09d07312d2078fefcd92ffeb3143c127.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 The French Revolution
The French Revolution
 n The French Revolution was a major transformation of the societal and political systems of France.
n The French Revolution was a major transformation of the societal and political systems of France.
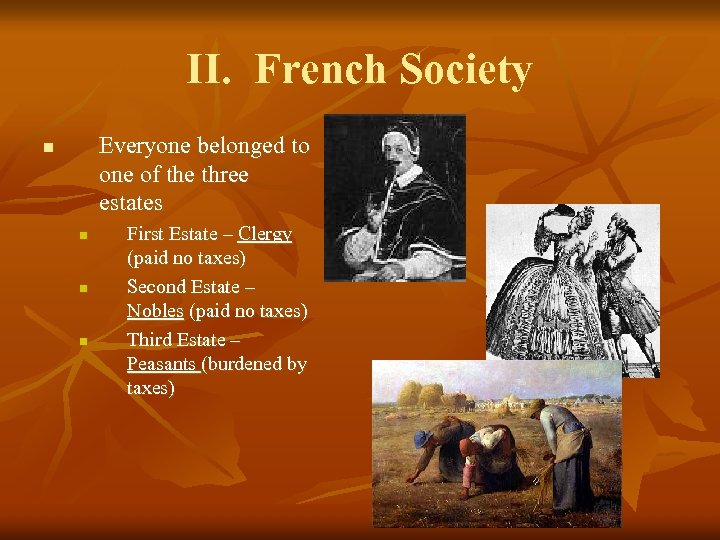 II. French Society Everyone belonged to one of the three estates n n First Estate – Clergy (paid no taxes) Second Estate – Nobles (paid no taxes) Third Estate – Peasants (burdened by taxes)
II. French Society Everyone belonged to one of the three estates n n First Estate – Clergy (paid no taxes) Second Estate – Nobles (paid no taxes) Third Estate – Peasants (burdened by taxes)
 III. France in Crisis n n n Government had spent more money than it had earned for many years. Bad harvests caused food prices to rise; many peasants did not have enough to eat; starving people rioting. King Louis XVI calls the Estates General n n Each estate has different ideas on how to solve nation’s problems Reach a stalemate on the voting issue n n First & Second Estates wanted each estate to vote separately with each group counting as one vote Third Estate wanted all three groups to meet as a single body and votes to be counted by head. n After weeks of deadlock, the Third Estate met and claimed to represent the people of France and declared themselves the National Assembly.
III. France in Crisis n n n Government had spent more money than it had earned for many years. Bad harvests caused food prices to rise; many peasants did not have enough to eat; starving people rioting. King Louis XVI calls the Estates General n n Each estate has different ideas on how to solve nation’s problems Reach a stalemate on the voting issue n n First & Second Estates wanted each estate to vote separately with each group counting as one vote Third Estate wanted all three groups to meet as a single body and votes to be counted by head. n After weeks of deadlock, the Third Estate met and claimed to represent the people of France and declared themselves the National Assembly.
 IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n n n The National Assembly is formed and the Tennis Oath taken July 14, 1789 – Storming of the Bastille France is in turmoil n n Famine causes violent attacks on nobles Paris – factions competing for power
IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n n n The National Assembly is formed and the Tennis Oath taken July 14, 1789 – Storming of the Bastille France is in turmoil n n Famine causes violent attacks on nobles Paris – factions competing for power
 IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n The National Assembly meets n n Feudalism is abolished Issues the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen. n n states all men have natural rights; government must protect those rights guarantees all male citizens equality under the law
IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n The National Assembly meets n n Feudalism is abolished Issues the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen. n n states all men have natural rights; government must protect those rights guarantees all male citizens equality under the law
 IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n 1791 the National Assembly completes the constitution n n creates a limited monarchy n executive - king n legislative – Legislative Assembly n judicial – Judicial Board reformed French laws supported free trade took control of French Catholic Church n seized lands to pay government debt n causes tensions between revolutionaries in Paris and peasants in provinces Stop!
IV. Phase I (1789 -1791) n 1791 the National Assembly completes the constitution n n creates a limited monarchy n executive - king n legislative – Legislative Assembly n judicial – Judicial Board reformed French laws supported free trade took control of French Catholic Church n seized lands to pay government debt n causes tensions between revolutionaries in Paris and peasants in provinces Stop!
 V. Phase 2 (1792 -1793) A period of escalating violence that leads to the Reign of Terror. n n 1792 France declares war on much of Europe n n many defeats; people believe King is helping the enemy Radical revolutionaries take control of the assembly in 1792 n n Ended the monarchy Made France a republic n Elected a new legislative body called the National Convention Wrote another constitution 1793 executed the king and queen for treason
V. Phase 2 (1792 -1793) A period of escalating violence that leads to the Reign of Terror. n n 1792 France declares war on much of Europe n n many defeats; people believe King is helping the enemy Radical revolutionaries take control of the assembly in 1792 n n Ended the monarchy Made France a republic n Elected a new legislative body called the National Convention Wrote another constitution 1793 executed the king and queen for treason
 VI. Phase 3 (1793 -1794) – “Reign of Terror” n 1793 – France in chaos n n n At war with most of Europe Peasants rioting for food Revolutionary groups fighting for power
VI. Phase 3 (1793 -1794) – “Reign of Terror” n 1793 – France in chaos n n n At war with most of Europe Peasants rioting for food Revolutionary groups fighting for power
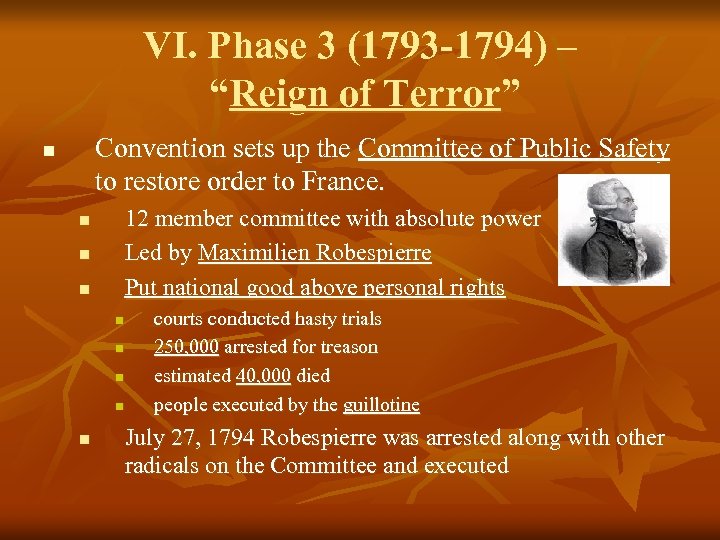 VI. Phase 3 (1793 -1794) – “Reign of Terror” Convention sets up the Committee of Public Safety to restore order to France. n n 12 member committee with absolute power Led by Maximilien Robespierre Put national good above personal rights n n n courts conducted hasty trials 250, 000 arrested for treason estimated 40, 000 died people executed by the guillotine July 27, 1794 Robespierre was arrested along with other radicals on the Committee and executed
VI. Phase 3 (1793 -1794) – “Reign of Terror” Convention sets up the Committee of Public Safety to restore order to France. n n 12 member committee with absolute power Led by Maximilien Robespierre Put national good above personal rights n n n courts conducted hasty trials 250, 000 arrested for treason estimated 40, 000 died people executed by the guillotine July 27, 1794 Robespierre was arrested along with other radicals on the Committee and executed

 VII. Phase 4 (1795 -1799) – “The Directory” n Constitution of 1795 n n Set up a five-man Directory and a two-house legislature elected by male citizens of property Discontent continued in France and many politicians looked to Napoleon Bonaparte to advance their own goals.
VII. Phase 4 (1795 -1799) – “The Directory” n Constitution of 1795 n n Set up a five-man Directory and a two-house legislature elected by male citizens of property Discontent continued in France and many politicians looked to Napoleon Bonaparte to advance their own goals.


