56e1e3eeb7ea0685448579d1503e81cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 The English in America Strangers in a Strange Land
The English in America Strangers in a Strange Land
 A Crowded Island n n Population of England rose 33% in the 1500 s Enclosure movement forced thousands off farms and to cites Decline in wool industry created massive unemployment Many (Richard Hakluyt) saw colonization as a way to remove excess population
A Crowded Island n n Population of England rose 33% in the 1500 s Enclosure movement forced thousands off farms and to cites Decline in wool industry created massive unemployment Many (Richard Hakluyt) saw colonization as a way to remove excess population
 The English Method of Colonization n Did not follow the English or French Model of founding colonies ¡ ¡ ¡ n Private efforts No government involvement intended Purpose was individual profit Individuals or groups received a Royal Charter(a license) to start a colony
The English Method of Colonization n Did not follow the English or French Model of founding colonies ¡ ¡ ¡ n Private efforts No government involvement intended Purpose was individual profit Individuals or groups received a Royal Charter(a license) to start a colony
 The First Attempt n n Sir Walter Raleigh received a charter from Elizabeth I for a colony in “Virginia” Settled 114 settlers on Roanoke Island in 1587 ¡ ¡ ¡ n Led by John White Virginia Dare - first English child born in America In modern N. C. “Lost Colony” ¡ ¡ Colony vanished “Croatoan”
The First Attempt n n Sir Walter Raleigh received a charter from Elizabeth I for a colony in “Virginia” Settled 114 settlers on Roanoke Island in 1587 ¡ ¡ ¡ n Led by John White Virginia Dare - first English child born in America In modern N. C. “Lost Colony” ¡ ¡ Colony vanished “Croatoan”
 A New Method of Colonization n n 1607 London (Virginia) Company receives a charter from James I for a colony in the Chesapeake Region Joint-stock company ¡ Investors pool resources for profit
A New Method of Colonization n n 1607 London (Virginia) Company receives a charter from James I for a colony in the Chesapeake Region Joint-stock company ¡ Investors pool resources for profit
 The First Permanent Settlement n London Company sent 3 ships and 104 men to found a settlement in 1607 ¡ ¡ n n Mostly 2 nd sons of wealthy men Purpose to gain wealth Called Jamestown the Virginia colony
The First Permanent Settlement n London Company sent 3 ships and 104 men to found a settlement in 1607 ¡ ¡ n n Mostly 2 nd sons of wealthy men Purpose to gain wealth Called Jamestown the Virginia colony
 Jamestown Colony n Poorly sited ¡ n Poorly prepared ¡ ¡ n n n On a malarial, swampy island on the James River Lazy unskilled No gold, spices, etc. Nearly starved Saved by John Smith ¡ ¡ Harsh discipline “No work, no food”
Jamestown Colony n Poorly sited ¡ n Poorly prepared ¡ ¡ n n n On a malarial, swampy island on the James River Lazy unskilled No gold, spices, etc. Nearly starved Saved by John Smith ¡ ¡ Harsh discipline “No work, no food”
 John Smith & Pocahontas n Smith tried to trade with Powhatan Indians for food ¡ ¡ n n Led by Chief Powhatan Had Smith sentenced to death Spared & given food after intervention of Pocahontas 38 survived 1 st winter
John Smith & Pocahontas n Smith tried to trade with Powhatan Indians for food ¡ ¡ n n Led by Chief Powhatan Had Smith sentenced to death Spared & given food after intervention of Pocahontas 38 survived 1 st winter
 Jamestown Today
Jamestown Today
 The Starving Time n Smith removed when new settlers arrived ¡ n Explored Massachusetts Coast & wrote a book Winter of 1609 -10 called the “Starving Time” ¡ ¡ Lost discipline 40 of 220 survived
The Starving Time n Smith removed when new settlers arrived ¡ n Explored Massachusetts Coast & wrote a book Winter of 1609 -10 called the “Starving Time” ¡ ¡ Lost discipline 40 of 220 survived
 Two Men Save Virginia n Lord de la Ware ¡ ¡ n restored strong leadership Scorched earth warfare against the Powhatans John Rolfe ¡ ¡ Introduced the cultivation of tobacco in 1616 Married Pocahontas
Two Men Save Virginia n Lord de la Ware ¡ ¡ n restored strong leadership Scorched earth warfare against the Powhatans John Rolfe ¡ ¡ Introduced the cultivation of tobacco in 1616 Married Pocahontas
 Life in Virginia n Society dominated by growing tobacco ¡ ¡ n n used as money 3 million lbs. shipped to England in 1638 Grown on river-side self-contained plantations Settlement followed the rivers
Life in Virginia n Society dominated by growing tobacco ¡ ¡ n n used as money 3 million lbs. shipped to England in 1638 Grown on river-side self-contained plantations Settlement followed the rivers
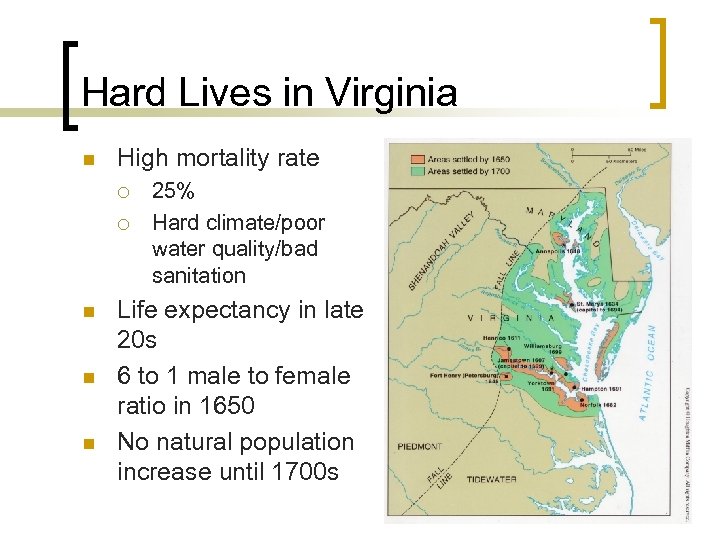 Hard Lives in Virginia n High mortality rate ¡ ¡ n n n 25% Hard climate/poor water quality/bad sanitation Life expectancy in late 20 s 6 to 1 male to female ratio in 1650 No natural population increase until 1700 s
Hard Lives in Virginia n High mortality rate ¡ ¡ n n n 25% Hard climate/poor water quality/bad sanitation Life expectancy in late 20 s 6 to 1 male to female ratio in 1650 No natural population increase until 1700 s
 The Problem n n Small population caused severe labor shortage Several attempted Solutions ¡ Head-Right System n ¡ Indentured servants n ¡ 50 acres of land for every person imported traded 7 years of labor for passage and land in the future Slavery n n first African slaves imported in 1620 Served for life Harder to escape Could handle climate
The Problem n n Small population caused severe labor shortage Several attempted Solutions ¡ Head-Right System n ¡ Indentured servants n ¡ 50 acres of land for every person imported traded 7 years of labor for passage and land in the future Slavery n n first African slaves imported in 1620 Served for life Harder to escape Could handle climate
 Popular Democracy n n London Company grants colonists selfgovernment by a “great charter” in 1618 House of Burgesses founded in 1619 ¡ ¡ First legislative assembly in America 22 elected reps. Made laws for colony Could be vetoed by appointed governor
Popular Democracy n n London Company grants colonists selfgovernment by a “great charter” in 1618 House of Burgesses founded in 1619 ¡ ¡ First legislative assembly in America 22 elected reps. Made laws for colony Could be vetoed by appointed governor
 Near Disaster n n Conflict with Powhatans over land Second Powhatan War (1622 -32) ¡ ¡ ¡ Indians under Opechancanough massacre 1/3 of the colonists in a surprise attack Colonist attack Indians food supplies 240 Powhatan poisoned at Peace Conference
Near Disaster n n Conflict with Powhatans over land Second Powhatan War (1622 -32) ¡ ¡ ¡ Indians under Opechancanough massacre 1/3 of the colonists in a surprise attack Colonist attack Indians food supplies 240 Powhatan poisoned at Peace Conference
 The King Takes Over n n n Charles I revokes the L. C. charter in 1624 because of war Sends a Royal governor Become a Royal or Crown Colony
The King Takes Over n n n Charles I revokes the L. C. charter in 1624 because of war Sends a Royal governor Become a Royal or Crown Colony
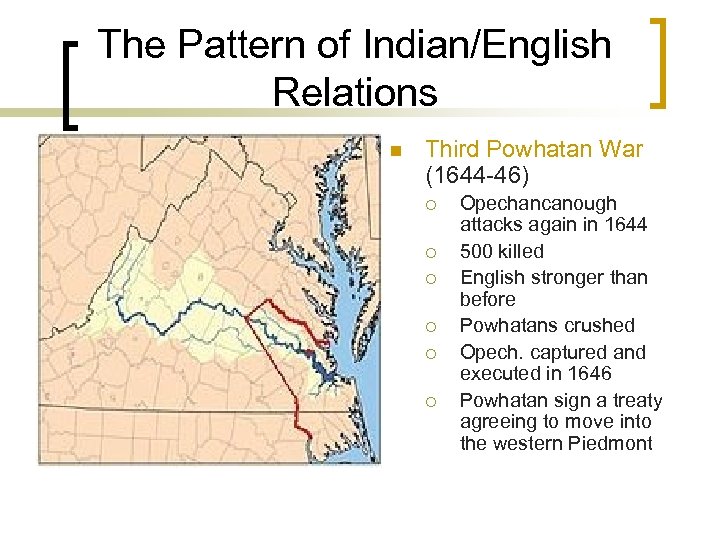 The Pattern of Indian/English Relations n Third Powhatan War (1644 -46) ¡ ¡ ¡ Opechancanough attacks again in 1644 500 killed English stronger than before Powhatans crushed Opech. captured and executed in 1646 Powhatan sign a treaty agreeing to move into the western Piedmont
The Pattern of Indian/English Relations n Third Powhatan War (1644 -46) ¡ ¡ ¡ Opechancanough attacks again in 1644 500 killed English stronger than before Powhatans crushed Opech. captured and executed in 1646 Powhatan sign a treaty agreeing to move into the western Piedmont
 Southern Social Structure n n Hierarchical society Planters ¡ ¡ ¡ Owned a plantation Grew tobacco with slave labor control wealth & gov. Will eventually extend to entire south called FFV’s in Virginia n Carter. Lee, Harrison, Fitzhugh, Rolfe, Randolph, Jefferson, Washington
Southern Social Structure n n Hierarchical society Planters ¡ ¡ ¡ Owned a plantation Grew tobacco with slave labor control wealth & gov. Will eventually extend to entire south called FFV’s in Virginia n Carter. Lee, Harrison, Fitzhugh, Rolfe, Randolph, Jefferson, Washington
 The Lower Classes n Yeoman farmers ¡ n n n small white farmers on their own land Landless whites Indentured servants African slaves
The Lower Classes n Yeoman farmers ¡ n n n small white farmers on their own land Landless whites Indentured servants African slaves
 Conflict in the Colonies n n n Most colonies experienced east/west conflict Wealthy plantation owners of the east vs. poor small farmers of the west Easterners had the money and dominated the colonial assemblies and the Governor’s office
Conflict in the Colonies n n n Most colonies experienced east/west conflict Wealthy plantation owners of the east vs. poor small farmers of the west Easterners had the money and dominated the colonial assemblies and the Governor’s office
 Bacon’s Rebellion n n Most famous example is Bacon’s Rebellion (1676) Nathaniel Bacon leads a rebellion of western farmers against Gov. William Berkeley
Bacon’s Rebellion n n Most famous example is Bacon’s Rebellion (1676) Nathaniel Bacon leads a rebellion of western farmers against Gov. William Berkeley
 Causes of Bacon’s Rebellion n n Thought Berkeley was soft on Indians Wanted cheap lands ¡ ¡ n n take from Indians Wealthy wanted peaceful relations Falling tobacco prices Under represented in the Burgesses
Causes of Bacon’s Rebellion n n Thought Berkeley was soft on Indians Wanted cheap lands ¡ ¡ n n take from Indians Wealthy wanted peaceful relations Falling tobacco prices Under represented in the Burgesses
 Events of Bacon’s Rebellion n n Bacon’s followers attack local tribes Berkeley condemns Bacon rebels and captures and burns Jamestown Bacon dies of dysentery Berkeley crushes and executes 20 rebels
Events of Bacon’s Rebellion n n Bacon’s followers attack local tribes Berkeley condemns Bacon rebels and captures and burns Jamestown Bacon dies of dysentery Berkeley crushes and executes 20 rebels


