797f686b1d47e54609f6420216c15d3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

The Executive Branch

Today’s Essential Question:

Why do you think the presidency is called a Glorious Burden? ?

Who assists the President? When George Washington was President, people recognized that one person could not carry out the duties of the President without advice and assistance.

The President receives help from the: Vice President Cabinet Members Heads of Independent and Executive Agencies. Unlike the powers of the President, their responsibilities are not defined in the Constitution.
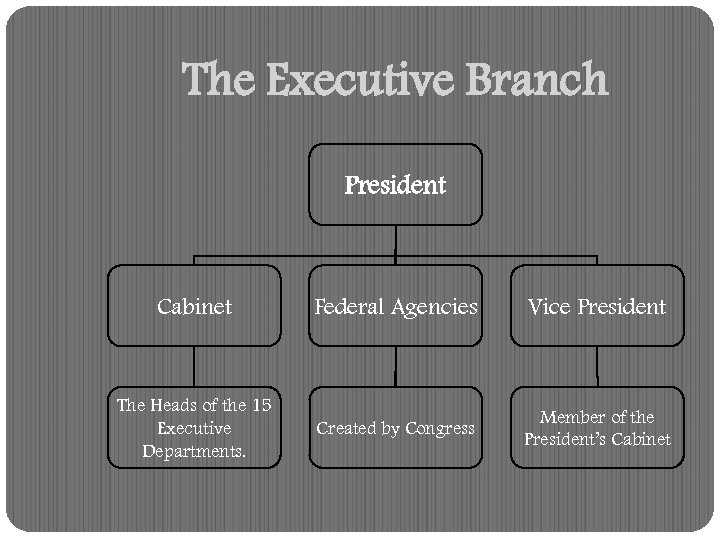
The Executive Branch President Cabinet Federal Agencies Vice President The Heads of the 15 Executive Departments. Created by Congress Member of the President’s Cabinet

The Presidency. A Glorious Burden. November 2007. Election Night. November 2011. Election Night.

Not Just President Obama…

Presidency Qualifications Native born citizen At least 35 years old U. S. Resident for 14 years I need to have all these Qualifications!!!!

Presidency Term of Office Elected to a 4 year term No term limits in the Constitution 22 nd Amendment set a 2 term limit

Presidency Salary and Benefits $400, 000 a year plus $50, 000 allowance Use of Air Force One and a fleet of cars and helicopters White House and Camp David
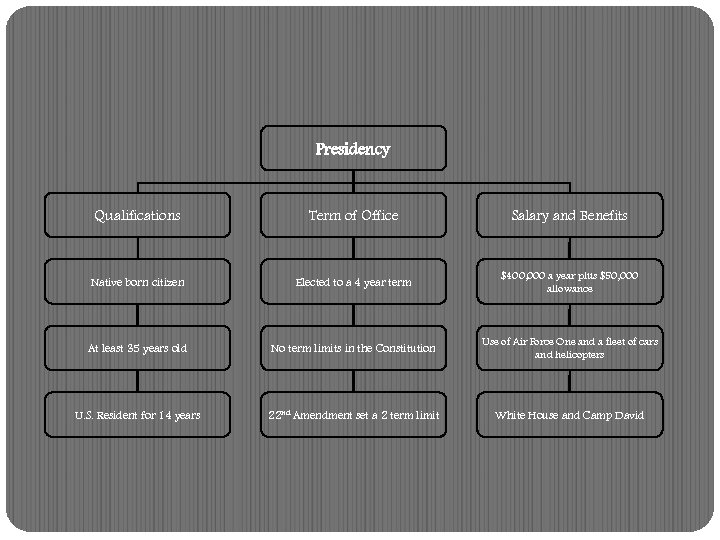
Presidency Qualifications Term of Office Salary and Benefits Native born citizen Elected to a 4 year term $400, 000 a year plus $50, 000 allowance At least 35 years old No term limits in the Constitution Use of Air Force One and a fleet of cars and helicopters U. S. Resident for 14 years 22 nd Amendment set a 2 term limit White House and Camp David

The Vice President You have a distinct old man smell, get away from me…… As soon as these cameras are gone so am I….
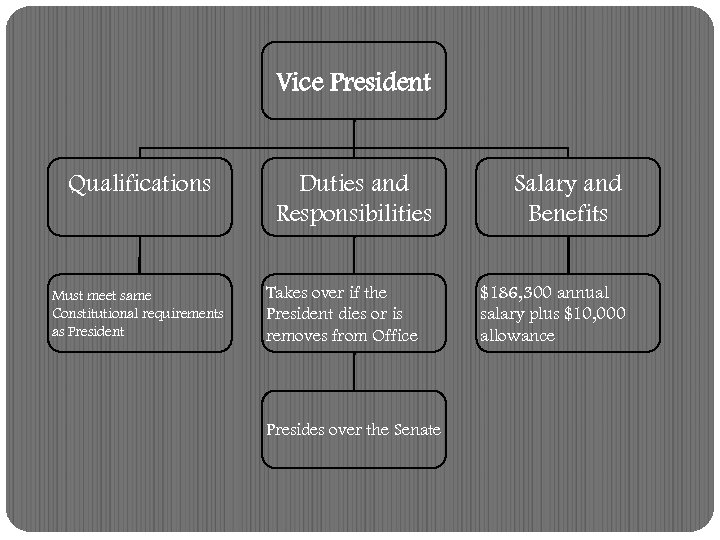
Vice President Qualifications Must meet same Constitutional requirements as President Duties and Responsibilities Takes over if the President dies or is removes from Office Presides over the Senate Salary and Benefits $186, 300 annual salary plus $10, 000 allowance

Presidential Succession Eight U. S. presidents have died while in office. One president resigned. In each case, the vice president took the oath of office and became president as provided by the Constitution.

William H. Harrison, Natural Causes John Tyler, Vice President

Zachary Taylor, Natural Causes Millard Fillmore, Vice President

Abraham Lincoln, Assassinated Andrew Johnson, Vice President

James A. Garfield, Assassinated Chester Author, Vice President

William Mc. Kinley, Assassinated Theodore Roosevelt, Vice President

Warren Harding, Natural Causes Calvin Coolidge, Vice President

Franklin D. Roosevelt, Natural Causes Harry Truman, Vice President

John F. Kennedy, Assassinated Lyndon Johnson, Vice President

Richard M. Nixon, Resigned Gerald R. Ford Vice President

Twenty-fifth Amendment adopted in 1967 new president nominates a new vice president Nomination must then be approved by a majority vote of both houses of Congress.

The Order of Presidential Succession The Vice President The Speaker of the House The President pro tempore of the Senate Members of the president’s cabinet in the order in which their departments were created

Departments in Succession Order Secretary of State Secretary of the Treasury Secretary of Defense Attorney General Secretary of the Interior Secretary of Agriculture Secretary of Commerce Secretary of Labor Secretary of Health and Human Services Secretary of Housing and Urban Development Secretary of Transportation Secretary of Energy Secretary of Education Secretary of Veterans Affairs Secretary of Homeland Security

7 Major Roles of the President 1. ) Chief Executive 2. ) Chief Diplomat 3. ) Commander in Chief 4. ) Political Party Leader 5. ) Legislative Leader 6. ) Judicial Leader 7. ) Chief of State

Powers and Duties of the President 1. ) Chief Executive § Carries out the nation’s laws § Issues Executive Orders (rule or command the President issues that has the force of law; usually during time of crisis) § Appoints cabinet members, ambassadors, judges, heads of govt. agencies

Powers and Duties of the President 2. ) Chief Diplomat § Responsible for making treaties with other countries with Senate approval § Meets with foreign leaders § Can make Executive Agreements with leaders of other countries ØHas the force of law but does not require Senate approval § Responsible for appointing ambassadors with Senate approval ØAn official representative of a country’s government

Powers and Duties of the President 3. ) Commander in Chief President is final authority over all military matters o Founding Fathers believed in civilian control over the military; person elected by the people has final say over all military matters President can use military in times of war. 1973: War Powers Act passed by Congress Ø President must notify Congress when troops sent anywhere Ø Troops must be brought home after 60 days unless Congress declares war, or gives approval for troops to stay. Controversial Law which has never been challenged in the Supreme Court; Checks and Balances issue?

When was the last time the United States passed a Formal Declaration of War? December 8, 1941. December 11, 1941. Japan Germany Italy

Powers and Duties of the President 4. ) Political Party Leader Supports party members in election campaigns and helps unify the party Appoints members of party to key govt. jobs

Powers and Duties of the President 5. ) Legislative Leader Proposes legislation and uses many tactics to get the bill passed Prepares the federal budget Approves or vetoes legislation

Powers and Duties of the President 6. ) Judicial Leader Appoints judges to Federal Courts and the U. S. Supreme Court § Appoints Justices whose point of view is similar to their own

Powers and Duties of the President 7. ) Chief of State Role is symbolic – President represents all Americans - Gives a human face to American govt. - Can be demonstrated in many ways Greeting heroes

Powers and Duties of the President 7. ) Chief of State (Continued) - Throwing first pitches at baseball games - Inviting musicians to perform at White House

Powers and Duties of the President 7. ) Chief of State (Continued) Attending funeral of another country’s leader. Speeches and Ceremonies

Checks and Balances

Executive Branch checks Legislative Branch on the Vetoes laws Calls Congress into special session

Executive Branch checks on the Judicial Branch Appoints federal judges

Legislative Branch Checks Powers OVER the President Senate approves treaties and presidential appointments The House of Representatives appropriates money; “power of the purse” Congress can override veto Congress can impeach and convict the President and Vice President

Judicial Branch Checks Powers over the President The Supreme Court can rule Executive Acts unconstitutional Hey What Do You Expect. . we only have one document to use here! Just follow it! Geez
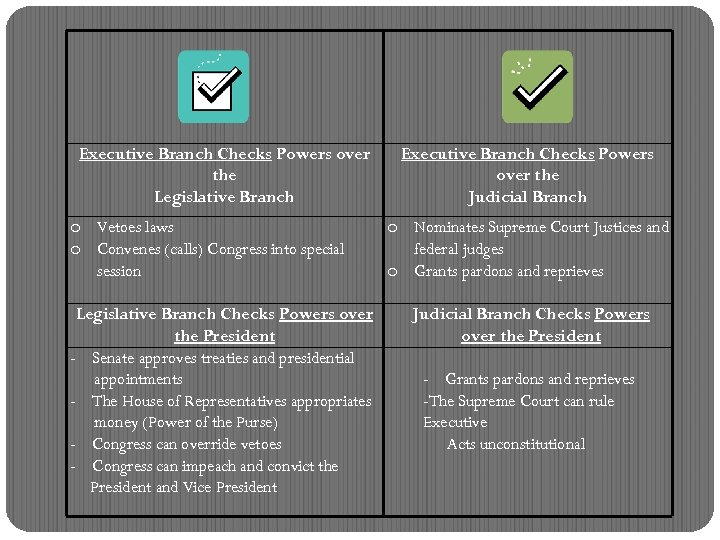
Executive Branch Checks Powers over the Legislative Branch o Vetoes laws o Convenes (calls) Congress into special session Legislative Branch Checks Powers over the President - Senate approves treaties and presidential appointments - The House of Representatives appropriates money (Power of the Purse) - Congress can override vetoes - Congress can impeach and convict the President and Vice President Executive Branch Checks Powers over the Judicial Branch o Nominates Supreme Court Justices and federal judges o Grants pardons and reprieves Judicial Branch Checks Powers over the President - Grants pardons and reprieves -The Supreme Court can rule Executive Acts unconstitutional

How the president influences policymaking (Laws/legislation)

The Executive Branch influences policymaking (laws) by: Proposing legislation (giving Congress ideas for laws) Giving the State of the Union Address Annual speech to Congress that is an important way for a President’s agenda to be communicated to the public and to Congress

The Executive Branch influences policymaking (laws) by: Approving or Vetoing bills
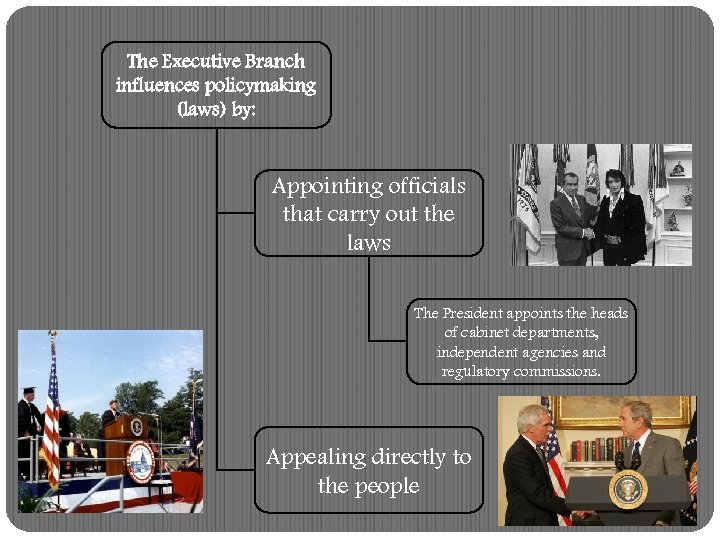
The Executive Branch influences policymaking (laws) by: Appointing officials that carry out the laws The President appoints the heads of cabinet departments, independent agencies and regulatory commissions. Appealing directly to the people

Executive Departments

Executive Departments Congress has the power to establish, reorganize and to eliminate executive departments

Executive Departments Each department as a specific area of responsibility

Executive Departments Heads of the Executive Departments make up the President’s Cabinet

Cabinet Not mentioned in the Constitution, but every President has had a Cabinet Advise the President and help implement federal laws Title of most cabinet members is secretary Head of the Department of Justice is the Attorney General
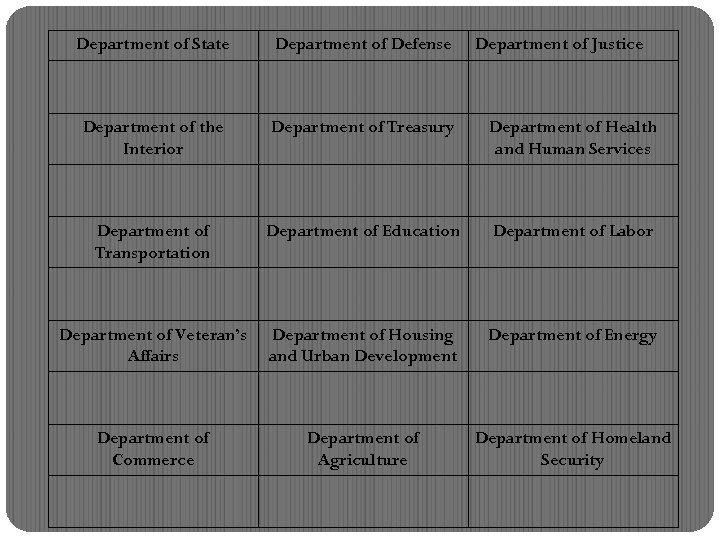
Department of State Department of Defense Department of Justice Department of the Interior Department of Treasury Department of Health and Human Services Department of Transportation Department of Education Department of Labor Department of Veteran’s Affairs Department of Housing and Urban Development Department of Energy Department of Commerce Department of Agriculture Department of Homeland Security

Independent Agencies and Regulatory Commissions

Independent Agencies and Regulatory Commissions Created by Congress Source of Administrative Laws: Laws not created by Congress, but by an agency Congress has given specific permission to create laws.

Independent Agencies and Regulatory Commissions Separate from the executive departments because they perform specialized duties. Help to carry out federal laws

Independent Agencies and Regulatory Commissions Internal Revenue Service Tasked with collecting taxes from all individuals and businesses in the United States Federal Communications Commission regulates interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite and cable


The Federal Bureaucracy Formed by the departments and agencies in the executive branch 3 million people work in the bureaucracy Operates under heavy rules and regulations that create “red tape
797f686b1d47e54609f6420216c15d3e.ppt