0c3114bf23a7a7885c2f8ee973fce994.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 The E-Authentication Initiative E-Authentication: Creating an Environment of Trust David Temoshok Director, Identity Policy and Management GSA Office of Governmentwide Policy
The E-Authentication Initiative E-Authentication: Creating an Environment of Trust David Temoshok Director, Identity Policy and Management GSA Office of Governmentwide Policy
 Session Objectives u Identity Federation Basics u Why the Federal Government is federating u Key infrastructure needed for ID Federation u Interoperability and ID Federation u E-Authentication Trust Framework u The Electronic Authentication Partnership and how it facilitates identity federation The E-Authentication Initiative 2
Session Objectives u Identity Federation Basics u Why the Federal Government is federating u Key infrastructure needed for ID Federation u Interoperability and ID Federation u E-Authentication Trust Framework u The Electronic Authentication Partnership and how it facilitates identity federation The E-Authentication Initiative 2
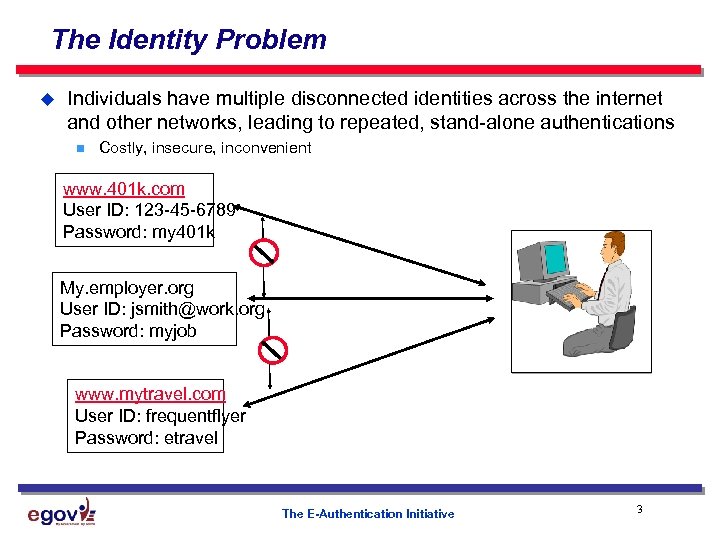 The Identity Problem u Individuals have multiple disconnected identities across the internet and other networks, leading to repeated, stand-alone authentications n Costly, insecure, inconvenient www. 401 k. com User ID: 123 -45 -6789 Password: my 401 k My. employer. org User ID: jsmith@work. org Password: myjob www. mytravel. com User ID: frequentflyer Password: etravel The E-Authentication Initiative 3
The Identity Problem u Individuals have multiple disconnected identities across the internet and other networks, leading to repeated, stand-alone authentications n Costly, insecure, inconvenient www. 401 k. com User ID: 123 -45 -6789 Password: my 401 k My. employer. org User ID: jsmith@work. org Password: myjob www. mytravel. com User ID: frequentflyer Password: etravel The E-Authentication Initiative 3
 Background u Federated identity definition n n u Federated identity technologies and standards n n n u Rules, agreements, standards, technologies that make identity and entitlements portable across autonomous domains Is critical for rich web services environment PKI – ISO X. 509 v 3 Security Assertion Markup Language – OASIS SAML 1. 0, 1. 1. 2. 0 Lacking standards • Biometrics • User ID/PIN/Password • Knowledge-based authentication • One-time passwords • Token-based authentication Federated identity specifications (SAML) n n Liberty Alliance Shibboleth The E-Authentication Initiative 4
Background u Federated identity definition n n u Federated identity technologies and standards n n n u Rules, agreements, standards, technologies that make identity and entitlements portable across autonomous domains Is critical for rich web services environment PKI – ISO X. 509 v 3 Security Assertion Markup Language – OASIS SAML 1. 0, 1. 1. 2. 0 Lacking standards • Biometrics • User ID/PIN/Password • Knowledge-based authentication • One-time passwords • Token-based authentication Federated identity specifications (SAML) n n Liberty Alliance Shibboleth The E-Authentication Initiative 4
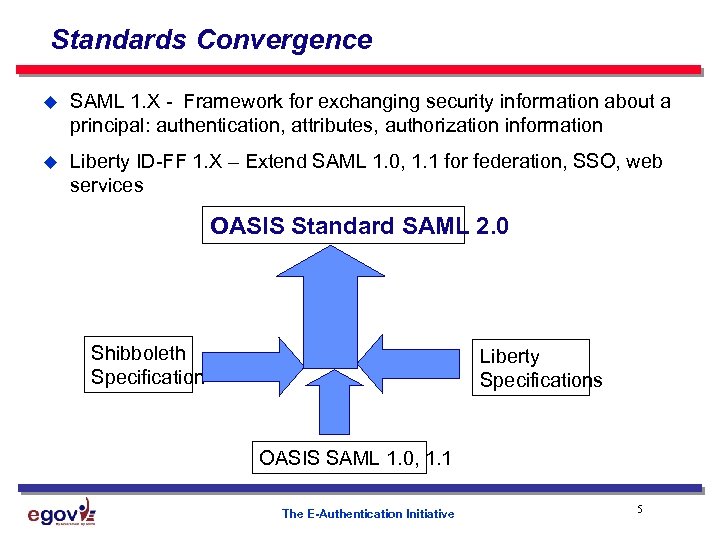 Standards Convergence u SAML 1. X - Framework for exchanging security information about a principal: authentication, attributes, authorization information u Liberty ID-FF 1. X – Extend SAML 1. 0, 1. 1 for federation, SSO, web services OASIS Standard SAML 2. 0 Shibboleth Specification Liberty Specifications OASIS SAML 1. 0, 1. 1 The E-Authentication Initiative 5
Standards Convergence u SAML 1. X - Framework for exchanging security information about a principal: authentication, attributes, authorization information u Liberty ID-FF 1. X – Extend SAML 1. 0, 1. 1 for federation, SSO, web services OASIS Standard SAML 2. 0 Shibboleth Specification Liberty Specifications OASIS SAML 1. 0, 1. 1 The E-Authentication Initiative 5
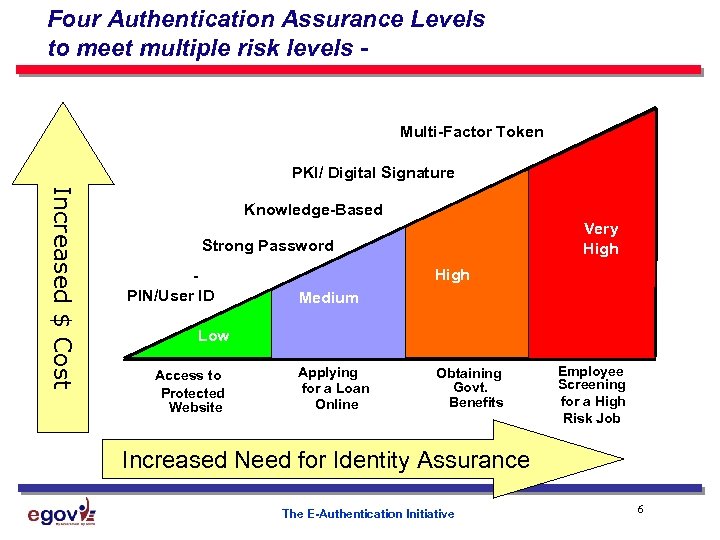 Four Authentication Assurance Levels to meet multiple risk levels - Multi-Factor Token PKI/ Digital Signature Increased $ Cost Knowledge-Based Very High Strong Password PIN/User ID High Medium Low Access to Protected Website Applying for a Loan Online Obtaining Govt. Benefits Employee Screening for a High Risk Job Increased Need for Identity Assurance The E-Authentication Initiative 6
Four Authentication Assurance Levels to meet multiple risk levels - Multi-Factor Token PKI/ Digital Signature Increased $ Cost Knowledge-Based Very High Strong Password PIN/User ID High Medium Low Access to Protected Website Applying for a Loan Online Obtaining Govt. Benefits Employee Screening for a High Risk Job Increased Need for Identity Assurance The E-Authentication Initiative 6
 President’s Management Agenda • • 1 st Priority: Make Government citizen-centered. 5 Key Government-wide Initiatives: ü Strategic Management of Human Capital ü Competitive Sourcing ü Improved Financial performance ü Expanded Electronic Government ü Budget and Performance Integration The E-Authentication Initiative 7
President’s Management Agenda • • 1 st Priority: Make Government citizen-centered. 5 Key Government-wide Initiatives: ü Strategic Management of Human Capital ü Competitive Sourcing ü Improved Financial performance ü Expanded Electronic Government ü Budget and Performance Integration The E-Authentication Initiative 7
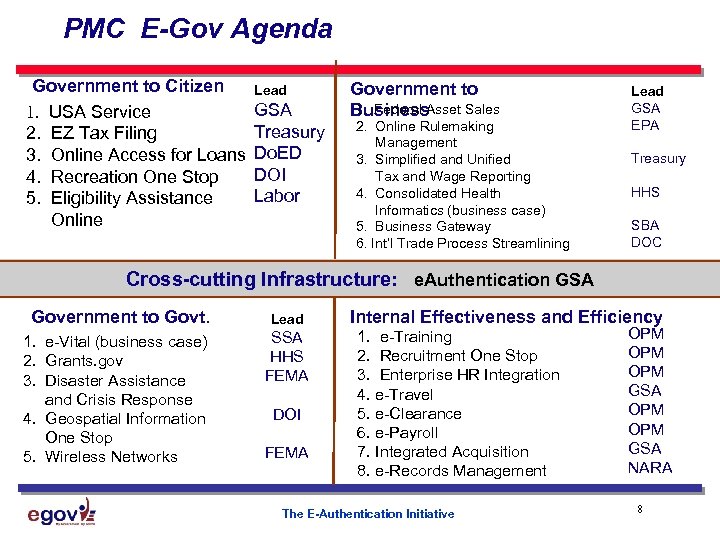 PMC E-Gov Agenda Government to Citizen 1. USA Service 2. EZ Tax Filing 3. Online Access for Loans 4. Recreation One Stop 5. Eligibility Assistance Online Lead GSA Treasury Do. ED DOI Labor Government to 1. Federal Asset Sales Business 2. Online Rulemaking Management 3. Simplified and Unified Tax and Wage Reporting 4. Consolidated Health Informatics (business case) 5. Business Gateway 6. Int’l Trade Process Streamlining Lead GSA EPA Treasury HHS SBA DOC Cross-cutting Infrastructure: e. Authentication GSA Government to Govt. 1. e-Vital (business case) 2. Grants. gov 3. Disaster Assistance and Crisis Response 4. Geospatial Information One Stop 5. Wireless Networks Lead SSA HHS FEMA DOI FEMA Internal Effectiveness and Efficiency 1. e-Training 2. Recruitment One Stop 3. Enterprise HR Integration 4. e-Travel 5. e-Clearance 6. e-Payroll 7. Integrated Acquisition 8. e-Records Management The E-Authentication Initiative OPM OPM GSA NARA 8
PMC E-Gov Agenda Government to Citizen 1. USA Service 2. EZ Tax Filing 3. Online Access for Loans 4. Recreation One Stop 5. Eligibility Assistance Online Lead GSA Treasury Do. ED DOI Labor Government to 1. Federal Asset Sales Business 2. Online Rulemaking Management 3. Simplified and Unified Tax and Wage Reporting 4. Consolidated Health Informatics (business case) 5. Business Gateway 6. Int’l Trade Process Streamlining Lead GSA EPA Treasury HHS SBA DOC Cross-cutting Infrastructure: e. Authentication GSA Government to Govt. 1. e-Vital (business case) 2. Grants. gov 3. Disaster Assistance and Crisis Response 4. Geospatial Information One Stop 5. Wireless Networks Lead SSA HHS FEMA DOI FEMA Internal Effectiveness and Efficiency 1. e-Training 2. Recruitment One Stop 3. Enterprise HR Integration 4. e-Travel 5. e-Clearance 6. e-Payroll 7. Integrated Acquisition 8. e-Records Management The E-Authentication Initiative OPM OPM GSA NARA 8
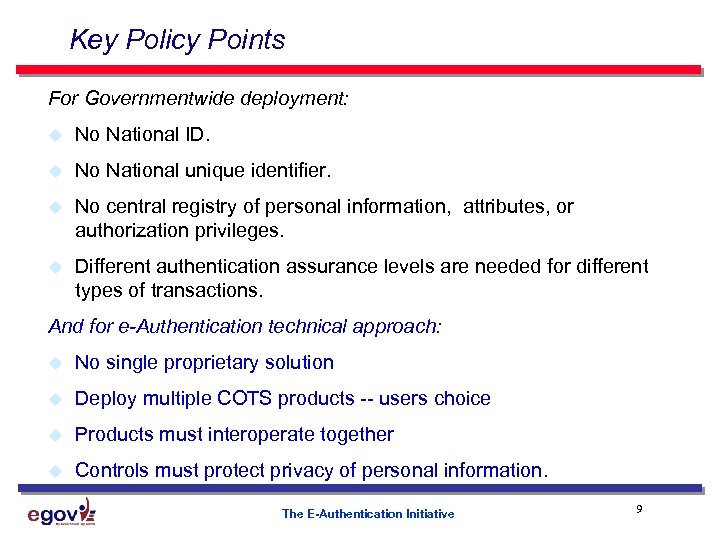 Key Policy Points For Governmentwide deployment: u No National ID. u No National unique identifier. u No central registry of personal information, attributes, or authorization privileges. u Different authentication assurance levels are needed for different types of transactions. And for e-Authentication technical approach: u No single proprietary solution u Deploy multiple COTS products -- users choice u Products must interoperate together u Controls must protect privacy of personal information. The E-Authentication Initiative 9
Key Policy Points For Governmentwide deployment: u No National ID. u No National unique identifier. u No central registry of personal information, attributes, or authorization privileges. u Different authentication assurance levels are needed for different types of transactions. And for e-Authentication technical approach: u No single proprietary solution u Deploy multiple COTS products -- users choice u Products must interoperate together u Controls must protect privacy of personal information. The E-Authentication Initiative 9
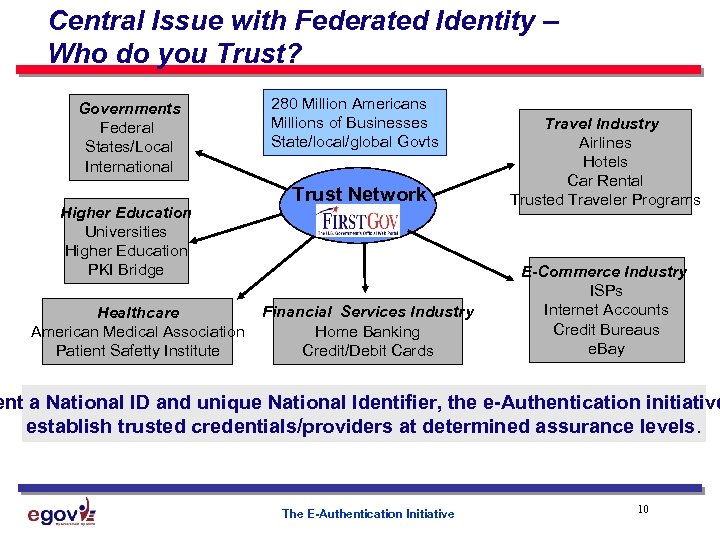 Central Issue with Federated Identity – Who do you Trust? Governments Federal States/Local International Higher Education Universities Higher Education PKI Bridge Healthcare American Medical Association Patient Safetty Institute 280 Million Americans Millions of Businesses State/local/global Govts Trust Network Financial Services Industry Home Banking Credit/Debit Cards Travel Industry Airlines Hotels Car Rental Trusted Traveler Programs E-Commerce Industry ISPs Internet Accounts Credit Bureaus e. Bay ent a National ID and unique National Identifier, the e-Authentication initiative establish trusted credentials/providers at determined assurance levels. The E-Authentication Initiative 10
Central Issue with Federated Identity – Who do you Trust? Governments Federal States/Local International Higher Education Universities Higher Education PKI Bridge Healthcare American Medical Association Patient Safetty Institute 280 Million Americans Millions of Businesses State/local/global Govts Trust Network Financial Services Industry Home Banking Credit/Debit Cards Travel Industry Airlines Hotels Car Rental Trusted Traveler Programs E-Commerce Industry ISPs Internet Accounts Credit Bureaus e. Bay ent a National ID and unique National Identifier, the e-Authentication initiative establish trusted credentials/providers at determined assurance levels. The E-Authentication Initiative 10
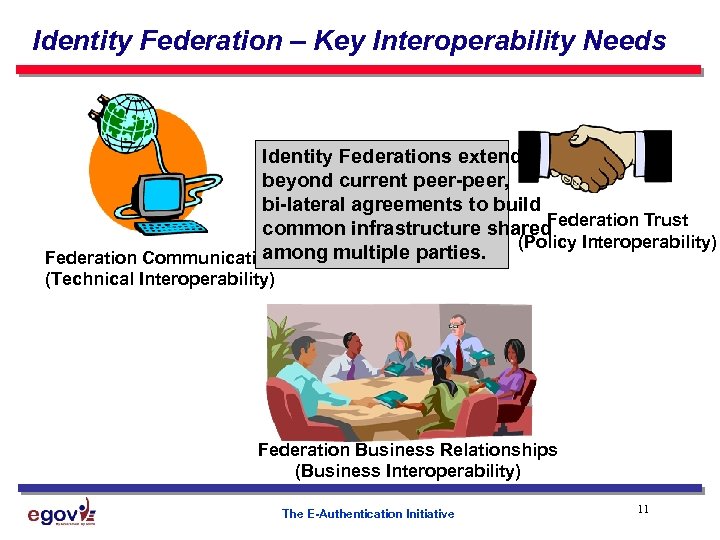 Identity Federation – Key Interoperability Needs Identity Federations extend beyond current peer-peer, bi-lateral agreements to build Federation Trust common infrastructure shared (Policy Interoperability) among multiple parties. Federation Communications (Technical Interoperability) Federation Business Relationships (Business Interoperability) The E-Authentication Initiative 11
Identity Federation – Key Interoperability Needs Identity Federations extend beyond current peer-peer, bi-lateral agreements to build Federation Trust common infrastructure shared (Policy Interoperability) among multiple parties. Federation Communications (Technical Interoperability) Federation Business Relationships (Business Interoperability) The E-Authentication Initiative 11
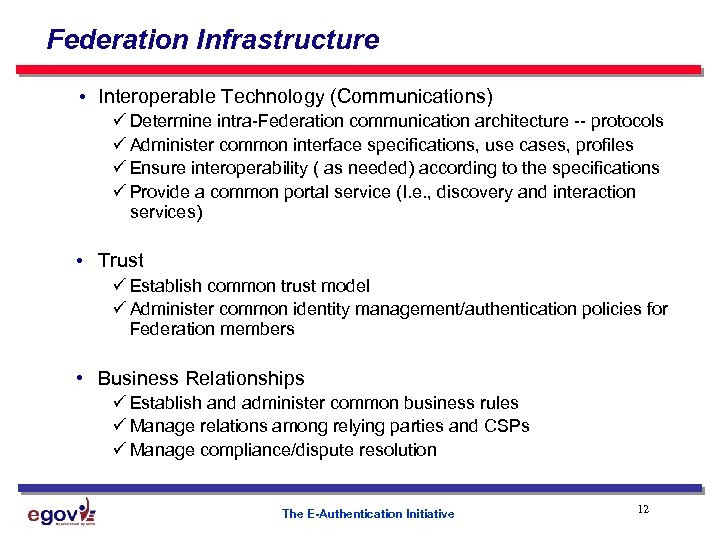 Federation Infrastructure • Interoperable Technology (Communications) ü Determine intra-Federation communication architecture -- protocols ü Administer common interface specifications, use cases, profiles ü Ensure interoperability ( as needed) according to the specifications ü Provide a common portal service (I. e. , discovery and interaction services) • Trust ü Establish common trust model ü Administer common identity management/authentication policies for Federation members • Business Relationships ü Establish and administer common business rules ü Manage relations among relying parties and CSPs ü Manage compliance/dispute resolution The E-Authentication Initiative 12
Federation Infrastructure • Interoperable Technology (Communications) ü Determine intra-Federation communication architecture -- protocols ü Administer common interface specifications, use cases, profiles ü Ensure interoperability ( as needed) according to the specifications ü Provide a common portal service (I. e. , discovery and interaction services) • Trust ü Establish common trust model ü Administer common identity management/authentication policies for Federation members • Business Relationships ü Establish and administer common business rules ü Manage relations among relying parties and CSPs ü Manage compliance/dispute resolution The E-Authentication Initiative 12
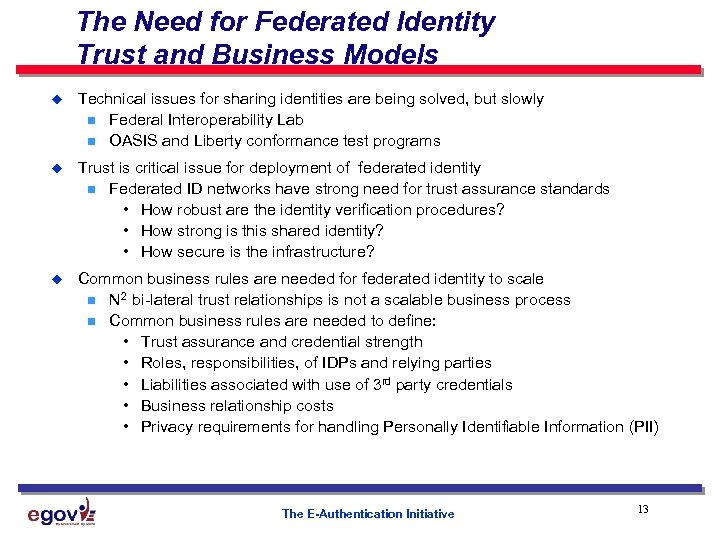 The Need for Federated Identity Trust and Business Models u Technical issues for sharing identities are being solved, but slowly n Federal Interoperability Lab n OASIS and Liberty conformance test programs u Trust is critical issue for deployment of federated identity n Federated ID networks have strong need for trust assurance standards • How robust are the identity verification procedures? • How strong is this shared identity? • How secure is the infrastructure? u Common business rules are needed for federated identity to scale n N 2 bi-lateral trust relationships is not a scalable business process n Common business rules are needed to define: • Trust assurance and credential strength • Roles, responsibilities, of IDPs and relying parties • Liabilities associated with use of 3 rd party credentials • Business relationship costs • Privacy requirements for handling Personally Identifiable Information (PII) The E-Authentication Initiative 13
The Need for Federated Identity Trust and Business Models u Technical issues for sharing identities are being solved, but slowly n Federal Interoperability Lab n OASIS and Liberty conformance test programs u Trust is critical issue for deployment of federated identity n Federated ID networks have strong need for trust assurance standards • How robust are the identity verification procedures? • How strong is this shared identity? • How secure is the infrastructure? u Common business rules are needed for federated identity to scale n N 2 bi-lateral trust relationships is not a scalable business process n Common business rules are needed to define: • Trust assurance and credential strength • Roles, responsibilities, of IDPs and relying parties • Liabilities associated with use of 3 rd party credentials • Business relationship costs • Privacy requirements for handling Personally Identifiable Information (PII) The E-Authentication Initiative 13
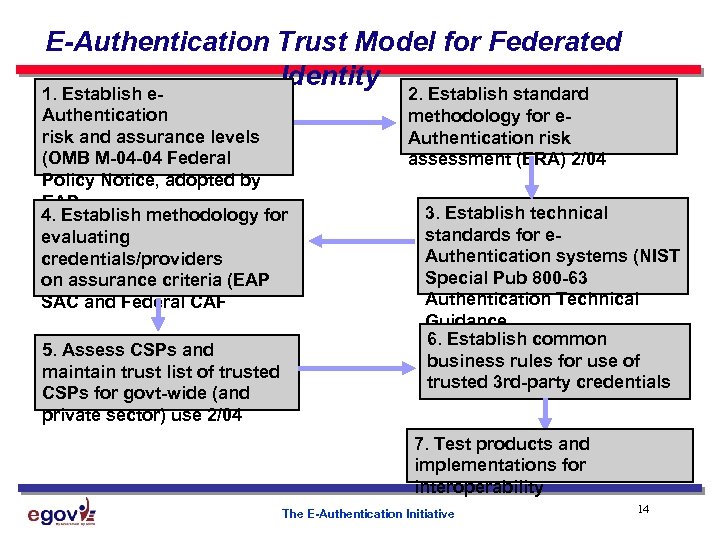 E-Authentication Trust Model for Federated Identity 1. Establish e. Authentication risk and assurance levels (OMB M-04 -04 Federal Policy Notice, adopted by EAP 4. Establish methodology for evaluating credentials/providers on assurance criteria (EAP SAC and Federal CAF 5. Assess CSPs and maintain trust list of trusted CSPs for govt-wide (and private sector) use 2/04 2. Establish standard methodology for e. Authentication risk assessment (ERA) 2/04 3. Establish technical standards for e. Authentication systems (NIST Special Pub 800 -63 Authentication Technical Guidance 6. Establish common business rules for use of trusted 3 rd-party credentials 7. Test products and implementations for interoperability The E-Authentication Initiative 14
E-Authentication Trust Model for Federated Identity 1. Establish e. Authentication risk and assurance levels (OMB M-04 -04 Federal Policy Notice, adopted by EAP 4. Establish methodology for evaluating credentials/providers on assurance criteria (EAP SAC and Federal CAF 5. Assess CSPs and maintain trust list of trusted CSPs for govt-wide (and private sector) use 2/04 2. Establish standard methodology for e. Authentication risk assessment (ERA) 2/04 3. Establish technical standards for e. Authentication systems (NIST Special Pub 800 -63 Authentication Technical Guidance 6. Establish common business rules for use of trusted 3 rd-party credentials 7. Test products and implementations for interoperability The E-Authentication Initiative 14
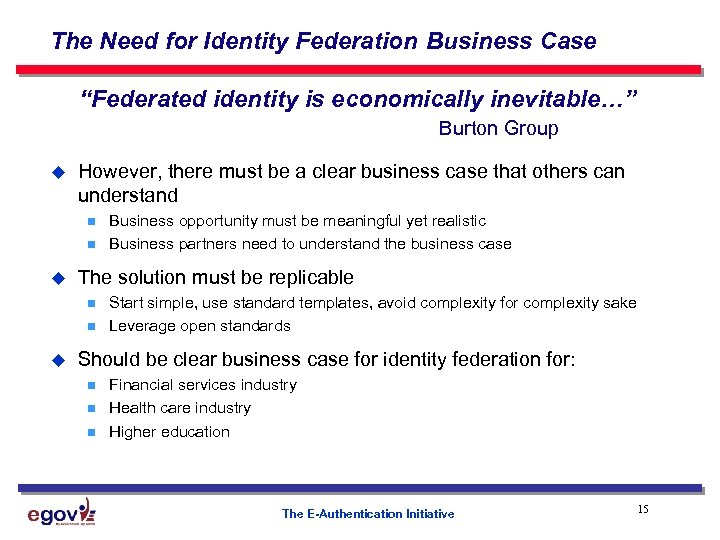 The Need for Identity Federation Business Case “Federated identity is economically inevitable…” Burton Group u However, there must be a clear business case that others can understand n n u The solution must be replicable n n u Business opportunity must be meaningful yet realistic Business partners need to understand the business case Start simple, use standard templates, avoid complexity for complexity sake Leverage open standards Should be clear business case for identity federation for: n n n Financial services industry Health care industry Higher education The E-Authentication Initiative 15
The Need for Identity Federation Business Case “Federated identity is economically inevitable…” Burton Group u However, there must be a clear business case that others can understand n n u The solution must be replicable n n u Business opportunity must be meaningful yet realistic Business partners need to understand the business case Start simple, use standard templates, avoid complexity for complexity sake Leverage open standards Should be clear business case for identity federation for: n n n Financial services industry Health care industry Higher education The E-Authentication Initiative 15
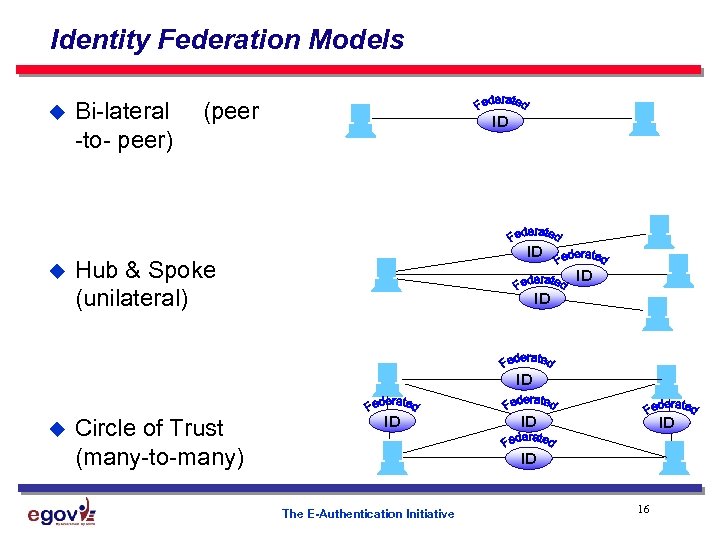 Identity Federation Models u u Bi-lateral -to- peer) (peer ID ID Hub & Spoke (unilateral) ID ID ID u Circle of Trust (many-to-many) ID ID The E-Authentication Initiative 16
Identity Federation Models u u Bi-lateral -to- peer) (peer ID ID Hub & Spoke (unilateral) ID ID ID u Circle of Trust (many-to-many) ID ID The E-Authentication Initiative 16
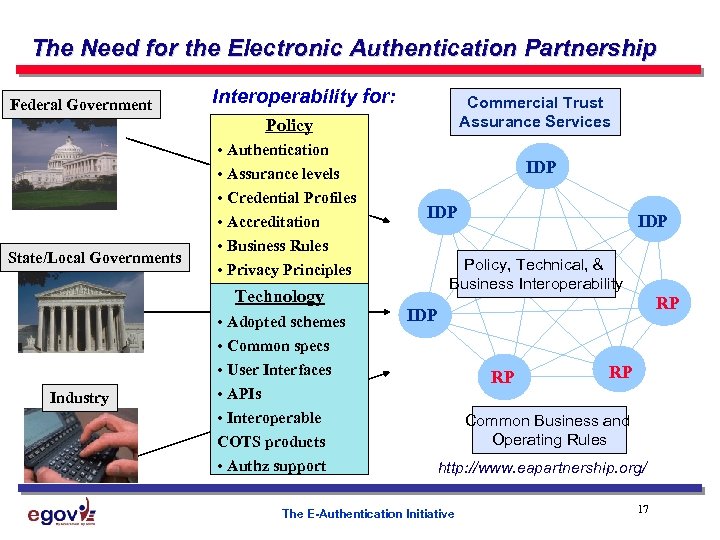 The Need for the Electronic Authentication Partnership Federal Government Interoperability for: Commercial Trust Assurance Services Policy State/Local Governments • Authentication • Assurance levels • Credential Profiles • Accreditation • Business Rules • Privacy Principles Technology Industry • Adopted schemes • Common specs • User Interfaces • APIs • Interoperable COTS products • Authz support IDP IDP Policy, Technical, & Business Interoperability RP IDP RP RP Common Business and Operating Rules http: //www. eapartnership. org/ The E-Authentication Initiative 17
The Need for the Electronic Authentication Partnership Federal Government Interoperability for: Commercial Trust Assurance Services Policy State/Local Governments • Authentication • Assurance levels • Credential Profiles • Accreditation • Business Rules • Privacy Principles Technology Industry • Adopted schemes • Common specs • User Interfaces • APIs • Interoperable COTS products • Authz support IDP IDP Policy, Technical, & Business Interoperability RP IDP RP RP Common Business and Operating Rules http: //www. eapartnership. org/ The E-Authentication Initiative 17
 What is the EAP • Multi-industry partnership creating a framework for interoperable, trustworthy authentication ü Incorporated non-profit association with 60 members ü Product and technology agnostic • Goals ü Provide organizations with a straightforward means of relying on digital credentials issued by a variety of authentication systems ü Eliminate or at least reduce the need for organizations to establish bilateral agreements ü Facilitate the creation of federations through replicable rules ü Enable federation-to-federation trust • In practice this means a federated approach The E-Authentication Initiative 18
What is the EAP • Multi-industry partnership creating a framework for interoperable, trustworthy authentication ü Incorporated non-profit association with 60 members ü Product and technology agnostic • Goals ü Provide organizations with a straightforward means of relying on digital credentials issued by a variety of authentication systems ü Eliminate or at least reduce the need for organizations to establish bilateral agreements ü Facilitate the creation of federations through replicable rules ü Enable federation-to-federation trust • In practice this means a federated approach The E-Authentication Initiative 18
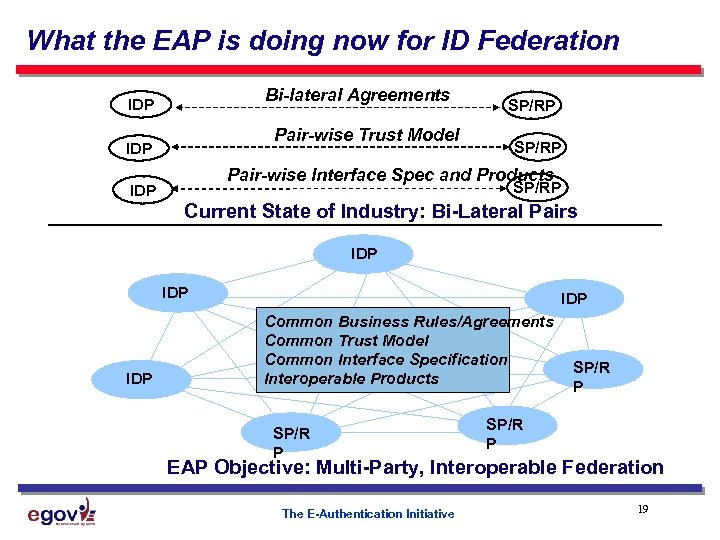 What the EAP is doing now for ID Federation Bi-lateral Agreements IDP Pair-wise Trust Model IDP SP/RP Pair-wise Interface Spec and Products SP/RP IDP Current State of Industry: Bi-Lateral Pairs IDP IDP Common Business Rules/Agreements Common Trust Model Common Interface Specification Interoperable Products SP/R P EAP Objective: Multi-Party, Interoperable Federation The E-Authentication Initiative 19
What the EAP is doing now for ID Federation Bi-lateral Agreements IDP Pair-wise Trust Model IDP SP/RP Pair-wise Interface Spec and Products SP/RP IDP Current State of Industry: Bi-Lateral Pairs IDP IDP Common Business Rules/Agreements Common Trust Model Common Interface Specification Interoperable Products SP/R P EAP Objective: Multi-Party, Interoperable Federation The E-Authentication Initiative 19
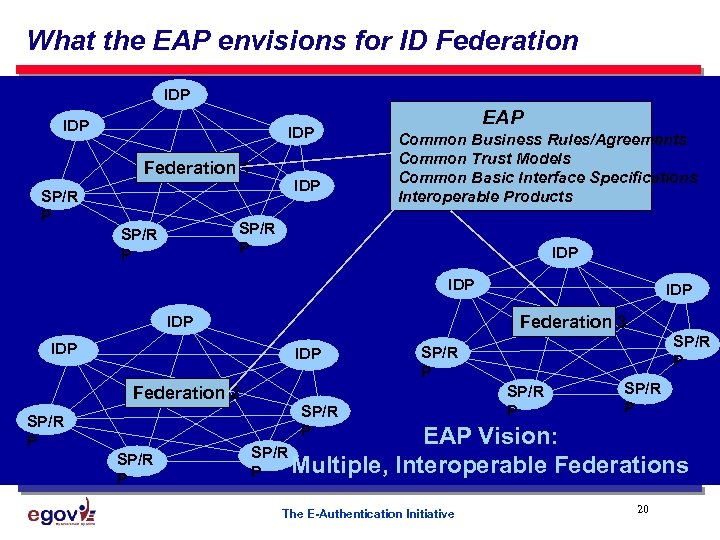 What the EAP envisions for ID Federation IDP IDP Federation 1 SP/R P IDP EAP Common Business Rules/Agreements Common Trust Models Common Basic Interface Specifications Interoperable Products SP/R P IDP Federation 3 IDP IDP Federation 2 SP/R P IDP SP/R P SP/R P EAP Vision: SP/R Multiple, Interoperable Federations P The E-Authentication Initiative 20
What the EAP envisions for ID Federation IDP IDP Federation 1 SP/R P IDP EAP Common Business Rules/Agreements Common Trust Models Common Basic Interface Specifications Interoperable Products SP/R P IDP Federation 3 IDP IDP Federation 2 SP/R P IDP SP/R P SP/R P EAP Vision: SP/R Multiple, Interoperable Federations P The E-Authentication Initiative 20
 For More Information Phone David Temoshok E-mail 202 -208 -7655 david. temoshok@gsa. gov Websites http: //cio. gov/eauthentication http: //www. eapartnership. org/ http: //cio. gov/fpkipa http: //cio. gov/ficc The E-Authentication Initiative
For More Information Phone David Temoshok E-mail 202 -208 -7655 david. temoshok@gsa. gov Websites http: //cio. gov/eauthentication http: //www. eapartnership. org/ http: //cio. gov/fpkipa http: //cio. gov/ficc The E-Authentication Initiative


