7c0faba74e891d520a836fbdce60d9cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 The Early phases of High Tech Startups Patrick Bultema Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Early phases of High Tech Startups Patrick Bultema Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Boundaries of Reflection Focused on Startups verses internal, new business initiative l Focused on high-tech startups verse new small business ventures l ¡ ¡ ¡ l Not geographically limited Pace of innovation different Emphasis on venture and liquidity destination verses small business cash flow Focused on startups that will be venture financed to enable and/or accelerate business creation and growth 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Boundaries of Reflection Focused on Startups verses internal, new business initiative l Focused on high-tech startups verse new small business ventures l ¡ ¡ ¡ l Not geographically limited Pace of innovation different Emphasis on venture and liquidity destination verses small business cash flow Focused on startups that will be venture financed to enable and/or accelerate business creation and growth 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 The problem of assumptions, or Conventional Business Wisdom l Most business wisdom is based on the success of large, established companies ¡ Collins, “Good to Great” l 15 years public, inflection point, 15 years great Most business growth is in the small business, new, innovation category l High-Tech Start Ups are an even more specialized form of small businesses, but are a significant percentage of new businesses, and the focus of most venture capital l 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The problem of assumptions, or Conventional Business Wisdom l Most business wisdom is based on the success of large, established companies ¡ Collins, “Good to Great” l 15 years public, inflection point, 15 years great Most business growth is in the small business, new, innovation category l High-Tech Start Ups are an even more specialized form of small businesses, but are a significant percentage of new businesses, and the focus of most venture capital l 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Premise … l Principles and Practices that make large established companies successful may have little or no relevancy to high tech start ups l A more forceful premise … The methods and criteria of big companies is actually detrimental to start up success 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Premise … l Principles and Practices that make large established companies successful may have little or no relevancy to high tech start ups l A more forceful premise … The methods and criteria of big companies is actually detrimental to start up success 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 The Objectives of this Process Methodology Study l l l Primary concern and boundary of reflection confined to venture financed start ups Improving Capital Efficiency Enhancing the Capital Risk Scenario Identifying correlation between process and success rates Identifying behaviors, leadership criteria, and key metrics that correlate with success and process Improving Success Rates through applying process methodology 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Objectives of this Process Methodology Study l l l Primary concern and boundary of reflection confined to venture financed start ups Improving Capital Efficiency Enhancing the Capital Risk Scenario Identifying correlation between process and success rates Identifying behaviors, leadership criteria, and key metrics that correlate with success and process Improving Success Rates through applying process methodology 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Understanding the High Tech Start Up Context … 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Understanding the High Tech Start Up Context … 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 The Adoption of Innovations l l l Most High-Tech Start Up’s are concerned with creating a “new” way of doing things These innovations create the need to customers to recognize a better value proposition than current approaches Researchers have studied the patterns of how and why people adopt new innovations Seminal work written by Everett M. Rodgers, “Diffusion of Innovations” in 1962 Primary work around Iowa corn farmers adopting hybrid corn varieties The Adoption curve and concepts was recently popularized and applied to the high tech space by Jeff Moore in Crossing the Chasm 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Adoption of Innovations l l l Most High-Tech Start Up’s are concerned with creating a “new” way of doing things These innovations create the need to customers to recognize a better value proposition than current approaches Researchers have studied the patterns of how and why people adopt new innovations Seminal work written by Everett M. Rodgers, “Diffusion of Innovations” in 1962 Primary work around Iowa corn farmers adopting hybrid corn varieties The Adoption curve and concepts was recently popularized and applied to the high tech space by Jeff Moore in Crossing the Chasm 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
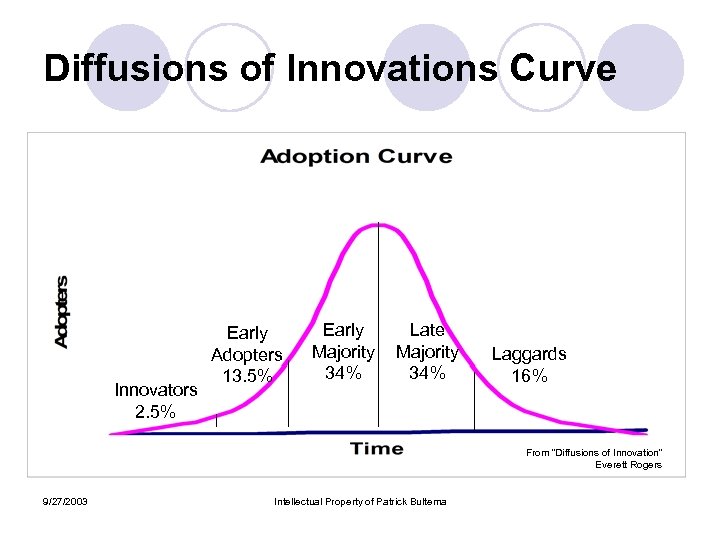 Diffusions of Innovations Curve Innovators 2. 5% Early Adopters 13. 5% Early Majority 34% Late Majority 34% Laggards 16% From “Diffusions of Innovation” Everett Rogers 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Diffusions of Innovations Curve Innovators 2. 5% Early Adopters 13. 5% Early Majority 34% Late Majority 34% Laggards 16% From “Diffusions of Innovation” Everett Rogers 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Categories of Adopters l Innovators ¡ l Early Adopters ¡ l Buy based on ROI. Typically looking for productivity improvement Late Majority ¡ l Looking for competitive advantage. Strategy buyers. Need some validation and references for Innovators Early Majority ¡ l New Technology adopters. Believers. Generally have the power to make their own decisions, even if just for their org. Motivated by Conventional Wisdom. Looking for case studies that verify others are adopting Laggards ¡ 9/27/2003 Don’t want to get fired. Adopt because they must to be credible Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Categories of Adopters l Innovators ¡ l Early Adopters ¡ l Buy based on ROI. Typically looking for productivity improvement Late Majority ¡ l Looking for competitive advantage. Strategy buyers. Need some validation and references for Innovators Early Majority ¡ l New Technology adopters. Believers. Generally have the power to make their own decisions, even if just for their org. Motivated by Conventional Wisdom. Looking for case studies that verify others are adopting Laggards ¡ 9/27/2003 Don’t want to get fired. Adopt because they must to be credible Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Distinctiveness of High Tech Start Up’s l Cycle time ¡ Measured in months verses years ¡ IPO in three years a possibility l Disruptive Innovation ¡ Fundamental change in how business is conducted ¡ Eg. Email l The concept of the Chasm ¡ You either win big or lose. Little in between. 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Distinctiveness of High Tech Start Up’s l Cycle time ¡ Measured in months verses years ¡ IPO in three years a possibility l Disruptive Innovation ¡ Fundamental change in how business is conducted ¡ Eg. Email l The concept of the Chasm ¡ You either win big or lose. Little in between. 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
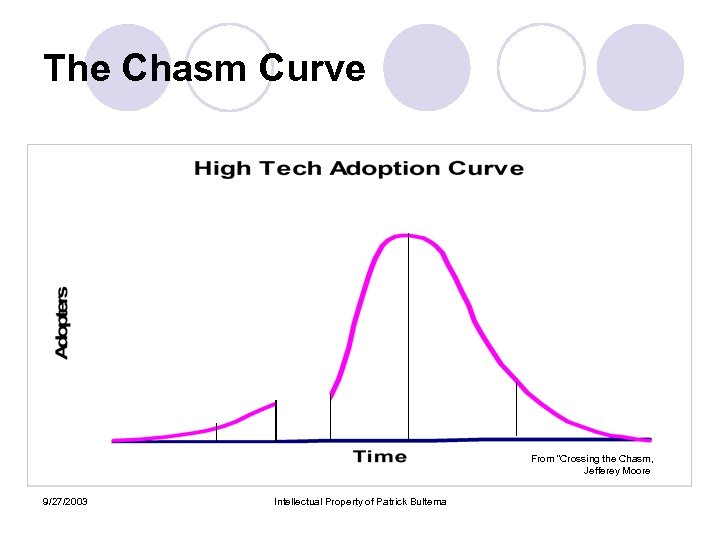 The Chasm Curve From “Crossing the Chasm, Jefferey Moore 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Chasm Curve From “Crossing the Chasm, Jefferey Moore 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Concepts of Crossing the Chasm Core idea: the Chasm is conceptually and operationally discontinuous with what makes early phase companies successful l Two key ingredients to Crossing the Chasm: l ¡ ¡ The ability to make the segue to being and execution oriented company The momentum to be able to play successful in the “majority oriented” marketplace l l ¡ The ability to re-introduce extensions to the core product/value proposition l l l ROI model and credibility Ability to establish “Conventional Wisdom” kind of positioning Services Plus one Extensions The Gorilla Game ¡ ¡ ¡ 9/27/2003 One Gorilla Two Chimps A handful of Monkeys Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Concepts of Crossing the Chasm Core idea: the Chasm is conceptually and operationally discontinuous with what makes early phase companies successful l Two key ingredients to Crossing the Chasm: l ¡ ¡ The ability to make the segue to being and execution oriented company The momentum to be able to play successful in the “majority oriented” marketplace l l ¡ The ability to re-introduce extensions to the core product/value proposition l l l ROI model and credibility Ability to establish “Conventional Wisdom” kind of positioning Services Plus one Extensions The Gorilla Game ¡ ¡ ¡ 9/27/2003 One Gorilla Two Chimps A handful of Monkeys Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
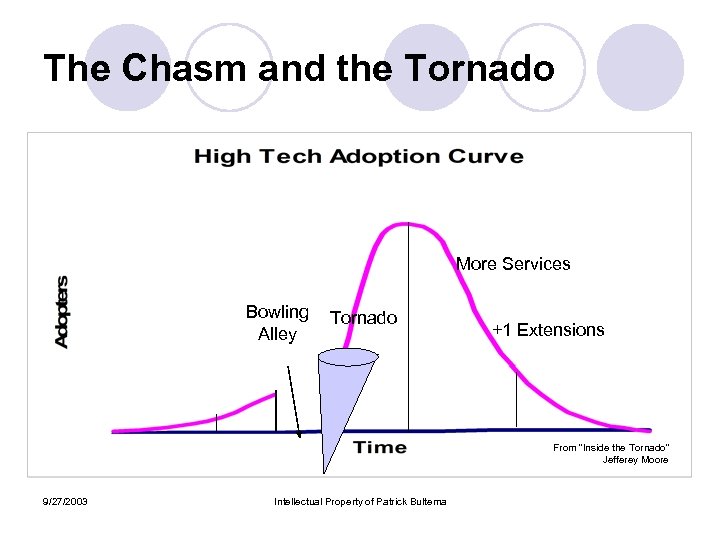 The Chasm and the Tornado More Services Bowling Alley Tornado +1 Extensions From “Inside the Tornado” Jefferey Moore 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Chasm and the Tornado More Services Bowling Alley Tornado +1 Extensions From “Inside the Tornado” Jefferey Moore 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Focus of Prior Attention l Most attention, research, and publishing has been on the Chasm and Mainstream Market l The pre-chasm stage has been treated like a voodoo, black art category l Yet, successful teams tend to be serial successes l But the reality for most … 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Focus of Prior Attention l Most attention, research, and publishing has been on the Chasm and Mainstream Market l The pre-chasm stage has been treated like a voodoo, black art category l Yet, successful teams tend to be serial successes l But the reality for most … 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Few Start Up’s Ever See the Chasm l Most fail not in the market scaling exercise, but in pre-chasm phases ¡ (need venture one data on stage failure) l They fail for a number of different reasons, related to process and experiment problems l The pre-chasm black hole 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Few Start Up’s Ever See the Chasm l Most fail not in the market scaling exercise, but in pre-chasm phases ¡ (need venture one data on stage failure) l They fail for a number of different reasons, related to process and experiment problems l The pre-chasm black hole 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
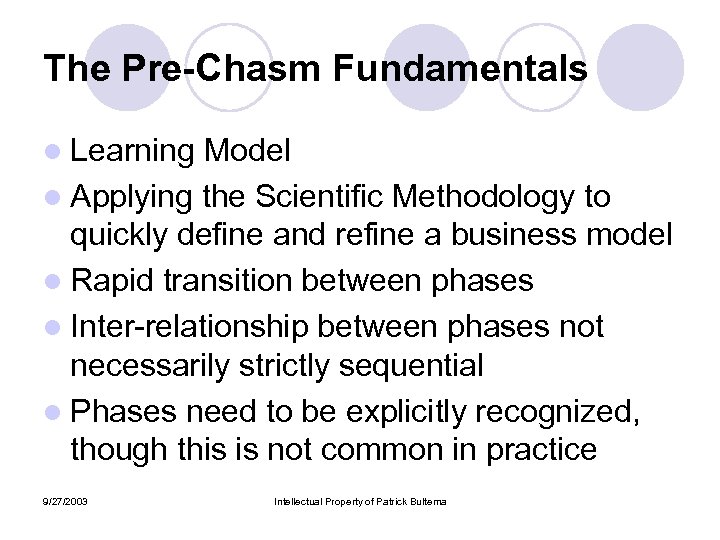 The Pre-Chasm Fundamentals l Learning Model l Applying the Scientific Methodology to quickly define and refine a business model l Rapid transition between phases l Inter-relationship between phases not necessarily strictly sequential l Phases need to be explicitly recognized, though this is not common in practice 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Pre-Chasm Fundamentals l Learning Model l Applying the Scientific Methodology to quickly define and refine a business model l Rapid transition between phases l Inter-relationship between phases not necessarily strictly sequential l Phases need to be explicitly recognized, though this is not common in practice 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
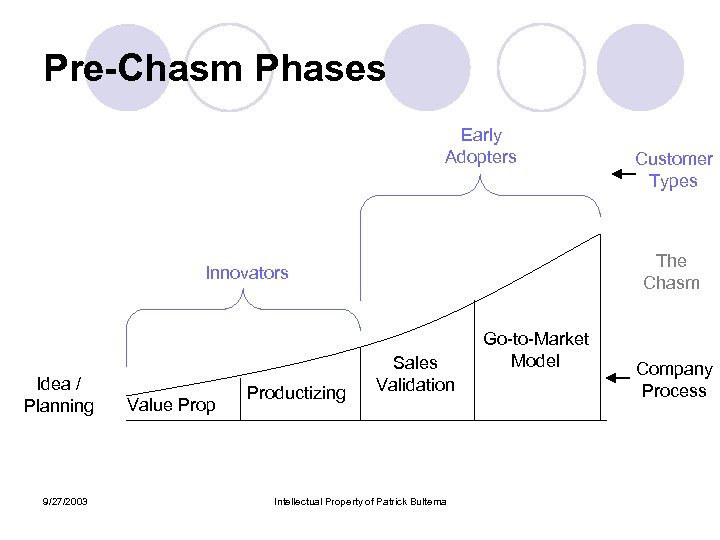 Pre-Chasm Phases Early Adopters The Chasm Innovators Idea / Planning 9/27/2003 Value Prop Productizing Customer Types Sales Validation Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema Go-to-Market Model Company Process
Pre-Chasm Phases Early Adopters The Chasm Innovators Idea / Planning 9/27/2003 Value Prop Productizing Customer Types Sales Validation Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema Go-to-Market Model Company Process
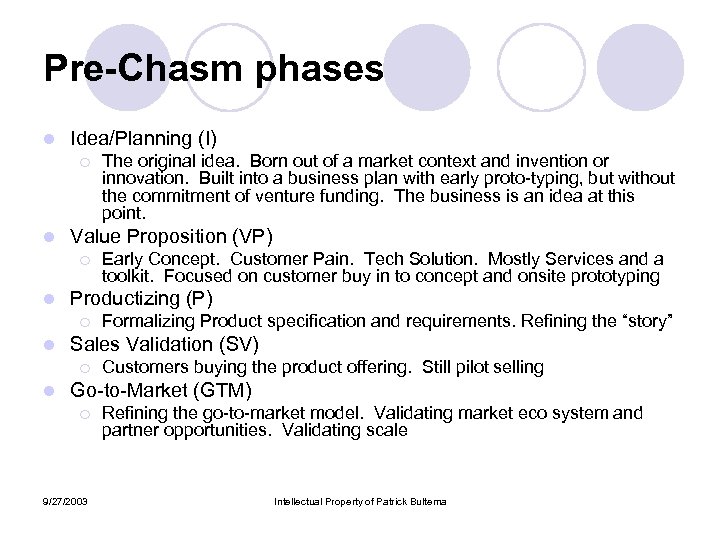 Pre-Chasm phases l Idea/Planning (I) ¡ l Value Proposition (VP) ¡ l Formalizing Product specification and requirements. Refining the “story” Sales Validation (SV) ¡ l Early Concept. Customer Pain. Tech Solution. Mostly Services and a toolkit. Focused on customer buy in to concept and onsite prototyping Productizing (P) ¡ l The original idea. Born out of a market context and invention or innovation. Built into a business plan with early proto-typing, but without the commitment of venture funding. The business is an idea at this point. Customers buying the product offering. Still pilot selling Go-to-Market (GTM) ¡ 9/27/2003 Refining the go-to-market model. Validating market eco system and partner opportunities. Validating scale Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Pre-Chasm phases l Idea/Planning (I) ¡ l Value Proposition (VP) ¡ l Formalizing Product specification and requirements. Refining the “story” Sales Validation (SV) ¡ l Early Concept. Customer Pain. Tech Solution. Mostly Services and a toolkit. Focused on customer buy in to concept and onsite prototyping Productizing (P) ¡ l The original idea. Born out of a market context and invention or innovation. Built into a business plan with early proto-typing, but without the commitment of venture funding. The business is an idea at this point. Customers buying the product offering. Still pilot selling Go-to-Market (GTM) ¡ 9/27/2003 Refining the go-to-market model. Validating market eco system and partner opportunities. Validating scale Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
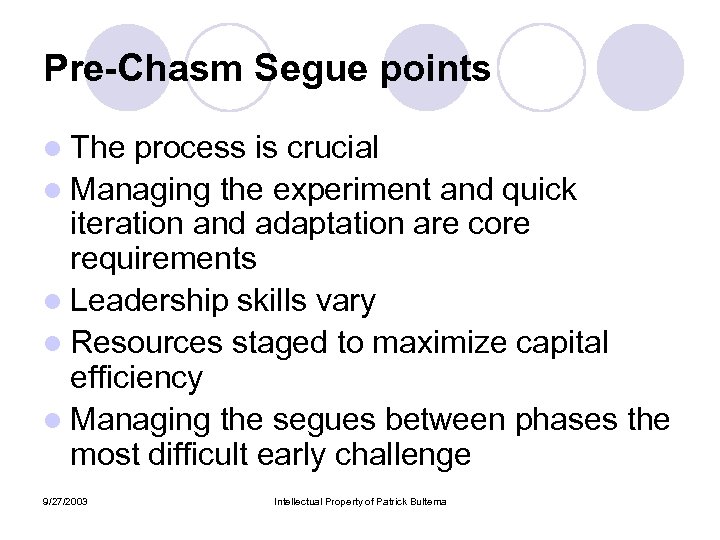 Pre-Chasm Segue points l The process is crucial l Managing the experiment and quick iteration and adaptation are core requirements l Leadership skills vary l Resources staged to maximize capital efficiency l Managing the segues between phases the most difficult early challenge 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Pre-Chasm Segue points l The process is crucial l Managing the experiment and quick iteration and adaptation are core requirements l Leadership skills vary l Resources staged to maximize capital efficiency l Managing the segues between phases the most difficult early challenge 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
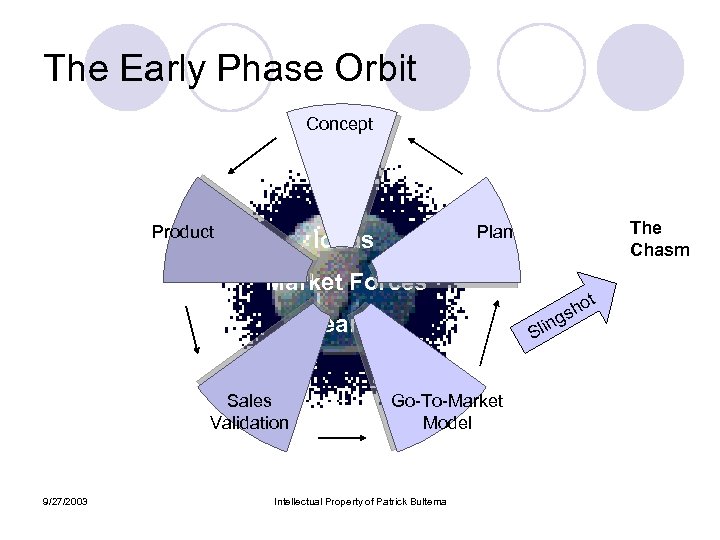 The Early Phase Orbit Concept Product The Chasm Plan Ideas Market Forces Teams Sales Validation 9/27/2003 ot h gs in Sl Go-To-Market Model Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Early Phase Orbit Concept Product The Chasm Plan Ideas Market Forces Teams Sales Validation 9/27/2003 ot h gs in Sl Go-To-Market Model Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Attributes of Early Phase Orbit l l l Companies may launch into orbit at any phase Most efficient is to launch into the plan phase If launch into a later phase, must be recursive to accomplish the earlier phases The goal of the orbit thru the phases is to gain momentum to “slingshot” across the chasm Many companies require more than one orbit to be successful If the phases of the orbit aren’t completed efficiently and sucessfully, the company runs the risk of degrading into the atmosphere and burning up 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Attributes of Early Phase Orbit l l l Companies may launch into orbit at any phase Most efficient is to launch into the plan phase If launch into a later phase, must be recursive to accomplish the earlier phases The goal of the orbit thru the phases is to gain momentum to “slingshot” across the chasm Many companies require more than one orbit to be successful If the phases of the orbit aren’t completed efficiently and sucessfully, the company runs the risk of degrading into the atmosphere and burning up 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 The Universe and its impact on the Orbit The process isn’t everything required for a high tech startup to be successful l Broader macro issues are the universe the process plays out in l ¡ ¡ Market drivers Competitive Landscape Disruptive Technologies Economic Trends In other words, a company can execute the process flawlessly and still fail due to the above macro issues l What’s more, the broader “universe” issues must be continuously monitored and factored into the learning processes of the orbit l And even the, the “universe” factors have the potential to destroy the orbit l 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
The Universe and its impact on the Orbit The process isn’t everything required for a high tech startup to be successful l Broader macro issues are the universe the process plays out in l ¡ ¡ Market drivers Competitive Landscape Disruptive Technologies Economic Trends In other words, a company can execute the process flawlessly and still fail due to the above macro issues l What’s more, the broader “universe” issues must be continuously monitored and factored into the learning processes of the orbit l And even the, the “universe” factors have the potential to destroy the orbit l 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Common Pre-Chasm Failure Points l l l l Spending your capital building the “organization” before the business concept is validated Valuing your idea of invention more than what the customer tells you Not creating mechanisms to listen to the customer Failure to run a disciplined experimental methodology Hiring the right people at the wrong time Not building a team to transition thru phases Building the prototype product before VP is complete Building V 1 of the “real” product before P results in a clear story Violating the Early BD verses later BD role Starting the branding effort before SV Ramping the marketing lead generation before SV Hiring the Sales leader “who can make the company big” before SV Staffing up the sales org before GTM As a rule, recruiting early channel before GTM 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Common Pre-Chasm Failure Points l l l l Spending your capital building the “organization” before the business concept is validated Valuing your idea of invention more than what the customer tells you Not creating mechanisms to listen to the customer Failure to run a disciplined experimental methodology Hiring the right people at the wrong time Not building a team to transition thru phases Building the prototype product before VP is complete Building V 1 of the “real” product before P results in a clear story Violating the Early BD verses later BD role Starting the branding effort before SV Ramping the marketing lead generation before SV Hiring the Sales leader “who can make the company big” before SV Staffing up the sales org before GTM As a rule, recruiting early channel before GTM 9/27/2003 Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Research project Test the premise here to see if there is a correlation between a process methodology and success l Modify process methodology based on learnings l Isolate further levels of granularity on early phase, high tech start up success l ¡ ¡ ¡ 9/27/2003 Process Leadership Team factors Early Customer selection process And so on Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Research project Test the premise here to see if there is a correlation between a process methodology and success l Modify process methodology based on learnings l Isolate further levels of granularity on early phase, high tech start up success l ¡ ¡ ¡ 9/27/2003 Process Leadership Team factors Early Customer selection process And so on Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
 Initial research project Phase 1: Qualitative Contact ~10 venture firms Ask for 5 -10 companies that have failed in their portofolio, where: 1. 2. 3. Business idea/premise was and still is promising No technology or marketplace change killed the company But the company failed anyway Ask for 5 -10 companies that have succeeded in their portfolio, where: 3. 1. 2. 3. Not because the space or idea was extraordinary, but Because the company just worked well Success is either realized thru liquidity event, or highly anticipated. Criteria for success is a company that is able to: 4. 1. 2. 5. 6. 7. 9/27/2003 Reach cash positive operations on venture investment And/or has already, or is projected with confidence, to be able to achieve a profitable liquidity event Failure is the absence of above Develop a series of questions that focus on what happened when, results, & why. Essentially a histogram for each Needs to be an individual interviewee who had in depth & comprehensive vision of the history. May be VC. May be CEO. May be one of the founders Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema
Initial research project Phase 1: Qualitative Contact ~10 venture firms Ask for 5 -10 companies that have failed in their portofolio, where: 1. 2. 3. Business idea/premise was and still is promising No technology or marketplace change killed the company But the company failed anyway Ask for 5 -10 companies that have succeeded in their portfolio, where: 3. 1. 2. 3. Not because the space or idea was extraordinary, but Because the company just worked well Success is either realized thru liquidity event, or highly anticipated. Criteria for success is a company that is able to: 4. 1. 2. 5. 6. 7. 9/27/2003 Reach cash positive operations on venture investment And/or has already, or is projected with confidence, to be able to achieve a profitable liquidity event Failure is the absence of above Develop a series of questions that focus on what happened when, results, & why. Essentially a histogram for each Needs to be an individual interviewee who had in depth & comprehensive vision of the history. May be VC. May be CEO. May be one of the founders Intellectual Property of Patrick Bultema


