6c523247e5edab1c7235139195a7549e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 The Entity. Relationship Model Part I. Instructor: Mohamed Eltabakh meltabakh@cs. wpi. edu CS 3431 -B 11 1
The Entity. Relationship Model Part I. Instructor: Mohamed Eltabakh meltabakh@cs. wpi. edu CS 3431 -B 11 1
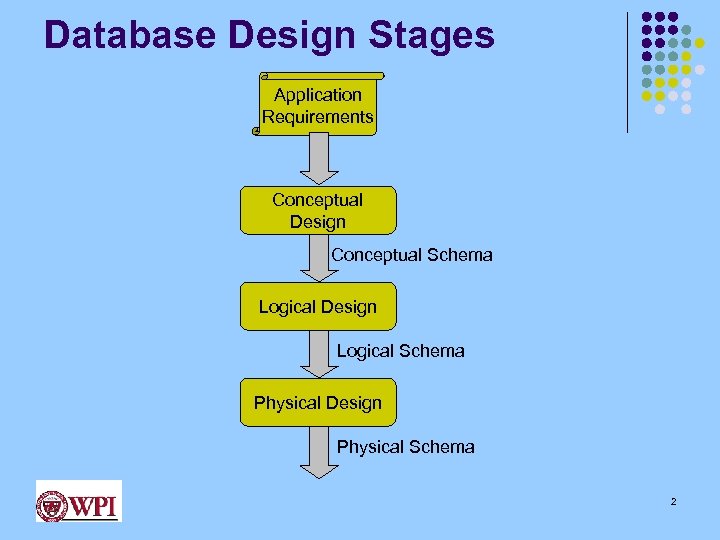 Database Design Stages Application Requirements Conceptual Design Conceptual Schema Logical Design Logical Schema Physical Design Physical Schema 2
Database Design Stages Application Requirements Conceptual Design Conceptual Schema Logical Design Logical Schema Physical Design Physical Schema 2
 Conceptual Design l What is Conceptual Design? l l Concise representation of the DB application requirements Why Conceptual Design ? l l l It helps to understand application requirements better It helps to communicate our understanding of application It helps to come up with a ‘good’ design 3
Conceptual Design l What is Conceptual Design? l l Concise representation of the DB application requirements Why Conceptual Design ? l l l It helps to understand application requirements better It helps to communicate our understanding of application It helps to come up with a ‘good’ design 3
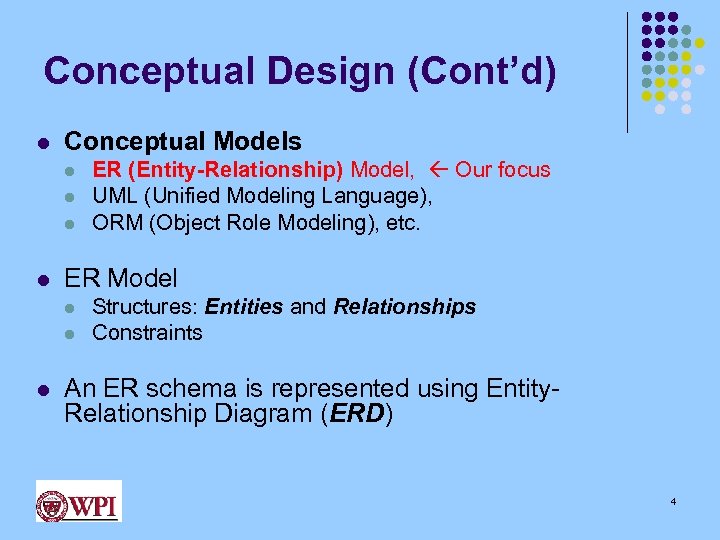 Conceptual Design (Cont’d) l Conceptual Models l l ER Model l ER (Entity-Relationship) Model, Our focus UML (Unified Modeling Language), ORM (Object Role Modeling), etc. Structures: Entities and Relationships Constraints An ER schema is represented using Entity. Relationship Diagram (ERD) 4
Conceptual Design (Cont’d) l Conceptual Models l l ER Model l ER (Entity-Relationship) Model, Our focus UML (Unified Modeling Language), ORM (Object Role Modeling), etc. Structures: Entities and Relationships Constraints An ER schema is represented using Entity. Relationship Diagram (ERD) 4
 Modeling l A database can be modeled as: l l l Collection of entities, Relationship among entities. An entity is an object that exists and is distinguishable from other objects. l l Example: a person, company, event, bank account, store, etc. Entities have attributes l l Example: a person have names and addresses An entity set is a set of entities of the same type that share the same properties. l Example: set of all persons, companies, trees, holidays 5
Modeling l A database can be modeled as: l l l Collection of entities, Relationship among entities. An entity is an object that exists and is distinguishable from other objects. l l Example: a person, company, event, bank account, store, etc. Entities have attributes l l Example: a person have names and addresses An entity set is a set of entities of the same type that share the same properties. l Example: set of all persons, companies, trees, holidays 5
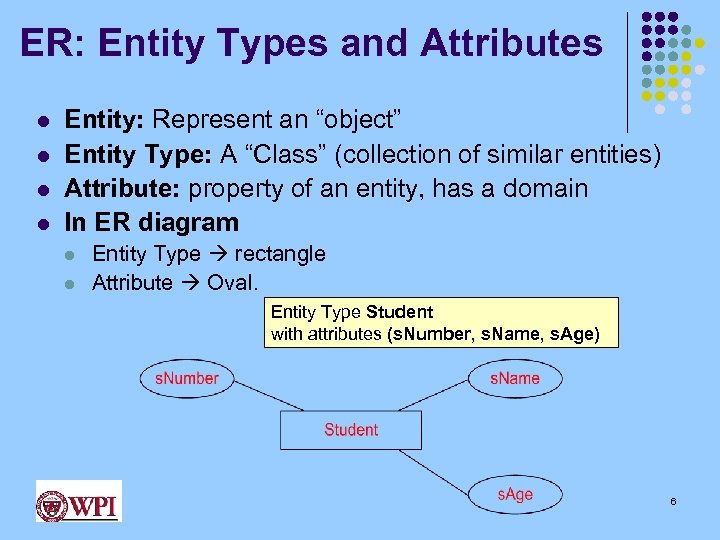 ER: Entity Types and Attributes l l Entity: Represent an “object” Entity Type: A “Class” (collection of similar entities) Attribute: property of an entity, has a domain In ER diagram l l Entity Type rectangle Attribute Oval. Entity Type Student with attributes (s. Number, s. Name, s. Age) 6
ER: Entity Types and Attributes l l Entity: Represent an “object” Entity Type: A “Class” (collection of similar entities) Attribute: property of an entity, has a domain In ER diagram l l Entity Type rectangle Attribute Oval. Entity Type Student with attributes (s. Number, s. Name, s. Age) 6
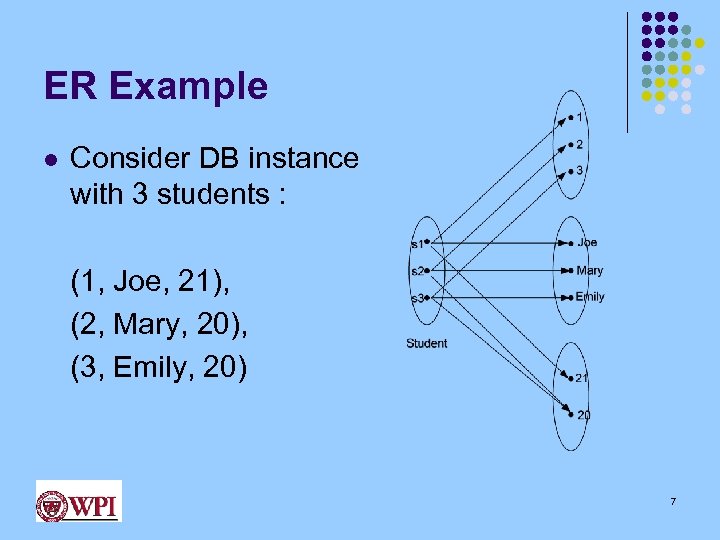 ER Example l Consider DB instance with 3 students : (1, Joe, 21), (2, Mary, 20), (3, Emily, 20) 7
ER Example l Consider DB instance with 3 students : (1, Joe, 21), (2, Mary, 20), (3, Emily, 20) 7
 Attributes Types l Primitive attributes: Attribute stores a single value (Number, String, Boolean, Date, …) l Composite attributes: An attribute can be divided into subattributes (each is primitive) l Multi-values attributes: Attribute with many values l Derived attributes: Attributes computed from others These are primitive attributes Do. B 8
Attributes Types l Primitive attributes: Attribute stores a single value (Number, String, Boolean, Date, …) l Composite attributes: An attribute can be divided into subattributes (each is primitive) l Multi-values attributes: Attribute with many values l Derived attributes: Attributes computed from others These are primitive attributes Do. B 8
 Complex Attributes Composite Attribute: address Multivalued Attribute: major Student entity type with all its attributes Derived Attribute: Age Do. B Age 9
Complex Attributes Composite Attribute: address Multivalued Attribute: major Student entity type with all its attributes Derived Attribute: Age Do. B Age 9
 Relationship Types l l l Relationship: Association (connection) between entities Relationship Type: Class of relationships Representation: Use a diamond shape Relationship type Has. Taken to represent Courses taken by Students 10
Relationship Types l l l Relationship: Association (connection) between entities Relationship Type: Class of relationships Representation: Use a diamond shape Relationship type Has. Taken to represent Courses taken by Students 10
 Relationships with Attributes l l A relationship may have attributes These attributes do not belong to any of the connected entities. But they belong the relationship Relationship Has. Taken has an attribute project which is the project the Student did for the Course 11
Relationships with Attributes l l A relationship may have attributes These attributes do not belong to any of the connected entities. But they belong the relationship Relationship Has. Taken has an attribute project which is the project the Student did for the Course 11
 Example: Relationship Instances l l l students {Hong, Song}, courses {DB 1, DB 2}, and relationships {(Hong, DB 1, 98), (Song, DB 1, 99), (Hong, DB 2, 97)} 12
Example: Relationship Instances l l l students {Hong, Song}, courses {DB 1, DB 2}, and relationships {(Hong, DB 1, 98), (Song, DB 1, 99), (Hong, DB 2, 97)} 12
 Example I (Simple Application) Suppliers have a name, and location. Products have a name, price, and number. Consumers have a name, and location. Suppliers supply products on certain dates, while consumers buy products of certain quantity How would you model this application? a) What are the entities and attributes? b) What are the relationships? 13
Example I (Simple Application) Suppliers have a name, and location. Products have a name, price, and number. Consumers have a name, and location. Suppliers supply products on certain dates, while consumers buy products of certain quantity How would you model this application? a) What are the entities and attributes? b) What are the relationships? 13
 Modeling of Example I p. Number s. Name s. Price product date quantity supplies buys s. Name c. Name supplier consumer s. Loc c. Loc This ER captures exactly what is written in text 14
Modeling of Example I p. Number s. Name s. Price product date quantity supplies buys s. Name c. Name supplier consumer s. Loc c. Loc This ER captures exactly what is written in text 14
 Example II (More Complicated) Suppliers have a name, and location. Products have a name, and number. Consumers have a name, and location. Some Suppliers have established contracts to supply a certain Product to a particular Consumer for specially negotiated price at a given quantity. How would you model this application? 15
Example II (More Complicated) Suppliers have a name, and location. Products have a name, and number. Consumers have a name, and location. Some Suppliers have established contracts to supply a certain Product to a particular Consumer for specially negotiated price at a given quantity. How would you model this application? 15
 Modeling of Example II Model the relationship Supplier supplies Products to Consumers Ternary relationship (three-way) Could we make two (or three) binary relationships instead? 16
Modeling of Example II Model the relationship Supplier supplies Products to Consumers Ternary relationship (three-way) Could we make two (or three) binary relationships instead? 16
 We Cannot !!! Binary vs. Multi-way Relationships p. Number s. Name product price quantity supplies buys s. Name c. Name supplier consumer s. Loc c. Loc This model for Example II is wrong !!! The link between quantity and price is now lost !!! 17
We Cannot !!! Binary vs. Multi-way Relationships p. Number s. Name product price quantity supplies buys s. Name c. Name supplier consumer s. Loc c. Loc This model for Example II is wrong !!! The link between quantity and price is now lost !!! 17
 Recursive Relationship Types and Roles Refer to the same entity in the relationship Recursive relationship type : Part-Subpart Roles: There are Parts that play the role of super. Part There are Parts that play the role of sub. Part 18
Recursive Relationship Types and Roles Refer to the same entity in the relationship Recursive relationship type : Part-Subpart Roles: There are Parts that play the role of super. Part There are Parts that play the role of sub. Part 18
 ER Model so far l Entities and entity types l Relationships l l l Binary, ternary, multi-way Recursive (roles) Attributes l l For entity types and relationship types Simple, composite, multi-valued, derived 19
ER Model so far l Entities and entity types l Relationships l l l Binary, ternary, multi-way Recursive (roles) Attributes l l For entity types and relationship types Simple, composite, multi-valued, derived 19
 What about an Exercise l Assume you are building a database for a “Car Dealership” l Like what you will do in the project, think about the entities, attributes, and relationships…. l As you think more, you can extend the design more 20
What about an Exercise l Assume you are building a database for a “Car Dealership” l Like what you will do in the project, think about the entities, attributes, and relationships…. l As you think more, you can extend the design more 20


