c4fe89c91b73d76571cc7ba0432d0afd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 The Effects of Filtering Malicious Traffic under Do. S Attacks Chinawat Wongvivitkul Sudsanguan Ngamsuriyaroj Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science Mahidol University, Thailand 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 1
The Effects of Filtering Malicious Traffic under Do. S Attacks Chinawat Wongvivitkul Sudsanguan Ngamsuriyaroj Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science Mahidol University, Thailand 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 1
 Agenda n Introduction & Motivation n Proposed Work n Implementation n Experiments & Results n Conclusions and Future Work 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 2
Agenda n Introduction & Motivation n Proposed Work n Implementation n Experiments & Results n Conclusions and Future Work 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 2
 Introduction § Do. S attacks have been well known for generating huge amount of adverse traffic to a target server and make the server unavailable for services. § Open Source IDS Software: Snort and Bro § IDS § Signature detection: based on predefined rules § Anomaly detection: learn first and then classify statistical patterns of incoming traffic 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 3
Introduction § Do. S attacks have been well known for generating huge amount of adverse traffic to a target server and make the server unavailable for services. § Open Source IDS Software: Snort and Bro § IDS § Signature detection: based on predefined rules § Anomaly detection: learn first and then classify statistical patterns of incoming traffic 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 3
 Motivation § Most studies used simulation tools, and only a few address the issues of server survivability under Do. S attacks § Questions § How to determine whether the incoming traffic is malicious in real time § How to create an anomaly detector using a simple statistics § How much traffic should be filtered out when the server is under attacks to make the server survives § No work does packet filtering interactively during the attack 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 4
Motivation § Most studies used simulation tools, and only a few address the issues of server survivability under Do. S attacks § Questions § How to determine whether the incoming traffic is malicious in real time § How to create an anomaly detector using a simple statistics § How much traffic should be filtered out when the server is under attacks to make the server survives § No work does packet filtering interactively during the attack 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 4
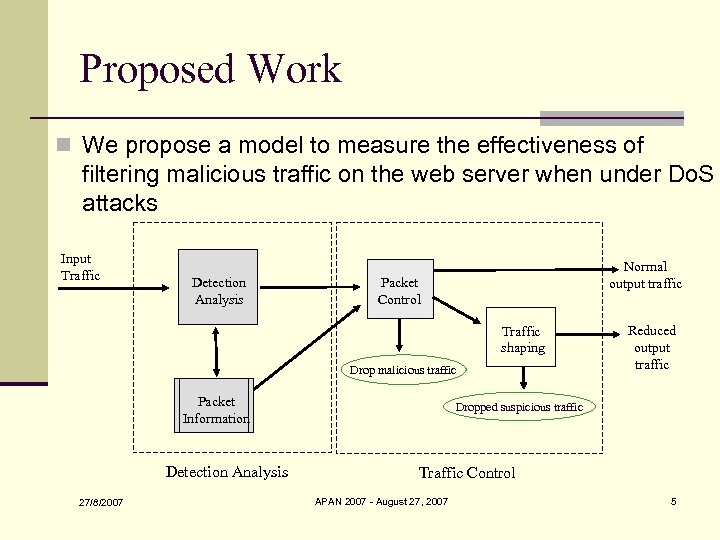 Proposed Work n We propose a model to measure the effectiveness of filtering malicious traffic on the web server when under Do. S attacks Input Traffic Detection Analysis Normal output traffic Packet Control Traffic shaping Drop malicious traffic Packet Information Detection Analysis 27/8/2007 Reduced output traffic Dropped suspicious traffic Traffic Control APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 5
Proposed Work n We propose a model to measure the effectiveness of filtering malicious traffic on the web server when under Do. S attacks Input Traffic Detection Analysis Normal output traffic Packet Control Traffic shaping Drop malicious traffic Packet Information Detection Analysis 27/8/2007 Reduced output traffic Dropped suspicious traffic Traffic Control APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 5
 Proposed Work n Have two phases n Detection Analysis n n Traffic Control n 27/8/2007 collect statistics of incoming traffic and classifies the status of the traffic. redirect traffic according to its status, and also filter traffic if the traffic is malicious APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 6
Proposed Work n Have two phases n Detection Analysis n n Traffic Control n 27/8/2007 collect statistics of incoming traffic and classifies the status of the traffic. redirect traffic according to its status, and also filter traffic if the traffic is malicious APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 6
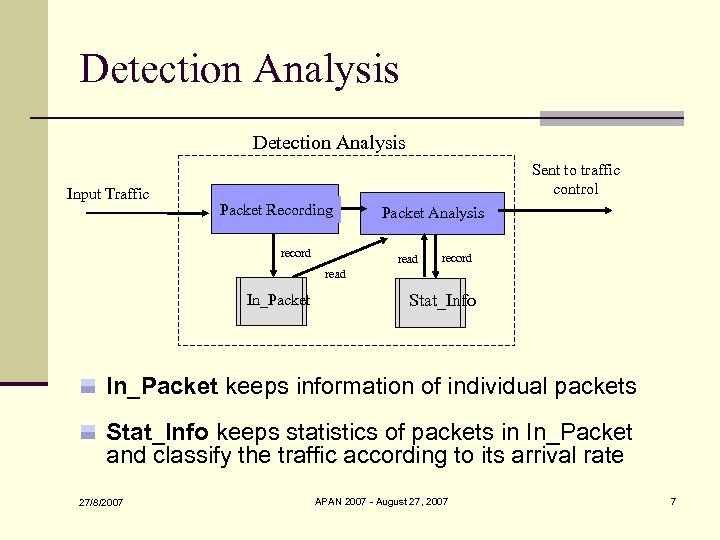 Detection Analysis Input Traffic Sent to traffic control Packet Recording record Packet Analysis read record read In_Packet Stat_Info In_Packet keeps information of individual packets Stat_Info keeps statistics of packets in In_Packet and classify the traffic according to its arrival rate 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 7
Detection Analysis Input Traffic Sent to traffic control Packet Recording record Packet Analysis read record read In_Packet Stat_Info In_Packet keeps information of individual packets Stat_Info keeps statistics of packets in In_Packet and classify the traffic according to its arrival rate 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 7
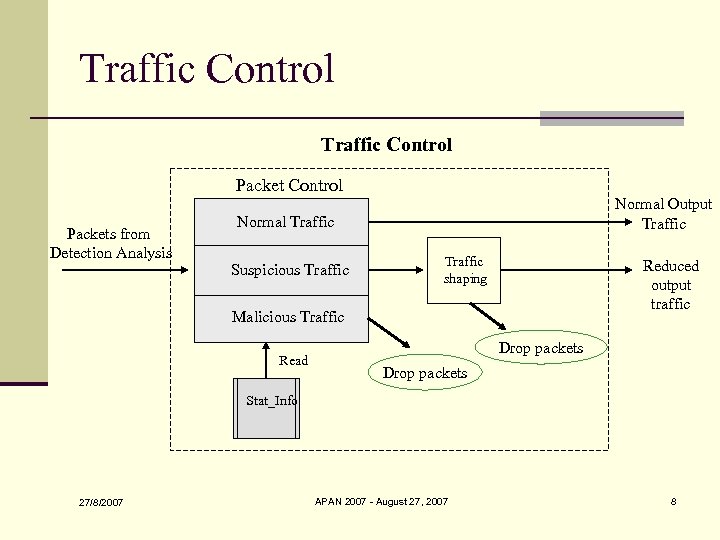 Traffic Control Packets from Detection Analysis Normal Output Traffic Normal Traffic Suspicious Traffic shaping Reduced output traffic Malicious Traffic Read Drop packets Stat_Info 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 8
Traffic Control Packets from Detection Analysis Normal Output Traffic Normal Traffic Suspicious Traffic shaping Reduced output traffic Malicious Traffic Read Drop packets Stat_Info 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 8
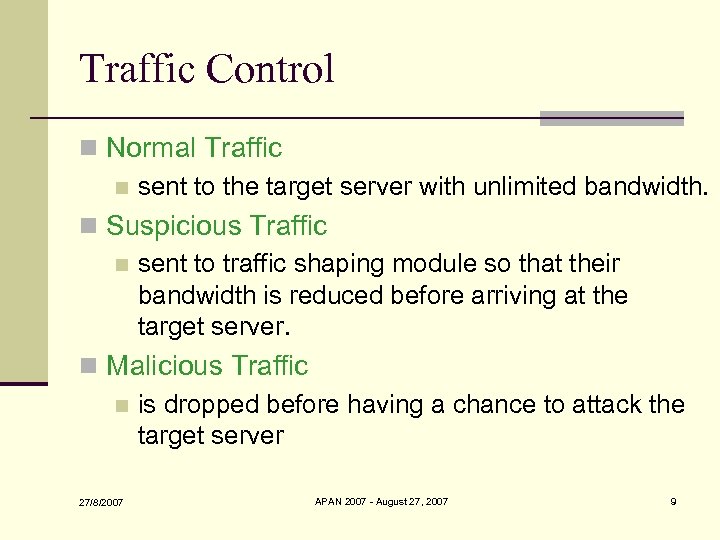 Traffic Control n Normal Traffic n sent to the target server with unlimited bandwidth. n Suspicious Traffic n sent to traffic shaping module so that their bandwidth is reduced before arriving at the target server. n Malicious Traffic n is dropped before having a chance to attack the target server 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 9
Traffic Control n Normal Traffic n sent to the target server with unlimited bandwidth. n Suspicious Traffic n sent to traffic shaping module so that their bandwidth is reduced before arriving at the target server. n Malicious Traffic n is dropped before having a chance to attack the target server 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 9
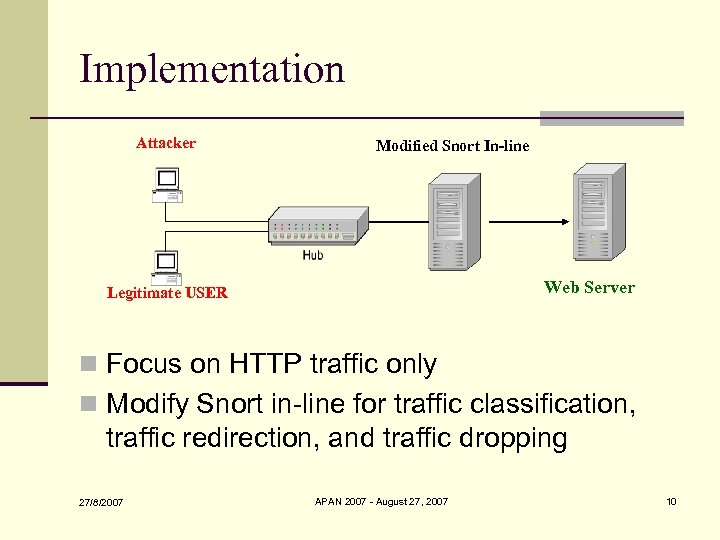 Implementation Attacker Modified Snort In-line Web Server Legitimate USER n Focus on HTTP traffic only n Modify Snort in-line for traffic classification, traffic redirection, and traffic dropping 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 10
Implementation Attacker Modified Snort In-line Web Server Legitimate USER n Focus on HTTP traffic only n Modify Snort in-line for traffic classification, traffic redirection, and traffic dropping 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 10
 Modified Snort In-Line n Packet capture/decode engine Do statistical analysis of each traffic stream n Detection engine n Compute the arrival rate at every 30 packets of one traffic stream n Classify traffic into normal, suspicious and malicious according to its arrival rate n Control engine n Add an extra module to redirect traffic to different paths according to its status. n Output engine n Perform traffic shaping by dropping suspicious and malicious traffic APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 11 27/8/2007 n
Modified Snort In-Line n Packet capture/decode engine Do statistical analysis of each traffic stream n Detection engine n Compute the arrival rate at every 30 packets of one traffic stream n Classify traffic into normal, suspicious and malicious according to its arrival rate n Control engine n Add an extra module to redirect traffic to different paths according to its status. n Output engine n Perform traffic shaping by dropping suspicious and malicious traffic APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 11 27/8/2007 n
 Modified Snort In-Line n Packet capture/decode engine add Input_traffic function in “detect. c” file of Snort In-line. n Detection engine n add the P_analysis function in “snort. c” file n Control engine n add p_control function in “snort. c” file. n Output engine n dropping the number of suspicious packets according to it arrival rate n Example rule for dropping suspicious and malicious traffic n drop tcp any -> any 20000 (msg: "D=Http IDS Malicious access tcp deny"; ) n drop tcp any -> any 40000 (msg: "D=Http IDS Suspicious access tcp deny"; ) 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 12
Modified Snort In-Line n Packet capture/decode engine add Input_traffic function in “detect. c” file of Snort In-line. n Detection engine n add the P_analysis function in “snort. c” file n Control engine n add p_control function in “snort. c” file. n Output engine n dropping the number of suspicious packets according to it arrival rate n Example rule for dropping suspicious and malicious traffic n drop tcp any -> any 20000 (msg: "D=Http IDS Malicious access tcp deny"; ) n drop tcp any -> any 40000 (msg: "D=Http IDS Suspicious access tcp deny"; ) 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 12
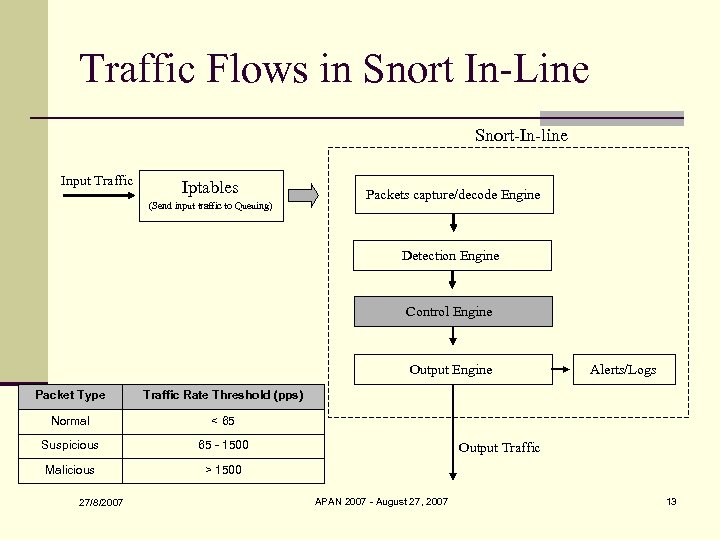 Traffic Flows in Snort In-Line Snort-In-line Input Traffic Iptables (Send input traffic to Queuing) Packets capture/decode Engine Detection Engine Control Engine Output Engine Packet Type Traffic Rate Threshold (pps) Normal < 65 Suspicious 65 - 1500 Malicious Alerts/Logs > 1500 27/8/2007 Output Traffic APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 13
Traffic Flows in Snort In-Line Snort-In-line Input Traffic Iptables (Send input traffic to Queuing) Packets capture/decode Engine Detection Engine Control Engine Output Engine Packet Type Traffic Rate Threshold (pps) Normal < 65 Suspicious 65 - 1500 Malicious Alerts/Logs > 1500 27/8/2007 Output Traffic APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 13
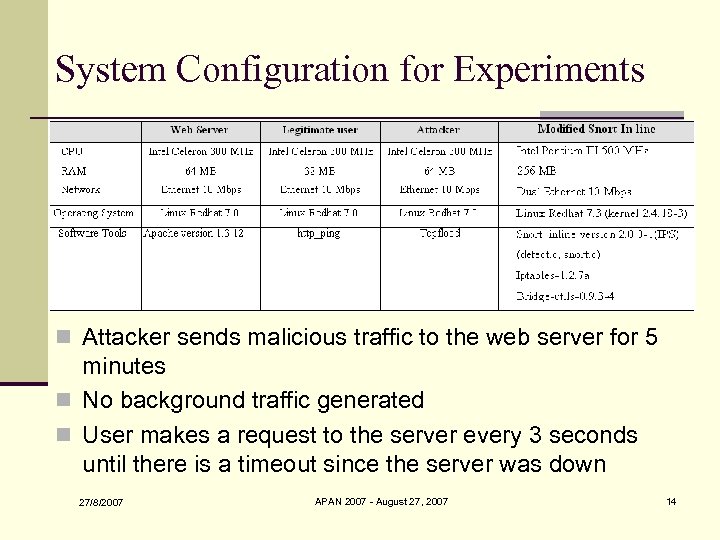 System Configuration for Experiments n Attacker sends malicious traffic to the web server for 5 minutes n No background traffic generated n User makes a request to the server every 3 seconds until there is a timeout since the server was down 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 14
System Configuration for Experiments n Attacker sends malicious traffic to the web server for 5 minutes n No background traffic generated n User makes a request to the server every 3 seconds until there is a timeout since the server was down 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 14
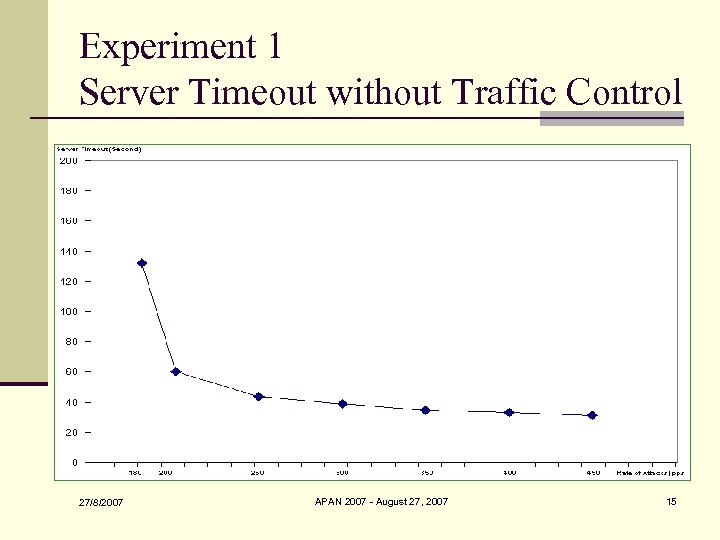 Experiment 1 Server Timeout without Traffic Control 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 15
Experiment 1 Server Timeout without Traffic Control 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 15
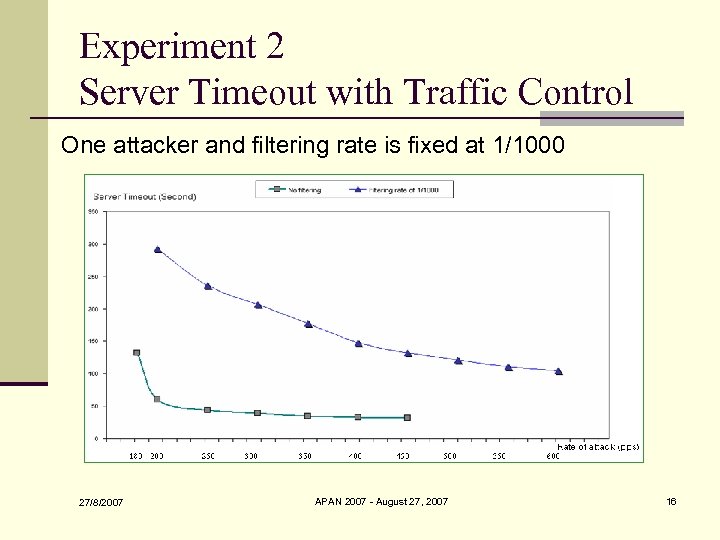 Experiment 2 Server Timeout with Traffic Control One attacker and filtering rate is fixed at 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 16
Experiment 2 Server Timeout with Traffic Control One attacker and filtering rate is fixed at 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 16
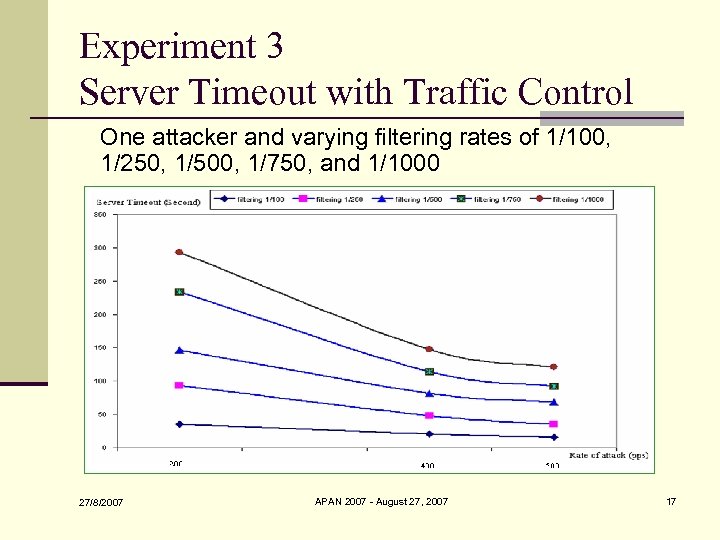 Experiment 3 Server Timeout with Traffic Control One attacker and varying filtering rates of 1/100, 1/250, 1/500, 1/750, and 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 17
Experiment 3 Server Timeout with Traffic Control One attacker and varying filtering rates of 1/100, 1/250, 1/500, 1/750, and 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 17
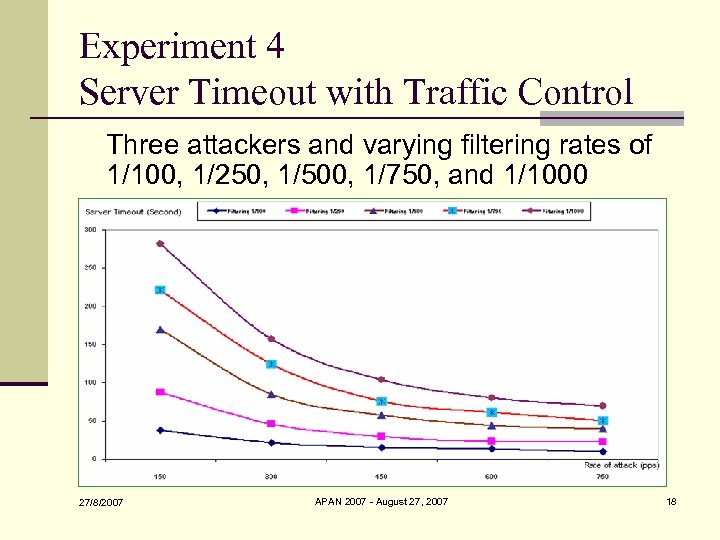 Experiment 4 Server Timeout with Traffic Control Three attackers and varying filtering rates of 1/100, 1/250, 1/500, 1/750, and 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 18
Experiment 4 Server Timeout with Traffic Control Three attackers and varying filtering rates of 1/100, 1/250, 1/500, 1/750, and 1/1000 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 18
 Conclusions n We show the effects of filtering malicious traffic to the survivability of the server under Do. S attacks n We show that a simple and fast anomaly detection is possible by using the traffic arrival rate n Future work: make Snort adaptive and can respond to different arrival rates with adaptive filtering rate 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 19
Conclusions n We show the effects of filtering malicious traffic to the survivability of the server under Do. S attacks n We show that a simple and fast anomaly detection is possible by using the traffic arrival rate n Future work: make Snort adaptive and can respond to different arrival rates with adaptive filtering rate 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 19
 References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Atighetchi M. , el. al. , Adaptive Cyberdefense for Survival and Intrusion Tolerance, IEEE Internet Computing, Nov-Dec 2004 Deri L. , Carbone R. , and Suin S. , Monitoring Networks Using ntop. Proceeding of the 2001 IEEE/IFIP International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, May 2001. Houle K. J. and Weaver G. M. , Trends in Denial of Services Attack Technology. CERT Coordination Center, Camegie Mellon University, October 2001. Hwang K, Chen Y, and Liu H. Defending Distributed Systems Against Malicious Intrusions and Network Anomalies. Proceedings of 19 th IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, April 2005. Kashiwa D, Chen E. Y. and Fuji H. Active Shaping: A Countermeasure Against DDo. S Attacks. Proceedings of 2 nd European Conference on Universal Multiservice Networks; April 2002. Keromytis A. , et. al. , A Holistic Approach to Service Survivability, Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Survivable and Self-Regenerative Systems, October 2003. Lan K. , Hussain A. and Dutta D. , Effect of Malicious Traffic on the Network, Proceedings of Passive and Active Measurement Workshop, April 2003. Lau F, Rubin S. H. , Smith M. H. and Trajkovic L. , Distributed Denial of Service Attacks. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, October 2000. 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 20
References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Atighetchi M. , el. al. , Adaptive Cyberdefense for Survival and Intrusion Tolerance, IEEE Internet Computing, Nov-Dec 2004 Deri L. , Carbone R. , and Suin S. , Monitoring Networks Using ntop. Proceeding of the 2001 IEEE/IFIP International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, May 2001. Houle K. J. and Weaver G. M. , Trends in Denial of Services Attack Technology. CERT Coordination Center, Camegie Mellon University, October 2001. Hwang K, Chen Y, and Liu H. Defending Distributed Systems Against Malicious Intrusions and Network Anomalies. Proceedings of 19 th IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, April 2005. Kashiwa D, Chen E. Y. and Fuji H. Active Shaping: A Countermeasure Against DDo. S Attacks. Proceedings of 2 nd European Conference on Universal Multiservice Networks; April 2002. Keromytis A. , et. al. , A Holistic Approach to Service Survivability, Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Survivable and Self-Regenerative Systems, October 2003. Lan K. , Hussain A. and Dutta D. , Effect of Malicious Traffic on the Network, Proceedings of Passive and Active Measurement Workshop, April 2003. Lau F, Rubin S. H. , Smith M. H. and Trajkovic L. , Distributed Denial of Service Attacks. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, October 2000. 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 20
 References 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Lee W. , Stolfo S. J. , and Mok K. , Mining in a Data-Flow Environment: Experience in Network Intrusion Detection, Proceedings of the 5 th ACM SIGKDD, August 1999. Lee W. and Stolfo S. J. , A Framework for Constructing Features and Models for Intrusion Detection Systems, ACM Transactions in Information and System Security, 3(4), November 2000. Long M. , Wu C-H, and Hung J. Y. , Denial of Service Attacks on Network-Based Control Systems: Impact and Mitigation, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 1 (2), May 2005. Mahoney M. V. , Network Traffic Anomaly Detection Based on Packet Bytes. Proceedings of ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, March 2003. Paxson V, Bro: A System for Detecting Network Intruders in Real-Time. Proceedings of the 7 th USENIX Security Symposium; January 1998. Roesch M, Snort–Lightweight Intrusion Detection for Networks. Proceedings of 13 th LISA: Systems Administration Conference; November 1999. Staniford S. , Hoagland J. A. and Mc. Alerney J. M. , Practical Automated Detection of Stealthy Portscans. Journal of Computer Security, 1(1 -2), 2002. Sterne D. , et. al. , Autonomic Response to Distributed Denial of Service Attacks. Proceedings of the 4 th International Symposium on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection, October 2001. Taylor C. and Alves-Foss J. NATE: Network Analysis of Anomalous Traffic Events – A Low-Cost Approach. Proceedings of the ACM workshop on New Security Paradigms, September 2001. Xu J. and Lee W. , Sustaining availability of Web Services under Distributed Denial of Service Attacks, IEEE Transactions on Computers, 52(2), February 2003. 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 21
References 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Lee W. , Stolfo S. J. , and Mok K. , Mining in a Data-Flow Environment: Experience in Network Intrusion Detection, Proceedings of the 5 th ACM SIGKDD, August 1999. Lee W. and Stolfo S. J. , A Framework for Constructing Features and Models for Intrusion Detection Systems, ACM Transactions in Information and System Security, 3(4), November 2000. Long M. , Wu C-H, and Hung J. Y. , Denial of Service Attacks on Network-Based Control Systems: Impact and Mitigation, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 1 (2), May 2005. Mahoney M. V. , Network Traffic Anomaly Detection Based on Packet Bytes. Proceedings of ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, March 2003. Paxson V, Bro: A System for Detecting Network Intruders in Real-Time. Proceedings of the 7 th USENIX Security Symposium; January 1998. Roesch M, Snort–Lightweight Intrusion Detection for Networks. Proceedings of 13 th LISA: Systems Administration Conference; November 1999. Staniford S. , Hoagland J. A. and Mc. Alerney J. M. , Practical Automated Detection of Stealthy Portscans. Journal of Computer Security, 1(1 -2), 2002. Sterne D. , et. al. , Autonomic Response to Distributed Denial of Service Attacks. Proceedings of the 4 th International Symposium on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection, October 2001. Taylor C. and Alves-Foss J. NATE: Network Analysis of Anomalous Traffic Events – A Low-Cost Approach. Proceedings of the ACM workshop on New Security Paradigms, September 2001. Xu J. and Lee W. , Sustaining availability of Web Services under Distributed Denial of Service Attacks, IEEE Transactions on Computers, 52(2), February 2003. 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 21
 Thank You Q&A 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 22
Thank You Q&A 27/8/2007 APAN 2007 - August 27, 2007 22


