17a2e912f357b5048d1be814cd563c19.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 The Evolving Computing Model: Michel Teyssedre VP Strategic Business Development i. GRID September 2002, Amsterdam
The Evolving Computing Model: Michel Teyssedre VP Strategic Business Development i. GRID September 2002, Amsterdam
 The Vision
The Vision
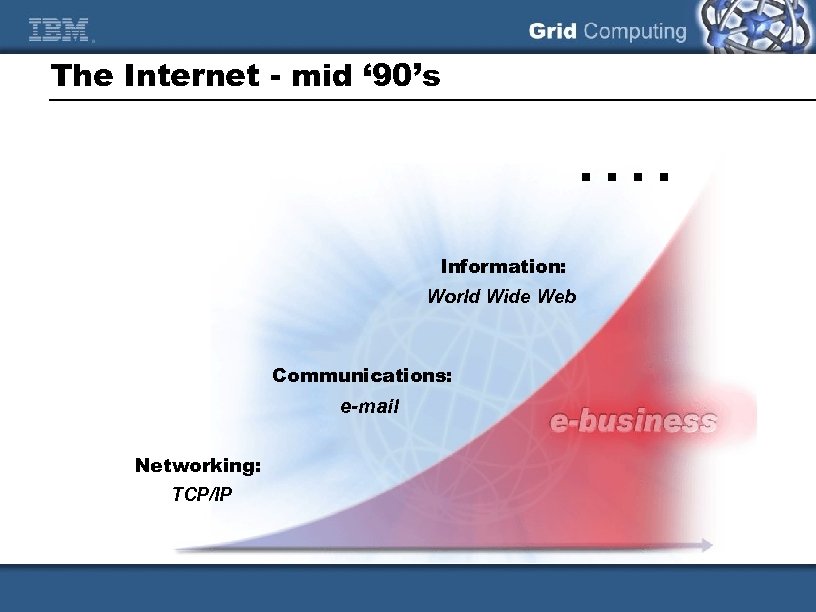 The Internet - mid ‘ 90’s . . Information: World Wide Web Communications: e-mail Networking: TCP/IP
The Internet - mid ‘ 90’s . . Information: World Wide Web Communications: e-mail Networking: TCP/IP
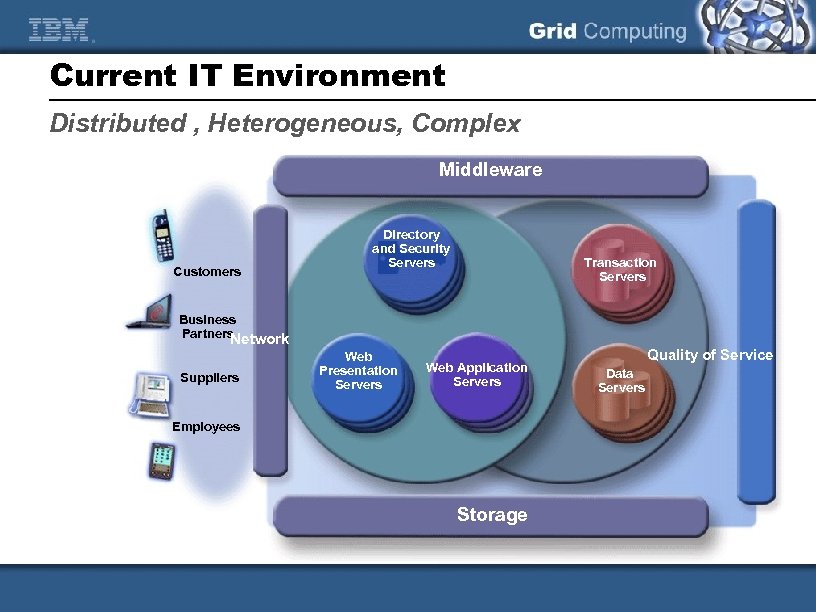 Current IT Environment Distributed , Heterogeneous, Complex Middleware Customers Directory and Security Servers Transaction Servers Business Partners Network Suppliers Web Presentation Servers Web Application Servers Employees Storage Quality of Service Data Servers
Current IT Environment Distributed , Heterogeneous, Complex Middleware Customers Directory and Security Servers Transaction Servers Business Partners Network Suppliers Web Presentation Servers Web Application Servers Employees Storage Quality of Service Data Servers
 The Management Problem Gartner 6/2001: "Considering current technologies, we expect that the total number of device administrators will exceed 220 millions by 2010. "
The Management Problem Gartner 6/2001: "Considering current technologies, we expect that the total number of device administrators will exceed 220 millions by 2010. "
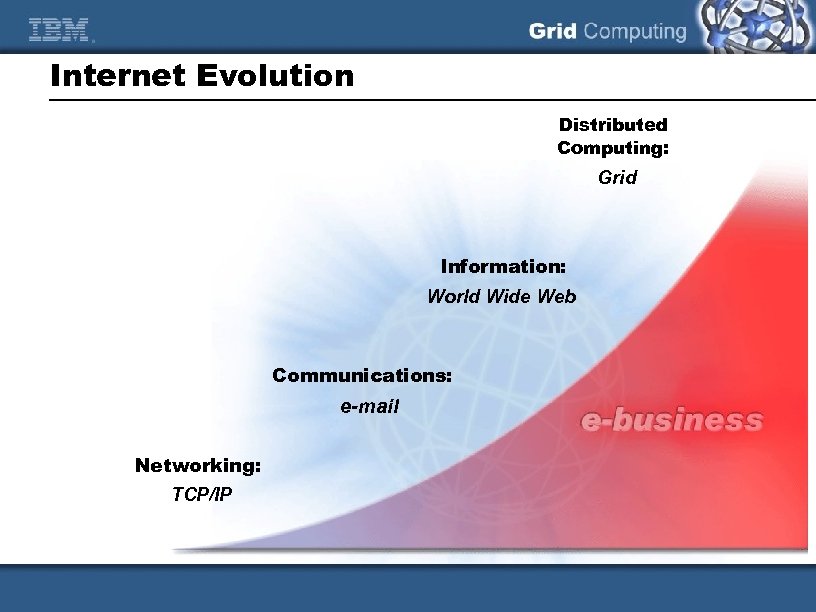 Internet Evolution Distributed Computing: Grid Information: World Wide Web Communications: e-mail Networking: TCP/IP
Internet Evolution Distributed Computing: Grid Information: World Wide Web Communications: e-mail Networking: TCP/IP
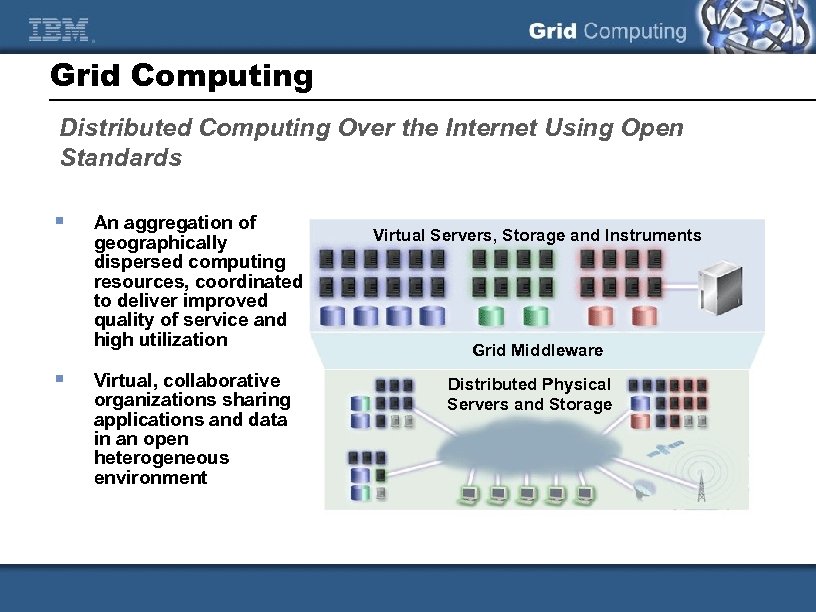 Grid Computing Distributed Computing Over the Internet Using Open Standards § § An aggregation of geographically dispersed computing resources, coordinated to deliver improved quality of service and high utilization Virtual, collaborative organizations sharing applications and data in an open heterogeneous environment Virtual Servers, Storage and Instruments Grid Middleware Distributed Physical Servers and Storage
Grid Computing Distributed Computing Over the Internet Using Open Standards § § An aggregation of geographically dispersed computing resources, coordinated to deliver improved quality of service and high utilization Virtual, collaborative organizations sharing applications and data in an open heterogeneous environment Virtual Servers, Storage and Instruments Grid Middleware Distributed Physical Servers and Storage
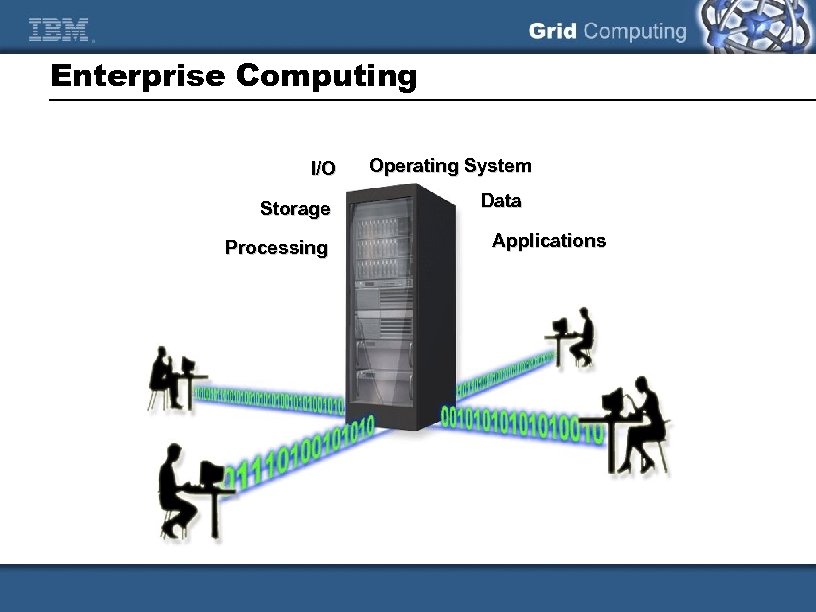 Enterprise Computing I/O Storage Processing Operating System Data Applications
Enterprise Computing I/O Storage Processing Operating System Data Applications
 Enterprise Computing
Enterprise Computing
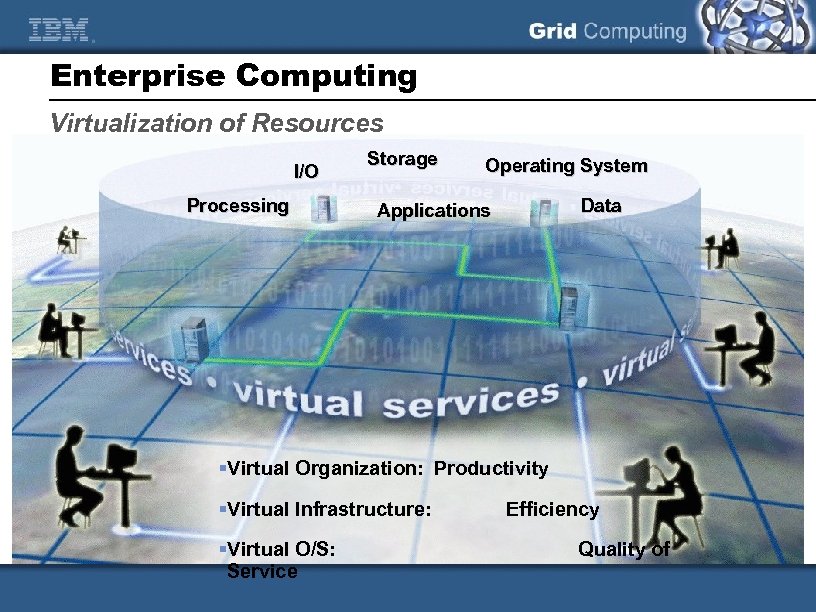 Enterprise Computing Virtualization of Resources I/O Processing Storage Operating System Data Applications §Virtual Organization: Productivity §Virtual Infrastructure: §Virtual O/S: Service Efficiency Quality of
Enterprise Computing Virtualization of Resources I/O Processing Storage Operating System Data Applications §Virtual Organization: Productivity §Virtual Infrastructure: §Virtual O/S: Service Efficiency Quality of
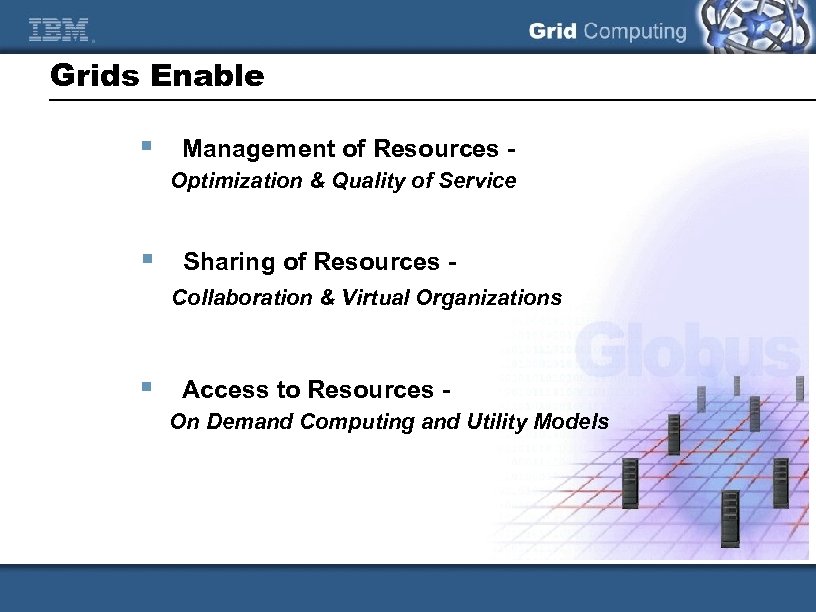 Grids Enable § Management of Resources Optimization & Quality of Service § Sharing of Resources Collaboration & Virtual Organizations § Access to Resources On Demand Computing and Utility Models
Grids Enable § Management of Resources Optimization & Quality of Service § Sharing of Resources Collaboration & Virtual Organizations § Access to Resources On Demand Computing and Utility Models
 The Architecture
The Architecture
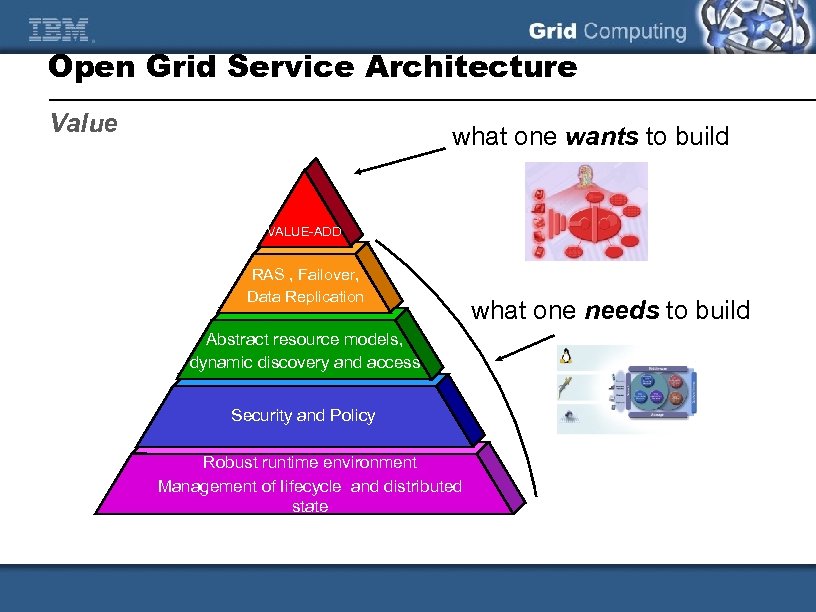 Open Grid Service Architecture Value what one wants to build VALUE-ADD RAS , Failover, Data Replication Abstract resource models, dynamic discovery and access Security and Policy Robust runtime environment Management of Iifecycle and distributed state what one needs to build
Open Grid Service Architecture Value what one wants to build VALUE-ADD RAS , Failover, Data Replication Abstract resource models, dynamic discovery and access Security and Policy Robust runtime environment Management of Iifecycle and distributed state what one needs to build
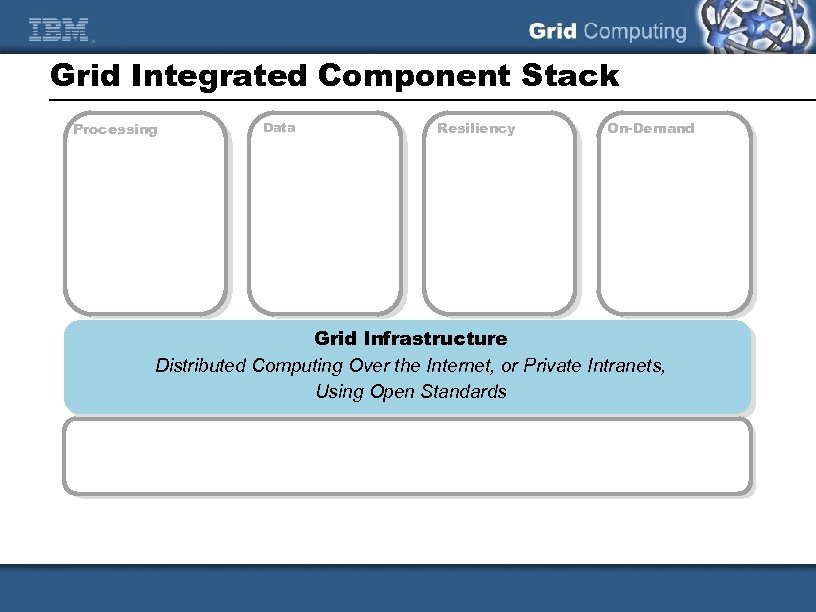 Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure Distributed Computing Over the Internet, or Private Intranets, Using Open Standards
Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure Distributed Computing Over the Internet, or Private Intranets, Using Open Standards
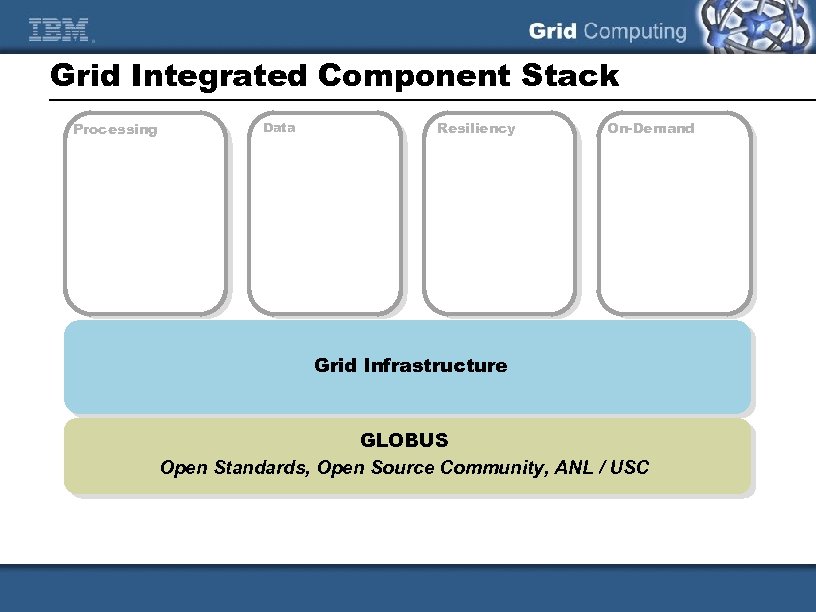 Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure GLOBUS Open Standards, Open Source Community, ANL / USC
Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure GLOBUS Open Standards, Open Source Community, ANL / USC
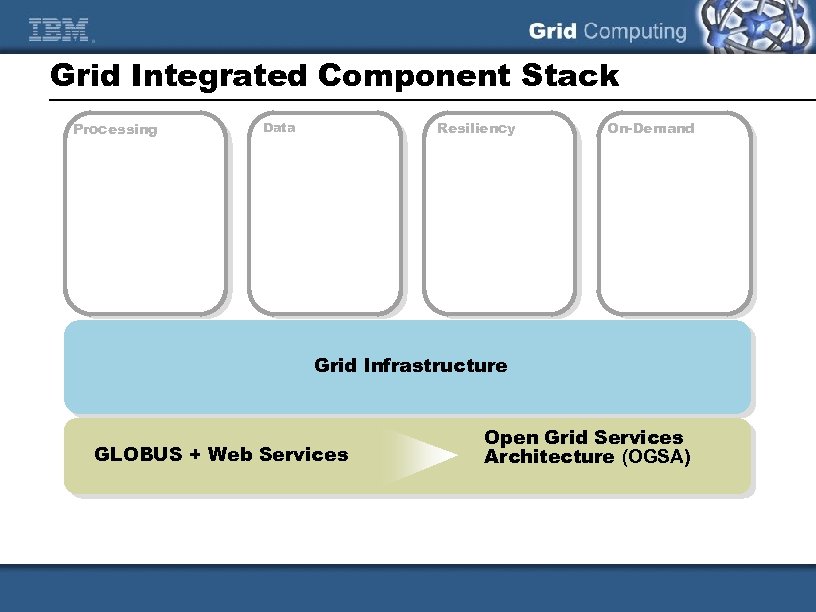 Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Resiliency Data On-Demand Grid Infrastructure GLOBUS + Web Services Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA)
Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Resiliency Data On-Demand Grid Infrastructure GLOBUS + Web Services Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA)
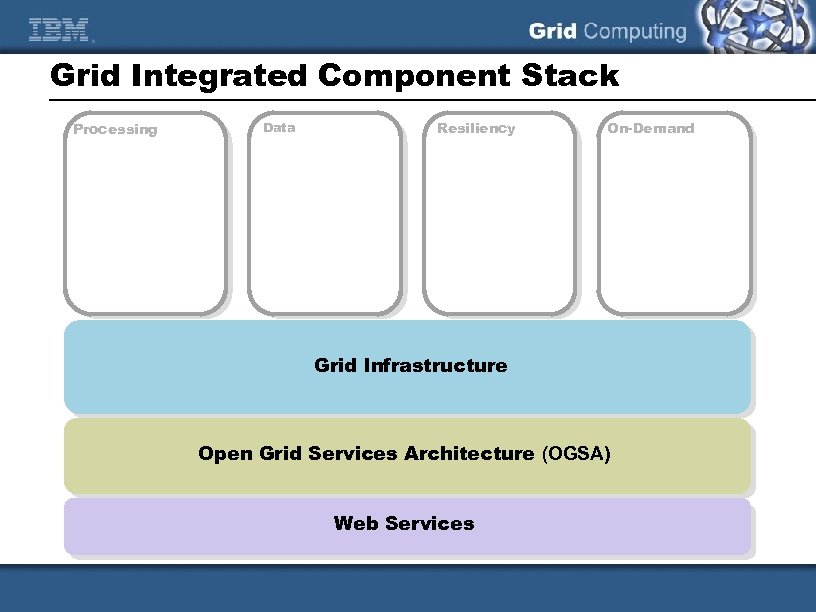 Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) Web Services
Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Grid Infrastructure Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) Web Services
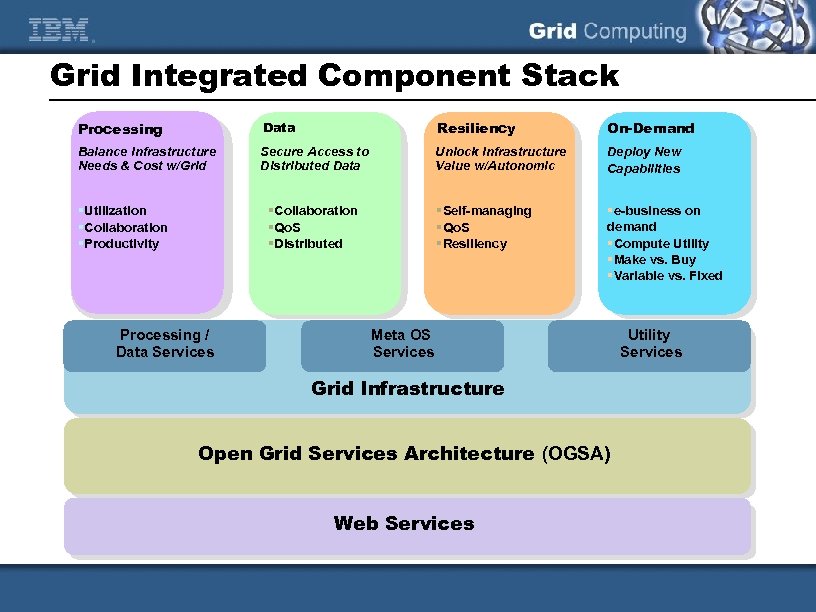 Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Balance Infrastructure Needs & Cost w/Grid Secure Access to Distributed Data Unlock Infrastructure Value w/Autonomic Deploy New Capabilities §Self-managing §Qo. S §Resiliency §e-business on demand §Compute Utility §Make vs. Buy §Variable vs. Fixed §Utilization §Collaboration §Productivity §Collaboration §Qo. S §Distributed Processing / Data Services Meta OS Services Grid Infrastructure Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) Web Services Utility Services
Grid Integrated Component Stack Processing Data Resiliency On-Demand Balance Infrastructure Needs & Cost w/Grid Secure Access to Distributed Data Unlock Infrastructure Value w/Autonomic Deploy New Capabilities §Self-managing §Qo. S §Resiliency §e-business on demand §Compute Utility §Make vs. Buy §Variable vs. Fixed §Utilization §Collaboration §Productivity §Collaboration §Qo. S §Distributed Processing / Data Services Meta OS Services Grid Infrastructure Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) Web Services Utility Services
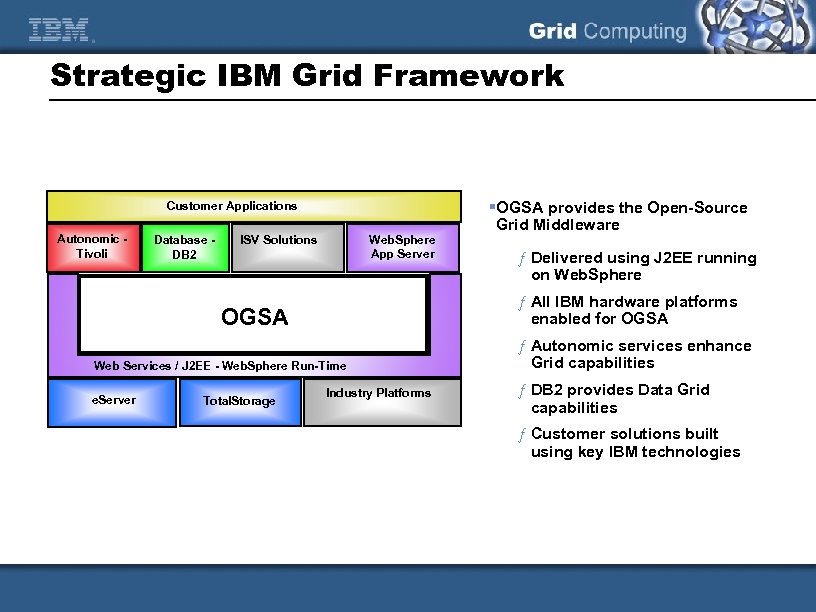 Strategic IBM Grid Framework Customer Applications Autonomic Tivoli Database DB 2 ISV Solutions Web. Sphere App Server Web Services / J 2 EE - Web. Sphere Run-Time Total. Storage ƒ Delivered using J 2 EE running on Web. Sphere ƒ All IBM hardware platforms enabled for OGSA e. Server §OGSA provides the Open-Source Grid Middleware Industry Platforms ƒ Autonomic services enhance Grid capabilities ƒ DB 2 provides Data Grid capabilities ƒ Customer solutions built using key IBM technologies
Strategic IBM Grid Framework Customer Applications Autonomic Tivoli Database DB 2 ISV Solutions Web. Sphere App Server Web Services / J 2 EE - Web. Sphere Run-Time Total. Storage ƒ Delivered using J 2 EE running on Web. Sphere ƒ All IBM hardware platforms enabled for OGSA e. Server §OGSA provides the Open-Source Grid Middleware Industry Platforms ƒ Autonomic services enhance Grid capabilities ƒ DB 2 provides Data Grid capabilities ƒ Customer solutions built using key IBM technologies
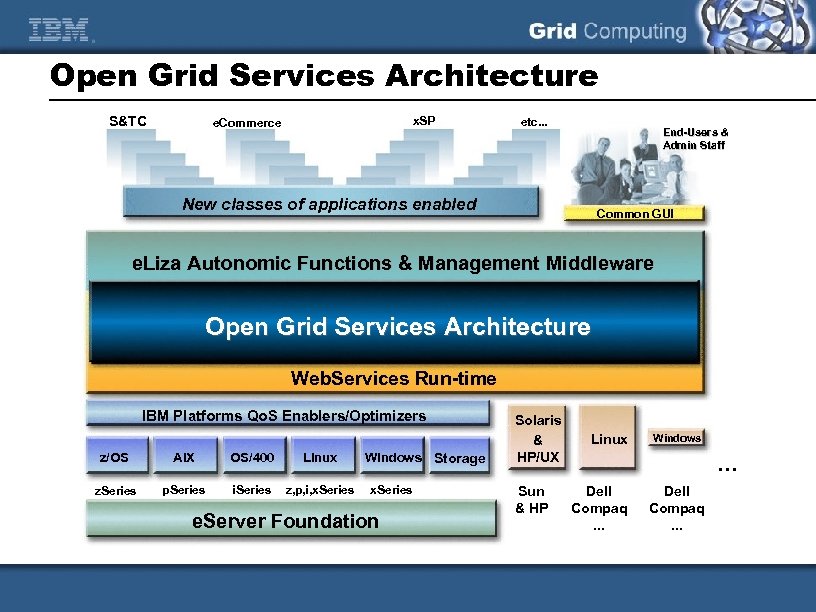 Open Grid Services Architecture S&TC x. SP e. Commerce etc. . . End-Users & Admin Staff New classes of applications enabled Common GUI e. Liza Autonomic Functions & Management Middleware Open Grid Services Architecture Web. Services Run-time IBM Platforms Qo. S Enablers/Optimizers z/OS AIX OS/400 Linux z. Series p. Series i. Series z, p, i, x. Series Windows Storage x. Series e. Server Foundation Solaris & HP/UX Sun & HP Linux Windows . . . Dell Compaq. . .
Open Grid Services Architecture S&TC x. SP e. Commerce etc. . . End-Users & Admin Staff New classes of applications enabled Common GUI e. Liza Autonomic Functions & Management Middleware Open Grid Services Architecture Web. Services Run-time IBM Platforms Qo. S Enablers/Optimizers z/OS AIX OS/400 Linux z. Series p. Series i. Series z, p, i, x. Series Windows Storage x. Series e. Server Foundation Solaris & HP/UX Sun & HP Linux Windows . . . Dell Compaq. . .
 Architecture framework OGSA
Architecture framework OGSA
 Architecture Framework OGSA
Architecture Framework OGSA
 Architecture Framework OGSA
Architecture Framework OGSA
 The Deliverables
The Deliverables
 IBM contributions to OGSA
IBM contributions to OGSA
 IBM Grid Toolbox Globus 2. 0 for AIX and Linux §A jump-start for Grid §Improved packaging and installation: ƒ AIX installp format ƒ Linux RPM format §Enhanced post install configuration tools ƒ Gather data and look for existing certificates ƒ Generate certificate requests if required ƒ Acquire certificates ƒ Install certificates ƒ Setup grid services and users ƒ Verify installation
IBM Grid Toolbox Globus 2. 0 for AIX and Linux §A jump-start for Grid §Improved packaging and installation: ƒ AIX installp format ƒ Linux RPM format §Enhanced post install configuration tools ƒ Gather data and look for existing certificates ƒ Generate certificate requests if required ƒ Acquire certificates ƒ Install certificates ƒ Setup grid services and users ƒ Verify installation
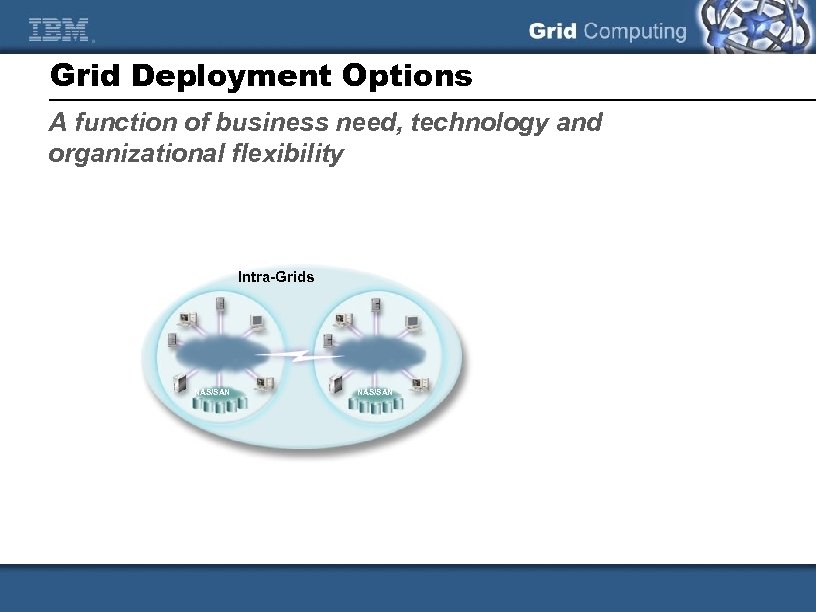 Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Intra-Grids NAS/SAN
Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Intra-Grids NAS/SAN
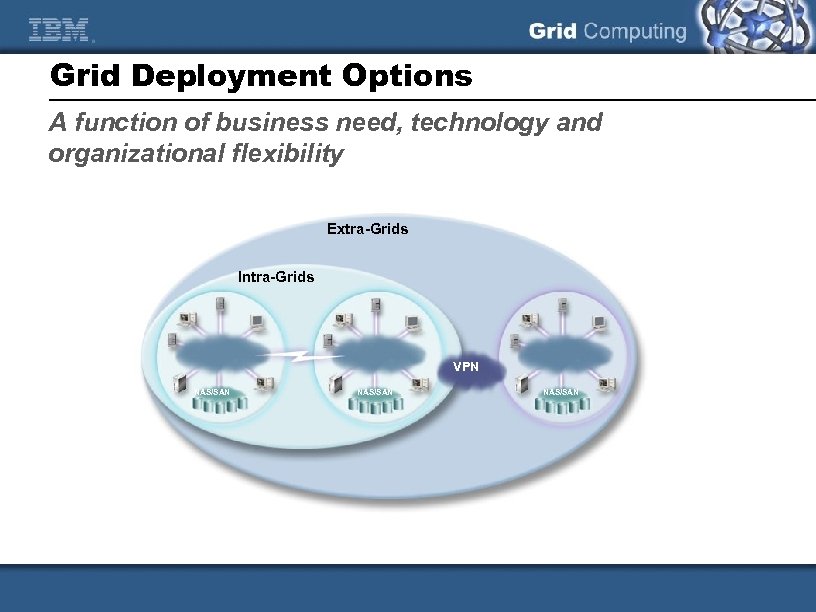 Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Extra-Grids Intra-Grids VPN NAS/SAN
Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Extra-Grids Intra-Grids VPN NAS/SAN
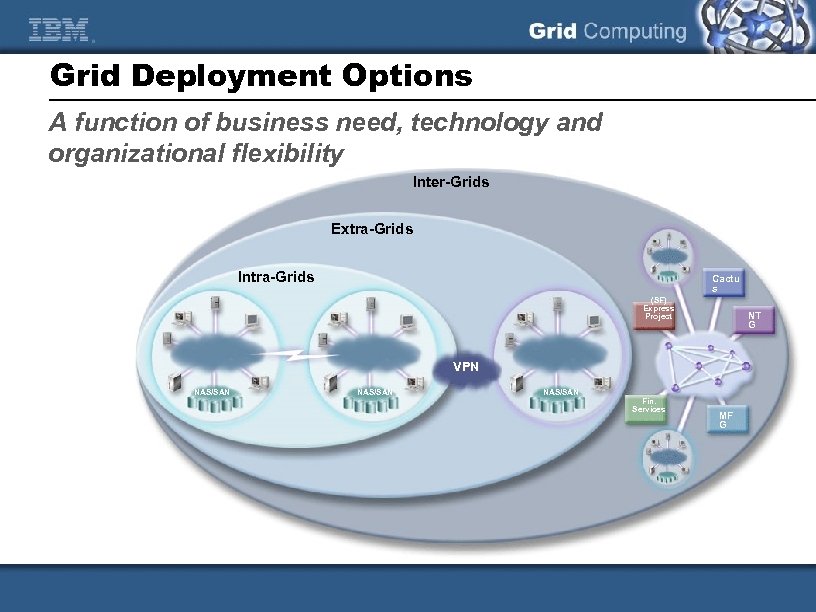 Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Inter-Grids Extra-Grids Intra-Grids Cactu s (SF) Express Project NT G VPN NAS/SAN Fin. Services MF G
Grid Deployment Options A function of business need, technology and organizational flexibility Inter-Grids Extra-Grids Intra-Grids Cactu s (SF) Express Project NT G VPN NAS/SAN Fin. Services MF G
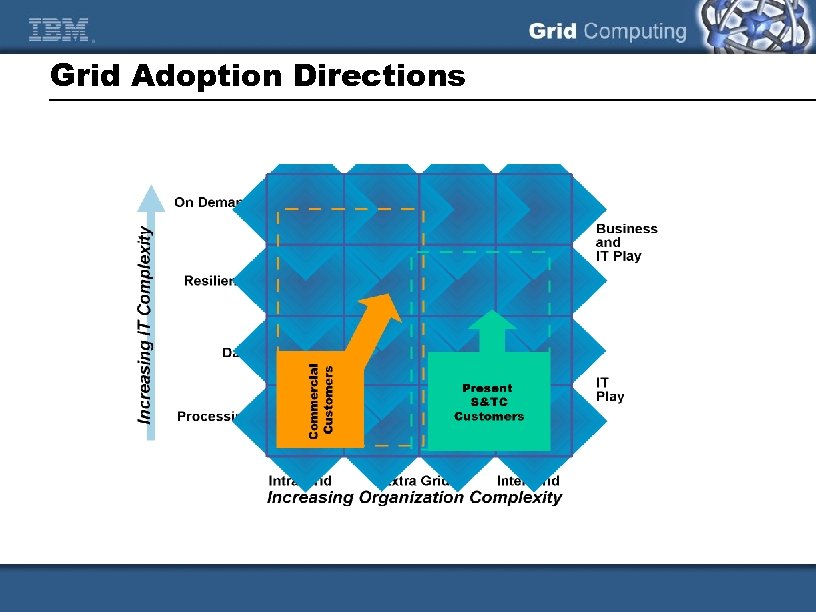 Grid Adoption Directions
Grid Adoption Directions
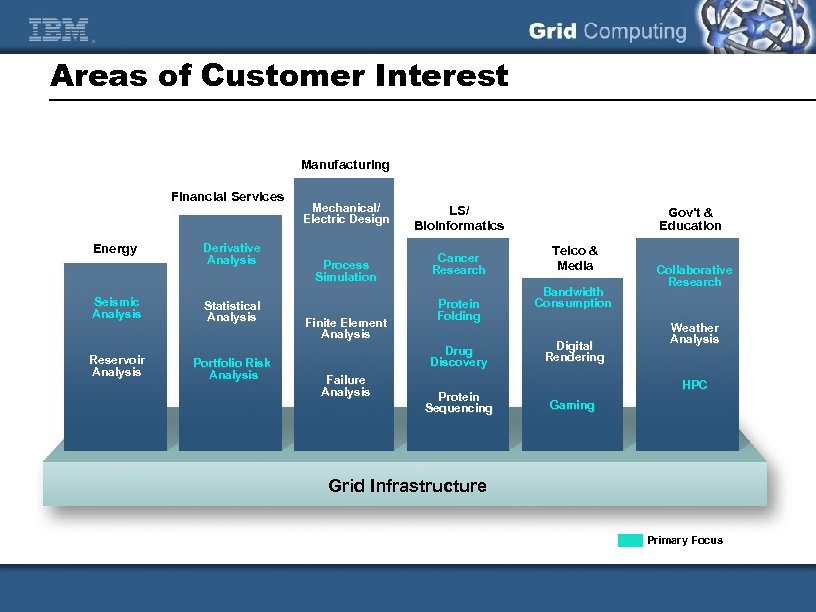 Areas of Customer Interest Manufacturing Financial Services Energy Seismic Analysis Reservoir Analysis Derivative Analysis Statistical Analysis Portfolio Risk Analysis Mechanical/ Electric Design Process Simulation Finite Element Analysis LS/ Bioinformatics Cancer Research Protein Folding Drug Discovery Failure Analysis Protein Sequencing Gov't & Education Telco & Media Bandwidth Consumption Digital Rendering Collaborative Research Weather Analysis HPC Gaming Grid Infrastructure Primary Focus
Areas of Customer Interest Manufacturing Financial Services Energy Seismic Analysis Reservoir Analysis Derivative Analysis Statistical Analysis Portfolio Risk Analysis Mechanical/ Electric Design Process Simulation Finite Element Analysis LS/ Bioinformatics Cancer Research Protein Folding Drug Discovery Failure Analysis Protein Sequencing Gov't & Education Telco & Media Bandwidth Consumption Digital Rendering Collaborative Research Weather Analysis HPC Gaming Grid Infrastructure Primary Focus
 Examples
Examples
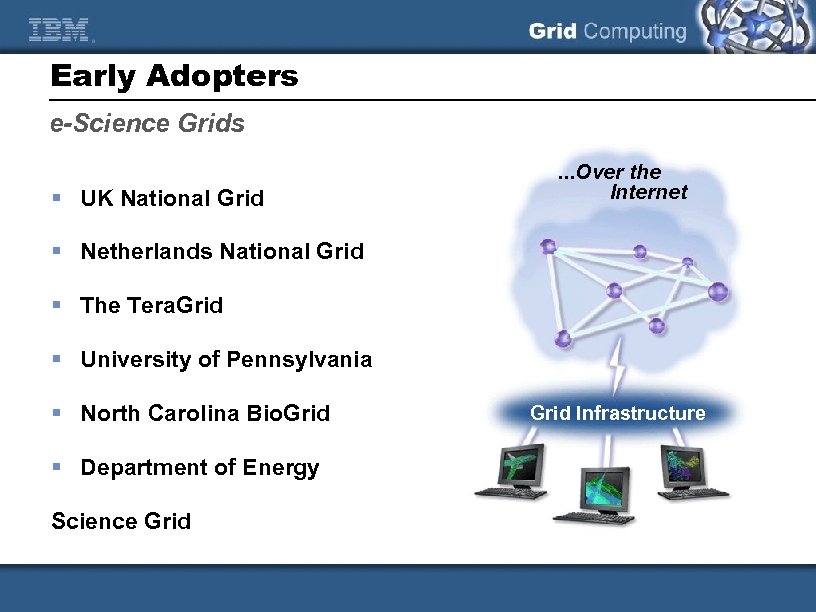 Early Adopters e-Science Grids § UK National Grid . . . Over the Internet § Netherlands National Grid § The Tera. Grid § University of Pennsylvania § North Carolina Bio. Grid § Department of Energy Science Grid Infrastructure
Early Adopters e-Science Grids § UK National Grid . . . Over the Internet § Netherlands National Grid § The Tera. Grid § University of Pennsylvania § North Carolina Bio. Grid § Department of Energy Science Grid Infrastructure
 The Tera. Grid Heterogeneous Systems: §National Center for Supercomputing Applications §San Diego Supercomputing Center §Argonne National Laboratory §California Institute of Technology 13. 6 trillion floating point operations per second 600 terabytes of data 40 gigabits per second Accessible to thousands of scientists working on advanced research
The Tera. Grid Heterogeneous Systems: §National Center for Supercomputing Applications §San Diego Supercomputing Center §Argonne National Laboratory §California Institute of Technology 13. 6 trillion floating point operations per second 600 terabytes of data 40 gigabits per second Accessible to thousands of scientists working on advanced research
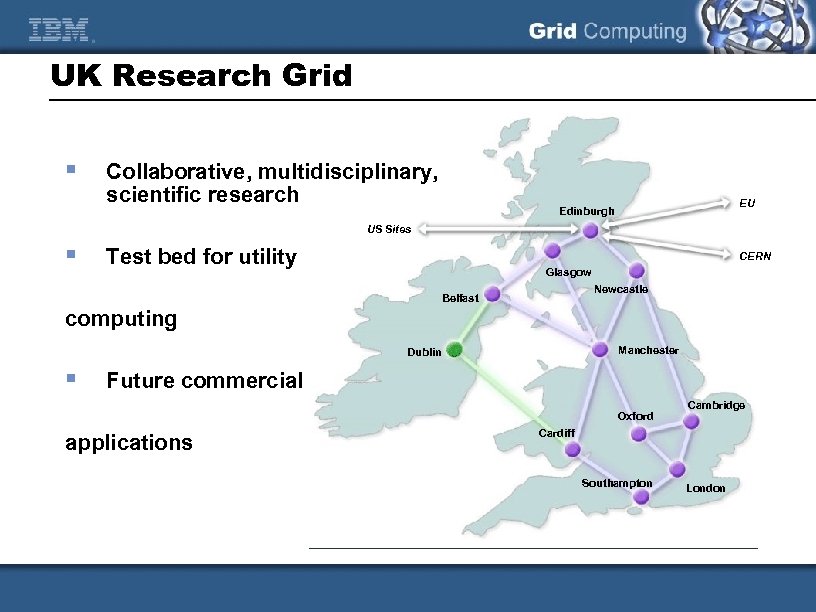 UK Research Grid § Collaborative, multidisciplinary, scientific research EU Edinburgh US Sites § Test bed for utility CERN Glasgow Newcastle Belfast computing Manchester Dublin § Future commercial Oxford applications Cambridge Cardiff Southampton London
UK Research Grid § Collaborative, multidisciplinary, scientific research EU Edinburgh US Sites § Test bed for utility CERN Glasgow Newcastle Belfast computing Manchester Dublin § Future commercial Oxford applications Cambridge Cardiff Southampton London
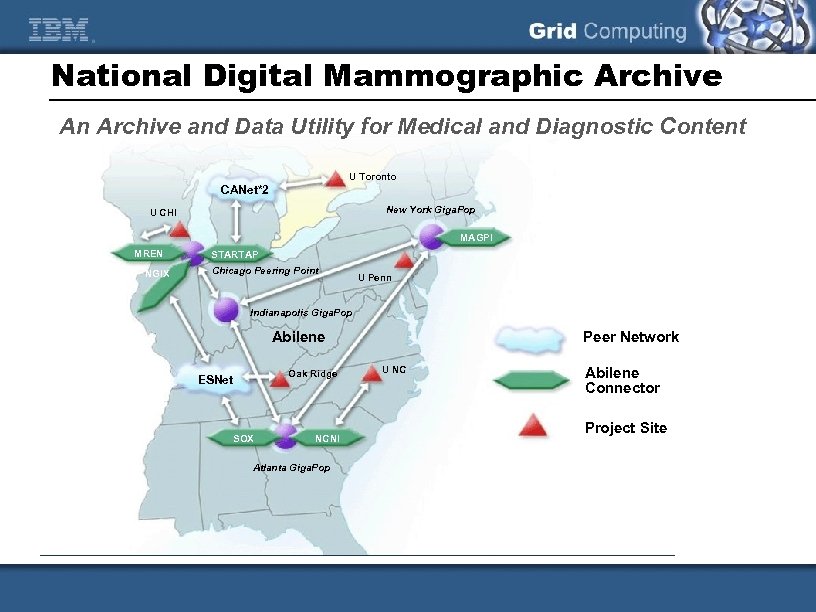 National Digital Mammographic Archive An Archive and Data Utility for Medical and Diagnostic Content U Toronto CANet*2 New York Giga. Pop U CHI MAGPI MREN NGIX STARTAP Chicago Peering Point U Penn Indianapolis Giga. Pop Peer Network Abilene Oak Ridge ESNet SOX NCNI Atlanta Giga. Pop U NC Abilene Connector Project Site
National Digital Mammographic Archive An Archive and Data Utility for Medical and Diagnostic Content U Toronto CANet*2 New York Giga. Pop U CHI MAGPI MREN NGIX STARTAP Chicago Peering Point U Penn Indianapolis Giga. Pop Peer Network Abilene Oak Ridge ESNet SOX NCNI Atlanta Giga. Pop U NC Abilene Connector Project Site
 Indiana Virtual Machine § Purdue and Indiana University Supercomputers Ÿ 1. 4 teraflops ŸHigh-speed optical fiber network § Sharing cycles and capacity § Ultra-large calculations § Simulating consumer behavior § Simulating homeland security
Indiana Virtual Machine § Purdue and Indiana University Supercomputers Ÿ 1. 4 teraflops ŸHigh-speed optical fiber network § Sharing cycles and capacity § Ultra-large calculations § Simulating consumer behavior § Simulating homeland security
 Butterfly. net §Unlimited Numbers of Players §Distributed Artificial Intelligence §Multiple Concurrent Players § 1, 000 downloads of developer’s §kit per week §Hot-swappable Components §Developers, Publishers, ESPs
Butterfly. net §Unlimited Numbers of Players §Distributed Artificial Intelligence §Multiple Concurrent Players § 1, 000 downloads of developer’s §kit per week §Hot-swappable Components §Developers, Publishers, ESPs
 Commercial Grid Computing Drivers § Maximize utilization of existing resources § Simplify operating environment § Improve availability & productivity § Enable collaboration & virtual organizations § Enhance & promote flexibility . . and enabled by Self-managing Technologies
Commercial Grid Computing Drivers § Maximize utilization of existing resources § Simplify operating environment § Improve availability & productivity § Enable collaboration & virtual organizations § Enhance & promote flexibility . . and enabled by Self-managing Technologies
 Key issues
Key issues
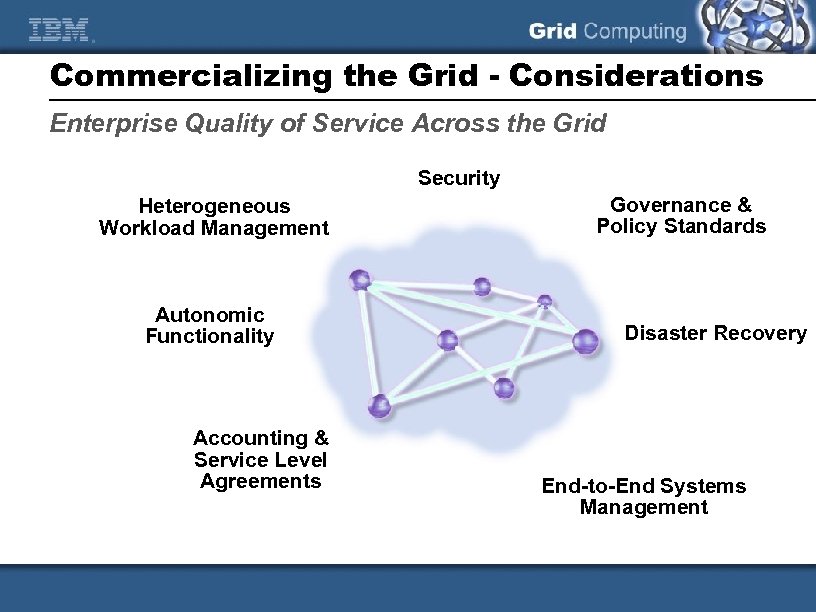 Commercializing the Grid - Considerations Enterprise Quality of Service Across the Grid Security Heterogeneous Workload Management Autonomic Functionality Accounting & Service Level Agreements Governance & Policy Standards Disaster Recovery End-to-End Systems Management
Commercializing the Grid - Considerations Enterprise Quality of Service Across the Grid Security Heterogeneous Workload Management Autonomic Functionality Accounting & Service Level Agreements Governance & Policy Standards Disaster Recovery End-to-End Systems Management
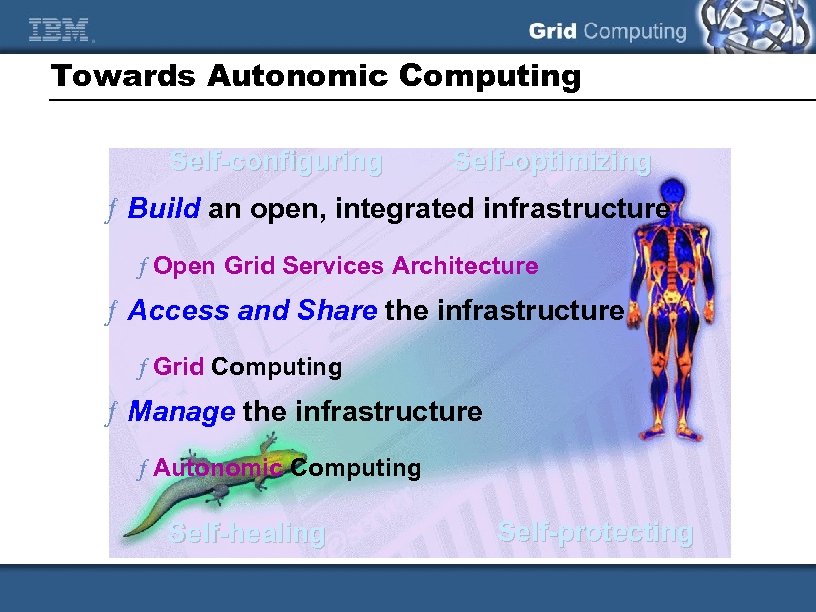 Towards Autonomic Computing Self-configuring Self-optimizing ƒ Build an open, integrated infrastructure ƒ Open Grid Services Architecture ƒ Access and Share the infrastructure ƒ Grid Computing ƒ Manage the infrastructure ƒ Autonomic Computing Self-healing Self-protecting
Towards Autonomic Computing Self-configuring Self-optimizing ƒ Build an open, integrated infrastructure ƒ Open Grid Services Architecture ƒ Access and Share the infrastructure ƒ Grid Computing ƒ Manage the infrastructure ƒ Autonomic Computing Self-healing Self-protecting
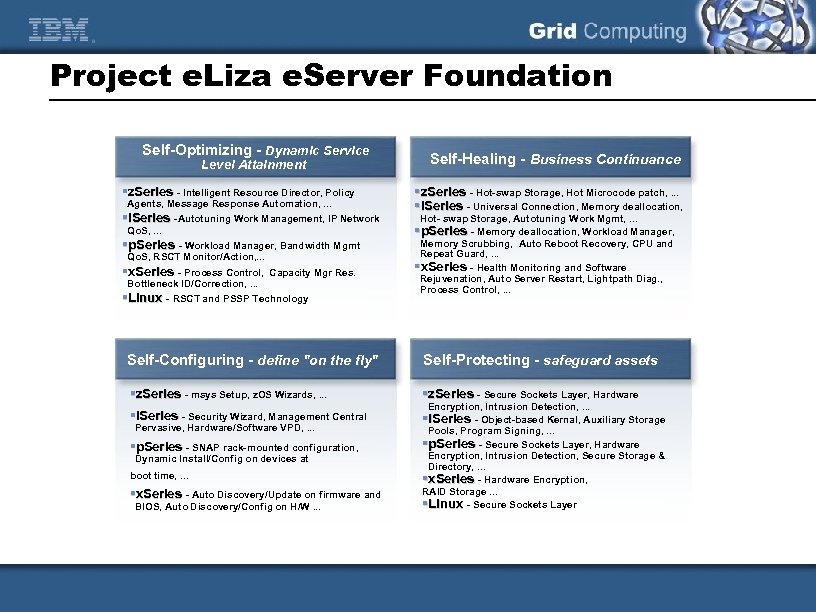 Project e. Liza e. Server Foundation Self-Optimizing - Dynamic Service Level Attainment §z. Series - Intelligent Resource Director, Policy Agents, Message Response Automation, . . . §i. Series -Autotuning Work Management, IP Network Qo. S, . . . §p. Series - Workload Manager, Bandwidth Mgmt Qo. S, RSCT Monitor/Action, . . . §x. Series - Process Control, Capacity Mgr Res. Bottleneck ID/Correction, . . . §Linux - RSCT and PSSP Technology Self-Healing - Business Continuance §z. Series - Hot-swap Storage, Hot Microcode patch, . . . §i. Series - Universal Connection, Memory deallocation, Hot- swap Storage, Autotuning Work Mgmt, . . . §p. Series - Memory deallocation, Workload Manager, Memory Scrubbing, Auto Reboot Recovery, CPU and Repeat Guard, . . . §x. Series - Health Monitoring and Software Rejuvenation, Auto Server Restart, Lightpath Diag. , Process Control, . . . Self-Configuring - define "on the fly" Self-Protecting - safeguard assets §z. Series - msys Setup, z. OS Wizards, . . . §z. Series - Secure Sockets Layer, Hardware §i. Series - Security Wizard, Management Central §i. Series - Object-based Kernal, Auxiliary Storage Pervasive, Hardware/Software VPD, . . . §p. Series - SNAP rack-mounted configuration, Dynamic Install/Config on devices at boot time, . . . §x. Series - Auto Discovery/Update on firmware and BIOS, Auto Discovery/Config on H/W. . . Encryption, Intrusion Detection, . . . Pools, Program Signing, . . . §p. Series - Secure Sockets Layer, Hardware Encryption, Intrusion Detection, Secure Storage & Directory, . . . §x. Series - Hardware Encryption, RAID Storage. . . §Linux - Secure Sockets Layer
Project e. Liza e. Server Foundation Self-Optimizing - Dynamic Service Level Attainment §z. Series - Intelligent Resource Director, Policy Agents, Message Response Automation, . . . §i. Series -Autotuning Work Management, IP Network Qo. S, . . . §p. Series - Workload Manager, Bandwidth Mgmt Qo. S, RSCT Monitor/Action, . . . §x. Series - Process Control, Capacity Mgr Res. Bottleneck ID/Correction, . . . §Linux - RSCT and PSSP Technology Self-Healing - Business Continuance §z. Series - Hot-swap Storage, Hot Microcode patch, . . . §i. Series - Universal Connection, Memory deallocation, Hot- swap Storage, Autotuning Work Mgmt, . . . §p. Series - Memory deallocation, Workload Manager, Memory Scrubbing, Auto Reboot Recovery, CPU and Repeat Guard, . . . §x. Series - Health Monitoring and Software Rejuvenation, Auto Server Restart, Lightpath Diag. , Process Control, . . . Self-Configuring - define "on the fly" Self-Protecting - safeguard assets §z. Series - msys Setup, z. OS Wizards, . . . §z. Series - Secure Sockets Layer, Hardware §i. Series - Security Wizard, Management Central §i. Series - Object-based Kernal, Auxiliary Storage Pervasive, Hardware/Software VPD, . . . §p. Series - SNAP rack-mounted configuration, Dynamic Install/Config on devices at boot time, . . . §x. Series - Auto Discovery/Update on firmware and BIOS, Auto Discovery/Config on H/W. . . Encryption, Intrusion Detection, . . . Pools, Program Signing, . . . §p. Series - Secure Sockets Layer, Hardware Encryption, Intrusion Detection, Secure Storage & Directory, . . . §x. Series - Hardware Encryption, RAID Storage. . . §Linux - Secure Sockets Layer
 On Demand Computing Realized Value Quality of Service Make vs. Buy Option Greater Productivity Variable Cost Flexibility Reduced Complexity
On Demand Computing Realized Value Quality of Service Make vs. Buy Option Greater Productivity Variable Cost Flexibility Reduced Complexity
 The Evolving Computing Model: Michel Teyssedre VP Strategic Business Development
The Evolving Computing Model: Michel Teyssedre VP Strategic Business Development


