805b263a128eaa4b440c372bfeb49db2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 The Energy Challenge Peter Nygren Manager Energy Procurement SCA Brussels Nov 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
The Energy Challenge Peter Nygren Manager Energy Procurement SCA Brussels Nov 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
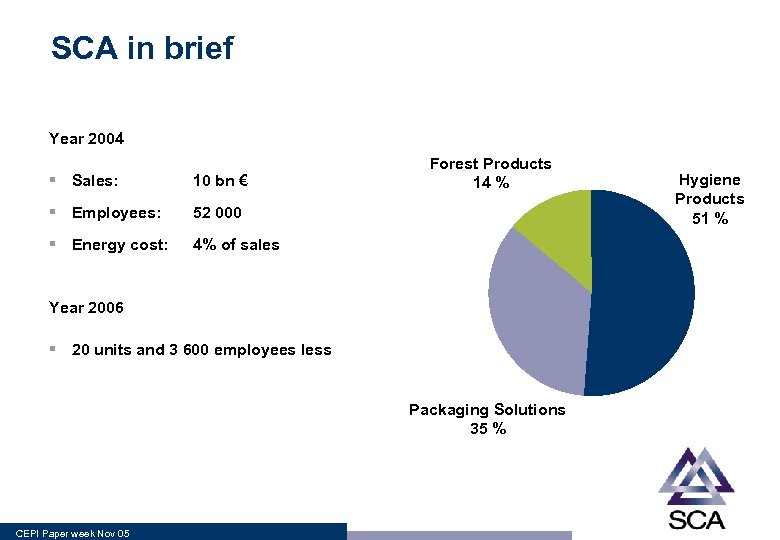 SCA in brief Year 2004 § Sales: 10 bn € § Employees: 52 000 § Energy cost: Forest Products 14 % 4% of sales Year 2006 § 20 units and 3 600 employees less Packaging Solutions 35 % CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Hygiene Products 51 %
SCA in brief Year 2004 § Sales: 10 bn € § Employees: 52 000 § Energy cost: Forest Products 14 % 4% of sales Year 2006 § 20 units and 3 600 employees less Packaging Solutions 35 % CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Hygiene Products 51 %
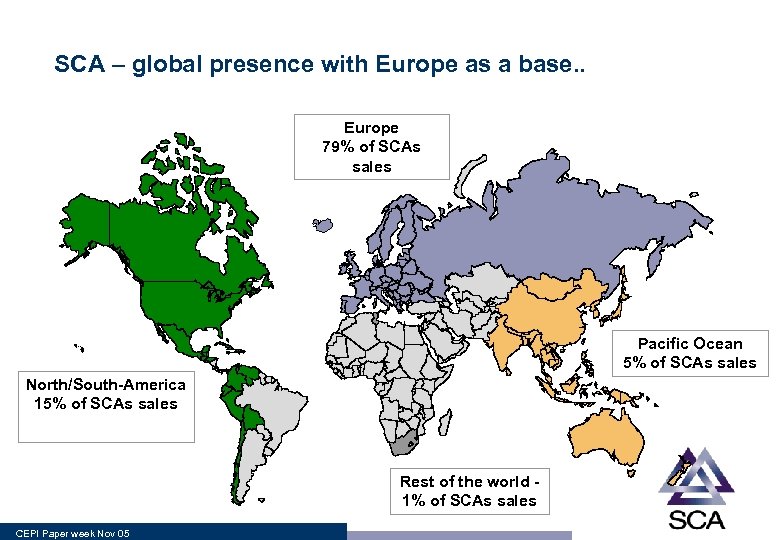 SCA – global presence with Europe as a base. . Europe 79% of SCAs sales Pacific Ocean 5% of SCAs sales North/South-America 15% of SCAs sales Rest of the world 1% of SCAs sales CEPI Paper week Nov 05
SCA – global presence with Europe as a base. . Europe 79% of SCAs sales Pacific Ocean 5% of SCAs sales North/South-America 15% of SCAs sales Rest of the world 1% of SCAs sales CEPI Paper week Nov 05
 Industrial power prices world wide 2003/04 (commodity €/MWh) Island: 12 -15 Nordic: 24 - 28 Europe: 30 - 36 Canada: 24 - 26 Spain 40+ USA: 30 - 32 Italy 50+ China: 30 + M East: 14 - 16 S-Africa: 20 -22 Brazil: 20 - 22 CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Russia: 14 - 16 Australia: 23 - 25
Industrial power prices world wide 2003/04 (commodity €/MWh) Island: 12 -15 Nordic: 24 - 28 Europe: 30 - 36 Canada: 24 - 26 Spain 40+ USA: 30 - 32 Italy 50+ China: 30 + M East: 14 - 16 S-Africa: 20 -22 Brazil: 20 - 22 CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Russia: 14 - 16 Australia: 23 - 25
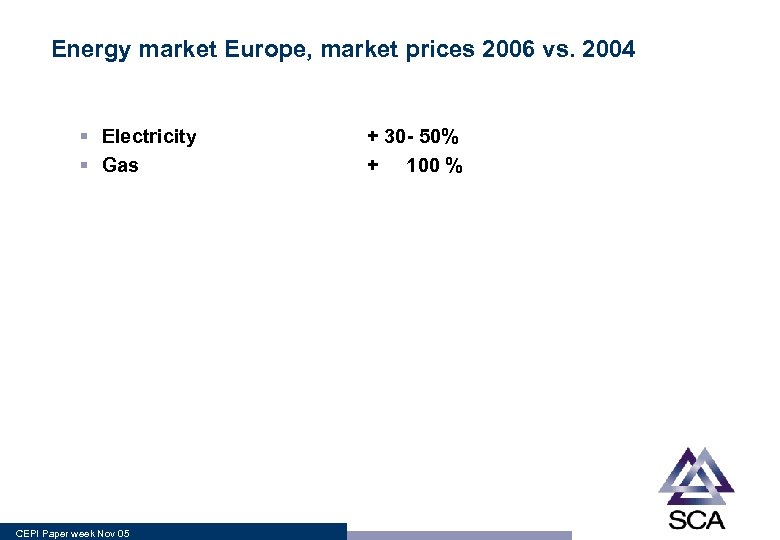 Energy market Europe, market prices 2006 vs. 2004 § Electricity § Gas CEPI Paper week Nov 05 + 30 - 50% + 100 %
Energy market Europe, market prices 2006 vs. 2004 § Electricity § Gas CEPI Paper week Nov 05 + 30 - 50% + 100 %
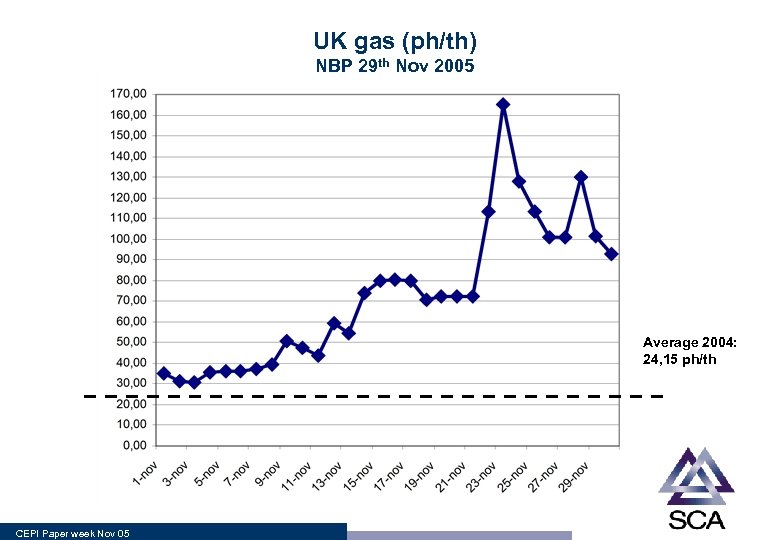 UK gas (ph/th) NBP 29 th Nov 2005 Average 2004: 24, 15 ph/th CEPI Paper week Nov 05
UK gas (ph/th) NBP 29 th Nov 2005 Average 2004: 24, 15 ph/th CEPI Paper week Nov 05
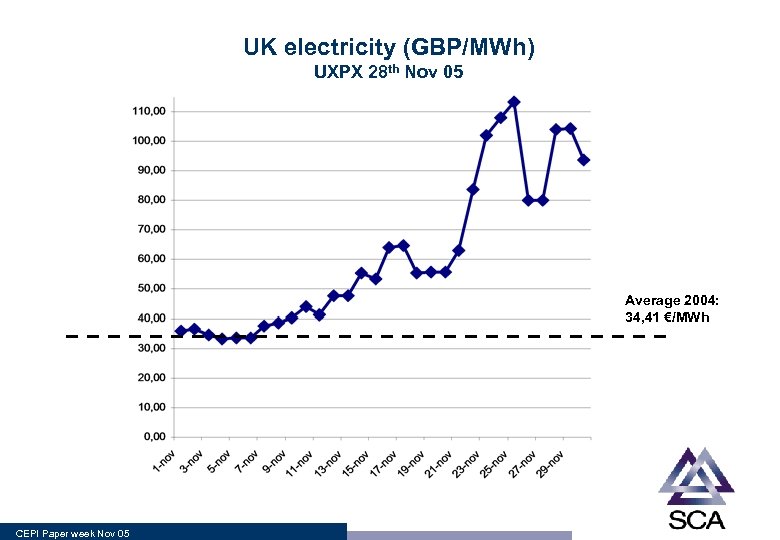 UK electricity (GBP/MWh) UXPX 28 th Nov 05 Average 2004: 34, 41 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
UK electricity (GBP/MWh) UXPX 28 th Nov 05 Average 2004: 34, 41 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
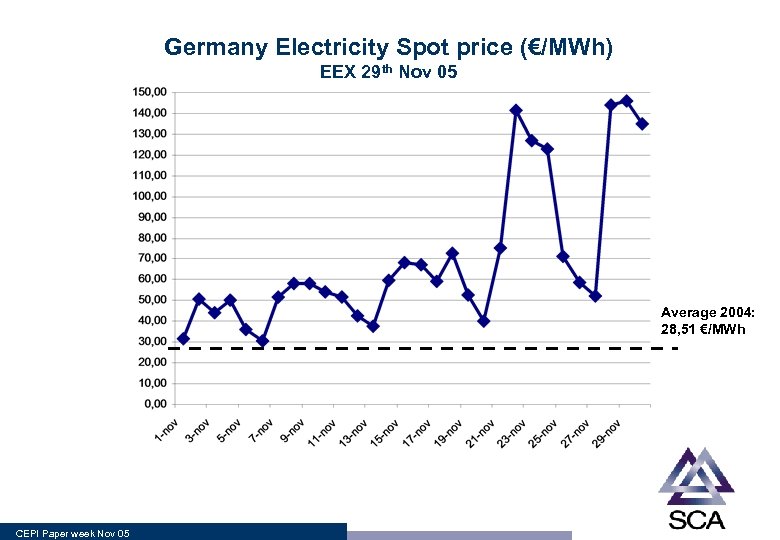 Germany Electricity Spot price (€/MWh) EEX 29 th Nov 05 Average 2004: 28, 51 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Germany Electricity Spot price (€/MWh) EEX 29 th Nov 05 Average 2004: 28, 51 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
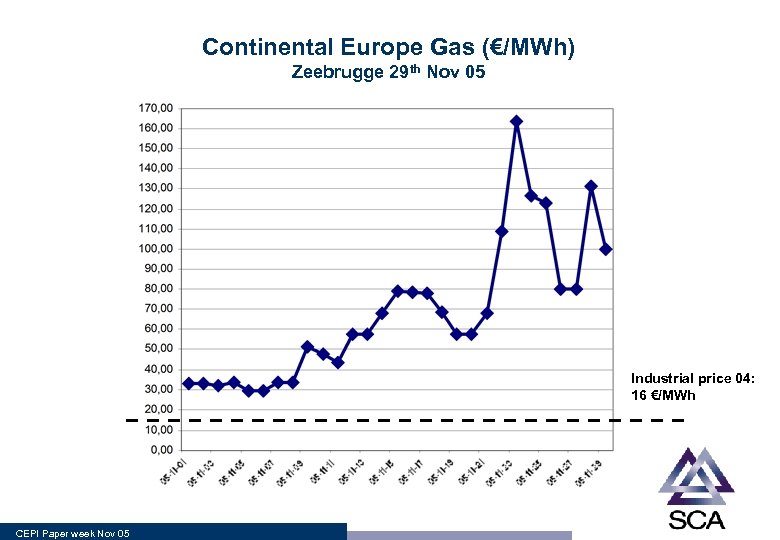 Continental Europe Gas (€/MWh) Zeebrugge 29 th Nov 05 Industrial price 04: 16 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Continental Europe Gas (€/MWh) Zeebrugge 29 th Nov 05 Industrial price 04: 16 €/MWh CEPI Paper week Nov 05
 What are the reasons for a heavy price increase on gas in Europe ? § Under supply in some regions (UK) § Market dominance by a few § Vertical integration gas electricity Oil price development combined with oil linked gas contracts CEPI Paper week Nov 05
What are the reasons for a heavy price increase on gas in Europe ? § Under supply in some regions (UK) § Market dominance by a few § Vertical integration gas electricity Oil price development combined with oil linked gas contracts CEPI Paper week Nov 05
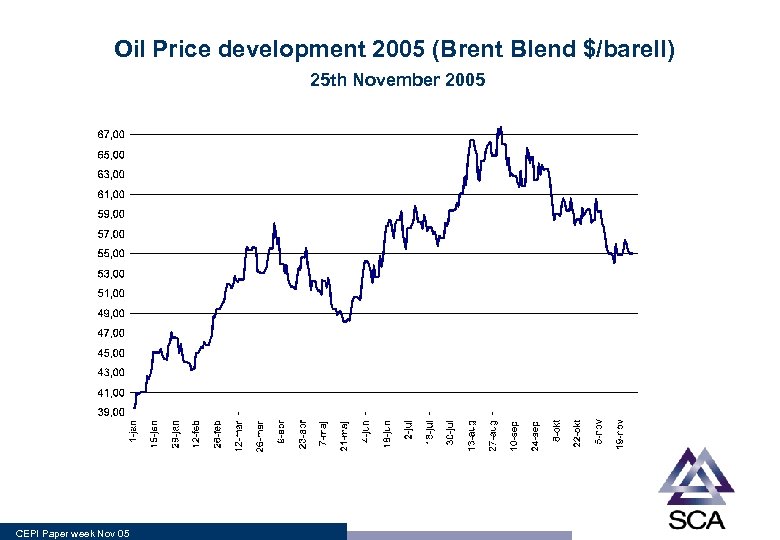 Oil Price development 2005 (Brent Blend $/barell) 25 th November 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Oil Price development 2005 (Brent Blend $/barell) 25 th November 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
 What are the reasons for a heavy price increase on electricity in Europe ? § Oil (-gas) price development § To some extent also coal price development (mostly domestic) § Market dominance by a few § Luck of price elasticity among the consumers combined with a market based price setting model The European Emission Trading Scheeme CEPI Paper week Nov 05
What are the reasons for a heavy price increase on electricity in Europe ? § Oil (-gas) price development § To some extent also coal price development (mostly domestic) § Market dominance by a few § Luck of price elasticity among the consumers combined with a market based price setting model The European Emission Trading Scheeme CEPI Paper week Nov 05
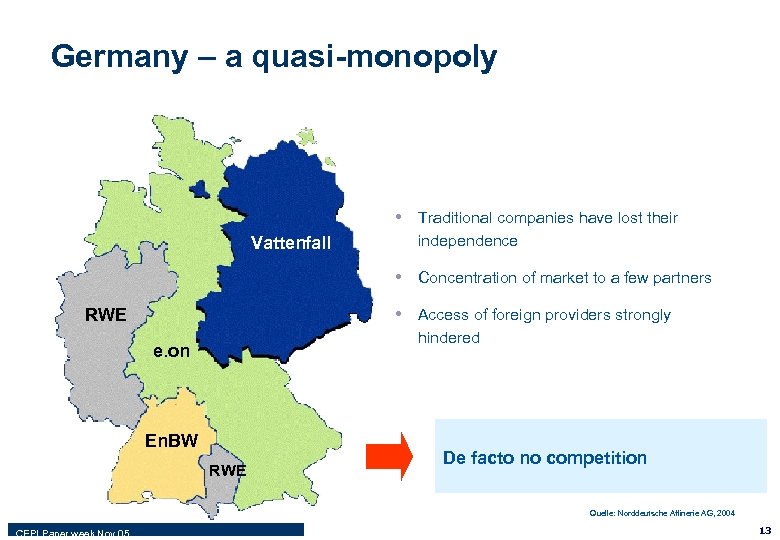 Germany – a quasi-monopoly • Traditional companies have lost their Vattenfall independence • Concentration of market to a few partners • Access of foreign providers strongly RWE hindered e. on En. BW RWE De facto no competition Quelle: Norddeutsche Affinerie AG, 2004 CEPI Paper week Nov 05 13
Germany – a quasi-monopoly • Traditional companies have lost their Vattenfall independence • Concentration of market to a few partners • Access of foreign providers strongly RWE hindered e. on En. BW RWE De facto no competition Quelle: Norddeutsche Affinerie AG, 2004 CEPI Paper week Nov 05 13
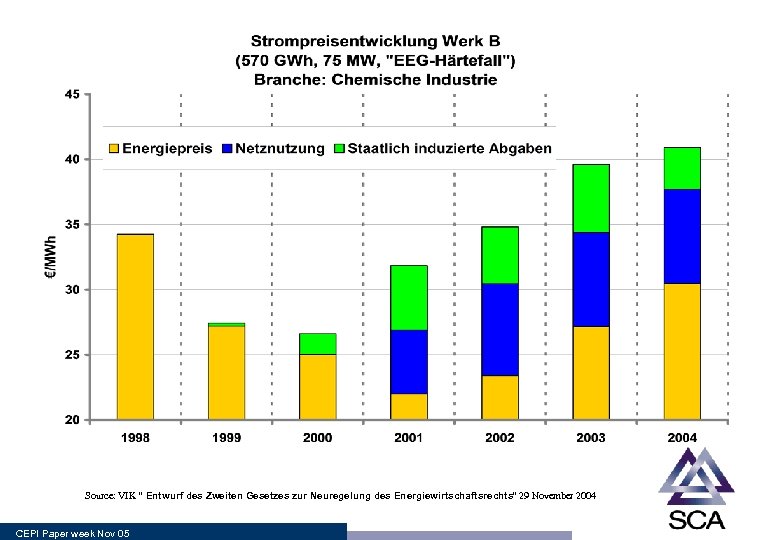 Source: VIK ” Entwurf des Zweiten Gesetzes zur Neuregelung des Energiewirtschaftsrechts” 29 November 2004 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Source: VIK ” Entwurf des Zweiten Gesetzes zur Neuregelung des Energiewirtschaftsrechts” 29 November 2004 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
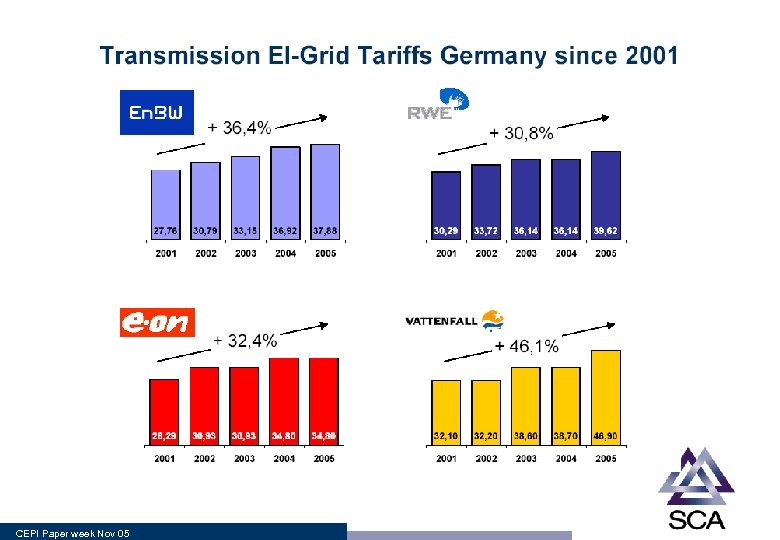 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
CEPI Paper week Nov 05
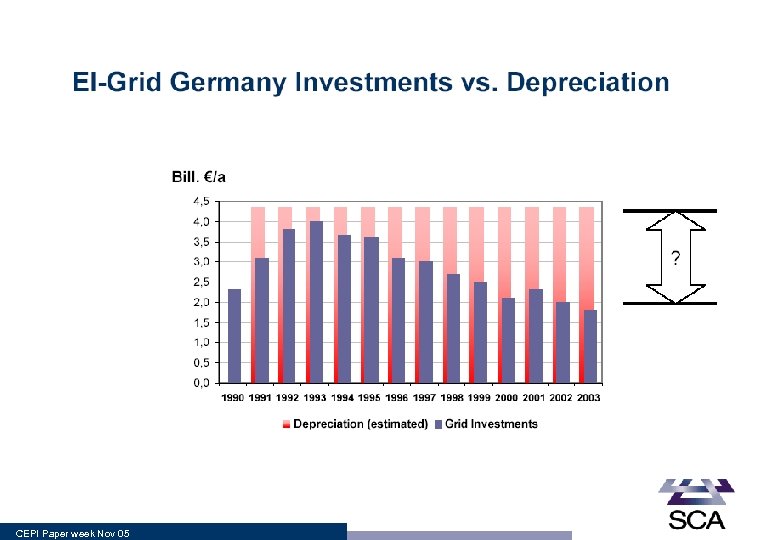 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
CEPI Paper week Nov 05
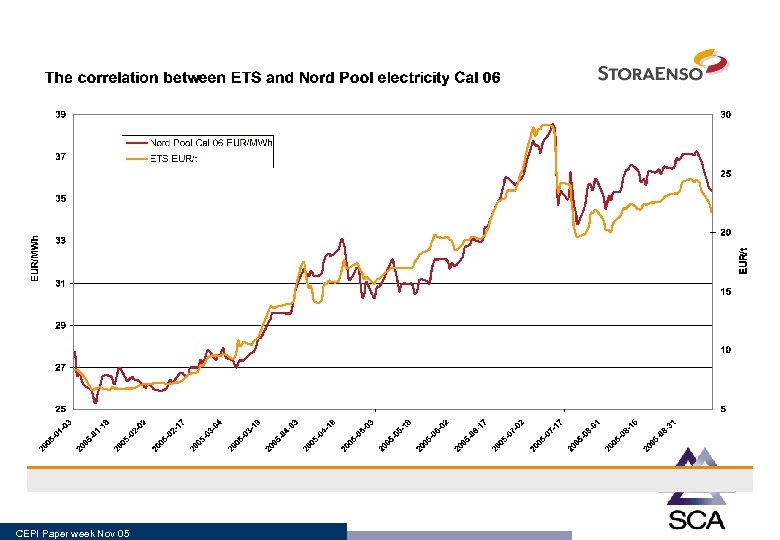 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
CEPI Paper week Nov 05
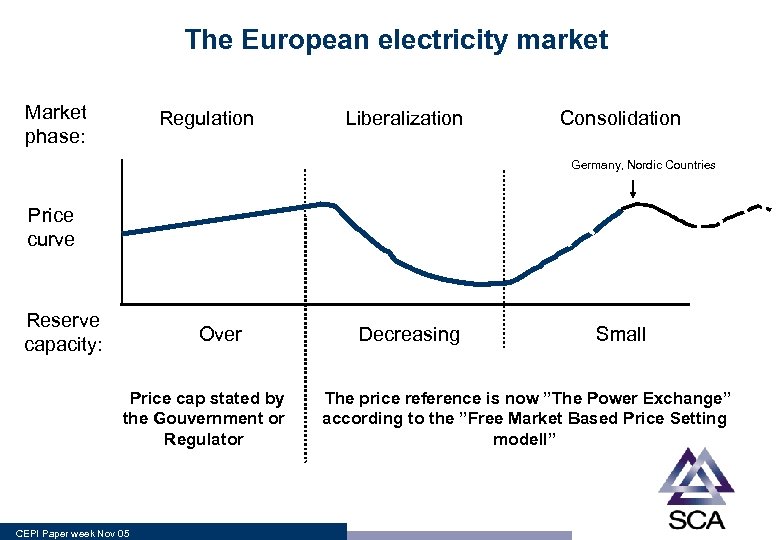 The European electricity market Market phase: Regulation Liberalization Consolidation Germany, Nordic Countries Price curve Reserve capacity: Over • Price cap stated by the Gouvernment or Regulator CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Decreasing Small • The price reference is now ”The Power Exchange” according to the ”Free Market Based Price Setting modell”
The European electricity market Market phase: Regulation Liberalization Consolidation Germany, Nordic Countries Price curve Reserve capacity: Over • Price cap stated by the Gouvernment or Regulator CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Decreasing Small • The price reference is now ”The Power Exchange” according to the ”Free Market Based Price Setting modell”
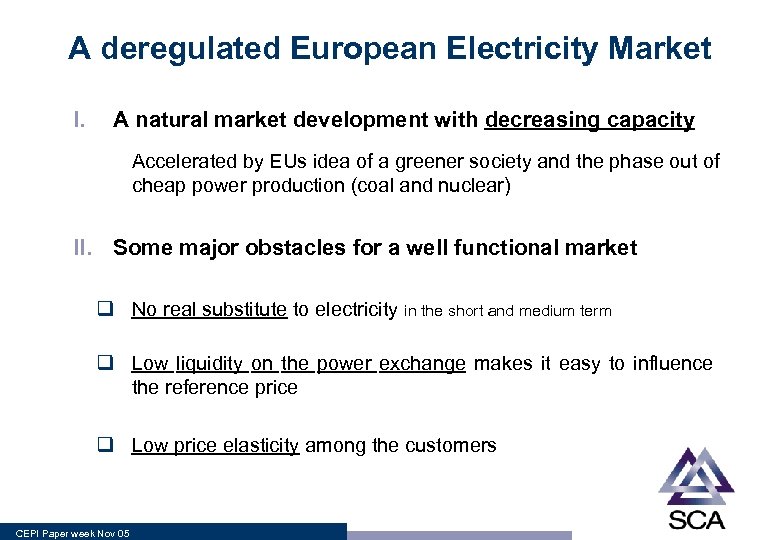 A deregulated European Electricity Market I. A natural market development with decreasing capacity Accelerated by EUs idea of a greener society and the phase out of cheap power production (coal and nuclear) II. Some major obstacles for a well functional market q No real substitute to electricity in the short and medium term q Low liquidity on the power exchange makes it easy to influence the reference price q Low price elasticity among the customers CEPI Paper week Nov 05
A deregulated European Electricity Market I. A natural market development with decreasing capacity Accelerated by EUs idea of a greener society and the phase out of cheap power production (coal and nuclear) II. Some major obstacles for a well functional market q No real substitute to electricity in the short and medium term q Low liquidity on the power exchange makes it easy to influence the reference price q Low price elasticity among the customers CEPI Paper week Nov 05
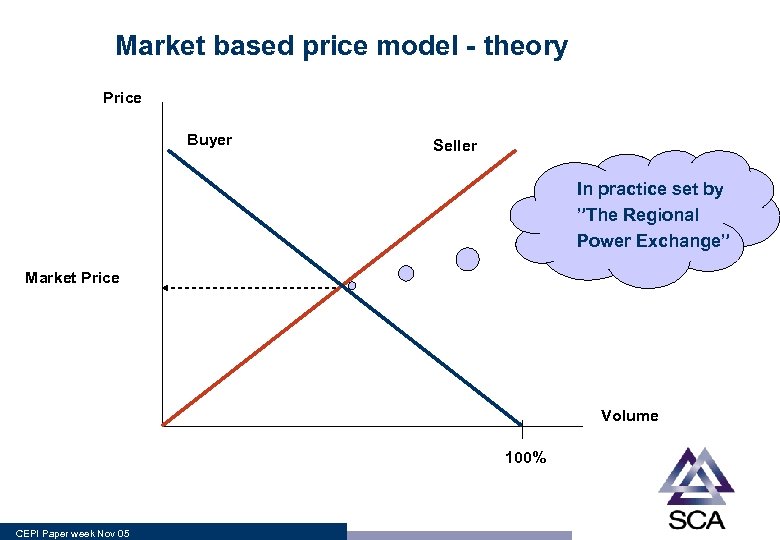 Market based price model - theory Price Buyer Seller In practice set by ”The Regional Power Exchange” Market Price Volume 100% CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Market based price model - theory Price Buyer Seller In practice set by ”The Regional Power Exchange” Market Price Volume 100% CEPI Paper week Nov 05
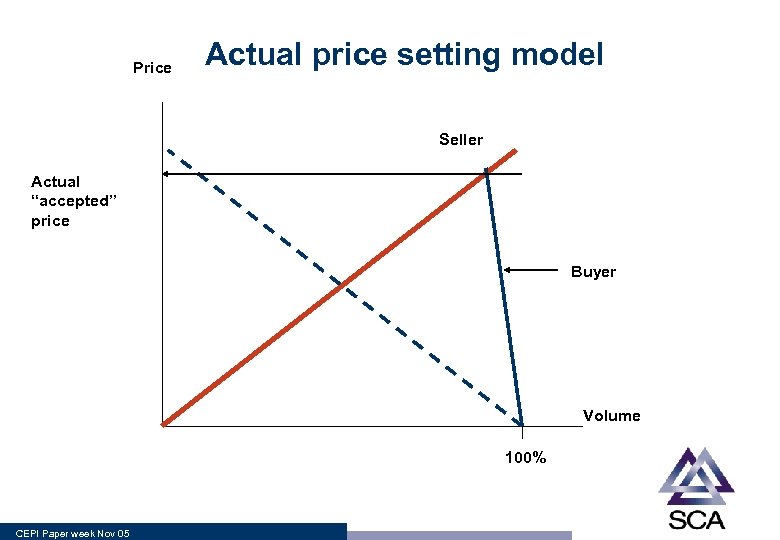 Price Actual price setting model Seller Actual “accepted” price Buyer Volume 100% CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Price Actual price setting model Seller Actual “accepted” price Buyer Volume 100% CEPI Paper week Nov 05
 What does it mean ? § To influence the price we either have to buy less or increase the supply in the region w Our price elasticity is and will remain low w Increased supply is not in the producers interest w We can not expect the producers to do the work for us and they do not have to in a deregulated market !! We therefore have to act our self to help the market work better ! The alternative is re-regulation of the market CEPI Paper week Nov 05
What does it mean ? § To influence the price we either have to buy less or increase the supply in the region w Our price elasticity is and will remain low w Increased supply is not in the producers interest w We can not expect the producers to do the work for us and they do not have to in a deregulated market !! We therefore have to act our self to help the market work better ! The alternative is re-regulation of the market CEPI Paper week Nov 05
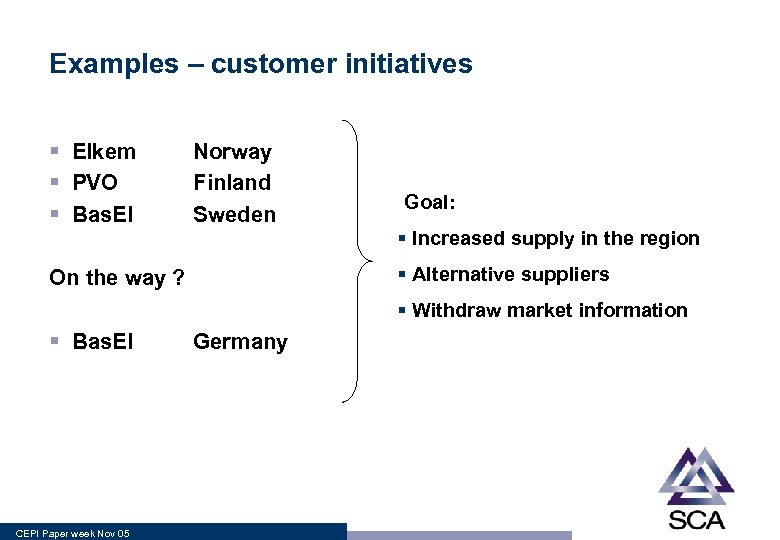 Examples – customer initiatives § Elkem § PVO § Bas. El Norway Finland Sweden • Goal: § Increased supply in the region § Alternative suppliers On the way ? § Withdraw market information § Bas. El CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Germany
Examples – customer initiatives § Elkem § PVO § Bas. El Norway Finland Sweden • Goal: § Increased supply in the region § Alternative suppliers On the way ? § Withdraw market information § Bas. El CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Germany
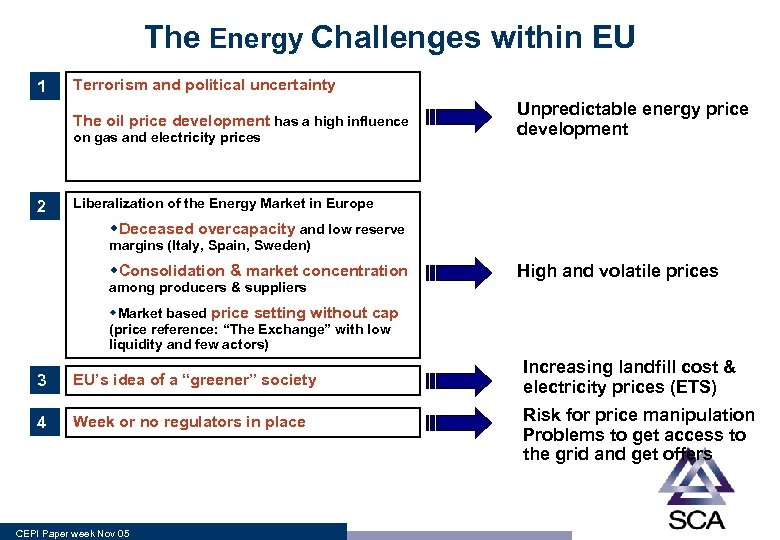 The Energy Challenges within EU 1 Terrorism and political uncertainty The oil price development has a high influence on gas and electricity prices Unpredictable energy price development • 2 Liberalization of the Energy Market in Europe w. Deceased overcapacity and low reserve margins (Italy, Spain, Sweden) w. Consolidation & market concentration among producers & suppliers High and volatile prices w. Market based price setting without cap (price reference: “The Exchange” with low liquidity and few actors) 3 EU’s idea of a “greener” society 4 Week or no regulators in place CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Increasing landfill cost & electricity prices (ETS) Risk for price manipulation Problems to get access to the grid and get offers
The Energy Challenges within EU 1 Terrorism and political uncertainty The oil price development has a high influence on gas and electricity prices Unpredictable energy price development • 2 Liberalization of the Energy Market in Europe w. Deceased overcapacity and low reserve margins (Italy, Spain, Sweden) w. Consolidation & market concentration among producers & suppliers High and volatile prices w. Market based price setting without cap (price reference: “The Exchange” with low liquidity and few actors) 3 EU’s idea of a “greener” society 4 Week or no regulators in place CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Increasing landfill cost & electricity prices (ETS) Risk for price manipulation Problems to get access to the grid and get offers
 Gas - what can we do ? The companies: CEPI: Focus: Decreased oil dependency: § Energy saving (10 - 20%) § Fuel switch to alternative fuels § Waste and own residuals (10%) Focus: Increased market comptition: § Access to the grid (pipe lines) § Official tariffs § State owned pipe lines and storages? Problem: § Time § CAPEX (not core, IFREC, IAS) Problem: § Vertical integration in the energy sector with weak or no regulators Action needed: § Review the strategy and consider if Energy not should be core CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Action needed: § Develop a strong and focused “gas lobbying strategy”
Gas - what can we do ? The companies: CEPI: Focus: Decreased oil dependency: § Energy saving (10 - 20%) § Fuel switch to alternative fuels § Waste and own residuals (10%) Focus: Increased market comptition: § Access to the grid (pipe lines) § Official tariffs § State owned pipe lines and storages? Problem: § Time § CAPEX (not core, IFREC, IAS) Problem: § Vertical integration in the energy sector with weak or no regulators Action needed: § Review the strategy and consider if Energy not should be core CEPI Paper week Nov 05 Action needed: § Develop a strong and focused “gas lobbying strategy”
 Electricity - what can we do ? The companies: CEPI: Focus: Increased supply & independency: § Regional solutions on ETS § Cooperation (“Bas. El”) § Buy out state owned production Focus: Prevent EU initatives with risk for extra burden on the industry within Europe § Emission Trading (CO 2, NOX, SOX) § Green certificates § Security of supply (more capacity) Problem: § ? Problem: § No common Energy policy within EU Action needed: § Increased cooperation with other energy intensive industries within EU Action needed: § Develop a strong and focused “electricity lobbying strategy” § Cooperation with others § Energy savings and own production CEPI Paper week Nov 05 (Energy initiatives is often used as an political tool to buy support from minority parties)
Electricity - what can we do ? The companies: CEPI: Focus: Increased supply & independency: § Regional solutions on ETS § Cooperation (“Bas. El”) § Buy out state owned production Focus: Prevent EU initatives with risk for extra burden on the industry within Europe § Emission Trading (CO 2, NOX, SOX) § Green certificates § Security of supply (more capacity) Problem: § ? Problem: § No common Energy policy within EU Action needed: § Increased cooperation with other energy intensive industries within EU Action needed: § Develop a strong and focused “electricity lobbying strategy” § Cooperation with others § Energy savings and own production CEPI Paper week Nov 05 (Energy initiatives is often used as an political tool to buy support from minority parties)
 Thank you for your attention! CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Thank you for your attention! CEPI Paper week Nov 05
 Reserve slides CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Reserve slides CEPI Paper week Nov 05
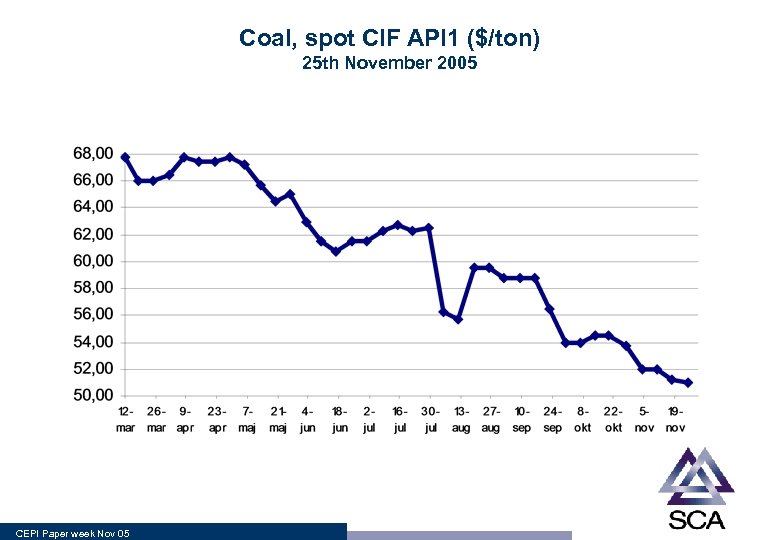 Coal, spot CIF API 1 ($/ton) 25 th November 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Coal, spot CIF API 1 ($/ton) 25 th November 2005 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
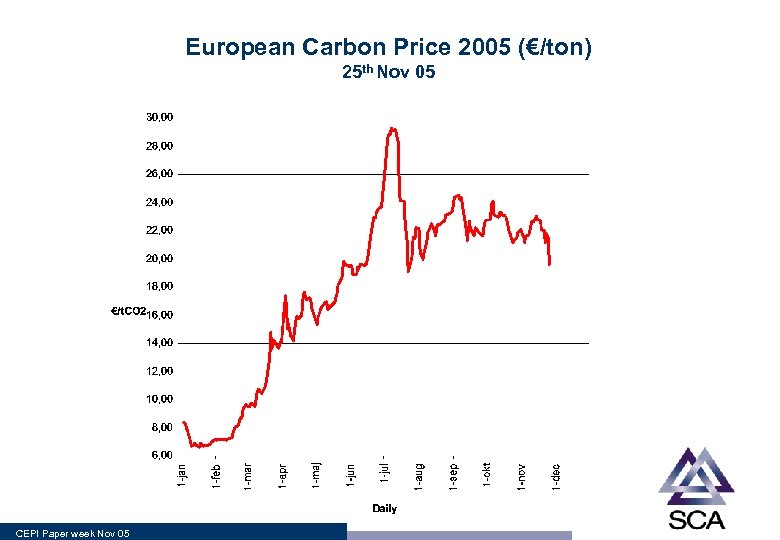 European Carbon Price 2005 (€/ton) 25 th Nov 05 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
European Carbon Price 2005 (€/ton) 25 th Nov 05 CEPI Paper week Nov 05
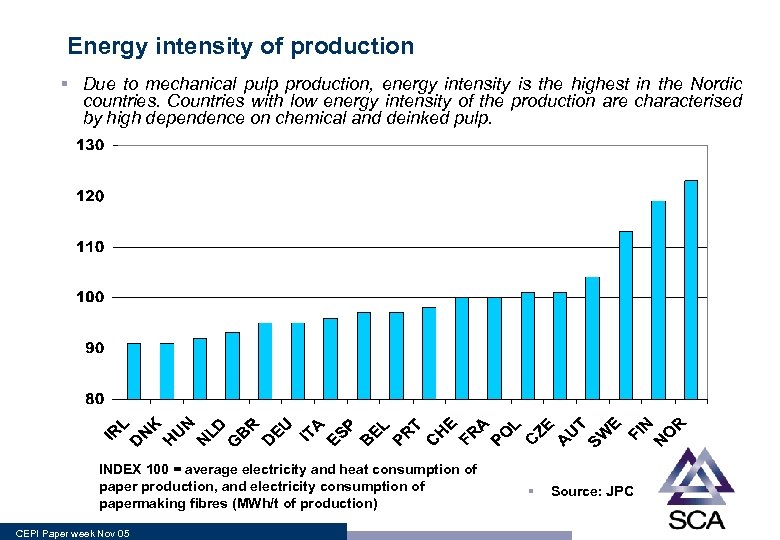 Energy intensity of production § Due to mechanical pulp production, energy intensity is the highest in the Nordic countries. Countries with low energy intensity of the production are characterised by high dependence on chemical and deinked pulp. INDEX 100 = average electricity and heat consumption of paper production, and electricity consumption of papermaking fibres (MWh/t of production) CEPI Paper week Nov 05 § Source: JPC
Energy intensity of production § Due to mechanical pulp production, energy intensity is the highest in the Nordic countries. Countries with low energy intensity of the production are characterised by high dependence on chemical and deinked pulp. INDEX 100 = average electricity and heat consumption of paper production, and electricity consumption of papermaking fibres (MWh/t of production) CEPI Paper week Nov 05 § Source: JPC
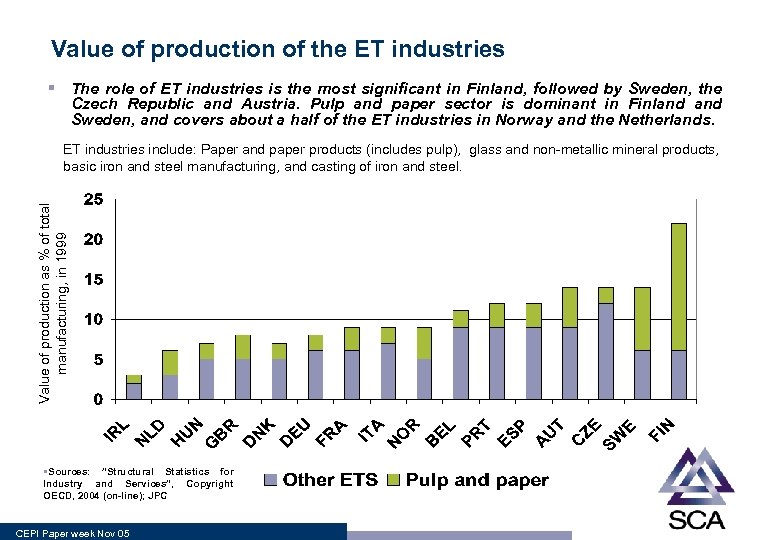 Value of production of the ET industries § The role of ET industries is the most significant in Finland, followed by Sweden, the Czech Republic and Austria. Pulp and paper sector is dominant in Finland Sweden, and covers about a half of the ET industries in Norway and the Netherlands. Value of production as % of total manufacturing, in 1999 ET industries include: Paper and paper products (includes pulp), glass and non-metallic mineral products, basic iron and steel manufacturing, and casting of iron and steel. §Sources: ”Structural Statistics for Industry and Services”, Copyright OECD, 2004 (on-line); JPC CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Value of production of the ET industries § The role of ET industries is the most significant in Finland, followed by Sweden, the Czech Republic and Austria. Pulp and paper sector is dominant in Finland Sweden, and covers about a half of the ET industries in Norway and the Netherlands. Value of production as % of total manufacturing, in 1999 ET industries include: Paper and paper products (includes pulp), glass and non-metallic mineral products, basic iron and steel manufacturing, and casting of iron and steel. §Sources: ”Structural Statistics for Industry and Services”, Copyright OECD, 2004 (on-line); JPC CEPI Paper week Nov 05
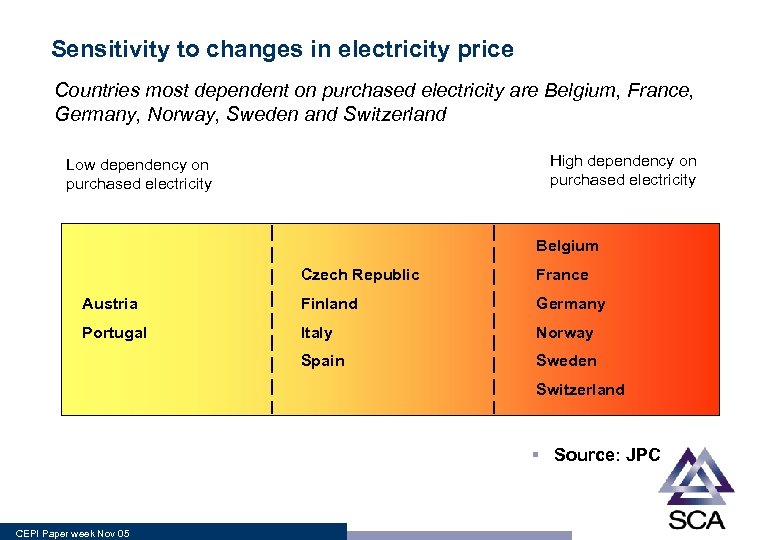 Sensitivity to changes in electricity price Countries most dependent on purchased electricity are Belgium, France, Germany, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland High dependency on purchased electricity Low dependency on purchased electricity Belgium Czech Republic France Austria Finland Germany Portugal Italy Norway Spain Sweden Switzerland § Source: JPC CEPI Paper week Nov 05
Sensitivity to changes in electricity price Countries most dependent on purchased electricity are Belgium, France, Germany, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland High dependency on purchased electricity Low dependency on purchased electricity Belgium Czech Republic France Austria Finland Germany Portugal Italy Norway Spain Sweden Switzerland § Source: JPC CEPI Paper week Nov 05


