ff288e9ff35d318ecb5d92d5ae288d1a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
The Future Narrowband Digital Terminal (FNBDT)* * Next generation signaling protocols for secure interoperable communications, or everything you always wanted to know about secure signaling. . . but were afraid to ask (this presentation has notes) 25 April 2002 1
The Global Context 25 April 2002 2
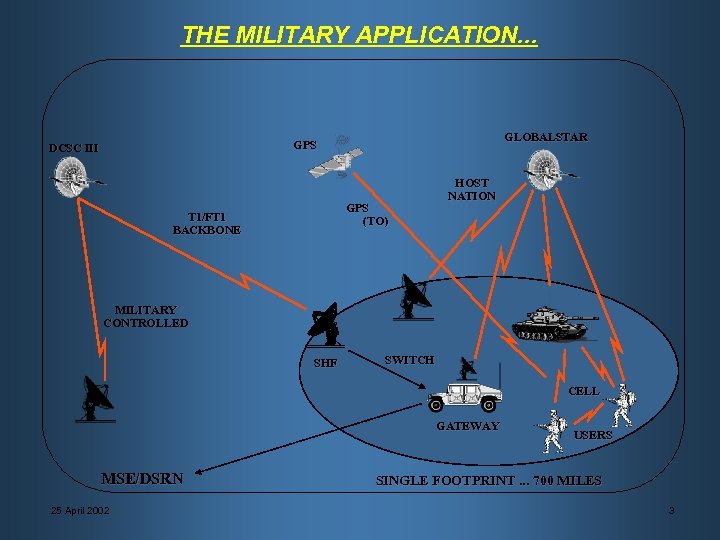
THE MILITARY APPLICATION. . . GLOBALSTAR GPS DCSC III GPS (TO) T 1/FT 1 BACKBONE HOST NATION MILITARY CONTROLLED SHF SWITCH CELL GATEWAY MSE/DSRN 25 April 2002 USERS SINGLE FOOTPRINT. . . 700 MILES 3
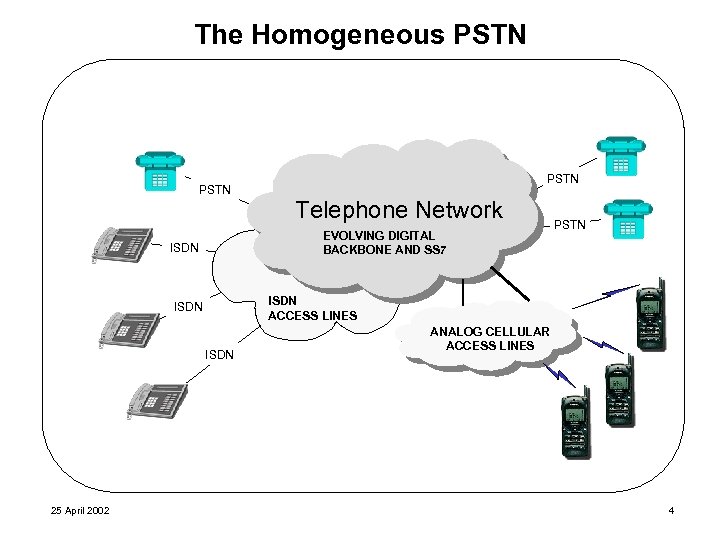
The Homogeneous PSTN Telephone Network EVOLVING DIGITAL BACKBONE AND SS 7 ISDN PSTN ISDN ACCESS LINES ISDN 25 April 2002 PSTN ANALOG CELLULAR ACCESS LINES 4
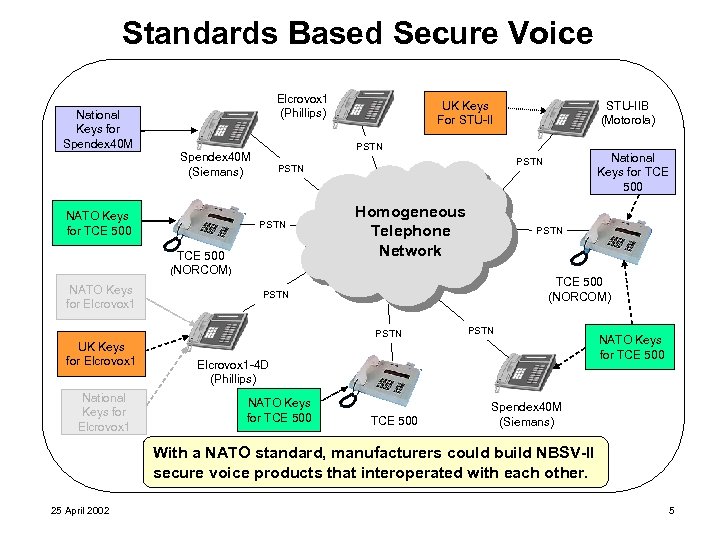
Standards Based Secure Voice Elcrovox 1 (Phillips) National Keys for Spendex 40 M PSTN Spendex 40 M (Siemans) NATO Keys for TCE 500 PSTN TCE 500 Homogeneous Telephone Network PSTN TCE 500 (NORCOM) PSTN UK Keys for Elcrovox 1 National Keys for TCE 500 PSTN (NORCOM) NATO Keys for Elcrovox 1 STU-IIB (Motorola) UK Keys For STU-II PSTN Elcrovox 1 -4 D (Phillips) NATO Keys for TCE 500 Spendex 40 M (Siemans) With a NATO standard, manufacturers could build NBSV-II secure voice products that interoperated with each other. 25 April 2002 5

Secure Voice Equipment - No Standards US Keys For STE US Keys For STU-IIB ISDN UK Keys For BRENT ISDN PSTN ISDN BRENT ISDN National Keys for Top. Sec-703 Homogeneous Telephone Network PSTN TCE 500/B PSTN UK Keys for Elcrovox 1 -4 D (Phillips) NATO Keys for TCE 500/B Analog Cellular STU-III AMPS TCE 500/B STU-III US Keys For STU-III Secure communications were achieved with many, non-interoperable families of secure telephone systems. 25 April 2002 6
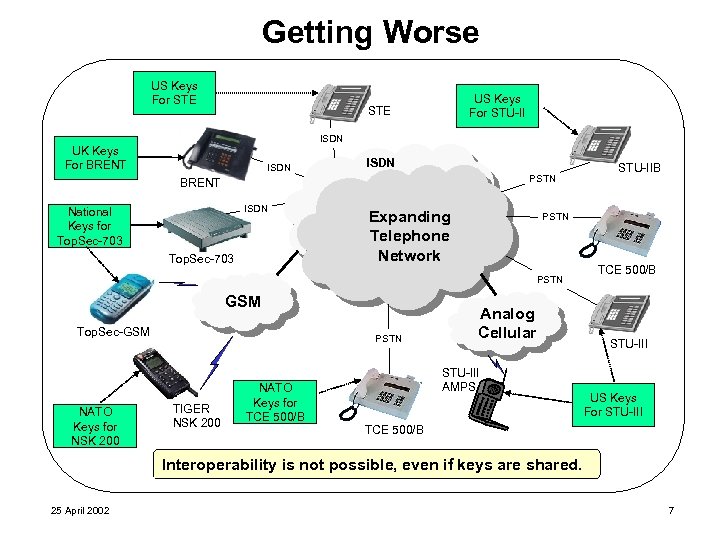
Getting Worse US Keys For STE US Keys For STU-II STE ISDN UK Keys For BRENT ISDN PSTN BRENT ISDN National Keys for Top. Sec-703 Expanding Telephone Network PSTN GSM Top. Sec-GSM NATO Keys for NSK 200 PSTN TIGER NSK 200 NATO Keys for TCE 500/B STU-IIB Analog Cellular STU-III AMPS TCE 500/B STU-III US Keys For STU-III TCE 500/B Interoperability is not possible, even if keys are shared. 25 April 2002 7
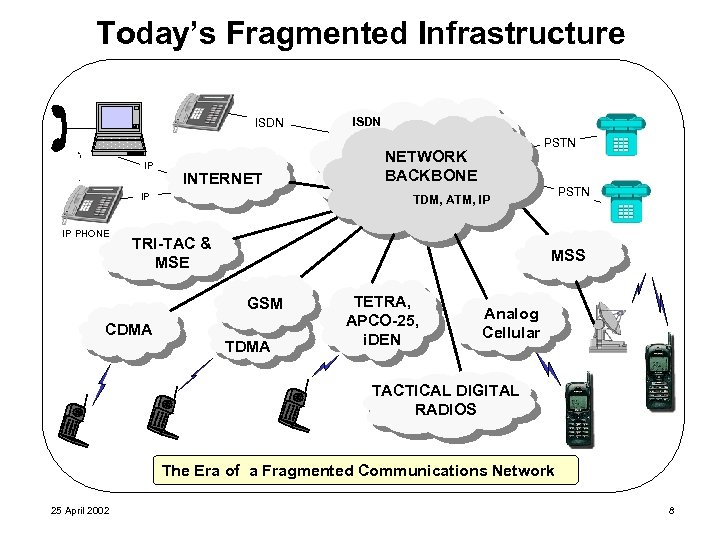
Today’s Fragmented Infrastructure ISDN IP INTERNET IP IP PHONE ISDN PSTN NETWORK BACKBONE TRI-TAC & MSE MSS GSM CDMA PSTN TDM, ATM, IP TDMA TETRA, APCO-25, i. DEN Analog Cellular TACTICAL DIGITAL RADIOS The Era of a Fragmented Communications Network 25 April 2002 8
The Interoperability Problem • The homogeneous communications network of the past is a fragmented collection of bearers and protocols - Many different network types and voice coders - Multiple backbones: CDM, TDM, ATM, IP - Multiple community of service providers • It is increasingly difficult to transmit secure voice over the traditional voice network - data services must be an integral component of design • One architecture for secure voice/data is difficult, but multiple architectures are impractical Multiple unique solutions for each bearer network are impractical at best So, NATO must work together to define a common architecture 25 April 2002 9
FNBDT Potential for Interoperability • Secure Global Interoperability – Using multiple networks of interest – End terminals possibly on different networks, and connected by intermediate disparate networks – End-to-end connections are defined by concatenation of network segments, problems and characteristics • Satisfy both NATO and individual national objectives – Flexibility to include new applications & different cryptographic suites – Flexibility to allow the standard to evolve with technologies and capabilities • Challenge is to design and build a family of interoperable FNBDT products to a single architectural standard 25 April 2002 10
Conceptual Approach • Create architecture that enables interoperability – Nations build products to an interoperable architecture • Accommodate network challenges for both 2 party and N party – secure voice and data – secure call setup and secure net key distribution • Define common interoperable modes of operation – STANAG-4591 MELPe vocoder for 2400 bps operation – Blank & Burst protocol for 2 -party and n-party secure voice maintains crypto sync and 2400 bps operation • Allows late entry into communications stream • Allows bridging deep fading or severe jamming conditions • Complete crypto sync information transmitted every 3 B&B frames • Provide negotiation to select or identify common modes, and cryptographic systems 25 April 2002 11
Basic Signaling Approach - Summary • FNBDT signaling is application layer signaling inserted into the data input capability of any network end point • Transported over concatenated network segments • Requiring only a data path from transmitter to receiver(s) • Blank & Burst secure voice and data signaling designed for N-party net broadcast and 2 -party communication • Additional point-to-point signaling designed for key management, rekey, or other pt-pt communication • May use asynchronous character transmission FNBDT point-to-point signaling designed for interaction with a KMS, 2 -party call setup, key agreement, and other point-to-point communications will be described in the companion briefing next. 25 April 2002 12
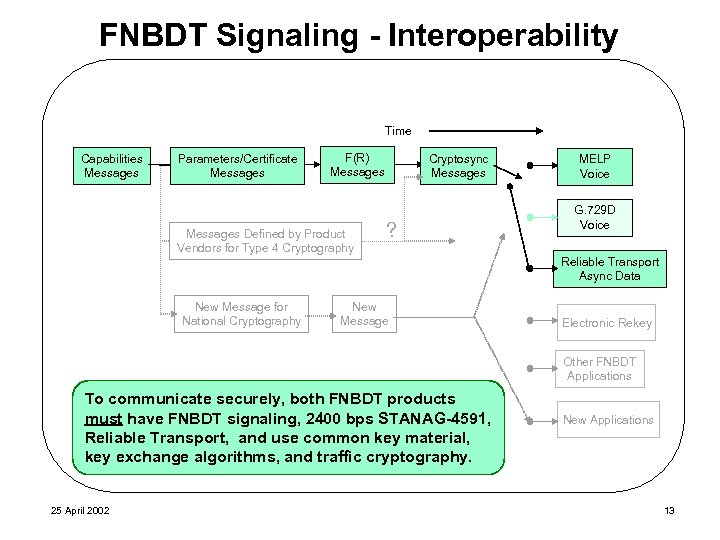
FNBDT Signaling - Interoperability Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications To communicate securely, both FNBDT products must have FNBDT signaling, 2400 bps STANAG-4591, Reliable Transport, and use common key material, key exchange algorithms, and traffic cryptography. 25 April 2002 New Applications 13
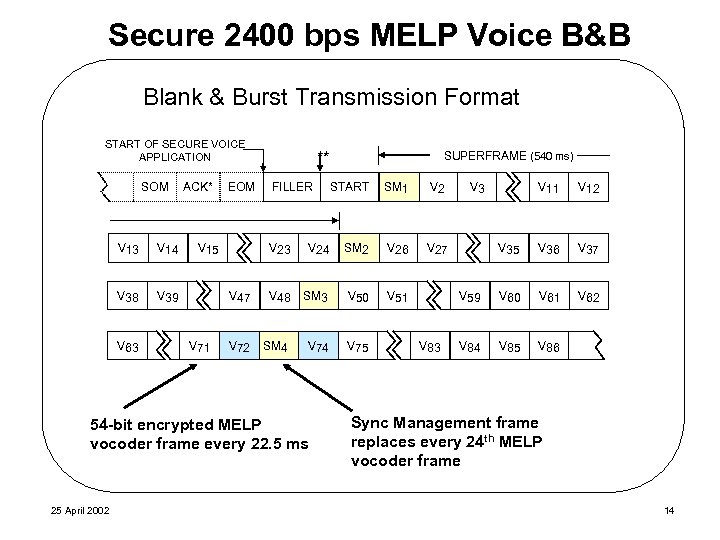
Secure 2400 bps MELP Voice B&B Blank & Burst Transmission Format START OF SECURE VOICE APPLICATION SOM V 13 V 14 V 38 ACK* V 39 V 63 EOM V 15 ** FILLER START SM 1 V 27 V 24 SM 2 V 26 V 47 V 71 V 23 V 48 SM 3 V 50 V 72 SM 4 V 75 V 83 V 11 V 12 V 35 V 36 V 37 V 59 V 51 54 -bit encrypted MELP vocoder frame every 22. 5 ms 25 April 2002 SUPERFRAME (540 ms) V 3 V 60 V 61 V 62 V 84 V 85 V 86 etc. Sync Management frame replaces every 24 th MELP vocoder frame 14
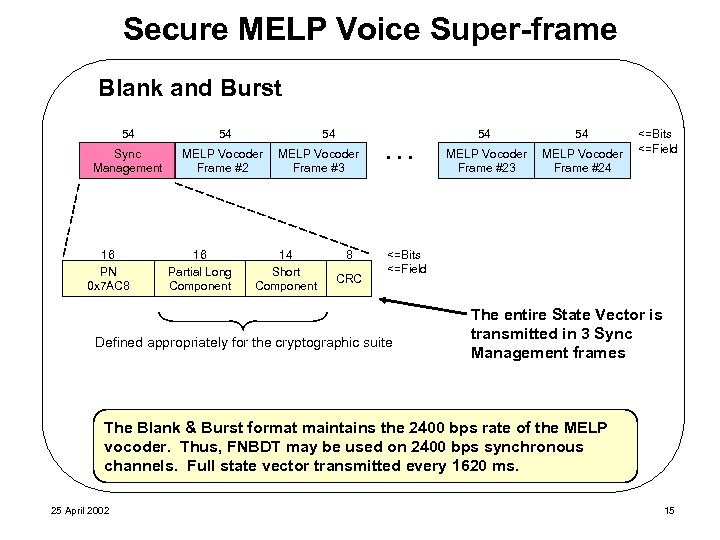
Secure MELP Voice Super-frame Blank and Burst 54 54 Sync Management MELP Vocoder Frame #2 16 PN 0 x 7 AC 8 16 Partial Long Component 54 54 MELP Vocoder Frame #3 14 Short Component 8 CRC . . . 54 MELP Vocoder Frame #23 MELP Vocoder Frame #24 <=Bits <=Field Defined appropriately for the cryptographic suite The entire State Vector is transmitted in 3 Sync Management frames The Blank & Burst format maintains the 2400 bps rate of the MELP vocoder. Thus, FNBDT may be used on 2400 bps synchronous channels. Full state vector transmitted every 1620 ms. 25 April 2002 15
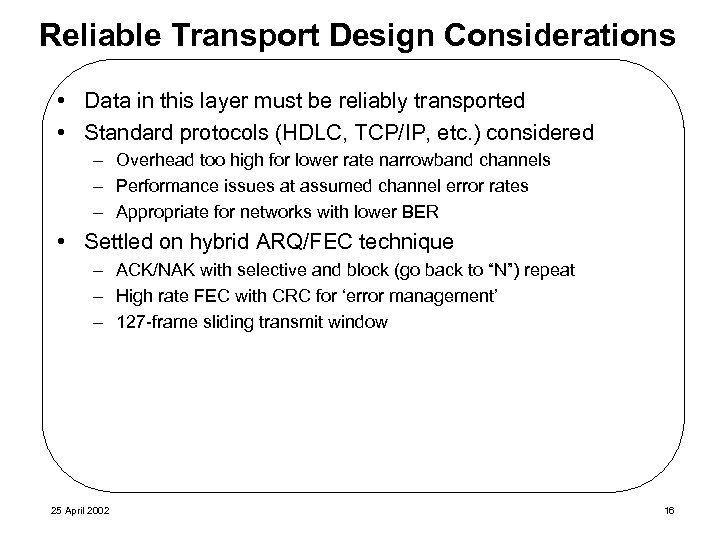
Reliable Transport Design Considerations • Data in this layer must be reliably transported • Standard protocols (HDLC, TCP/IP, etc. ) considered – Overhead too high for lower rate narrowband channels – Performance issues at assumed channel error rates – Appropriate for networks with lower BER • Settled on hybrid ARQ/FEC technique – ACK/NAK with selective and block (go back to “N”) repeat – High rate FEC with CRC for ‘error management’ – 127 -frame sliding transmit window 25 April 2002 16
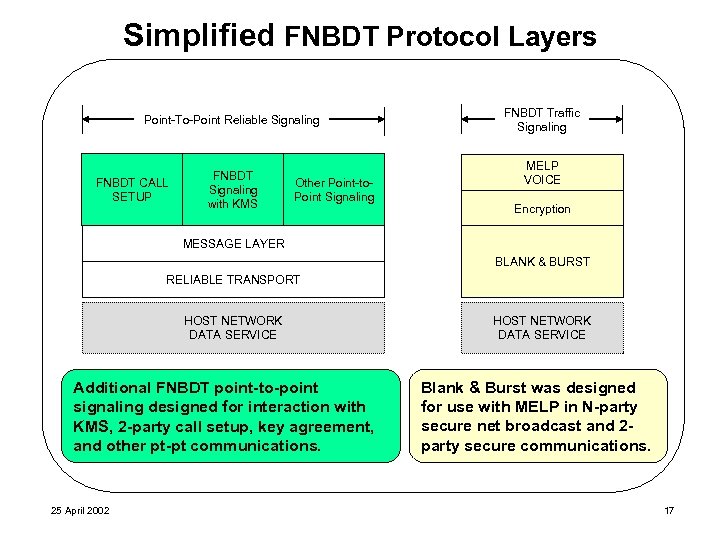
Simplified FNBDT Protocol Layers Point-To-Point Reliable Signaling FNBDT CALL SETUP FNBDT Signaling with KMS Other Point-to. Point Signaling FNBDT Traffic Signaling MELP VOICE Encryption MESSAGE LAYER BLANK & BURST RELIABLE TRANSPORT HOST NETWORK DATA SERVICE Additional FNBDT point-to-point signaling designed for interaction with KMS, 2 -party call setup, key agreement, and other pt-pt communications. 25 April 2002 HOST NETWORK DATA SERVICE Blank & Burst was designed for use with MELP in N-party secure net broadcast and 2 party secure communications. 17
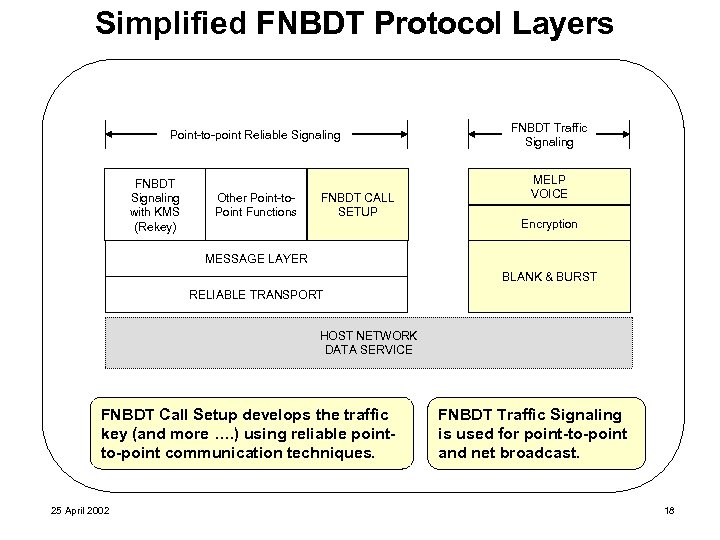
Simplified FNBDT Protocol Layers Point-to-point Reliable Signaling FNBDT Signaling with KMS (Rekey) Other Point-to. Point Functions FNBDT CALL SETUP FNBDT Traffic Signaling MELP VOICE Encryption MESSAGE LAYER BLANK & BURST RELIABLE TRANSPORT HOST NETWORK DATA SERVICE FNBDT Call Setup develops the traffic key (and more …. ) using reliable pointto-point communication techniques. 25 April 2002 FNBDT Traffic Signaling is used for point-to-point and net broadcast. 18
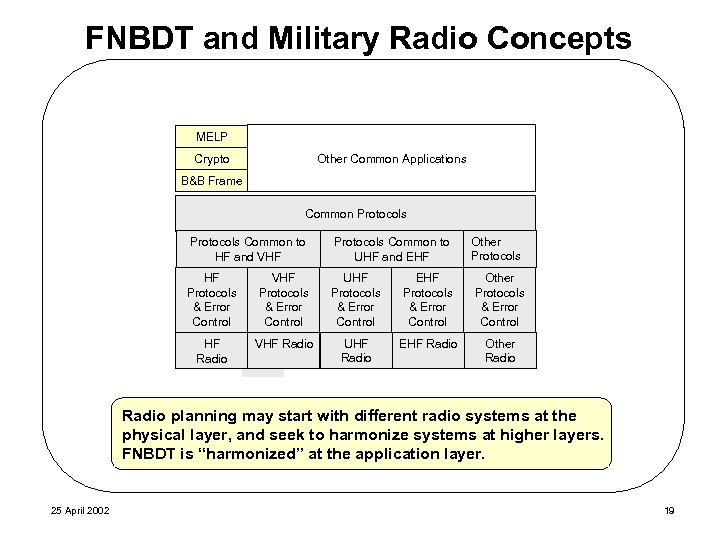
FNBDT and Military Radio Concepts MELP Crypto Other Common Applications B&B Frame Common Protocols Common to HF and VHF Protocols Common to UHF and EHF Other Protocols HF Protocols & Error Control VHF Protocols & Error Control UHF Protocols & Error Control EHF Protocols & Error Control Other Protocols & Error Control HF Radio VHF Radio UHF Radio EHF Radio Other Radio planning may start with different radio systems at the physical layer, and seek to harmonize systems at higher layers. FNBDT is “harmonized” at the application layer. 25 April 2002 19
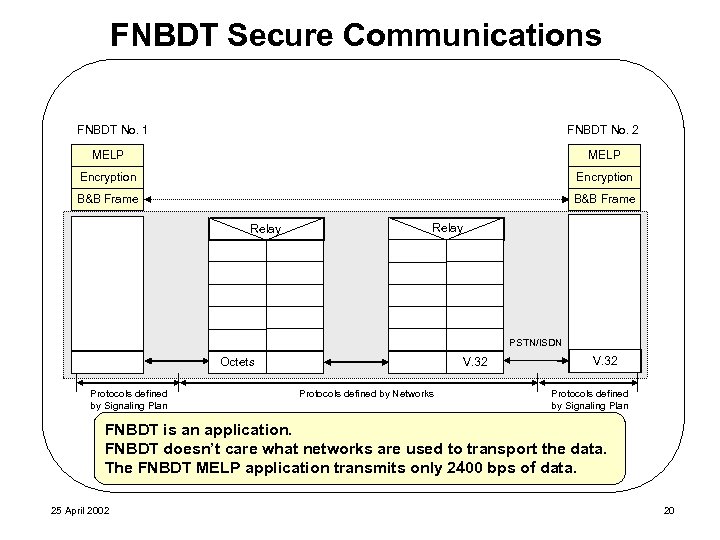
FNBDT Secure Communications FNBDT No. 1 FNBDT No. 2 MELP Encryption B&B Frame Relay PSTN/ISDN Octets Protocols defined by Signaling Plan V. 32 Protocols defined by Networks V. 32 Protocols defined by Signaling Plan FNBDT is an application. FNBDT doesn’t care what networks are used to transport the data. The FNBDT MELP application transmits only 2400 bps of data. 25 April 2002 20
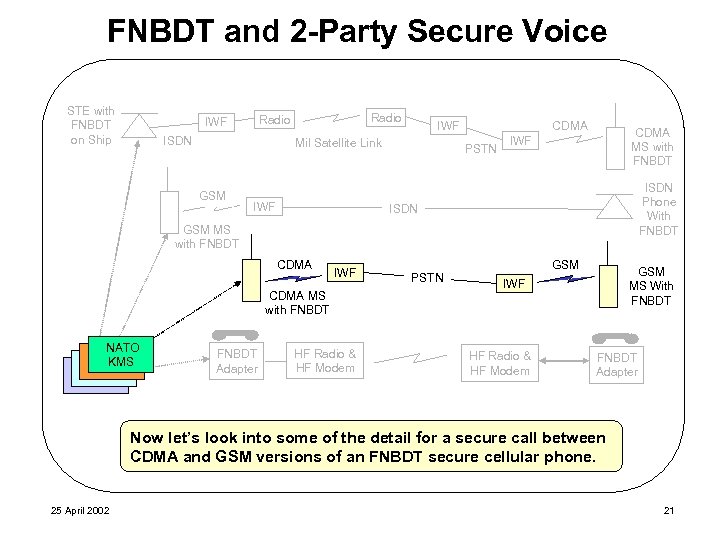
FNBDT and 2 -Party Secure Voice STE with FNBDT on Ship Radio IWF ISDN Mil Satellite Link GSM IWF CDMA IWF PSTN CDMA MS with FNBDT IWF ISDN Phone With FNBDT ISDN GSM MS with FNBDT CDMA IWF CDMA MS with FNBDT NATO UK U. S. KMS Norway KMS KMS FNBDT Adapter HF Radio & HF Modem PSTN GSM MS With FNBDT IWF HF Radio & HF Modem FNBDT Adapter Now let’s look into some of the detail for a secure call between CDMA and GSM versions of an FNBDT secure cellular phone. 25 April 2002 21
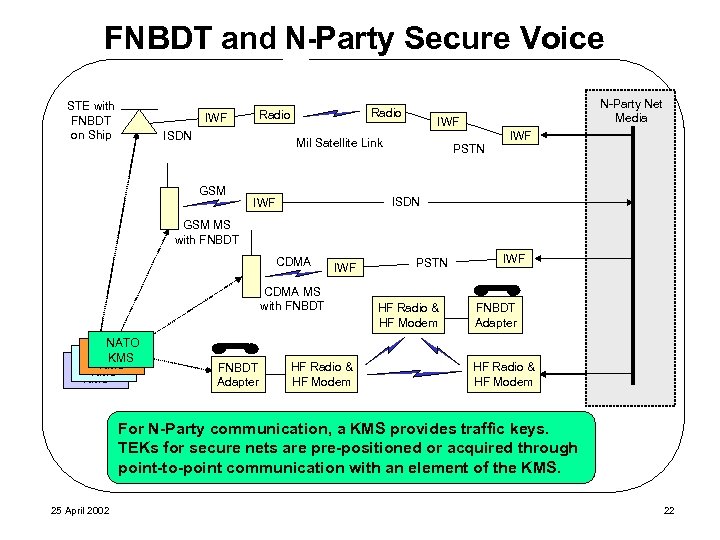
FNBDT and N 2 -Party Secure Voice STE with FNBDT on Ship IWF Radio ISDN IWF Mil Satellite Link GSM PSTN IWF ISDN Phone With FNBDT ISDN IWF GSM MS with FNBDT CDMA IWF CDMA MS with FNBDT NATO UK U. S. KMS Norway KMS KMS FNBDT Adapter HF Radio & HF Modem PSTN HF Radio & HF Modem N-Party Net Media CDMA MS with FNBDT IWF FNBDT Adapter HF Radio & HF Modem GSM MS With FNBDT Adapter For N-Party communication, a KMS the keying material. Key Management Systems provides traffic keys. FNBDT secure traffic signaling allows terminals on TEKs for secure. FNBDT terminals use “Call acquired through In 2 -party calls, nets are pre-positioned or Setup” signaling different networks to participate in a secure net. point-to-point communication withandelement of the KMS. to negotiate a cryptographic suite an a secure traffic mode. 25 April 2002 22
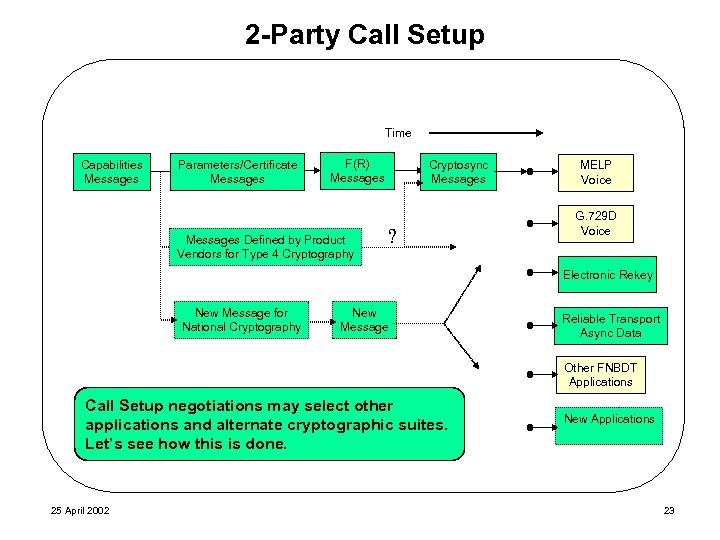
2 -Party Call Setup Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Electronic Rekey New Message for National Cryptography New Message Reliable Transport Async Data Other FNBDT Applications Call Setup negotiations may select other applications and alternate cryptographic suites. Let’s see how this is done. 25 April 2002 New Applications 23
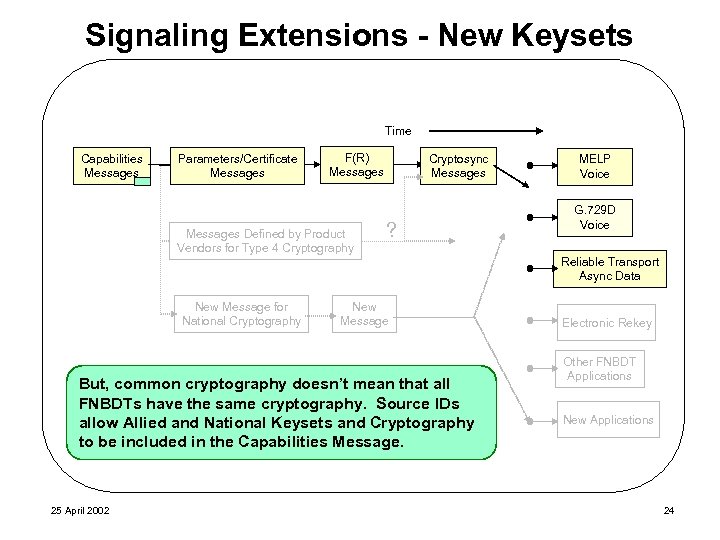
Signaling Extensions - New Keysets Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message But, common cryptography doesn’t mean that all FNBDTs have the same cryptography. Source IDs allow Allied and National Keysets and Cryptography to be included in the Capabilities Message. 25 April 2002 Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications New Applications 24
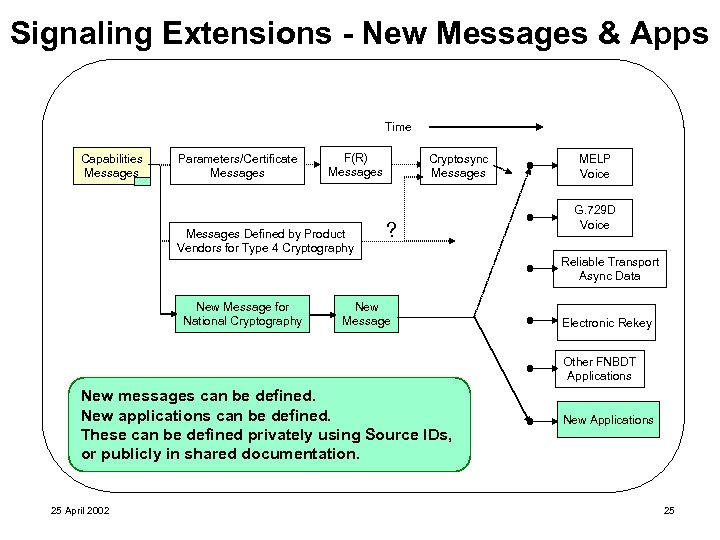
Signaling Extensions - New Messages & Apps Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications New messages can be defined. New applications can be defined. These can be defined privately using Source IDs, or publicly in shared documentation. 25 April 2002 New Applications 25
Interoperability and Extensions - Summary • In the past - Interoperability was not generally achievable – Basic designs were different – Private national implementations unique designs – Interoperability was denied with incompatible designs • FNBDT provides future interoperability – Basic FNBDT designs can be the same – Private national implementations unique FNBDT extensions – Interoperability can still be denied using different national key material FNBDT is designed to permit -Global, international interoperability And private, national implementations --The best of both worlds 25 April 2002 26
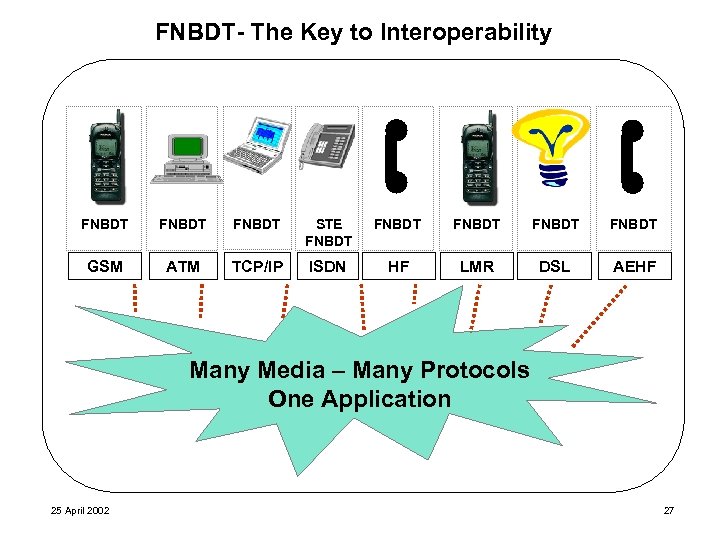
FNBDT- The Key to Interoperability FNBDT STE FNBDT FNBDT GSM ATM TCP/IP ISDN HF LMR DSL AEHF Many Media – Many Protocols One Application 25 April 2002 27
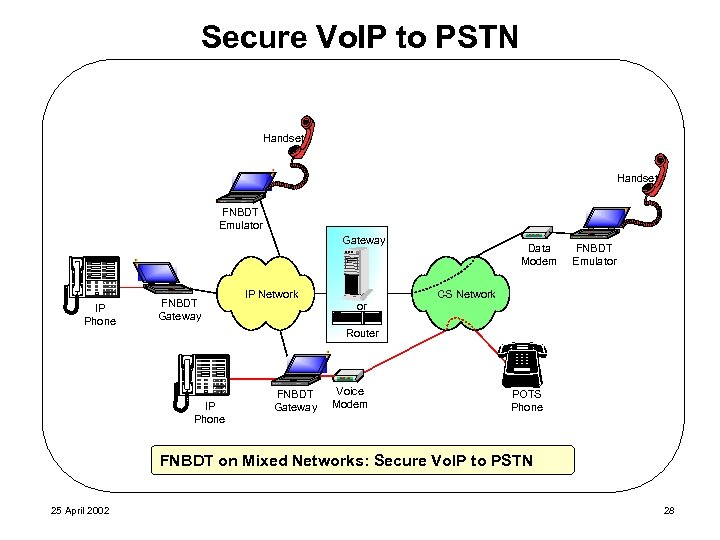
Secure Vo. IP to PSTN Handset FNBDT Emulator Gateway IP Phone FNBDT Gateway IP Network or Data Modem FNBDT Emulator CS Network Router IP Phone FNBDT Gateway Voice Modem POTS Phone FNBDT on Mixed Networks: Secure Vo. IP to PSTN 25 April 2002 28
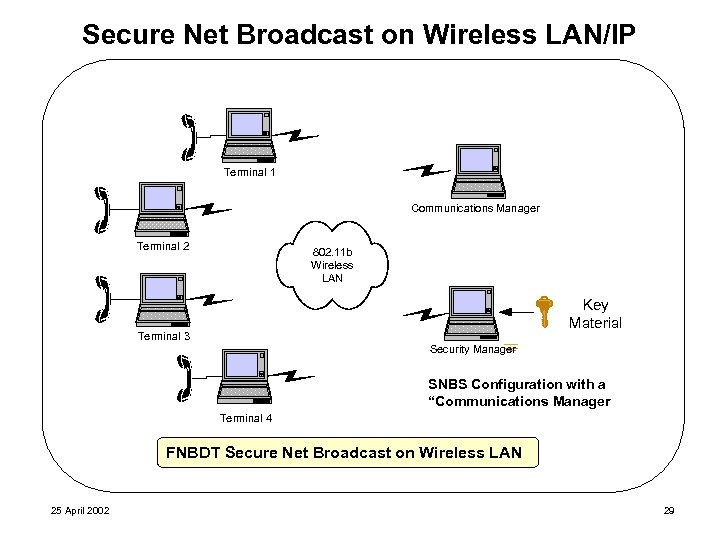
Secure Net Broadcast on Wireless LAN/IP Terminal 1 Communications Manager Terminal 2 802. 11 b Wireless LAN Key Material Terminal 3 Security Manager SNBS Configuration with a “Communications Manager Terminal 4 FNBDT Secure Net Broadcast on Wireless LAN 25 April 2002 29

Discussion/ Questions? 25 April 2002 30
FNBDT ----------Miscellaneous Examples 25 April 2002 31
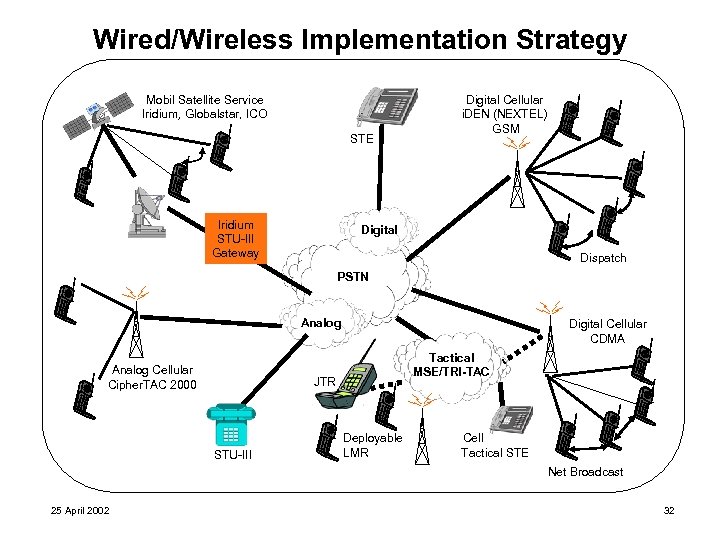
Wired/Wireless Implementation Strategy Mobil Satellite Service Iridium, Globalstar, ICO STE Iridium STU-III Gateway Digital Cellular i. DEN (NEXTEL) GSM Digital Dispatch PSTN Analog Cellular Cipher. TAC 2000 Digital Cellular CDMA Tactical MSE/TRI-TAC JTR STU-III Deployable LMR Cell Tactical STE Net Broadcast 25 April 2002 32
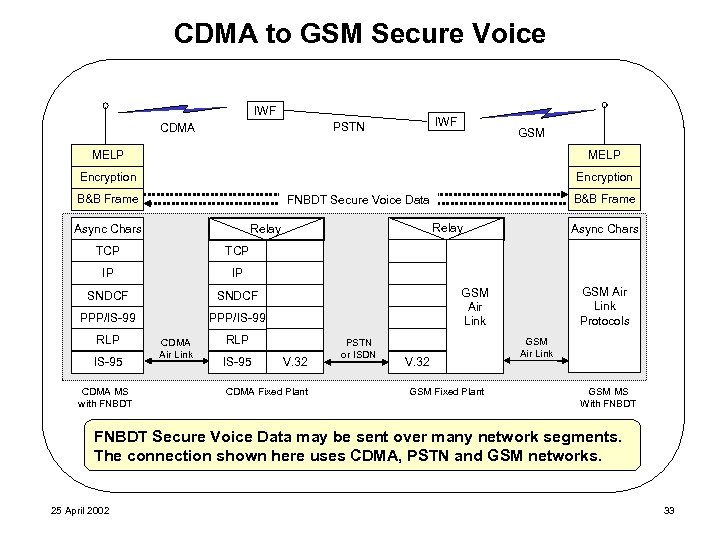
CDMA to GSM Secure Voice IWF PSTN CDMA GSM MELP Encryption B&B Frame FNBDT Secure Voice Data CDMA MS Async Chars with FNBDT TCP IP IP SNDCF PPP/IS-99 RLP IS-95 CDMA MS with FNBDT CDMA Air Link GSM Air Link Protocols GSM Air Link RLP IS-95 GS Chars Async MS With FNBDT Relay V. 32 CDMA Fixed Plant PSTN or ISDN V. 32 GSM Fixed Plant GSM Air Link GSM MS With FNBDT Secure Voice Data may be sent over many network segments. The connection shown here uses CDMA, PSTN and GSM networks. 25 April 2002 33
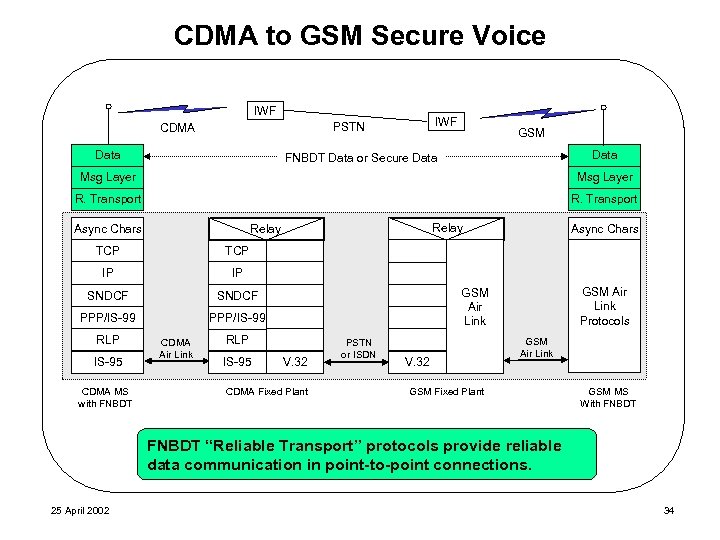
CDMA to GSM Secure Voice IWF PSTN CDMA MELP Data GSM MELP Data FNBDT Data or Secure Data Encryption Msg Layer R. Transport B&B Frame Async Chars Relay TCP IP IP SNDCF PPP/IS-99 Async Chars RLP IS-95 CDMA MS with FNBDT CDMA Air Link RLP IS-95 GSM Air Link Protocols GSM Air Link V. 32 CDMA Fixed Plant PSTN or ISDN V. 32 GSM Air Link GSM Fixed Plant GSM MS With FNBDT “Reliable Transport” protocols provide reliable data communication in point-to-point connections. 25 April 2002 34
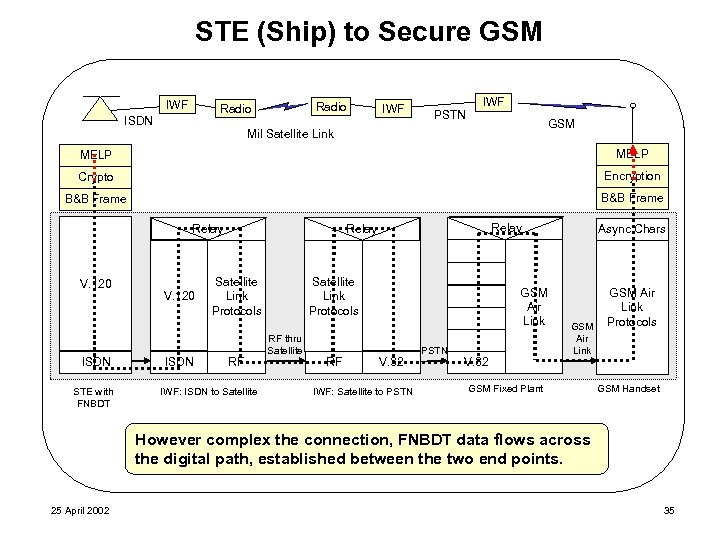
STE (Ship) to Secure GSM IWF Radio ISDN IWF PSTN IWF GSM Mil Satellite Link MELP Crypto Encryption B&B Frame Relay V. 120 ISDN STE with FNBDT V. 120 ISDN Relay Satellite Link Protocols RF IWF: ISDN to Satellite Link Protocols RF thru Satellite RF GSM Air Link V. 32 IWF: Satellite to PSTN V. 32 Async Chars GSM Air Link GSM Fixed Plant GSM Air Link Protocols GSM Handset However complex the connection, FNBDT data flows across the digital path, established between the two end points. 25 April 2002 35
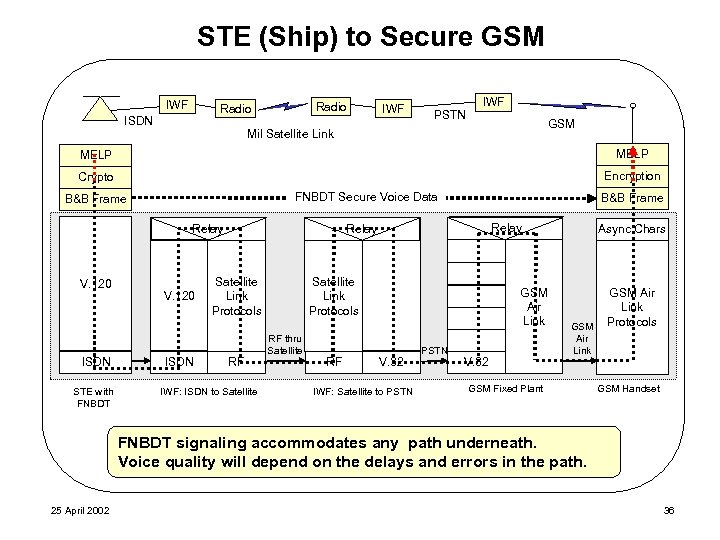
STE (Ship) to Secure GSM IWF Radio ISDN IWF PSTN IWF GSM Mil Satellite Link MELP Crypto Encryption FNBDT Secure Voice Data B&B Frame Relay V. 120 ISDN STE with FNBDT V. 120 ISDN B&B Frame Relay Satellite Link Protocols RF IWF: ISDN to Satellite Link Protocols RF thru Satellite RF GSM Air Link V. 32 IWF: Satellite to PSTN V. 32 Async Chars GSM Air Link GSM Fixed Plant GSM Air Link Protocols GSM Handset FNBDT signaling accommodates any path underneath. Voice quality will depend on the delays and errors in the path. 25 April 2002 36
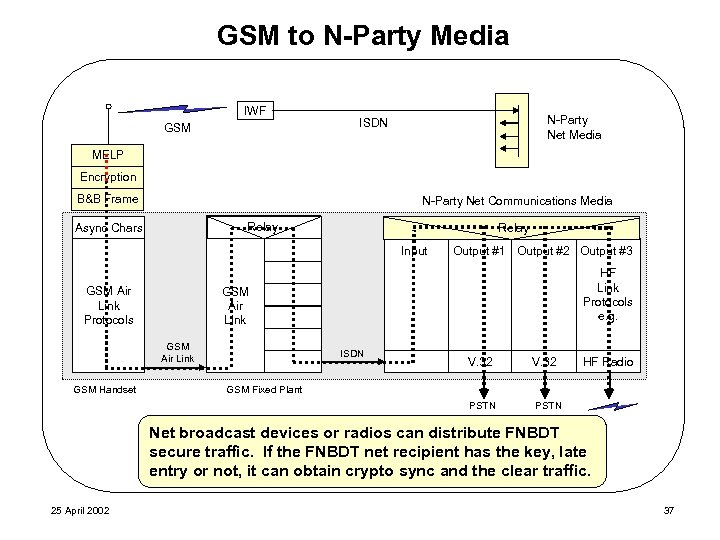
GSM to N-Party Media IWF GSM N-Party Net Media ISDN MELP Encryption B&B Frame N-Party Net Communications Media Relay Async Chars Relay Input GSM Air Link Protocols HF Link Protocols e. g. GSM Air Link GSM Handset Output #1 Output #2 Output #3 ISDN V. 32 HF Radio GSM Fixed Plant PSTN Net broadcast devices or radios can distribute FNBDT secure traffic. If the FNBDT net recipient has the key, late entry or not, it can obtain crypto sync and the clear traffic. 25 April 2002 37
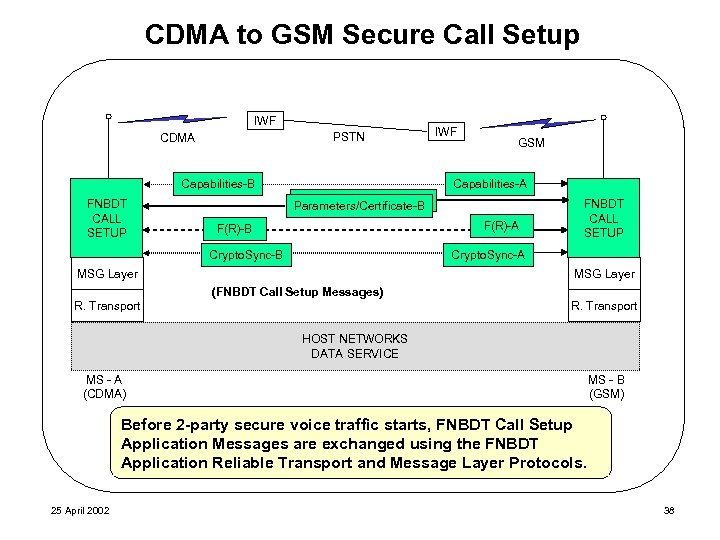
CDMA to GSM Secure Call Setup IWF PSTN CDMA Capabilities-B FNBDT CALL SETUP IWF GSM Capabilities-A Parameters/Certificate-B F(R)-A F(R)-B Crypto. Sync-B FNBDT CALL SETUP Crypto. Sync-A MSG Layer (FNBDT Call Setup Messages) R. Transport HOST NETWORKS DATA SERVICE MS - A (CDMA) MS - B (GSM) Before 2 -party secure voice traffic starts, FNBDT Call Setup Application Messages are exchanged using the FNBDT Application Reliable Transport and Message Layer Protocols. 25 April 2002 38
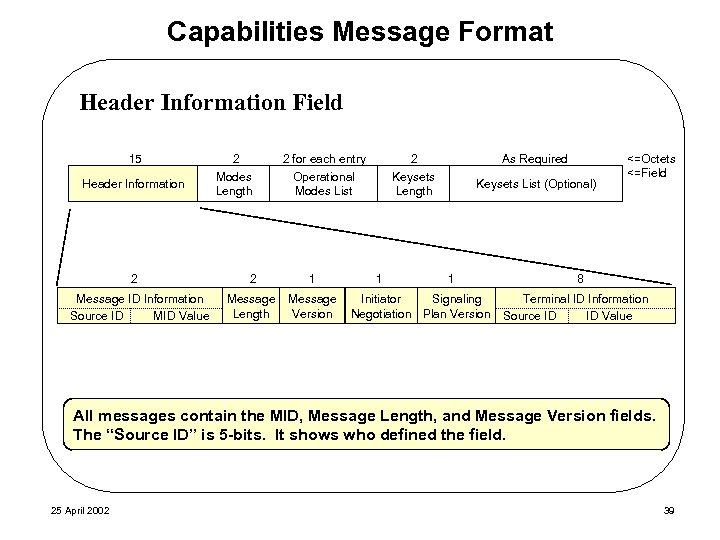
Capabilities Message Format Header Information Field 15 Header Information 2 Message ID Information Source ID MID Value 2 Modes Length 2 for each entry Operational Modes List 2 1 Message Length Message Version 2 Keysets Length 1 As Required Keysets List (Optional) 1 Initiator Signaling Negotiation Plan Version <=Octets <=Field 8 Terminal ID Information Source ID ID Value All messages contain the MID, Message Length, and Message Version fields. The “Source ID” is 5 -bits. It shows who defined the field. 25 April 2002 39
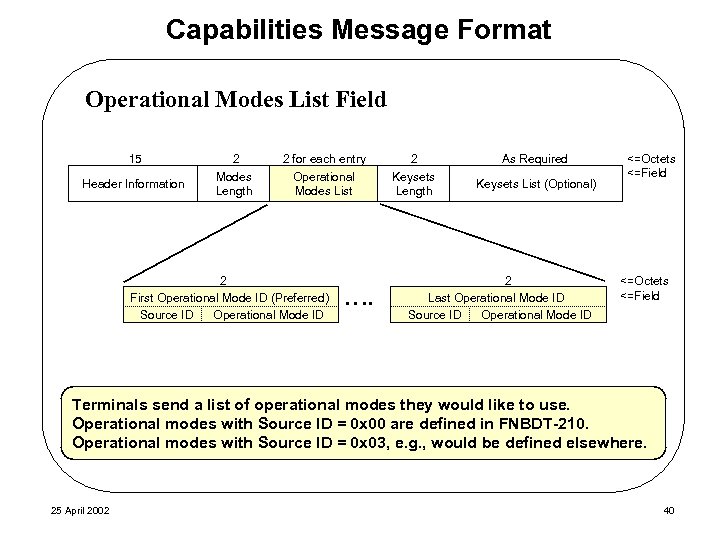
Capabilities Message Format Operational Modes List Field 15 Header Information 2 Modes Length 2 for each entry Operational Modes List 2 First Operational Mode ID (Preferred) Source ID Operational Mode ID …. 2 Keysets Length As Required Keysets List (Optional) 2 Last Operational Mode ID Source ID Operational Mode ID <=Octets <=Field Terminals send a list of operational modes they would like to use. Operational modes with Source ID = 0 x 00 are defined in FNBDT-210. Operational modes with Source ID = 0 x 03, e. g. , would be defined elsewhere. 25 April 2002 40
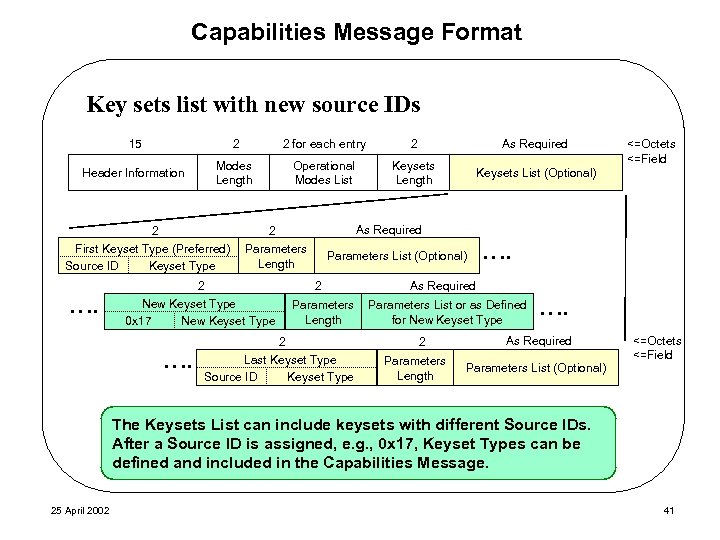
Capabilities Message Format Key sets list with new source IDs 15 2 2 for each entry 2 As Required Header Information Modes Length Operational Modes List Keysets Length Keysets List (Optional) 2 First Keyset Type (Preferred) Source ID Keyset Type …. As Required 2 Parameters Length 2 New Keyset Type 0 x 17 New Keyset Type <=Octets <=Field Parameters List (Optional) 2 Parameters Length 2 Last Keyset Type Source ID Keyset Type …. As Required Parameters List or as Defined for New Keyset Type 2 Parameters Length …. As Required Parameters List (Optional) <=Octets <=Field The Keysets List can include keysets with different Source IDs. After a Source ID is assigned, e. g. , 0 x 17, Keyset Types can be defined and included in the Capabilities Message. 25 April 2002 41
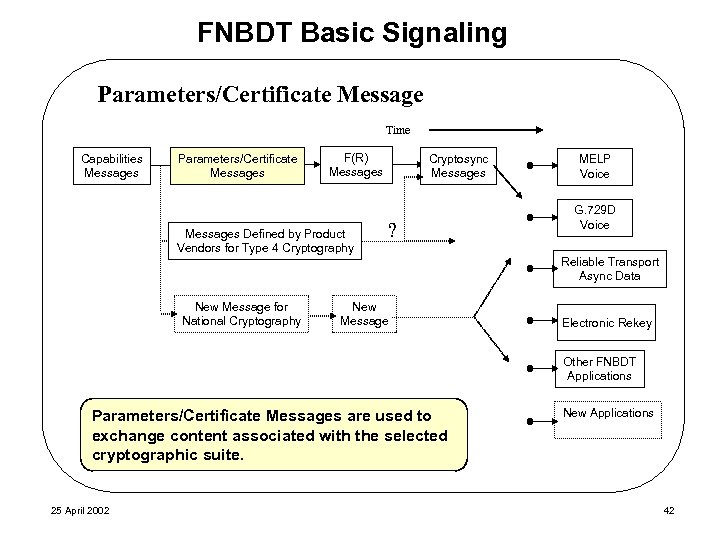
FNBDT Basic Signaling Parameters/Certificate Message Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications Parameters/Certificate Messages are used to exchange content associated with the selected cryptographic suite. 25 April 2002 New Applications 42
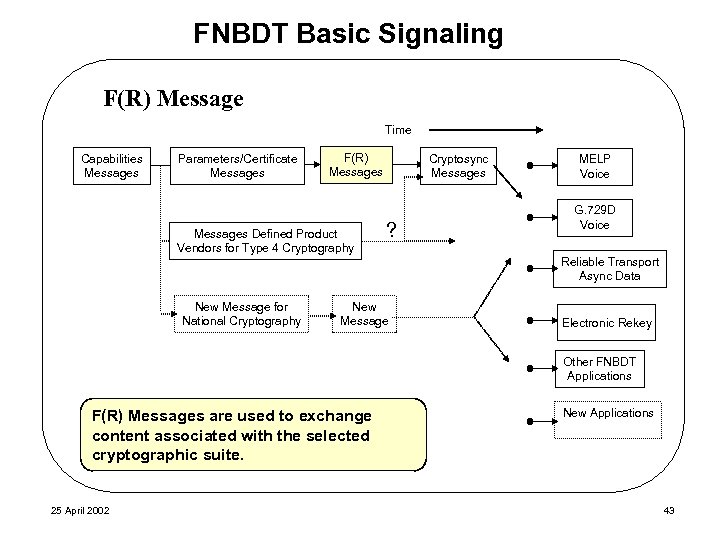
FNBDT Basic Signaling F(R) Message Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications F(R) Messages are used to exchange content associated with the selected cryptographic suite. 25 April 2002 New Applications 43
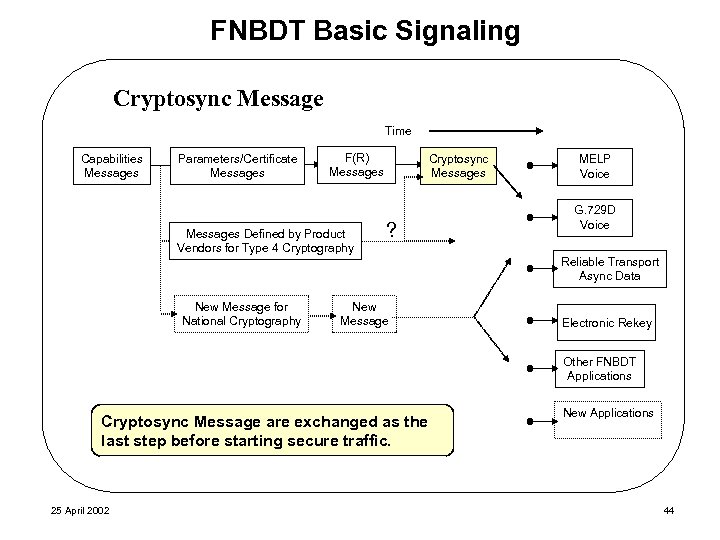
FNBDT Basic Signaling Cryptosync Message Time Capabilities Messages Parameters/Certificate Messages F(R) Messages Defined by Product Vendors for Type 4 Cryptography Cryptosync Messages ? MELP Voice G. 729 D Voice Reliable Transport Async Data New Message for National Cryptography New Message Electronic Rekey Other FNBDT Applications Cryptosync Message are exchanged as the last step before starting secure traffic. 25 April 2002 New Applications 44
ff288e9ff35d318ecb5d92d5ae288d1a.ppt