ef10006c63dc9275c0f4ac0f64bc1c03.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

The factor label method • A way to solve math problems in chemistry • Used to convert km to miles, m to km, mol to g, g to mol, etc. • To use this we need: 1) desired quantity, 2) given quantity, 3) conversion factors • Conversion factors are valid relationships or equities expressed as a fraction E. g. for 1 km=0. 6 miles the conversion factor is Q. write conversion factors for 1 foot =12 inches Q. what conversion factors can you think of that involve meters?

Conversion factors for 1 ft = 12 in There almost an infinite number of conversion factors that include meters:

Conversion factors • We have looked at conversion factors that are always true. There are conversion factors that are only true for specific questions • E. g. A recipe calls for 2 eggs, 1 cup of flour and 0. 5 cups of sugar • We can use these conversion factors

The steps to follow Now we are ready to solve problems using the factor label method. The steps involved are: 1. Write down the desired quantity/units 2. Equate the desired quantity to given quantity 3. Determine what conversion factors you can use (both universal and question specific) 4. Multiply given quantity by the appropriate conversion factors to eliminate units you don’t want and leave units you do want 5. Complete the math

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km First write down the desired quantity

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi Next, equate desired quantity to the given quantity
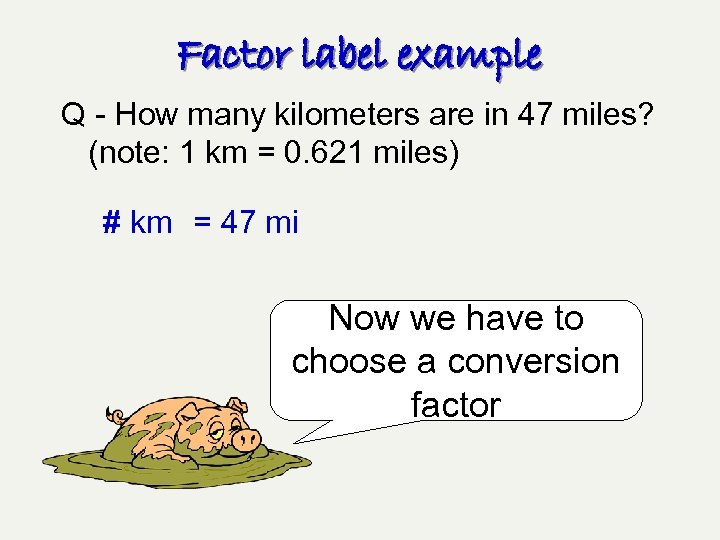
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi Now we have to choose a conversion factor

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi 1 km 0. 621 mi 1 km What conversion factors are possible?

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi 1 km 0. 621 mi 1 km Pick the one that will allow you to cancel out miles

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi 1 km 0. 621 mi 1 km Pick the one that will allow you to cancel out miles

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi 1 km 0. 621 mi 1 km Multiply given quantity by chosen conversion factor
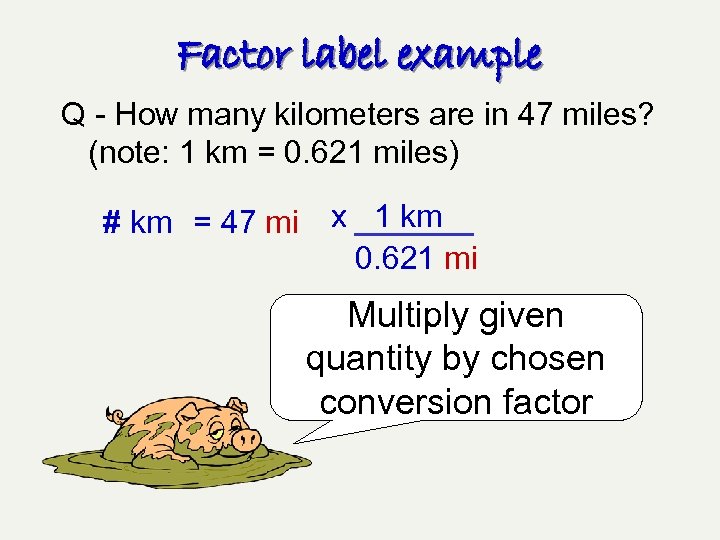
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi x 1 km 0. 621 mi Multiply given quantity by chosen conversion factor
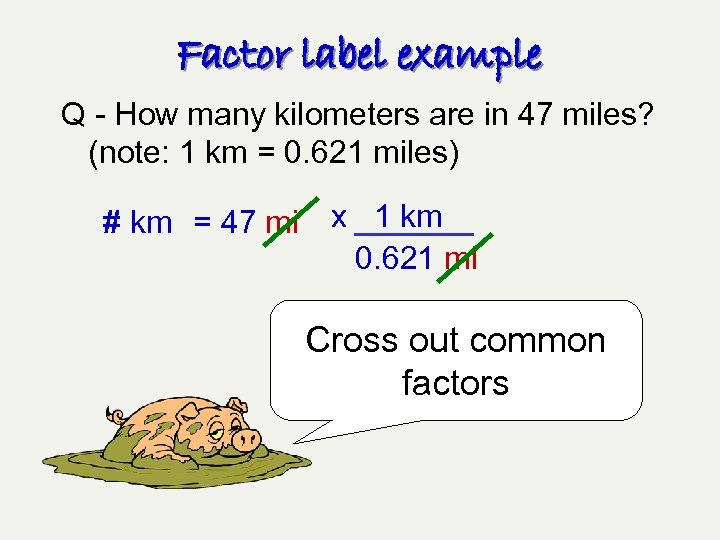
Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 mi x 1 km 0. 621 mi Cross out common factors

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 Cross out common factors

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 Are the units now correct?

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 Yes. Both sides have km as units.

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 Yes. Both sides have km as units.

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 = 75. 7 km Now finish the math.

Factor label example Q - How many kilometers are in 47 miles? (note: 1 km = 0. 621 miles) # km = 47 x 1 km 0. 621 = 75. 7 km The final answer is 75. 7 km

Summary The previous problem was not that hard (direct conversion). In other words, you probably could have done it faster using a different method; However, for harder problems (indirect conversions) the factor label method is easiest! Let’s try a few more direct conversions, then we can move to the indirect ones!!

More examples(Direct Conversion) 1. You want to buy 100 U. S. dollars. If the exchange rate is 1 Can$ = 0. 65 US$, how much will it cost? # Can$ = 100 US$ x 1 Can$ = 153. 85 Can$ 0. 65 US$

More examples(Direct Conversion) Conversion Factors Comparing Customary and Metric Units Length Mass/Weight Capacity 1 in = 2. 5 cm 1 kg = 2. 2 lb 1 L = 1. 1 qt 1 m = 1. 1 yd 1 oz = 28 g 1 k. L = 275 gal 1 mi = 1. 6 km Let’s get busy! 1. 20 yd = _______ m 2. 40 g = ________ oz 3. 15 mi = ________ km 4. 10 L = ________ qt 5. 4 km = ________ mi 6. 150 gal = _______ k. L
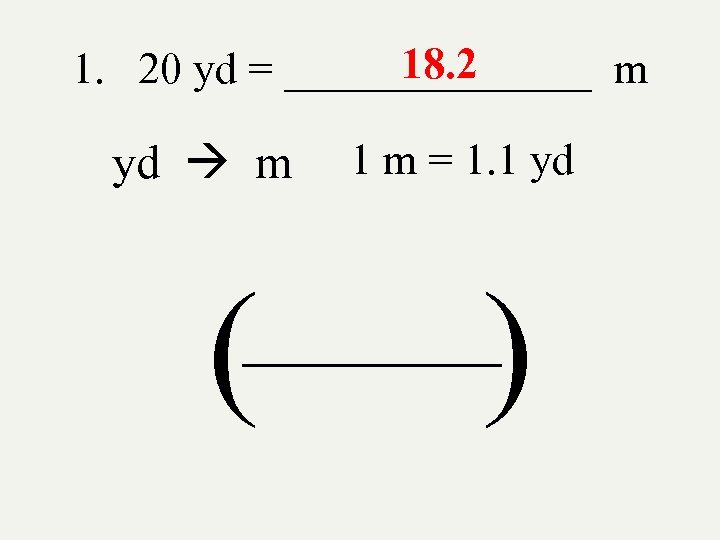
18. 2 1. 20 yd = _______ m yd m ( 1 m = 1. 1 yd ) _______
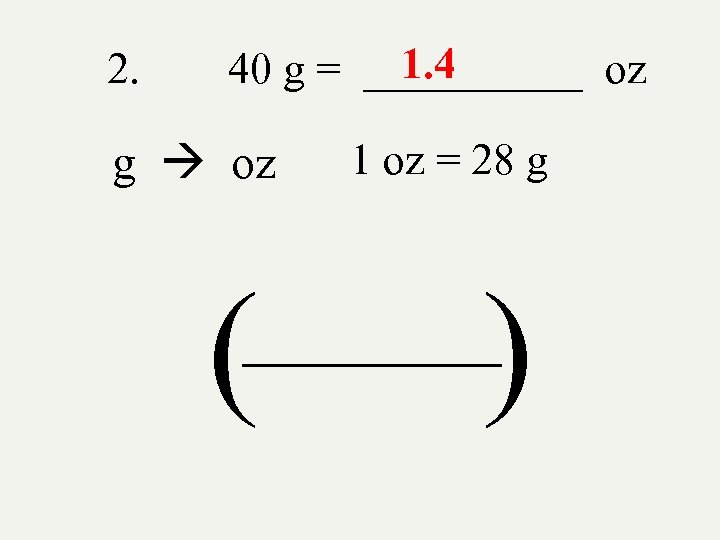
2. 1. 4 40 g = _____ oz g oz ( 1 oz = 28 g ) _______
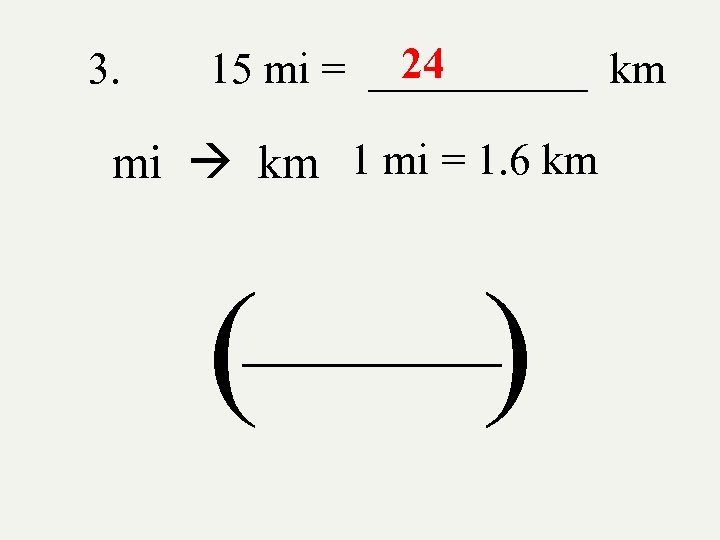
3. 24 15 mi = _____ km mi km 1 mi = 1. 6 km ( ) _______
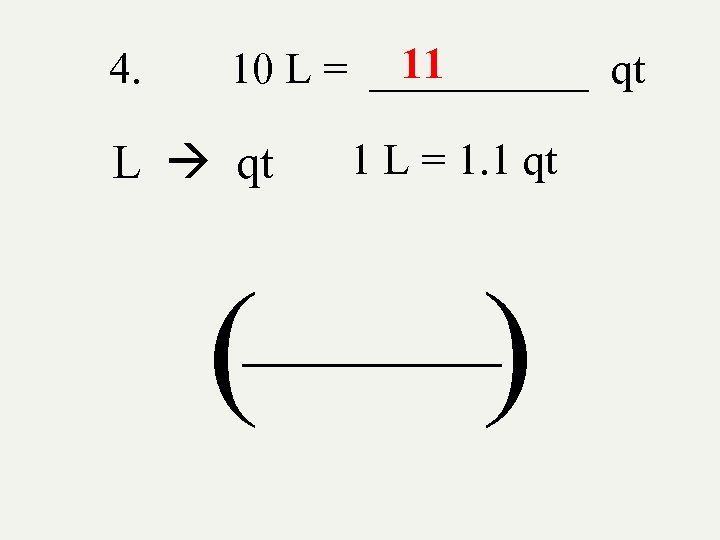
4. 11 10 L = _____ qt L qt ( 1 L = 1. 1 qt ) _______
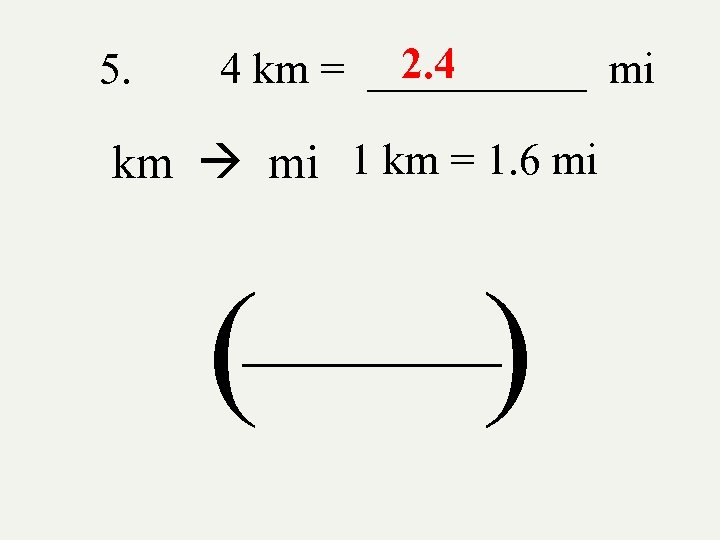
5. 2. 4 4 km = _____ mi km mi 1 km = 1. 6 mi ( ) _______
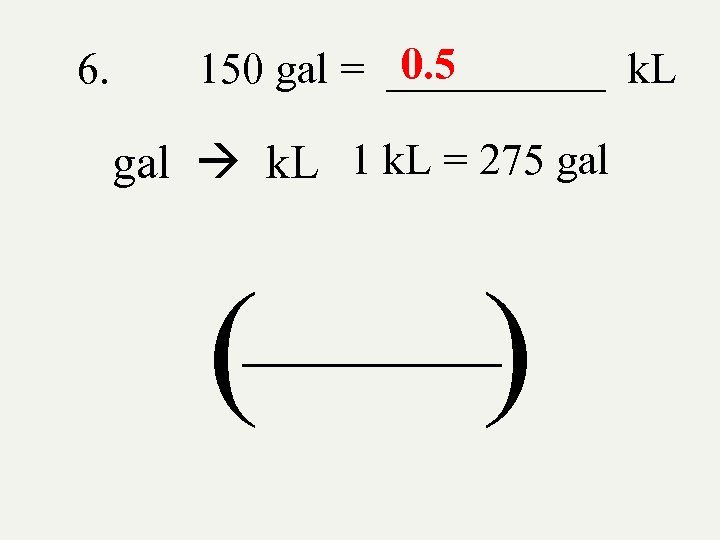
6. 0. 5 150 gal = _____ k. L gal k. L 1 k. L = 275 gal ( ) _______

More examples (Indirect Conversions) 1. There are 12 inches in a foot, 0. 394 inches in a centimeter, and 3 feet in a yard. How many cm are in one yard? yd ft in cm # cm = 1 yd x 3 ft x 12 in x 1 cm = 91. 37 cm 1 yd 1 ft 0. 394 in

Assignment Answer questions using the factor label method: 1. Calculate how many feet are in 1 meter (use information from the examples above). 2. With a U. S. dollar you can buy 1. 1 Euros, 130 Yen, or 25 Rubles. How many Yen can you buy with one Ruble?
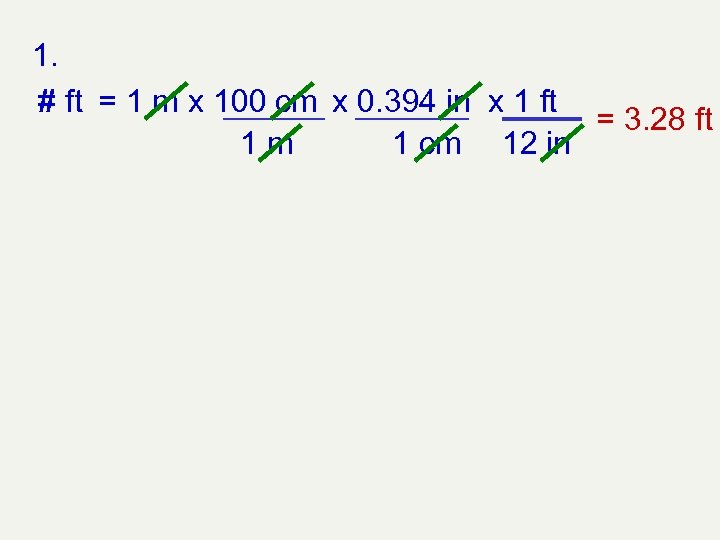
1. # ft = 1 m x 100 cm x 0. 394 in x 1 ft = 3. 28 ft 1 m 1 cm 12 in

2. # Yen = 1 Ruble x 1 US $ x 130 Yen = 5. 2 Yen 25 Rubles 1 US $
ef10006c63dc9275c0f4ac0f64bc1c03.ppt