a4afa9806d51cf5f2a3d2342599a1deb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 The Future of Information SecurityAssurance Marc Rogers Senior Manager ETS Group Deloitte & Touche LLP Dept. of Psychology University of Manitoba
The Future of Information SecurityAssurance Marc Rogers Senior Manager ETS Group Deloitte & Touche LLP Dept. of Psychology University of Manitoba
 Agenda F Current state of information securityassurance F Future Trends – Cyber-terrorism – Information Warfare – Cyber-crime F Conclusions 2
Agenda F Current state of information securityassurance F Future Trends – Cyber-terrorism – Information Warfare – Cyber-crime F Conclusions 2
 Current State F Growth rate of the Internet is staggering – 65 Million users in the U. S in 1998 – 100 Million users in the U. S. in 1999 – 177 Million by the end of 2003 – Worldwide by 2003 502 Million users F Business to Business e-commerce – $100 Billion US in 1999 – $1 Trillion US by 2003 *Source: Report of the President’s Working Group on Unlawful Conduct on the Internet 3
Current State F Growth rate of the Internet is staggering – 65 Million users in the U. S in 1998 – 100 Million users in the U. S. in 1999 – 177 Million by the end of 2003 – Worldwide by 2003 502 Million users F Business to Business e-commerce – $100 Billion US in 1999 – $1 Trillion US by 2003 *Source: Report of the President’s Working Group on Unlawful Conduct on the Internet 3
 Current State F 2000 CSI/FBI Survey – N=303 – 273 Reported attacks (90%) – $265 Million USD* – Only 42% willing and able to quantify losses – 71% detected inside attacks – 59% Internet point of frequent attacks – 38% Internal systems point of attack * Telecom Fraud not included 4
Current State F 2000 CSI/FBI Survey – N=303 – 273 Reported attacks (90%) – $265 Million USD* – Only 42% willing and able to quantify losses – 71% detected inside attacks – 59% Internet point of frequent attacks – 38% Internal systems point of attack * Telecom Fraud not included 4
 Current State F E-Commerce Attacks on the rise – Credit Card Numbers – Visa source code – Smart Cards – Bank Account – Distributed Denial of Service Attacks – Extortion – Organized Crime – Identity Theft 5
Current State F E-Commerce Attacks on the rise – Credit Card Numbers – Visa source code – Smart Cards – Bank Account – Distributed Denial of Service Attacks – Extortion – Organized Crime – Identity Theft 5
 Current State F Hacktavism F Attacks on Government Sites F Attacks on e-Business F Inability to separate Government infrastructure from business infrastructure 6
Current State F Hacktavism F Attacks on Government Sites F Attacks on e-Business F Inability to separate Government infrastructure from business infrastructure 6
 Current State F Malicious Code Attacks – Viruses – Macro-Viruses – Worms – Trojan Horse – Logic Bombs 7
Current State F Malicious Code Attacks – Viruses – Macro-Viruses – Worms – Trojan Horse – Logic Bombs 7
 Current State F Poor laws dealing with technological crimes F Attempting to legislate by metaphor F Reinforcing criminal behavior F Too much focus on technical controls – Technological problem vs. societal and behavioral problem – Not just a hardware, software problem, but a “peopleware” problem as well 8
Current State F Poor laws dealing with technological crimes F Attempting to legislate by metaphor F Reinforcing criminal behavior F Too much focus on technical controls – Technological problem vs. societal and behavioral problem – Not just a hardware, software problem, but a “peopleware” problem as well 8
 Future Trends F Cyber-terrorism – Buzz word – Inaccurately used by media F Information Warfare – Replace conventional? – Support role for conventional? F Cyber-crime – Mere tool – Target 9
Future Trends F Cyber-terrorism – Buzz word – Inaccurately used by media F Information Warfare – Replace conventional? – Support role for conventional? F Cyber-crime – Mere tool – Target 9
 Cyber-Terrorism F Terrorism: F FBI Definition: “. . the unlawful use of force or violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives”. 10
Cyber-Terrorism F Terrorism: F FBI Definition: “. . the unlawful use of force or violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives”. 10
 Cyber-Terrorism F Terrorist: “. . one who causes intense fear; one who controls, dominates, or coerces through the use of terror in furtherance of political or social objectives”. F Cyber-Terrorist: An individual that uses computernetwork technology (i. e. , networks, computers, Internet) to cause intense fear; one who uses computernetwork technology to control, dominate, or coerce through the use of terror in furtherance of political or social objectives. 11
Cyber-Terrorism F Terrorist: “. . one who causes intense fear; one who controls, dominates, or coerces through the use of terror in furtherance of political or social objectives”. F Cyber-Terrorist: An individual that uses computernetwork technology (i. e. , networks, computers, Internet) to cause intense fear; one who uses computernetwork technology to control, dominate, or coerce through the use of terror in furtherance of political or social objectives. 11
 Cyber-Terrorism F National Information Infrastructure (NII) – Weak overall security – Operation Eligible Receiver – Documented attacks on 911, air traffic control, stock exchanges, military sites, banks F Global Information Infrastructure (GII) – Weak overall security – No borders – Few if any international agreements 12
Cyber-Terrorism F National Information Infrastructure (NII) – Weak overall security – Operation Eligible Receiver – Documented attacks on 911, air traffic control, stock exchanges, military sites, banks F Global Information Infrastructure (GII) – Weak overall security – No borders – Few if any international agreements 12
 Information Warfare F Definition: “. . actions taken to achieve information superiority in support of national military strategy by affecting adversary information and information systems” Source: U. S Defense Information Systems Agency DISA 13
Information Warfare F Definition: “. . actions taken to achieve information superiority in support of national military strategy by affecting adversary information and information systems” Source: U. S Defense Information Systems Agency DISA 13
 Information Warfare F Three General Categories: F Offensive – To deny, corrupt, destroy, or exploit adversary’s information F Defensive – To safeguard ourselves and allies from similar actions F Exploitation – To exploit information in a timely fashion, to enhance our decision/action cycle and disrupt the adversary’s cycle 14
Information Warfare F Three General Categories: F Offensive – To deny, corrupt, destroy, or exploit adversary’s information F Defensive – To safeguard ourselves and allies from similar actions F Exploitation – To exploit information in a timely fashion, to enhance our decision/action cycle and disrupt the adversary’s cycle 14
 Information Warfare F IW & Information-Psychological Operations – IW is a technical and psychological activity F Move from IW to Knowledge Warfare F Information-Psychological Security: – The condition and use of information to guarantee the functional reliability of the psyche and consciousness of a person in peacetime or wartime. F Intense interest in this area by Russia and China 15
Information Warfare F IW & Information-Psychological Operations – IW is a technical and psychological activity F Move from IW to Knowledge Warfare F Information-Psychological Security: – The condition and use of information to guarantee the functional reliability of the psyche and consciousness of a person in peacetime or wartime. F Intense interest in this area by Russia and China 15
 Information Warfare F Operation Desert Storm – Knocked out communications systems – Attempted to disrupt economy prior to the operation F UN in Bosnia – Knocked out communications – Disrupt the economy – Propaganda and Misinformation F China vs. Taiwan 16
Information Warfare F Operation Desert Storm – Knocked out communications systems – Attempted to disrupt economy prior to the operation F UN in Bosnia – Knocked out communications – Disrupt the economy – Propaganda and Misinformation F China vs. Taiwan 16
 Cyber-criminals Robert Morris Abbie Hoffman John Draper “Captain Crunch” 17
Cyber-criminals Robert Morris Abbie Hoffman John Draper “Captain Crunch” 17
 Cyber-criminals Mark Abene “Phiber Optik” Kevin Mitnick Vladimir Levin 18
Cyber-criminals Mark Abene “Phiber Optik” Kevin Mitnick Vladimir Levin 18
 Hackers F Definitions: – 1) “an expert at programming and solving problems with a computer”. – 2) “a person who illegally gains access to and sometimes tampers with information in a computer system”. Source: Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary 19
Hackers F Definitions: – 1) “an expert at programming and solving problems with a computer”. – 2) “a person who illegally gains access to and sometimes tampers with information in a computer system”. Source: Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary 19
 Hackers: Evolution of the Term F 4 Generations of the term Hacker – Steven Levy (3 Generations) – 1 st Generation: Creative Programmer: MIT/Stanford (1960’s) – 2 nd Generation: Computer Evolutionaries (1970’s) – 3 rd Generation: Games & Copyright breaking (1980’s) – *4 th Generation: Criminals & Cyberpunks (1990’s) 20
Hackers: Evolution of the Term F 4 Generations of the term Hacker – Steven Levy (3 Generations) – 1 st Generation: Creative Programmer: MIT/Stanford (1960’s) – 2 nd Generation: Computer Evolutionaries (1970’s) – 3 rd Generation: Games & Copyright breaking (1980’s) – *4 th Generation: Criminals & Cyberpunks (1990’s) 20
 Cyber-Crime F Cyber-Crime: “. . a crime committed where the use or knowledge of computers is required” (e. g. , denial of service, attacking passwords) F Computer-assisted Crime: “a crime in which the computer is used to assist in perpetrating the crime” (e. g. , fraud, child pornography) 21
Cyber-Crime F Cyber-Crime: “. . a crime committed where the use or knowledge of computers is required” (e. g. , denial of service, attacking passwords) F Computer-assisted Crime: “a crime in which the computer is used to assist in perpetrating the crime” (e. g. , fraud, child pornography) 21
 Cyber-Crime F U. S. Has defined three distinct types of cyber-crimes: – Computer as Targets – Computer as Storage Devices – Computers as Communication Tools 22
Cyber-Crime F U. S. Has defined three distinct types of cyber-crimes: – Computer as Targets – Computer as Storage Devices – Computers as Communication Tools 22
 Cyber-Crime F First Documented Computer Crime: – (1805) Textile Industry – Joseph Jacquard, automated steps in weaving – Forerunner of the punch card – Employees upset about possibility of being replaced – Sabotaged the system 23
Cyber-Crime F First Documented Computer Crime: – (1805) Textile Industry – Joseph Jacquard, automated steps in weaving – Forerunner of the punch card – Employees upset about possibility of being replaced – Sabotaged the system 23
 Cyber-Crime F Types of Cyber-criminals F Outsider – Hackers – Extensive media coverage F Insiders – Cause the most damage 24
Cyber-Crime F Types of Cyber-criminals F Outsider – Hackers – Extensive media coverage F Insiders – Cause the most damage 24
 Criminal Outsider F Social-Demographics – Male – 12 -30 years old – Caucasian – Single – Grade 12 Education F Characteristics – Perform poorly in school: aptitude for computers & – – technology Limited social skills: loners Compulsive Loners yet appear to crave membership Robin Hood Syndrome 25
Criminal Outsider F Social-Demographics – Male – 12 -30 years old – Caucasian – Single – Grade 12 Education F Characteristics – Perform poorly in school: aptitude for computers & – – technology Limited social skills: loners Compulsive Loners yet appear to crave membership Robin Hood Syndrome 25
 Criminal Insiders F Characteristics: – Technology Specialists – Introverted – Poor social skills – Over-exaggerated sense of self worth – Lack of empathy – Loose ethical boundaries 26
Criminal Insiders F Characteristics: – Technology Specialists – Introverted – Poor social skills – Over-exaggerated sense of self worth – Lack of empathy – Loose ethical boundaries 26
 Criminal Insiders F Characteristics: – Prone to emotional distress – Disappointment – Disgruntlement – Consequent failures of judgment – Sense of entitlement – Anger at authority – Revenge syndrome 27
Criminal Insiders F Characteristics: – Prone to emotional distress – Disappointment – Disgruntlement – Consequent failures of judgment – Sense of entitlement – Anger at authority – Revenge syndrome 27
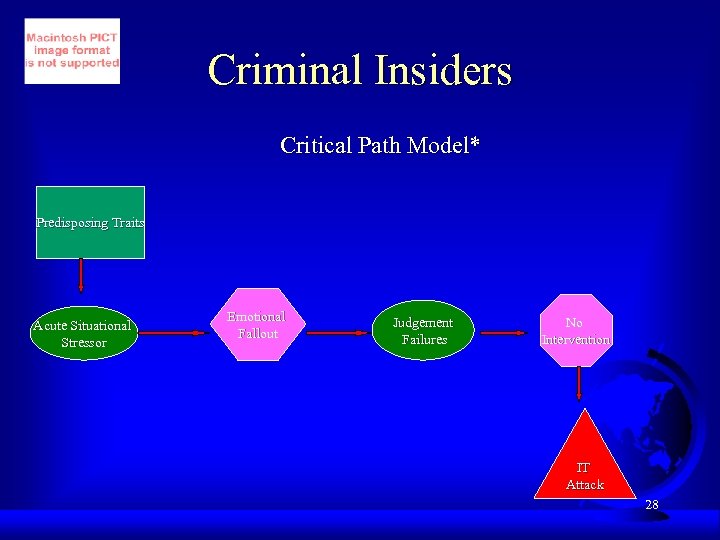 Criminal Insiders Critical Path Model* Predisposing Traits Acute Situational Stressor Emotional Fallout Judgement Failures No Intervention IT Attack 28
Criminal Insiders Critical Path Model* Predisposing Traits Acute Situational Stressor Emotional Fallout Judgement Failures No Intervention IT Attack 28
 Conclusions F E-commerce attractive target for cyber-crime F Increase in organized criminal activity F Increase in distributed attacks F Actual cyber-terrorism F Cyber-psychopaths F IW attacks on businesses F Creation of a “Global Policing Agency” for cyber- crimes 29
Conclusions F E-commerce attractive target for cyber-crime F Increase in organized criminal activity F Increase in distributed attacks F Actual cyber-terrorism F Cyber-psychopaths F IW attacks on businesses F Creation of a “Global Policing Agency” for cyber- crimes 29
 Contact Information F E-Mail: marcusrogers@deloitte. ca F Phone: 944 -3642 F Web Site: www. escape. ca/~mkr 30
Contact Information F E-Mail: marcusrogers@deloitte. ca F Phone: 944 -3642 F Web Site: www. escape. ca/~mkr 30


