @ 1 Hz Possible data rate: 600 k. B/sec ~ 50 GB/day May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Data Acquisition Data acquisition uses 3 Data Collecting Units (DCUs) with (in total) : 64 channels @ 16384 Hz 64 channels @ 512 Hz ~ 1000 channels @ 1 Hz Possible data rate: 600 k. B/sec ~ 50 GB/day May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
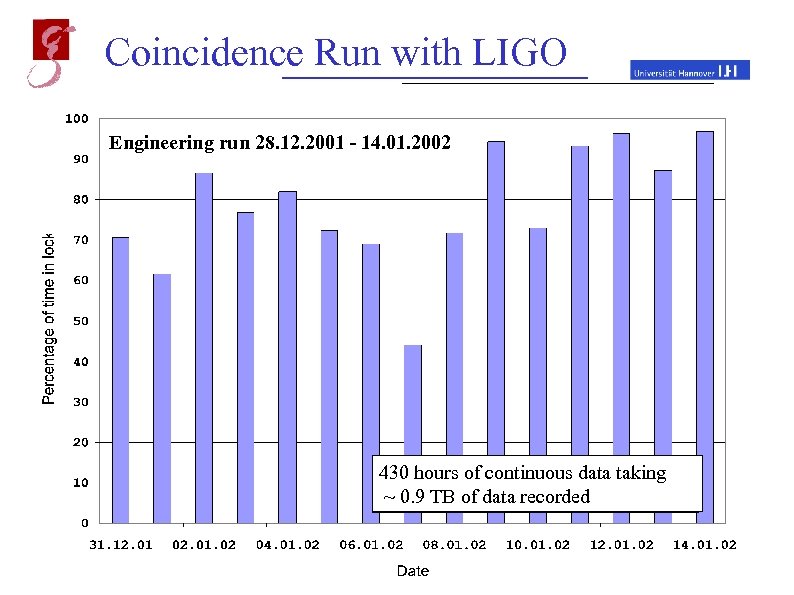 Coincidence Run with LIGO Engineering run 28. 12. 2001 - 14. 01. 2002 430 hours of duty cycles, maintenance Daily overall continuous data taking ~ 0. 9 TB of data recorded periods not subtracted May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Coincidence Run with LIGO Engineering run 28. 12. 2001 - 14. 01. 2002 430 hours of duty cycles, maintenance Daily overall continuous data taking ~ 0. 9 TB of data recorded periods not subtracted May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
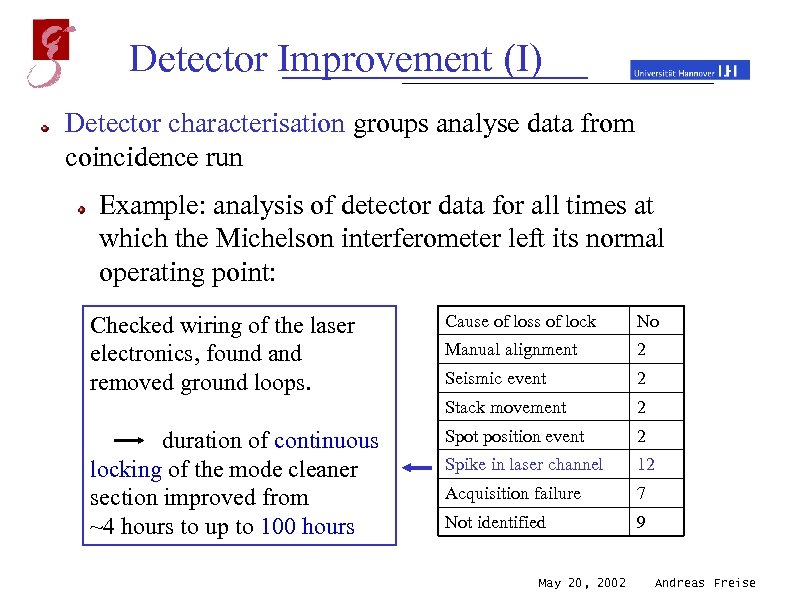 Detector Improvement (I) Detector characterisation groups analyse data from coincidence run Example: analysis of detector data for all times at which the Michelson interferometer left its normal operating point: duration of 36 lock losses continuous locking of the mode cleaner (on 10. 01. 2002) section improved from ~4 hours to up to 100 hours Cause of loss of lock No Manual alignment 2 Seismic event 2 Stack movement Checked wiring of the laser electronics, found and removed ground loops. 2 Spot position event 2 Spike in laser channel 12 Acquisition failure 7 Not identified 9 May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Detector Improvement (I) Detector characterisation groups analyse data from coincidence run Example: analysis of detector data for all times at which the Michelson interferometer left its normal operating point: duration of 36 lock losses continuous locking of the mode cleaner (on 10. 01. 2002) section improved from ~4 hours to up to 100 hours Cause of loss of lock No Manual alignment 2 Seismic event 2 Stack movement Checked wiring of the laser electronics, found and removed ground loops. 2 Spot position event 2 Spike in laser channel 12 Acquisition failure 7 Not identified 9 May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
 Detector Improvement (II) Experimental optimisation period: electronics for Michelson servo loops are being completed Michelson automatic alignment is completed losses inside interferometer have been reduced (PR gain improved from 15 to 200) known problem with beam splitter suspension has been fixed sensitivity has been improved from 10 -17 1/sqrt(Hz) to 10 -18 1/sqrt(Hz) @ ~ 300 Hz May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Detector Improvement (II) Experimental optimisation period: electronics for Michelson servo loops are being completed Michelson automatic alignment is completed losses inside interferometer have been reduced (PR gain improved from 15 to 200) known problem with beam splitter suspension has been fixed sensitivity has been improved from 10 -17 1/sqrt(Hz) to 10 -18 1/sqrt(Hz) @ ~ 300 Hz May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
 Future steps Optimisation (Michelson) June 02 Coincidence run with LIGO (S 1) July 02 Implementation of Signal-Recycling end of July 02 Optimisation (Dual-Recycling) Aug. -Oct. 02 Installation of final subsystems starting Nov. 02 Coincidence run with LIGO (S 2) end of Nov. 02 May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise
Future steps Optimisation (Michelson) June 02 Coincidence run with LIGO (S 1) July 02 Implementation of Signal-Recycling end of July 02 Optimisation (Dual-Recycling) Aug. -Oct. 02 Installation of final subsystems starting Nov. 02 Coincidence run with LIGO (S 2) end of Nov. 02 May 20, 2002 Andreas Freise


