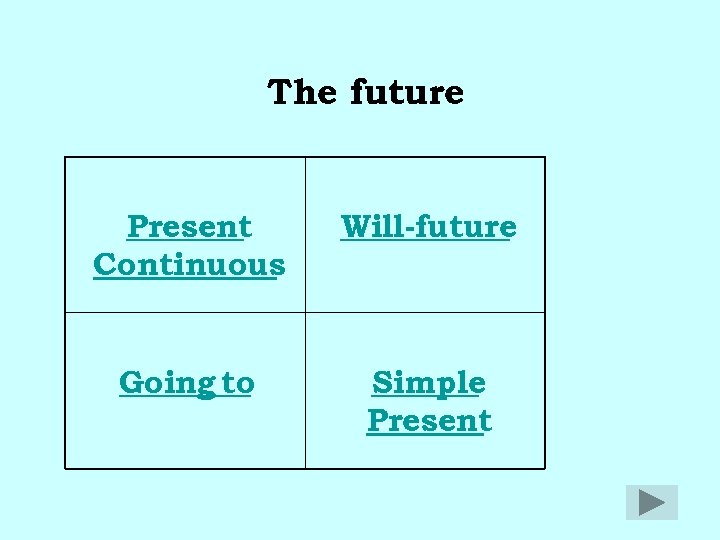
 The future Present Continuous Will-future Going to Simple Present
The future Present Continuous Will-future Going to Simple Present
 Present Continuous Si usa per parlare di arrangementscioè , di azioni programmate che si svolgeranno (nel futuro) in un luogo e/o momento preciso e prestabilito. He’s staying in Berlin on Friday night. I’m startinga new job next week.
Present Continuous Si usa per parlare di arrangementscioè , di azioni programmate che si svolgeranno (nel futuro) in un luogo e/o momento preciso e prestabilito. He’s staying in Berlin on Friday night. I’m startinga new job next week.
 Will-future q Si usa per parlare di predictionscioè per dire , ciò che pensiamo, prevediamo, sappiamo sul futuro. Si tratta di previsioni del tutto personali, cioè non necessariamente supportate da fattori esterni. I think it will snow tomorrow. q Si usa per parlare di azioni non predeterminate, ma decise e immediatamente mese in attodal soggetto. What a nice hat! I’ll buy it for my sister.
Will-future q Si usa per parlare di predictionscioè per dire , ciò che pensiamo, prevediamo, sappiamo sul futuro. Si tratta di previsioni del tutto personali, cioè non necessariamente supportate da fattori esterni. I think it will snow tomorrow. q Si usa per parlare di azioni non predeterminate, ma decise e immediatamente mese in attodal soggetto. What a nice hat! I’ll buy it for my sister.
 Will-future q Si usa per: ü offrirsi di fare qlco: I’ll give you a hand ü accettare/rifiutare di fare qlco: ‘I need some money’ ‘Ok, I’ll lend you some’ ü promettere qlco: Ok, I really will stopsmoking ü fare una richiesta cortese: Will you open the window, please? q Si usa nella main clause del 1 st conditional : If I find your wallet, I’ll phoneyou.
Will-future q Si usa per: ü offrirsi di fare qlco: I’ll give you a hand ü accettare/rifiutare di fare qlco: ‘I need some money’ ‘Ok, I’ll lend you some’ ü promettere qlco: Ok, I really will stopsmoking ü fare una richiesta cortese: Will you open the window, please? q Si usa nella main clause del 1 st conditional : If I find your wallet, I’ll phoneyou.
 Will-future (form) AFFERMATIVA INTERROGATIVA NEGATIVA I will+forma base You will He will She will It will We will You will They will Will I +forma base? Will you? Will he? Will she? Will It? Will We? Will you? Will they? I will not + f. base You will not He will not She will not It will not We will not You will not They will not I’ll + forma base I won’t + f. base
Will-future (form) AFFERMATIVA INTERROGATIVA NEGATIVA I will+forma base You will He will She will It will We will You will They will Will I +forma base? Will you? Will he? Will she? Will It? Will We? Will you? Will they? I will not + f. base You will not He will not She will not It will not We will not You will not They will not I’ll + forma base I won’t + f. base
 First conditional Esistono tre tipi fondamentali di IF-CLAUSES. La scelta di uno dei tre tipi dipende: a) dal tempo cui si riferisce la condizione; b) dal maggiore o minore grado di probabilitàche essa ha di verificarsi. RICORDA: il periodo ipotetico è formato da una proposizione principale [MAIN CLAUSE] e da una proposizione secondaria introdotta da IF [IF-CLAUSE]. 1° TIPO (cioè 1 st conditional = possibile o probabile ) IF + PR. SIMPLE WILL+ INF senza TO If I have time, If it rains, I’ll give you a hand. I’ll stay at home.
First conditional Esistono tre tipi fondamentali di IF-CLAUSES. La scelta di uno dei tre tipi dipende: a) dal tempo cui si riferisce la condizione; b) dal maggiore o minore grado di probabilitàche essa ha di verificarsi. RICORDA: il periodo ipotetico è formato da una proposizione principale [MAIN CLAUSE] e da una proposizione secondaria introdotta da IF [IF-CLAUSE]. 1° TIPO (cioè 1 st conditional = possibile o probabile ) IF + PR. SIMPLE WILL+ INF senza TO If I have time, If it rains, I’ll give you a hand. I’ll stay at home.
 Going to q Si usa per parlare di intentionscioè di , decisioni già prese. I’m going to take a holiday next week. q Si usa per parlare di un’azione che sta per accadere o è molto probabile che accada perché ne abbiamo le prove evidenti. Rebecca’s going to have a baby.
Going to q Si usa per parlare di intentionscioè di , decisioni già prese. I’m going to take a holiday next week. q Si usa per parlare di un’azione che sta per accadere o è molto probabile che accada perché ne abbiamo le prove evidenti. Rebecca’s going to have a baby.
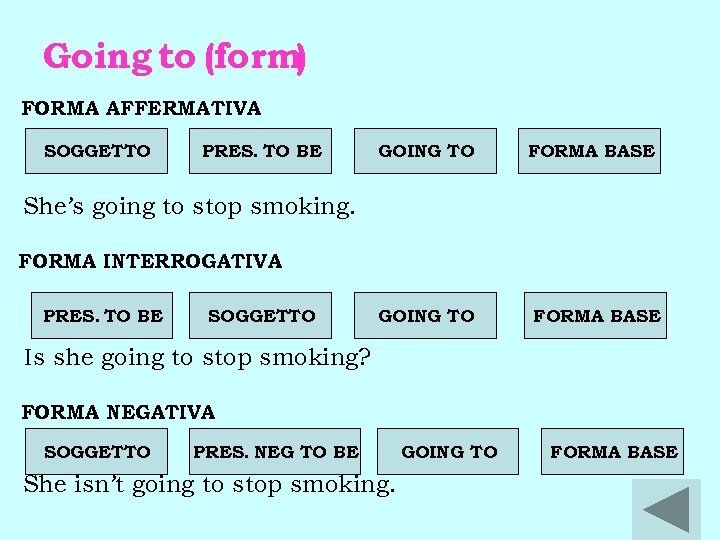 Going to (form) FORMA AFFERMATIVA SOGGETTO PRES. TO BE GOING TO FORMA BASE She’s going to stop smoking. FORMA INTERROGATIVA PRES. TO BE SOGGETTO GOING TO FORMA BASE Is she going to stop smoking? FORMA NEGATIVA SOGGETTO PRES. NEG TO BE She isn’t going to stop smoking. GOING TO FORMA BASE
Going to (form) FORMA AFFERMATIVA SOGGETTO PRES. TO BE GOING TO FORMA BASE She’s going to stop smoking. FORMA INTERROGATIVA PRES. TO BE SOGGETTO GOING TO FORMA BASE Is she going to stop smoking? FORMA NEGATIVA SOGGETTO PRES. NEG TO BE She isn’t going to stop smoking. GOING TO FORMA BASE
 Simple Present (for future) Si usa per parlare di timetables cioè di , orari di mezzi di trasporto, orari di programmi (TV, cinema, teatro) e date. Our train leaves at 8. 10. This term finishes on 12 th March.
Simple Present (for future) Si usa per parlare di timetables cioè di , orari di mezzi di trasporto, orari di programmi (TV, cinema, teatro) e date. Our train leaves at 8. 10. This term finishes on 12 th March.