8b2a41b369c3ed125b1ace26738874af.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 The Exam on Monday will cover… n n n n The reign of Solomon Wisdom literature The divided kingdom Introduction to prophets Hosea, Amos, Jonah, Nahum Isaiah, Micah, Joel Matt’s review this evening – 7: 00 in J 112 A list of names to know has been posted on Blackboard
The Exam on Monday will cover… n n n n The reign of Solomon Wisdom literature The divided kingdom Introduction to prophets Hosea, Amos, Jonah, Nahum Isaiah, Micah, Joel Matt’s review this evening – 7: 00 in J 112 A list of names to know has been posted on Blackboard
 Psalm 100: 5 KI TOV ADONAI n Because good (is) the LORD n LE’OLAM H ASDO (2 X) n To eternity (is) His hesed n VE’AD DOR VE-DOR (2 X) n And unto generation and generation n EMUNATO n His faithfulness n
Psalm 100: 5 KI TOV ADONAI n Because good (is) the LORD n LE’OLAM H ASDO (2 X) n To eternity (is) His hesed n VE’AD DOR VE-DOR (2 X) n And unto generation and generation n EMUNATO n His faithfulness n
 Prophets to the North and to Assyria Covenant Enforcement Mediators
Prophets to the North and to Assyria Covenant Enforcement Mediators
 Review Questions Why were the prophets called “covenant enforcement mediators”? n What was the rabbinic parable? n What “media” did the prophets employ? n
Review Questions Why were the prophets called “covenant enforcement mediators”? n What was the rabbinic parable? n What “media” did the prophets employ? n
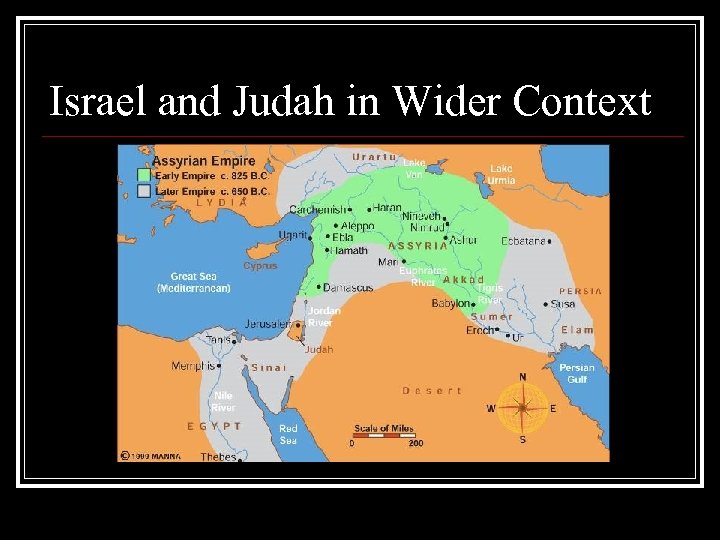 Israel and Judah in Wider Context
Israel and Judah in Wider Context
 Jehu Pays Tribute to Shalmaneser III
Jehu Pays Tribute to Shalmaneser III
 Jonah n n n Historical background: II Kings 14: 25 – Jeroboam and the looming presence of Assyria Purpose of the book – a comprehensive demonstration of God’s sovereignty God’s command to Jonah/Jonah’s “logical” disobedience The storm, sea, fish – and Jonah’s rescue by the fish Repentance of Nineveh and the lesson to Jonah Jesus’ reference to Jonah – “the sign of Jonah” (Matthew 12: 39 -41; 16: 4; Luke 11: 30) – location of Gath -Hepher
Jonah n n n Historical background: II Kings 14: 25 – Jeroboam and the looming presence of Assyria Purpose of the book – a comprehensive demonstration of God’s sovereignty God’s command to Jonah/Jonah’s “logical” disobedience The storm, sea, fish – and Jonah’s rescue by the fish Repentance of Nineveh and the lesson to Jonah Jesus’ reference to Jonah – “the sign of Jonah” (Matthew 12: 39 -41; 16: 4; Luke 11: 30) – location of Gath -Hepher
 The Background for Amos n n During reigns of Jeroboam II and Uzziah (ca. 750 BCE) A sheep herder and tender of fig trees from Tekoa Compelled to prophesy (3: 2 -8) Prophesied at Bethel (7: 10) – echoes of “the man of God” from Judah
The Background for Amos n n During reigns of Jeroboam II and Uzziah (ca. 750 BCE) A sheep herder and tender of fig trees from Tekoa Compelled to prophesy (3: 2 -8) Prophesied at Bethel (7: 10) – echoes of “the man of God” from Judah
 Structure and Messages of Amos n Oracles against Israel’s neighbors n n n n Damascus – destruction (genocide) of Gilead Philistia – selling Hebrew slaves to Edom Tyre – selling whole communities as captives to Edom – pursuing brother with sword Ammon – destruction of Gilead (genocide) Moab – vengeance and hatred Judah – rejected Torah and embraced idolatry Oracles against Israel – the “day of the Lord” (5: 18) n n n Social sins Idolatry Complacency
Structure and Messages of Amos n Oracles against Israel’s neighbors n n n n Damascus – destruction (genocide) of Gilead Philistia – selling Hebrew slaves to Edom Tyre – selling whole communities as captives to Edom – pursuing brother with sword Ammon – destruction of Gilead (genocide) Moab – vengeance and hatred Judah – rejected Torah and embraced idolatry Oracles against Israel – the “day of the Lord” (5: 18) n n n Social sins Idolatry Complacency
 A Threshing Sledge
A Threshing Sledge
 Amos and the Future n Visions – “the Lord showed me” and “I saw the Lord” n n n Locusts Judgment by fire Plumb line Ripe fruit Amos in the New Testament (Acts 15: 1618) – restoration of David’s fallen tent
Amos and the Future n Visions – “the Lord showed me” and “I saw the Lord” n n n Locusts Judgment by fire Plumb line Ripe fruit Amos in the New Testament (Acts 15: 1618) – restoration of David’s fallen tent
 Hosea n n Historical background – time of Jeroboam II Hosea’s marriage n n n Israel’s sins – chapter 4 begins the lawsuit n n His wife and children: Jezreel, Lo-Ruhamah, Lo-Ammi The significance of God’s command to Hosea Idolatry and dependence on other gods (ba’al) – spiritual adultery Breaking covenant stipulations Dependence on Assyria and Egypt God’s response – the wounded Lover
Hosea n n Historical background – time of Jeroboam II Hosea’s marriage n n n Israel’s sins – chapter 4 begins the lawsuit n n His wife and children: Jezreel, Lo-Ruhamah, Lo-Ammi The significance of God’s command to Hosea Idolatry and dependence on other gods (ba’al) – spiritual adultery Breaking covenant stipulations Dependence on Assyria and Egypt God’s response – the wounded Lover
 Hosea in the New Testament n n n “not my people” – 1: 10, 2: 23 in Romans 9: 25 -26; I Peter 2: 10 “I desire mercy, not sacrifice” – 6: 6 in Matt 9: 13; 12: 7 “out of Egypt have I called my son” – 11: 1 in Matt 2: 15 [terrors in the last days] – 10: 8 b in Luke 23: 30 and Rev 6: 16 “death, where is your victory? ” – 13: 14 in I Cor 15: 55
Hosea in the New Testament n n n “not my people” – 1: 10, 2: 23 in Romans 9: 25 -26; I Peter 2: 10 “I desire mercy, not sacrifice” – 6: 6 in Matt 9: 13; 12: 7 “out of Egypt have I called my son” – 11: 1 in Matt 2: 15 [terrors in the last days] – 10: 8 b in Luke 23: 30 and Rev 6: 16 “death, where is your victory? ” – 13: 14 in I Cor 15: 55
 Nahum n Historical background n n n From Elkosh (unknown location) Sometime before the fall of Nineveh (612 BCE) and after fall of Thebes (No-Amon in 3: 8) which occurred in 650 BCE Fall of Nineveh in extra-biblical sources Poetry of Nahum – short, punctuated sentences – abruptness of war situation The Message n n Validity of the prophecy based on the sovereignty of God Nineveh’s violent end because of atrocities and idolatry
Nahum n Historical background n n n From Elkosh (unknown location) Sometime before the fall of Nineveh (612 BCE) and after fall of Thebes (No-Amon in 3: 8) which occurred in 650 BCE Fall of Nineveh in extra-biblical sources Poetry of Nahum – short, punctuated sentences – abruptness of war situation The Message n n Validity of the prophecy based on the sovereignty of God Nineveh’s violent end because of atrocities and idolatry


