71c8db29941dd5293cddf7f91fb26524.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 The Formal Approach to Computer Game Rule Development Automation Elena Pavlova Moscow Engineering-Physics Institute (National Nuclear Research University), Ph. D student 05. 13. 11
The Formal Approach to Computer Game Rule Development Automation Elena Pavlova Moscow Engineering-Physics Institute (National Nuclear Research University), Ph. D student 05. 13. 11
 Agenda • Game rule development: automation problem • Turn-based strategy game rule description language • Formal game rule verification method • Prototype rules development environment • Summary
Agenda • Game rule development: automation problem • Turn-based strategy game rule description language • Formal game rule verification method • Prototype rules development environment • Summary
 Game rules include the definition of • specific game world entities • entity interaction rules • the main goal of the game and secondary goals • start conditions and winning conditions • player state definition Rule examples: • A troop, moved to a map cell with an enemy’s town, must fight or run away • Building a castle requires 3000 stones and 100 bars of gold
Game rules include the definition of • specific game world entities • entity interaction rules • the main goal of the game and secondary goals • start conditions and winning conditions • player state definition Rule examples: • A troop, moved to a map cell with an enemy’s town, must fight or run away • Building a castle requires 3000 stones and 100 bars of gold
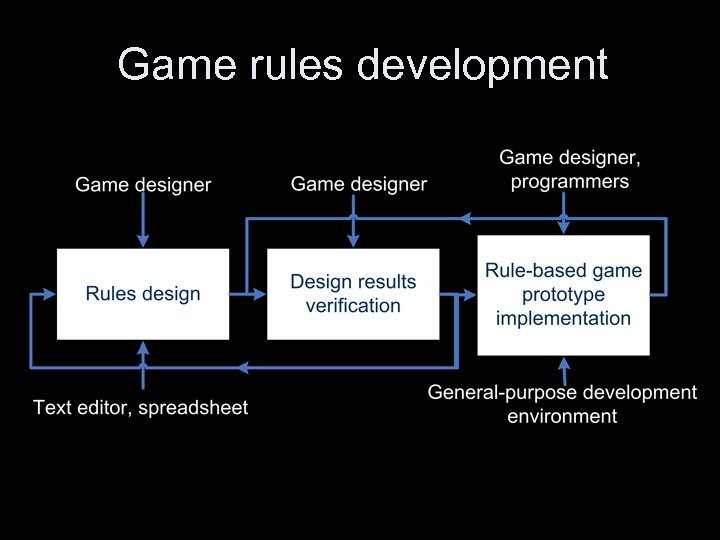 Game rules development
Game rules development
 Object The object of this paper is to develop an approach to game rule development allowing • formal visual rule design • automated rule verification • rule-based code and data generation • Game class specificity consideration
Object The object of this paper is to develop an approach to game rule development allowing • formal visual rule design • automated rule verification • rule-based code and data generation • Game class specificity consideration
 Rules description language The language allows to describe • specific game domain entities (entity data and behavior) • entity behavior constraints • entity relations • the reaction of entities to another entity behavior
Rules description language The language allows to describe • specific game domain entities (entity data and behavior) • entity behavior constraints • entity relations • the reaction of entities to another entity behavior
 Game rule example “The town attack” An army may attack a town if • it is an enemy’s town • army move’s count is greater than 0 (the army still can make a move) When the army attacks the town, the army move’s count is decreased by 1. The population of the town may defend it. The player who possesses the town should be informed about the attack.
Game rule example “The town attack” An army may attack a town if • it is an enemy’s town • army move’s count is greater than 0 (the army still can make a move) When the army attacks the town, the army move’s count is decreased by 1. The population of the town may defend it. The player who possesses the town should be informed about the attack.
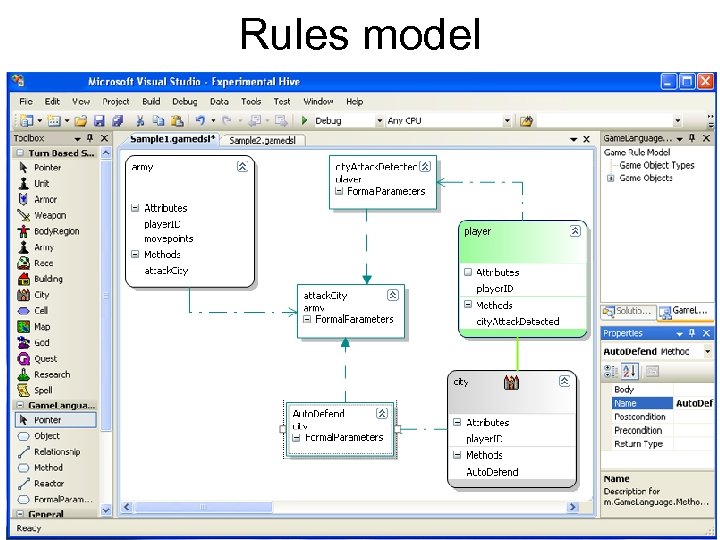 Rules model
Rules model
 Rules in the language textual notation army = Army, player. ID : 1, movepoints : 5, attack. City ( city : City ) { ((army. player. ID != city. player. ID) and ( army. movepoints > 0 )) attack. City. Body (army. movepoints = army. movepoints - 1) } ; player = Player, player. ID : 1, city. Attack. Detected ( city : City ) { city. Attack. Detected. Precondition Body city. Attack. Detected. Post. Condition } ; city = City, player. ID : 1, auto. Defend () { auto. Defend. Precondition auto. Defend. Body auto. Defend. Post. Condition } ; Add. Reactor ( army. attack. City, city. auto. Defend); Add. Reactor (army. attack. City, player. city. Attack. Detected);
Rules in the language textual notation army = Army, player. ID : 1, movepoints : 5, attack. City ( city : City ) { ((army. player. ID != city. player. ID) and ( army. movepoints > 0 )) attack. City. Body (army. movepoints = army. movepoints - 1) } ; player = Player, player. ID : 1, city. Attack. Detected ( city : City ) { city. Attack. Detected. Precondition Body city. Attack. Detected. Post. Condition } ; city = City, player. ID : 1, auto. Defend () { auto. Defend. Precondition auto. Defend. Body auto. Defend. Post. Condition } ; Add. Reactor ( army. attack. City, city. auto. Defend); Add. Reactor (army. attack. City, player. city. Attack. Detected);
 Type System • Static typing • Type inference Language library includes • simple types for behavior constraints • types for turn-based strategy domain
Type System • Static typing • Type inference Language library includes • simple types for behavior constraints • types for turn-based strategy domain
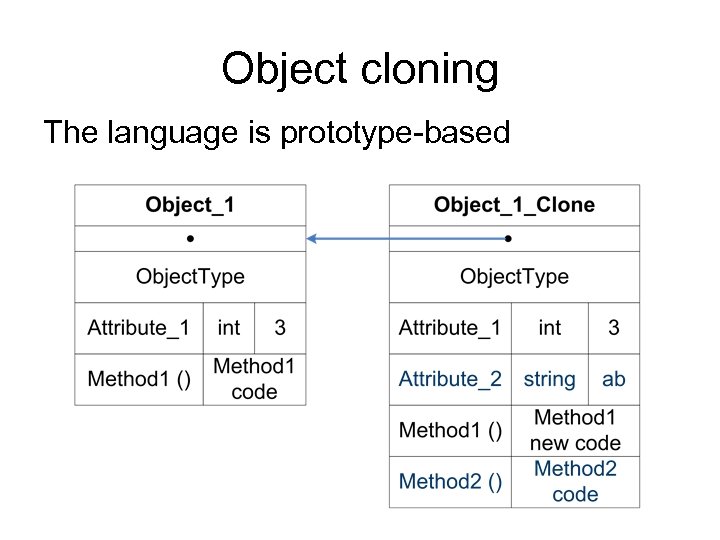 Object cloning The language is prototype-based
Object cloning The language is prototype-based
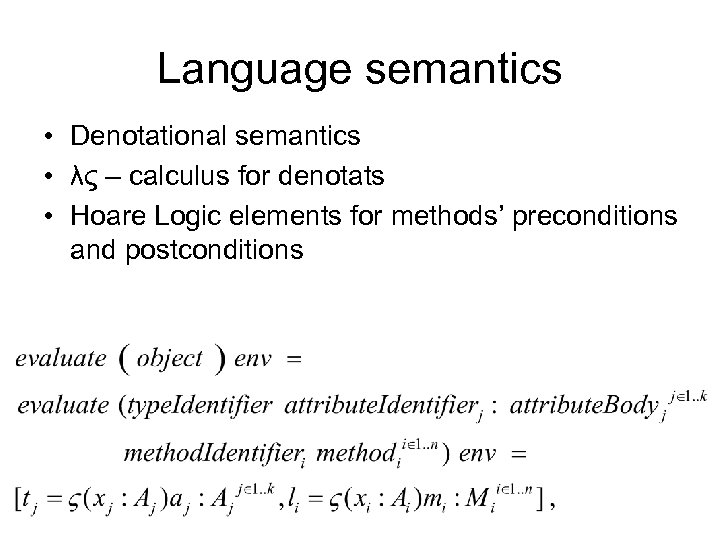 Language semantics • Denotational semantics • λς – calculus for denotats • Hoare Logic elements for methods’ preconditions and postconditions
Language semantics • Denotational semantics • λς – calculus for denotats • Hoare Logic elements for methods’ preconditions and postconditions
 Rules model verification • Rules model consistency – static analysis § Syntactic model consistency § Semantic model consistency • Static balance – formal properties monitoring § Superior side detection § Invincible troops detection § First turn superiority detection • Dynamic balance - automated theorem proving § Turn result superiority detection
Rules model verification • Rules model consistency – static analysis § Syntactic model consistency § Semantic model consistency • Static balance – formal properties monitoring § Superior side detection § Invincible troops detection § First turn superiority detection • Dynamic balance - automated theorem proving § Turn result superiority detection
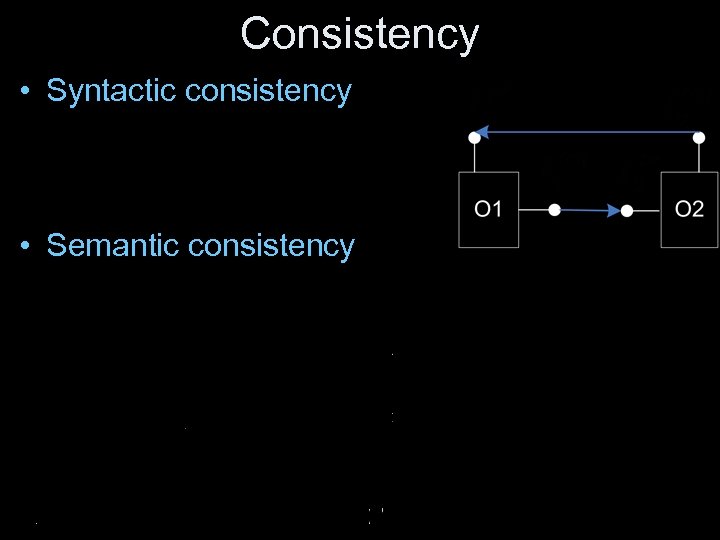 Consistency • Syntactic consistency • Semantic consistency
Consistency • Syntactic consistency • Semantic consistency
 Dynamic balance Each turn the game is fair. • The turn invariant is placed into appropriate methods (related to the end of turn event) • Rule model described in the formal language designed is converted into the automatic theorem prover input format (ESC/Java) • The theorem prover attempts to verify the model
Dynamic balance Each turn the game is fair. • The turn invariant is placed into appropriate methods (related to the end of turn event) • Rule model described in the formal language designed is converted into the automatic theorem prover input format (ESC/Java) • The theorem prover attempts to verify the model
 Summary The approach to game rule development was suggested. The approach allows • • formal visual rule design rule verification rule-based code and data generation game class specificity consideration
Summary The approach to game rule development was suggested. The approach allows • • formal visual rule design rule verification rule-based code and data generation game class specificity consideration
 References • • • Torque. Engine. Advanced – http: //www. garagegames. com/products/torque/tgea/features/ FPS Creator – http: //www. darkgamestudio. com/ Neo. Axis. Engine – http: //www. neoaxisgroup. com/description. htm Offset Engine – http: //www. projectoffset. com/game. html Unreal Engine – http: //www. unrealtechnology. com/html/technology/ue 30. shtml C 4 Engine – http: //www. terathon. com/c 4 engine/features. php • Moreno-Ger P. , Martinez-Ortiz I. , Sierra J. L. , Fernandez-Manjon B. Language-Driven Development of Videogames: The
References • • • Torque. Engine. Advanced – http: //www. garagegames. com/products/torque/tgea/features/ FPS Creator – http: //www. darkgamestudio. com/ Neo. Axis. Engine – http: //www. neoaxisgroup. com/description. htm Offset Engine – http: //www. projectoffset. com/game. html Unreal Engine – http: //www. unrealtechnology. com/html/technology/ue 30. shtml C 4 Engine – http: //www. terathon. com/c 4 engine/features. php • Moreno-Ger P. , Martinez-Ortiz I. , Sierra J. L. , Fernandez-Manjon B. Language-Driven Development of Videogames: The
 References 2 • • Clarke E. M. , Grumberg O. , Peled D. A. Model Checking. - The MIT Press, 1999 V. V. Kulyamin, “Software verification methods, ” Russian State Analytical-Review Articles Contest for Priority Concept “Information-Telecommunication Systems, 2008. (in Russian. ). Baier Ch. , Katoen J. -P. , Larsen K. G. Principles of Model Checking. - The MIT Press, 2008 Mosses P. D. Fundamental Concepts and Formal Semantics of Programming Languages – An Introductory Course. – http: //wiki. daimi. au. dk/d. Sprog. Sem-01, 2002 Abadi M. , Cardelli L. A Theory of Objects. – New York: Springer, 1996 Hoare C. An Axiomatic Basis of Computer Programming. Communications of the ACM, v. 12. – New York: ACM Press, 1969 A. V. Gavrilov, E. A. Pavlova, “Functional interface analysis formalization of complex information system design, ” Information Technologies, #9, pp. 9 -15, 2008. (in Russian). E. A. Pavlova, “Design of formal domain-specific language for computer game rules development for turn-based strategy game genre, ” Computer and Information Technology Reporter #4, April. 2009. (in Russian).
References 2 • • Clarke E. M. , Grumberg O. , Peled D. A. Model Checking. - The MIT Press, 1999 V. V. Kulyamin, “Software verification methods, ” Russian State Analytical-Review Articles Contest for Priority Concept “Information-Telecommunication Systems, 2008. (in Russian. ). Baier Ch. , Katoen J. -P. , Larsen K. G. Principles of Model Checking. - The MIT Press, 2008 Mosses P. D. Fundamental Concepts and Formal Semantics of Programming Languages – An Introductory Course. – http: //wiki. daimi. au. dk/d. Sprog. Sem-01, 2002 Abadi M. , Cardelli L. A Theory of Objects. – New York: Springer, 1996 Hoare C. An Axiomatic Basis of Computer Programming. Communications of the ACM, v. 12. – New York: ACM Press, 1969 A. V. Gavrilov, E. A. Pavlova, “Functional interface analysis formalization of complex information system design, ” Information Technologies, #9, pp. 9 -15, 2008. (in Russian). E. A. Pavlova, “Design of formal domain-specific language for computer game rules development for turn-based strategy game genre, ” Computer and Information Technology Reporter #4, April. 2009. (in Russian).
 Summary The approach to game rule development was suggested. The approach allows • • formal visual rule design rule verification rule-based code and data generation game class specificity consideration Elena. pav@gmail. com
Summary The approach to game rule development was suggested. The approach allows • • formal visual rule design rule verification rule-based code and data generation game class specificity consideration Elena. pav@gmail. com
 A type system is a tractable syntactic method for proving the absence of certain program behaviors by classifying phrases according to the kinds of values they compute. Benjamin Pierce ”Types and Programming Languages”
A type system is a tractable syntactic method for proving the absence of certain program behaviors by classifying phrases according to the kinds of values they compute. Benjamin Pierce ”Types and Programming Languages”
 Object unit = Unit, power : 2, arrows_count : 5, attack. Method ( unit_to_attack : Unit, cell : Cell ) { precondition method. Body postcondition };
Object unit = Unit, power : 2, arrows_count : 5, attack. Method ( unit_to_attack : Unit, cell : Cell ) { precondition method. Body postcondition };
 Method attack. Method ( unit_to_attack : Unit, cell : Cell ) { ( arrows_count > 0 ) and ( power > 1) method. Body ( arrows_count = arrows_count – 1) and ( power = power – 2 ) };
Method attack. Method ( unit_to_attack : Unit, cell : Cell ) { ( arrows_count > 0 ) and ( power > 1) method. Body ( arrows_count = arrows_count – 1) and ( power = power – 2 ) };
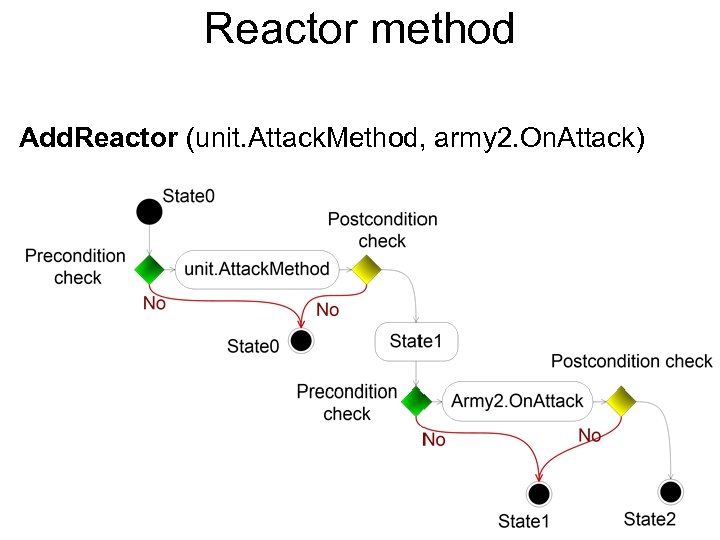 Reactor method Add. Reactor (unit. Attack. Method, army 2. On. Attack)
Reactor method Add. Reactor (unit. Attack. Method, army 2. On. Attack)
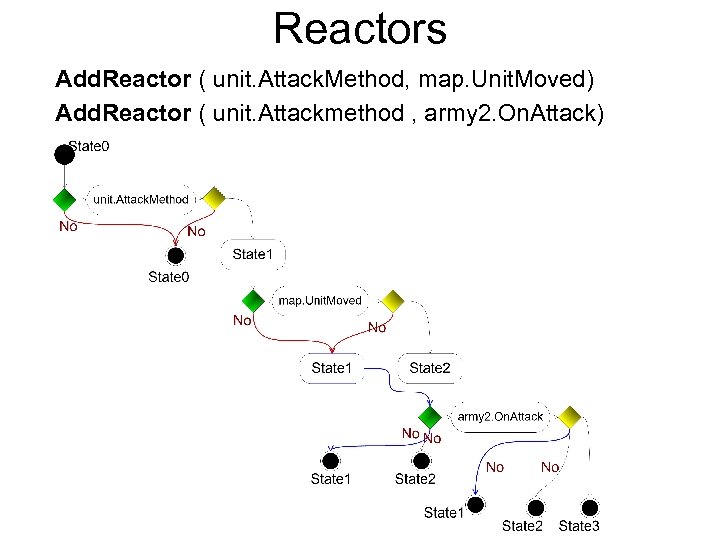 Reactors Add. Reactor ( unit. Attack. Method, map. Unit. Moved) Add. Reactor ( unit. Attackmethod , army 2. On. Attack)
Reactors Add. Reactor ( unit. Attack. Method, map. Unit. Moved) Add. Reactor ( unit. Attackmethod , army 2. On. Attack)
 Static balance • Superior side detection • Invincible troops detection • First turn superiority detection The game is played according to the rules defined. Players are represented by simple AI module.
Static balance • Superior side detection • Invincible troops detection • First turn superiority detection The game is played according to the rules defined. Players are represented by simple AI module.
 Computer game is a game represented by a program for personal computer. Thus, we don’t consider games for mobile devices, consoles, etc.
Computer game is a game represented by a program for personal computer. Thus, we don’t consider games for mobile devices, consoles, etc.


