190c8f6f9362b0de4c417f4926a361f7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Quelle: Wikipedia The release of this image had an effect in leading to the proposition that the Earth is alive. GCM – 1. Semester: Physical Fundamentals of GC, Juliane Gnau
The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Quelle: Wikipedia The release of this image had an effect in leading to the proposition that the Earth is alive. GCM – 1. Semester: Physical Fundamentals of GC, Juliane Gnau
 The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Content • Earth System Science • Earth System Modelling • The GAIA Hypothesis • Recent research • “Official proof of acceptance”
The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Content • Earth System Science • Earth System Modelling • The GAIA Hypothesis • Recent research • “Official proof of acceptance”
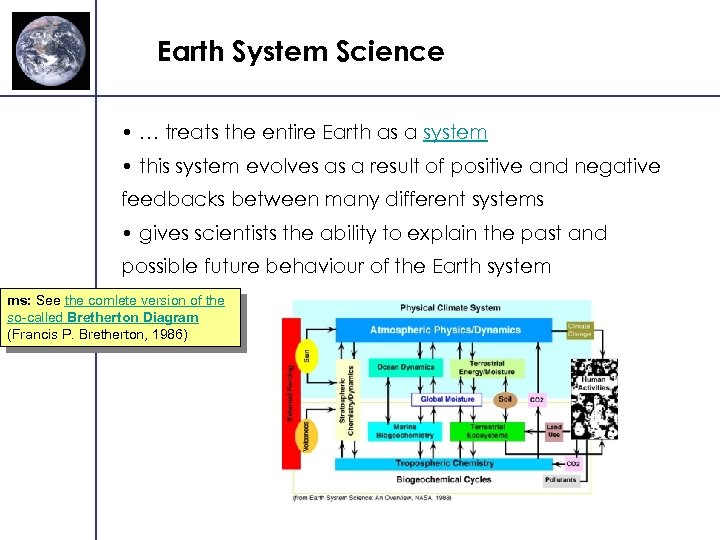 Earth System Science • … treats the entire Earth as a system • this system evolves as a result of positive and negative feedbacks between many different systems • gives scientists the ability to explain the past and possible future behaviour of the Earth system ms: See the comlete version of the so-called Bretherton Diagram (Francis P. Bretherton, 1986)
Earth System Science • … treats the entire Earth as a system • this system evolves as a result of positive and negative feedbacks between many different systems • gives scientists the ability to explain the past and possible future behaviour of the Earth system ms: See the comlete version of the so-called Bretherton Diagram (Francis P. Bretherton, 1986)
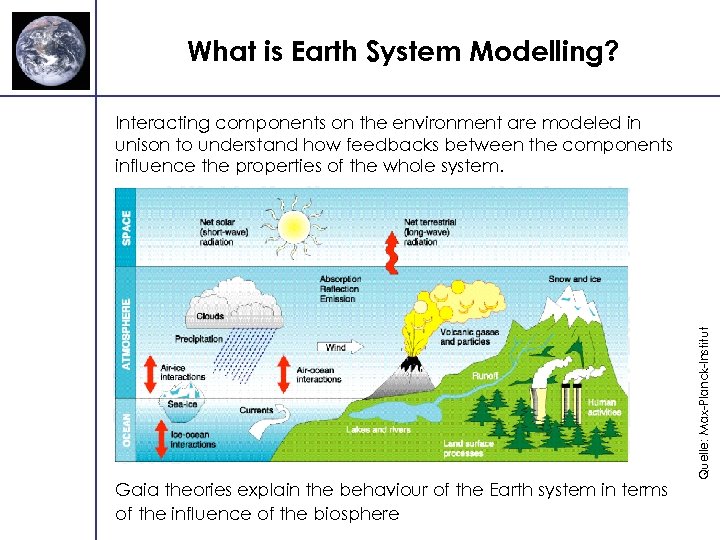 What is Earth System Modelling? Gaia theories explain the behaviour of the Earth system in terms of the influence of the biosphere Quelle: Max-Planck-Institut Interacting components on the environment are modeled in unison to understand how feedbacks between the components influence the properties of the whole system.
What is Earth System Modelling? Gaia theories explain the behaviour of the Earth system in terms of the influence of the biosphere Quelle: Max-Planck-Institut Interacting components on the environment are modeled in unison to understand how feedbacks between the components influence the properties of the whole system.
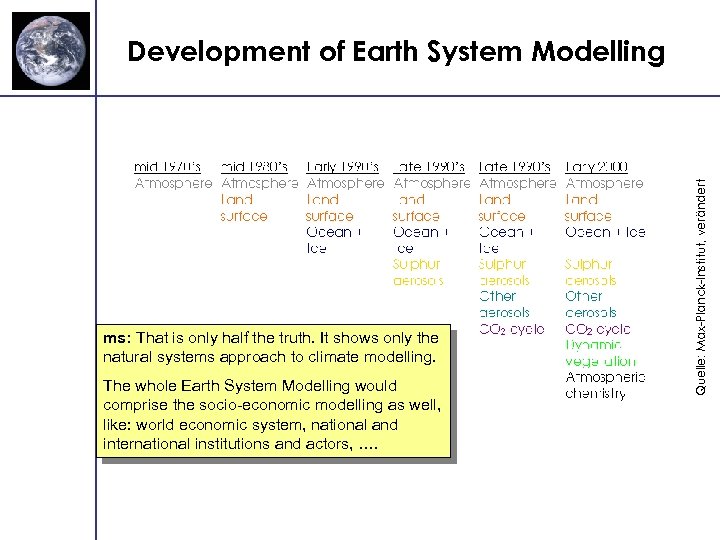 ms: That is only half the truth. It shows only the natural systems approach to climate modelling. The whole Earth System Modelling would comprise the socio-economic modelling as well, like: world economic system, national and international institutions and actors, …. Quelle: Max-Planck-Institut, verändert Development of Earth System Modelling
ms: That is only half the truth. It shows only the natural systems approach to climate modelling. The whole Earth System Modelling would comprise the socio-economic modelling as well, like: world economic system, national and international institutions and actors, …. Quelle: Max-Planck-Institut, verändert Development of Earth System Modelling
 Goals of Earth System Modelling • to predict the future of the planet Earth • instrument to take appropriate actions in the future within the framework of future management of the Earth
Goals of Earth System Modelling • to predict the future of the planet Earth • instrument to take appropriate actions in the future within the framework of future management of the Earth
 The GAIA Hypothesis James Lovelock‘s definition: a complex entity involving the Earth's biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and soil; the totality constituting a feedback or cybernetic system which seeks an optimal physical and chemical environment for life on this planet
The GAIA Hypothesis James Lovelock‘s definition: a complex entity involving the Earth's biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and soil; the totality constituting a feedback or cybernetic system which seeks an optimal physical and chemical environment for life on this planet
 The Initial Hypothesis • biomass modifies conditions on planet • hospitality = homeostasis • homeostatic feedback system operated by the biota leads to stabilization of global temperature and chemical composition Global control system: • surface temperature • atmospheric composition • ocean salinity
The Initial Hypothesis • biomass modifies conditions on planet • hospitality = homeostasis • homeostatic feedback system operated by the biota leads to stabilization of global temperature and chemical composition Global control system: • surface temperature • atmospheric composition • ocean salinity
 The Development of the Hypothesis • 1960: Ecological theory: the Earth as an organism • Core assumption of hypothesis: „Lives of a cell“ • Scientifically formulated by J. Lovelock • Supported by scientific experiments + providing useful predictions Theory • 1972: "Gaia as seen through the atmosphere" • Until 1975 almost totally ignored • 1979: book “Gaia: A new look at life on Earth”
The Development of the Hypothesis • 1960: Ecological theory: the Earth as an organism • Core assumption of hypothesis: „Lives of a cell“ • Scientifically formulated by J. Lovelock • Supported by scientific experiments + providing useful predictions Theory • 1972: "Gaia as seen through the atmosphere" • Until 1975 almost totally ignored • 1979: book “Gaia: A new look at life on Earth”
 History The Development of the Hypothesis • Acception took many years • 1980’s: still confusion what the GAIA theory really is • Criticism: 1. view is too theological 2. lack of scientific evidence 3. GAIA is not a living organism
History The Development of the Hypothesis • Acception took many years • 1980’s: still confusion what the GAIA theory really is • Criticism: 1. view is too theological 2. lack of scientific evidence 3. GAIA is not a living organism
 History The Development of the Hypothesis • response to criticism = math. Daisyworld proof for existance of feedback mechanisms • Lovelock‘s reframing as geophysiology • growing acceptance of Earth System Science • silenced many critics
History The Development of the Hypothesis • response to criticism = math. Daisyworld proof for existance of feedback mechanisms • Lovelock‘s reframing as geophysiology • growing acceptance of Earth System Science • silenced many critics
 Recent developments • Gaia Theory has developed considerably • 1998 book: “The Symbiotic Planet”(L. Margulis) "Gaia is not an organism", but "an emergent property of interaction among organisms". New definition: “…the series of interacting ecosystems that compose a single huge ecosystem at the Earth's surface. “ • both theories are valid today
Recent developments • Gaia Theory has developed considerably • 1998 book: “The Symbiotic Planet”(L. Margulis) "Gaia is not an organism", but "an emergent property of interaction among organisms". New definition: “…the series of interacting ecosystems that compose a single huge ecosystem at the Earth's surface. “ • both theories are valid today
 Recent developments The GAIA Hypothesis • two GAIA Conferences 1. 1988: the Gaian teological views or "types" of Gaia Theory 2. 2000: specific mechanisms: • has Gaia changed in time? • how can the feedbacks influence the climate? • how can mechanisms be modeled?
Recent developments The GAIA Hypothesis • two GAIA Conferences 1. 1988: the Gaian teological views or "types" of Gaia Theory 2. 2000: specific mechanisms: • has Gaia changed in time? • how can the feedbacks influence the climate? • how can mechanisms be modeled?
 Today The GAIA Hypothesis - Summary • the Gaia hypothesis is modified • biosphere = ecosystem • the Gaia hypothesis is consistent with a modern vision of global ecology, relaying on the concepts of common usage, use the biosphere and biodiversity ms: Intheory to signify apeople often an opinion, word conjecture, • not a theory anymore (? ) or a speculation. In science however, a theory is a proposed description, explanation, or model of the manner of interaction of a set of natural phenomena, capable of predicting future occurrences or observations! • part of Earth System Science • scientific model in geo-biosphere • non-scientists: self-regulating Earth
Today The GAIA Hypothesis - Summary • the Gaia hypothesis is modified • biosphere = ecosystem • the Gaia hypothesis is consistent with a modern vision of global ecology, relaying on the concepts of common usage, use the biosphere and biodiversity ms: Intheory to signify apeople often an opinion, word conjecture, • not a theory anymore (? ) or a speculation. In science however, a theory is a proposed description, explanation, or model of the manner of interaction of a set of natural phenomena, capable of predicting future occurrences or observations! • part of Earth System Science • scientific model in geo-biosphere • non-scientists: self-regulating Earth
 More recent research The GAIA Hypothesis • modelling real biochemical cycles of Earth Daisyworld-like regulation • today: simple feedback mechanisms accepted carbon dioxide • more difficult homeostatic mechanisms ? planetary albedo
More recent research The GAIA Hypothesis • modelling real biochemical cycles of Earth Daisyworld-like regulation • today: simple feedback mechanisms accepted carbon dioxide • more difficult homeostatic mechanisms ? planetary albedo
 More recent research “Official proof of acceptance“ • Amsterdam declaration of the scientific communities of 4 international global change research programmes: • threat of significant climate change • increasing human modification of global environment findings and statements seem to be fully consistent with the Gaia theory The Earth System behaves as a single, self-regulating system comprised of physical, chemical, biological and human components.
More recent research “Official proof of acceptance“ • Amsterdam declaration of the scientific communities of 4 international global change research programmes: • threat of significant climate change • increasing human modification of global environment findings and statements seem to be fully consistent with the Gaia theory The Earth System behaves as a single, self-regulating system comprised of physical, chemical, biological and human components.
 More recent research “Official proof of acceptance“ “The interactions and feedbacks between the component parts are complex and exhibit multi-scale temporal and spatial variability. ” “Global change cannot be understood in terms of a simple cause-effect paradigm. Human-driven changes cause multiple effects that cascade through the Earth System in complex ways. ” “These effects interact with each other and with local- and regional-scale changes in multidimensional patterns that are difficult to understand even more difficult to predict. ”
More recent research “Official proof of acceptance“ “The interactions and feedbacks between the component parts are complex and exhibit multi-scale temporal and spatial variability. ” “Global change cannot be understood in terms of a simple cause-effect paradigm. Human-driven changes cause multiple effects that cascade through the Earth System in complex ways. ” “These effects interact with each other and with local- and regional-scale changes in multidimensional patterns that are difficult to understand even more difficult to predict. ”
 The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Thank you for listening ms: Richard Mabey reviews The revenge of Gaia by James Lovelock: “After Hurricane Katrina, a black Gaian joke went the rounds, couched in White House newspeak: Successful mission against the Gulf of Mexico oilfields. Some collateral damage in New Orleans. ” Sources: • Wikipedia • Max-Planck-Institut • http: //serc. carleton. edu/introgeo/earthsystem/nutshell/index. html
The GAIA Hypothesis and it‘s role in Earth System Modelling Thank you for listening ms: Richard Mabey reviews The revenge of Gaia by James Lovelock: “After Hurricane Katrina, a black Gaian joke went the rounds, couched in White House newspeak: Successful mission against the Gulf of Mexico oilfields. Some collateral damage in New Orleans. ” Sources: • Wikipedia • Max-Planck-Institut • http: //serc. carleton. edu/introgeo/earthsystem/nutshell/index. html
 Comments for Juliane Gnau from Manfred Stock 1. To be finished. . .
Comments for Juliane Gnau from Manfred Stock 1. To be finished. . .


