3531e5de421abcd4623c8a3df9f6e6e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The effects of viscosity on hydrodynamical evolution of QGP 苏中乾 大连理 大学 2010 -4 -18 Dalian University of Technology
The effects of viscosity on hydrodynamical evolution of QGP 苏中乾 大连理 大学 2010 -4 -18 Dalian University of Technology
 The effects of viscosity on hydrodynamical evolution of QGP Contents • I. Formalization of viscous hydrodynamics • II. Equation of state (EOS) and initial conditions • III. Numerical results • IV. Summery
The effects of viscosity on hydrodynamical evolution of QGP Contents • I. Formalization of viscous hydrodynamics • II. Equation of state (EOS) and initial conditions • III. Numerical results • IV. Summery
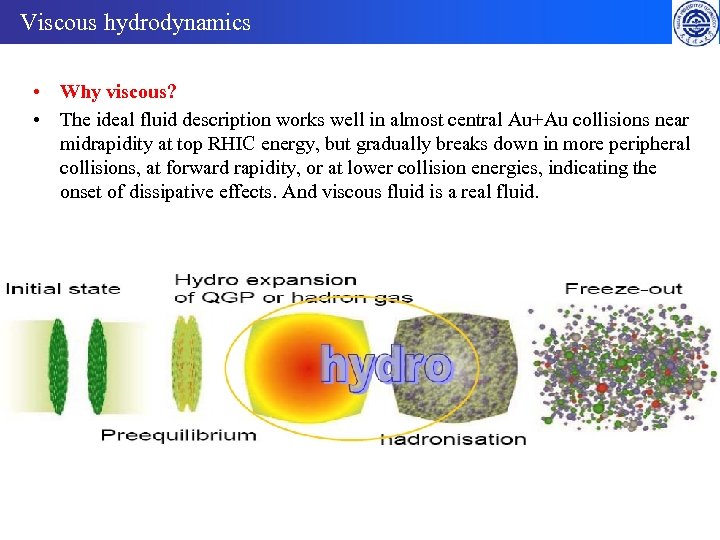 Viscous hydrodynamics • Why viscous? • The ideal fluid description works well in almost central Au+Au collisions near midrapidity at top RHIC energy, but gradually breaks down in more peripheral collisions, at forward rapidity, or at lower collision energies, indicating the onset of dissipative effects. And viscous fluid is a real fluid.
Viscous hydrodynamics • Why viscous? • The ideal fluid description works well in almost central Au+Au collisions near midrapidity at top RHIC energy, but gradually breaks down in more peripheral collisions, at forward rapidity, or at lower collision energies, indicating the onset of dissipative effects. And viscous fluid is a real fluid.
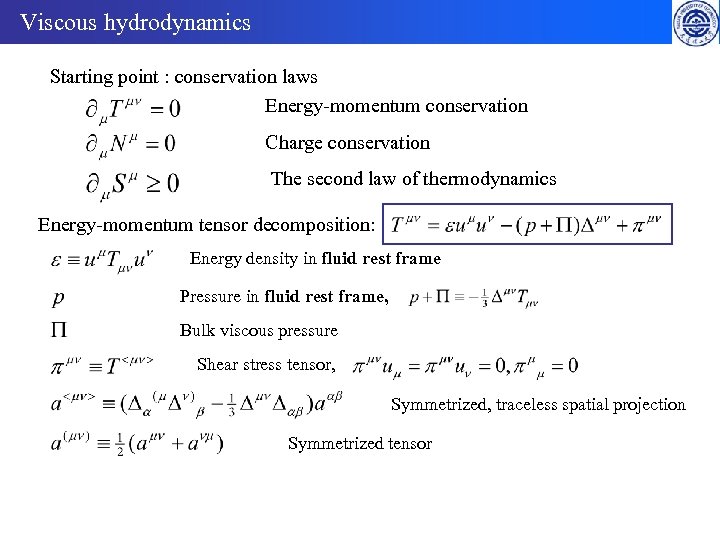 Viscous hydrodynamics Starting point : conservation laws Energy-momentum conservation Charge conservation The second law of thermodynamics Energy-momentum tensor decomposition: Energy density in fluid rest frame Pressure in fluid rest frame, Bulk viscous pressure Shear stress tensor, Symmetrized, traceless spatial projection Symmetrized tensor
Viscous hydrodynamics Starting point : conservation laws Energy-momentum conservation Charge conservation The second law of thermodynamics Energy-momentum tensor decomposition: Energy density in fluid rest frame Pressure in fluid rest frame, Bulk viscous pressure Shear stress tensor, Symmetrized, traceless spatial projection Symmetrized tensor
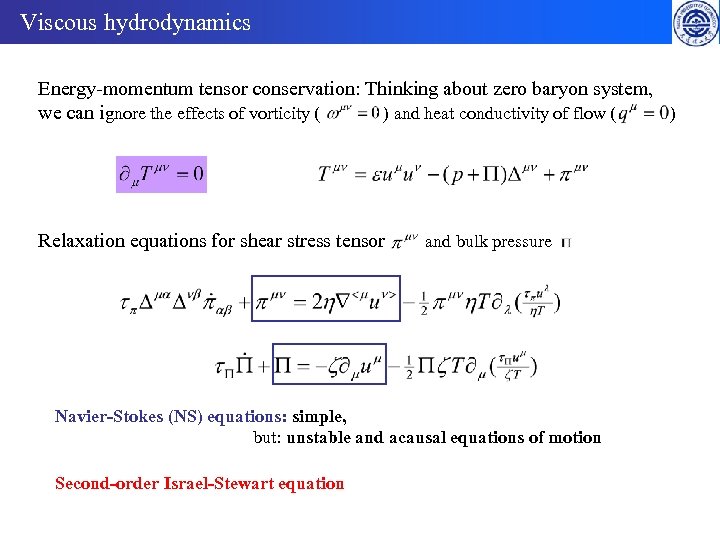 Viscous hydrodynamics Energy-momentum tensor conservation: Thinking about zero baryon system, we can ignore the effects of vorticity ( ) and heat conductivity of flow ( ) Relaxation equations for shear stress tensor and bulk pressure Navier-Stokes (NS) equations: simple, but: unstable and acausal equations of motion Second-order Israel-Stewart equation
Viscous hydrodynamics Energy-momentum tensor conservation: Thinking about zero baryon system, we can ignore the effects of vorticity ( ) and heat conductivity of flow ( ) Relaxation equations for shear stress tensor and bulk pressure Navier-Stokes (NS) equations: simple, but: unstable and acausal equations of motion Second-order Israel-Stewart equation
 Viscous hydrodynamics With , viscous hydrodynamics reduces to ideal hydrodynamics • Use Bjorken picture and thinking about azimuthally symmetric systems: (Boost invariant) Notice: once we know velocity and the temperature at by Lorentz boost: and , will be Obtained
Viscous hydrodynamics With , viscous hydrodynamics reduces to ideal hydrodynamics • Use Bjorken picture and thinking about azimuthally symmetric systems: (Boost invariant) Notice: once we know velocity and the temperature at by Lorentz boost: and , will be Obtained
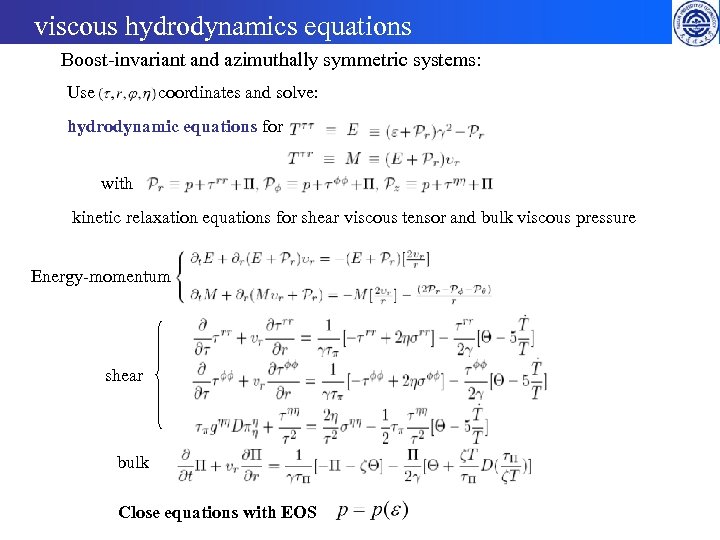 viscous hydrodynamics equations Boost-invariant and azimuthally symmetric systems: Use coordinates and solve: hydrodynamic equations for with kinetic relaxation equations for shear viscous tensor and bulk viscous pressure Energy-momentum shear bulk Close equations with EOS
viscous hydrodynamics equations Boost-invariant and azimuthally symmetric systems: Use coordinates and solve: hydrodynamic equations for with kinetic relaxation equations for shear viscous tensor and bulk viscous pressure Energy-momentum shear bulk Close equations with EOS
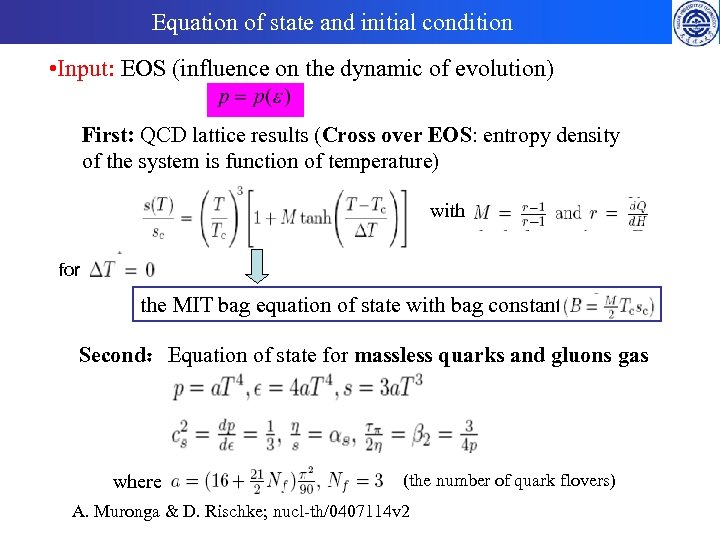 Equation of state and initial condition • Input: EOS (influence on the dynamic of evolution) First: QCD lattice results (Cross over EOS: entropy density of the system is function of temperature) with for the MIT bag equation of state with bag constant Second:Equation of state for massless quarks and gluons gas where (the number of quark flovers) A. Muronga & D. Rischke; nucl-th/0407114 v 2
Equation of state and initial condition • Input: EOS (influence on the dynamic of evolution) First: QCD lattice results (Cross over EOS: entropy density of the system is function of temperature) with for the MIT bag equation of state with bag constant Second:Equation of state for massless quarks and gluons gas where (the number of quark flovers) A. Muronga & D. Rischke; nucl-th/0407114 v 2
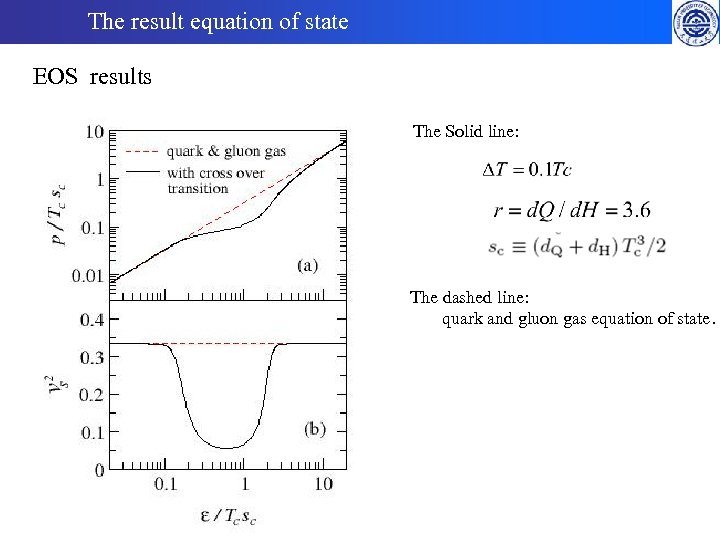 The result equation of state EOS results The Solid line: The dashed line: quark and gluon gas equation of state.
The result equation of state EOS results The Solid line: The dashed line: quark and gluon gas equation of state.
 The initial conditions Initial conditions: Initial energy density distribution in the transverse plane use Woods-saxon parameterization maximum energy density for central collisions at initial time initial transverse radius of source. the initial temperature at the center of source and initial proper time The components of the shear tensor and bulk pressure
The initial conditions Initial conditions: Initial energy density distribution in the transverse plane use Woods-saxon parameterization maximum energy density for central collisions at initial time initial transverse radius of source. the initial temperature at the center of source and initial proper time The components of the shear tensor and bulk pressure
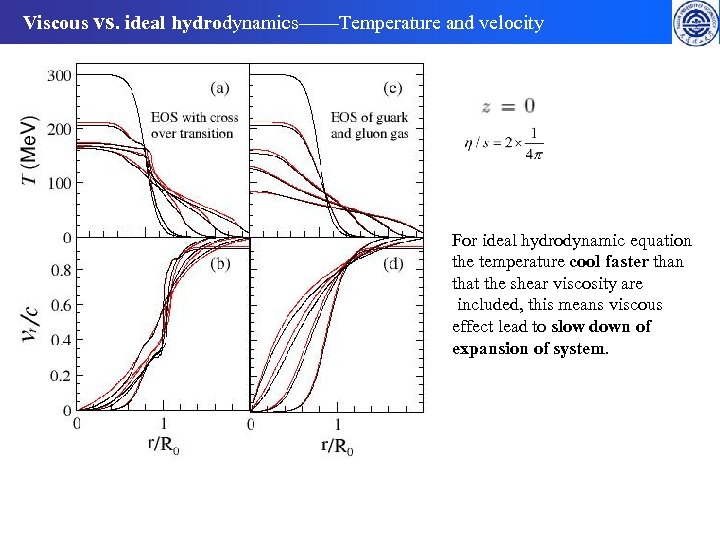 Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——Temperature and velocity For ideal hydrodynamic equation the temperature cool faster than that the shear viscosity are included, this means viscous effect lead to slow down of expansion of system.
Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——Temperature and velocity For ideal hydrodynamic equation the temperature cool faster than that the shear viscosity are included, this means viscous effect lead to slow down of expansion of system.
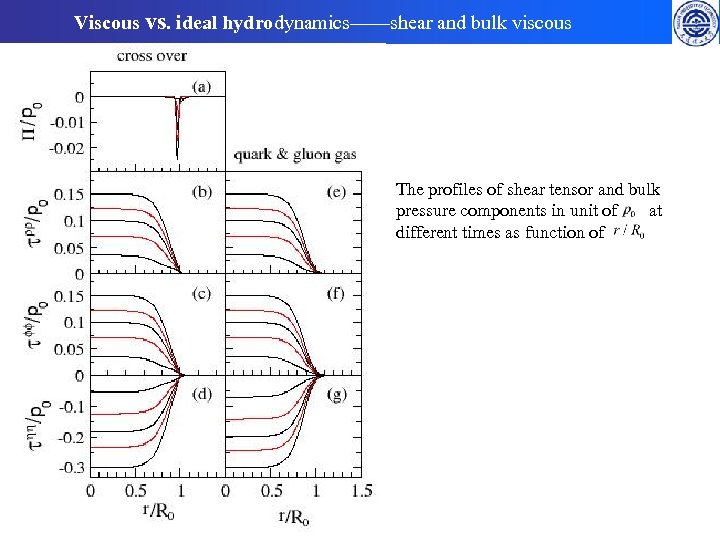 Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——shear and bulk viscous The profiles of shear tensor and bulk pressure components in unit of at different times as function of
Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——shear and bulk viscous The profiles of shear tensor and bulk pressure components in unit of at different times as function of
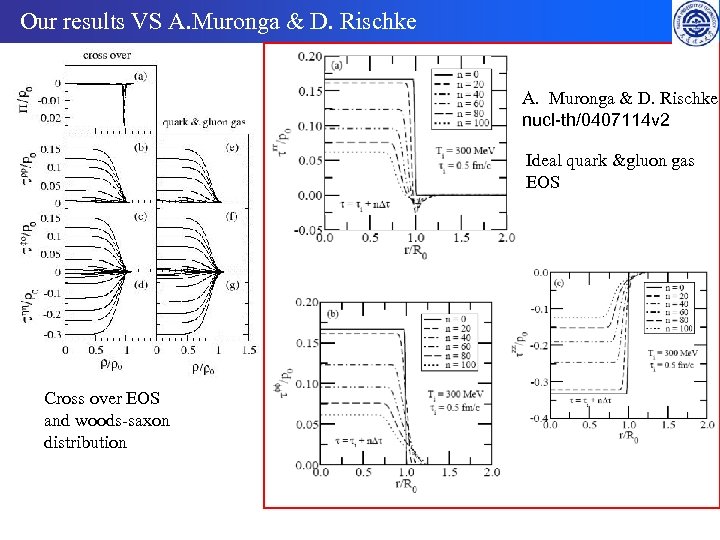 Our results VS A. Muronga & D. Rischke nucl-th/0407114 v 2 Ideal quark &gluon gas EOS Cross over EOS and woods-saxon distribution
Our results VS A. Muronga & D. Rischke nucl-th/0407114 v 2 Ideal quark &gluon gas EOS Cross over EOS and woods-saxon distribution
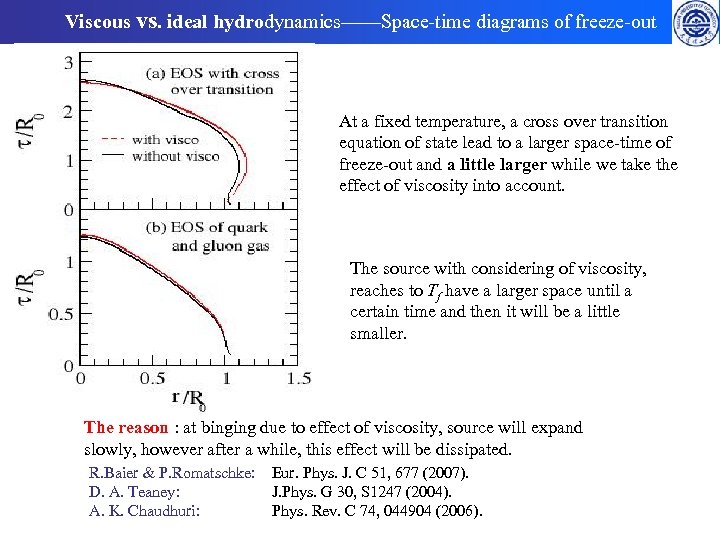 Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——Space-time diagrams of freeze-out At a fixed temperature, a cross over transition equation of state lead to a larger space-time of freeze-out and a little larger while we take the effect of viscosity into account. The source with considering of viscosity, reaches to Tf have a larger space until a certain time and then it will be a little smaller. The reason : at binging due to effect of viscosity, source will expand slowly, however after a while, this effect will be dissipated. R. Baier & P. Romatschke: D. A. Teaney: A. K. Chaudhuri: Eur. Phys. J. C 51, 677 (2007). J. Phys. G 30, S 1247 (2004). Phys. Rev. C 74, 044904 (2006).
Viscous vs. ideal hydrodynamics——Space-time diagrams of freeze-out At a fixed temperature, a cross over transition equation of state lead to a larger space-time of freeze-out and a little larger while we take the effect of viscosity into account. The source with considering of viscosity, reaches to Tf have a larger space until a certain time and then it will be a little smaller. The reason : at binging due to effect of viscosity, source will expand slowly, however after a while, this effect will be dissipated. R. Baier & P. Romatschke: D. A. Teaney: A. K. Chaudhuri: Eur. Phys. J. C 51, 677 (2007). J. Phys. G 30, S 1247 (2004). Phys. Rev. C 74, 044904 (2006).
 Summery • I. For ideal fluid the temperature cool faster than that the viscosity are included, this means viscous effect lead to slow down of the temperature decrease and the expansion of system. II. A cross over transition equation of state lead to a larger space-time of freeze-out than no phase transition and a little larger while we take the effect of viscosity into account.
Summery • I. For ideal fluid the temperature cool faster than that the viscosity are included, this means viscous effect lead to slow down of the temperature decrease and the expansion of system. II. A cross over transition equation of state lead to a larger space-time of freeze-out than no phase transition and a little larger while we take the effect of viscosity into account.
 Thank you!
Thank you!


