 The Digestive System No Guts - No Glory!
The Digestive System No Guts - No Glory!
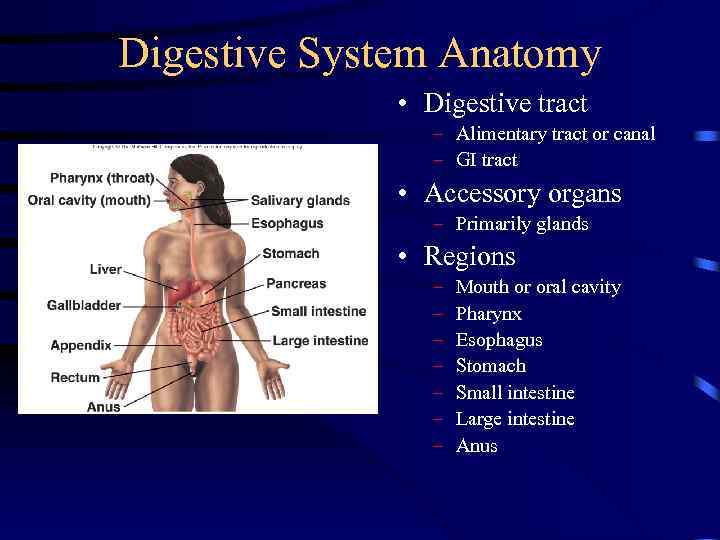 Digestive System Anatomy • Digestive tract – Alimentary tract or canal – GI tract • Accessory organs – Primarily glands • Regions – – – – Mouth or oral cavity Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus
Digestive System Anatomy • Digestive tract – Alimentary tract or canal – GI tract • Accessory organs – Primarily glands • Regions – – – – Mouth or oral cavity Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus
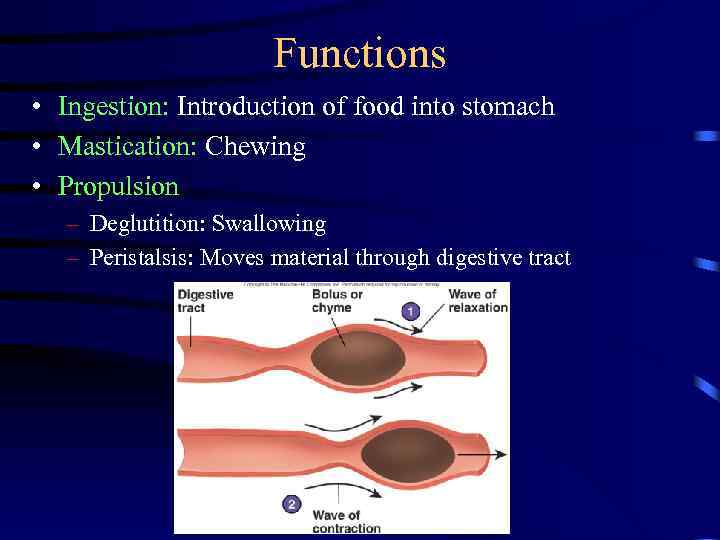 Functions • Ingestion: Introduction of food into stomach • Mastication: Chewing • Propulsion – Deglutition: Swallowing – Peristalsis: Moves material through digestive tract
Functions • Ingestion: Introduction of food into stomach • Mastication: Chewing • Propulsion – Deglutition: Swallowing – Peristalsis: Moves material through digestive tract
 Functions • • • Mixing: Segmental contraction that occurs in small intestine Secretion: Lubricate, liquefy, digest Digestion: Mechanical and chemical Absorption: Movement from tract into circulation or lymph Elimination: Waste products removed from body
Functions • • • Mixing: Segmental contraction that occurs in small intestine Secretion: Lubricate, liquefy, digest Digestion: Mechanical and chemical Absorption: Movement from tract into circulation or lymph Elimination: Waste products removed from body
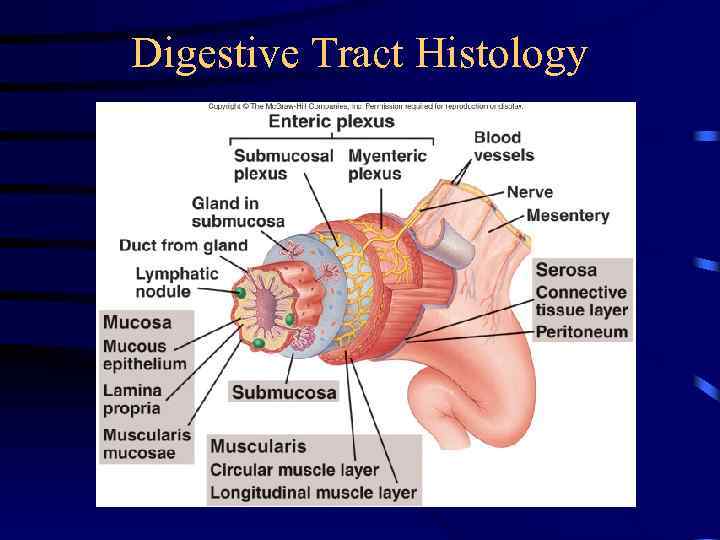 Digestive Tract Histology
Digestive Tract Histology
 Digestive System Regulation • Nervous regulation – Involves enteric nervous system • Types of neurons: sensory, motor, interneurons – Coordinates peristalsis and regulates local reflexes • Chemical regulation – Production of hormones • Gastrin, secretin – Production of paracrine chemicals • Histamine • Help local reflexes in ENS control digestive environments as p. H levels
Digestive System Regulation • Nervous regulation – Involves enteric nervous system • Types of neurons: sensory, motor, interneurons – Coordinates peristalsis and regulates local reflexes • Chemical regulation – Production of hormones • Gastrin, secretin – Production of paracrine chemicals • Histamine • Help local reflexes in ENS control digestive environments as p. H levels
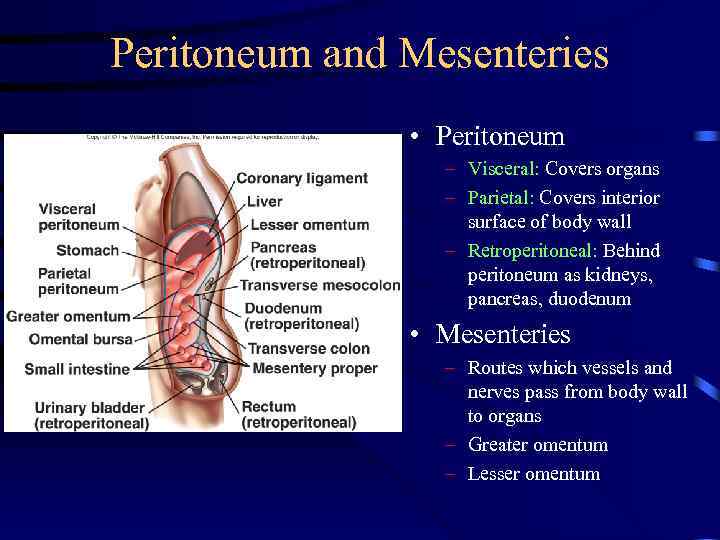 Peritoneum and Mesenteries • Peritoneum – Visceral: Covers organs – Parietal: Covers interior surface of body wall – Retroperitoneal: Behind peritoneum as kidneys, pancreas, duodenum • Mesenteries – Routes which vessels and nerves pass from body wall to organs – Greater omentum – Lesser omentum
Peritoneum and Mesenteries • Peritoneum – Visceral: Covers organs – Parietal: Covers interior surface of body wall – Retroperitoneal: Behind peritoneum as kidneys, pancreas, duodenum • Mesenteries – Routes which vessels and nerves pass from body wall to organs – Greater omentum – Lesser omentum
 Peritonitis • Acute inflammation of the peritoneal cavity • Caused by: Stab -, or bullet wounds, perforating ulcers of GI tract, ruptured appendix • Bacterial infection, if generalized often fatal • Mega-dose antibiotic therapy
Peritonitis • Acute inflammation of the peritoneal cavity • Caused by: Stab -, or bullet wounds, perforating ulcers of GI tract, ruptured appendix • Bacterial infection, if generalized often fatal • Mega-dose antibiotic therapy
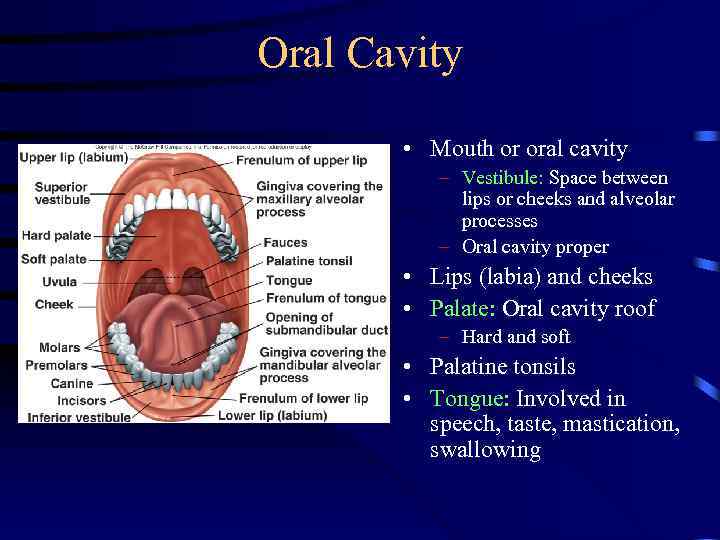 Oral Cavity • Mouth or oral cavity – Vestibule: Space between lips or cheeks and alveolar processes – Oral cavity proper • Lips (labia) and cheeks • Palate: Oral cavity roof – Hard and soft • Palatine tonsils • Tongue: Involved in speech, taste, mastication, swallowing
Oral Cavity • Mouth or oral cavity – Vestibule: Space between lips or cheeks and alveolar processes – Oral cavity proper • Lips (labia) and cheeks • Palate: Oral cavity roof – Hard and soft • Palatine tonsils • Tongue: Involved in speech, taste, mastication, swallowing
 Teeth • 20 deciduous, 32 permanent teeth • Anatomy • Enamel: Hydroxyapatite Ca 5(PO 4)3 OH, lack of collagen, irreparable • Dentin: similar to bone, avascular, dentinal tubules house extensions of odontoblasts, maintain dentin structure (incl. repair)
Teeth • 20 deciduous, 32 permanent teeth • Anatomy • Enamel: Hydroxyapatite Ca 5(PO 4)3 OH, lack of collagen, irreparable • Dentin: similar to bone, avascular, dentinal tubules house extensions of odontoblasts, maintain dentin structure (incl. repair)
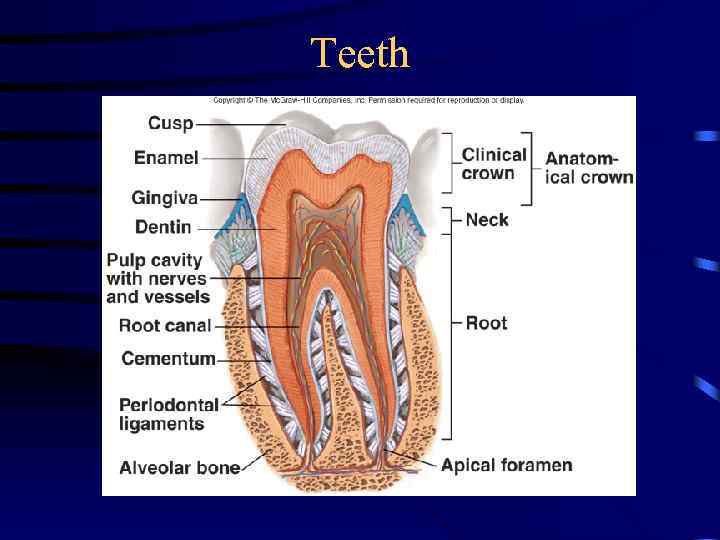 Teeth
Teeth
 Teeth – Impacted teeth - fail to emerge from gums, pressure, pain (common with “wisdom teeth”) (3 rd molars) – Root canal therapy - death of nerve, cessation of blood supply pulp cavity frequently becomes infected sterilization treatment filling capping – Dental caries - gradual demineralization, erosion of enamel & dentin, via dental plaques, lactic acid producing bacteria, proteases break down collagen of dentin
Teeth – Impacted teeth - fail to emerge from gums, pressure, pain (common with “wisdom teeth”) (3 rd molars) – Root canal therapy - death of nerve, cessation of blood supply pulp cavity frequently becomes infected sterilization treatment filling capping – Dental caries - gradual demineralization, erosion of enamel & dentin, via dental plaques, lactic acid producing bacteria, proteases break down collagen of dentin
 Teeth • Dental calculus - dental plaque precipitates calcium salts calculus may compromise seal b/w gingiva & teeth risk of infection gum disease gingivitis (bleeding, swelling, pain) infection spread to jaw bone erosion tooth loss peridontitis • 95% of people > 35, cause of ca. 85% of tooth loss in adults
Teeth • Dental calculus - dental plaque precipitates calcium salts calculus may compromise seal b/w gingiva & teeth risk of infection gum disease gingivitis (bleeding, swelling, pain) infection spread to jaw bone erosion tooth loss peridontitis • 95% of people > 35, cause of ca. 85% of tooth loss in adults
 The Mouth & Associated Organs • Walls of mouth - stratified, squamous epithelium (friction) – gums, hard palate & dorsum of tongue slightly keratinized – upon injury: secretion of defensins (protection against microorganisms in oral flora) • Lips - muscular, red margins poorly keratinized, translucent, no sweat or sebaceous glands
The Mouth & Associated Organs • Walls of mouth - stratified, squamous epithelium (friction) – gums, hard palate & dorsum of tongue slightly keratinized – upon injury: secretion of defensins (protection against microorganisms in oral flora) • Lips - muscular, red margins poorly keratinized, translucent, no sweat or sebaceous glands
 The Mouth & Associated Organs • Cheeks - buccinator muscles • Tongue - intrinsic (shape change) and extrinsic muscle (movement, attached to skull bones)
The Mouth & Associated Organs • Cheeks - buccinator muscles • Tongue - intrinsic (shape change) and extrinsic muscle (movement, attached to skull bones)
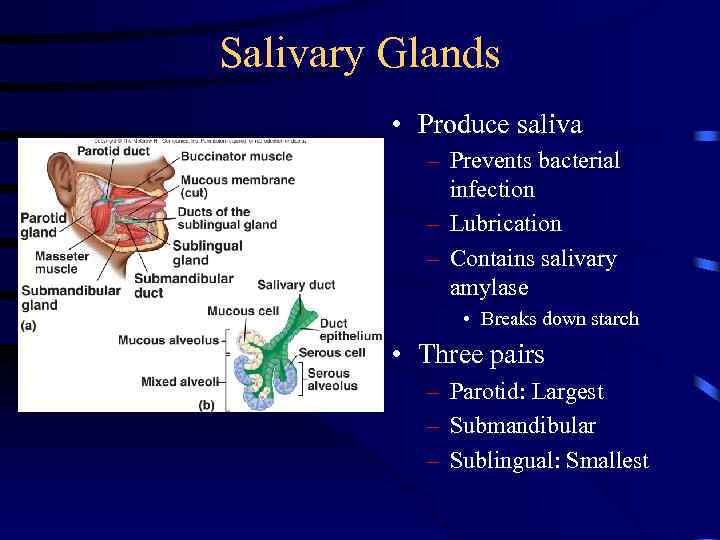 Salivary Glands • Produce saliva – Prevents bacterial infection – Lubrication – Contains salivary amylase • Breaks down starch • Three pairs – Parotid: Largest – Submandibular – Sublingual: Smallest
Salivary Glands • Produce saliva – Prevents bacterial infection – Lubrication – Contains salivary amylase • Breaks down starch • Three pairs – Parotid: Largest – Submandibular – Sublingual: Smallest
 Composition of Saliva • • • Hypo-osmotic solution ( 97 -99. 5% water) p. H 6. 75 - 7. 00 Na, K, phosphate, bicarbonate, chloride proteins: amylase, Lysozyme, Ig. A metabolic wastes: urea, uric acid Resident bacteria reduce nitrate (NO 3 -) into nitrite (NO 2 -), converted into NO (nitric oxide), esp. in acidic environment (around gums, acids produced by caries producing bacteria), NO - bactericical
Composition of Saliva • • • Hypo-osmotic solution ( 97 -99. 5% water) p. H 6. 75 - 7. 00 Na, K, phosphate, bicarbonate, chloride proteins: amylase, Lysozyme, Ig. A metabolic wastes: urea, uric acid Resident bacteria reduce nitrate (NO 3 -) into nitrite (NO 2 -), converted into NO (nitric oxide), esp. in acidic environment (around gums, acids produced by caries producing bacteria), NO - bactericical
 Control of Salivation • 1 -1. 5 l/day • Basal secretion to moisten oral cavity • Increased output via response to stimuli – chemoreceptors, pressoreceptors brain stem parasympathicus output increased salivation esp. in response to acidic foods (fruit juices, vinegar) or hot spices – also triggered via cortical stimulation (thought, smell)
Control of Salivation • 1 -1. 5 l/day • Basal secretion to moisten oral cavity • Increased output via response to stimuli – chemoreceptors, pressoreceptors brain stem parasympathicus output increased salivation esp. in response to acidic foods (fruit juices, vinegar) or hot spices – also triggered via cortical stimulation (thought, smell)
 Control of Salivation • Effect of symapthicus – decreases overall secretion – change to thick, mucous secretion – strong sympathicus stimulation vasoconstriction of vessels serving glands near cessation of salivation (dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, talking) – accumulation of food particles enhanced bacterial growth halitosis • Salivary glands Infection – Mumps (myxovirus infection) spread to testes in male adults 25% chance of sterility
Control of Salivation • Effect of symapthicus – decreases overall secretion – change to thick, mucous secretion – strong sympathicus stimulation vasoconstriction of vessels serving glands near cessation of salivation (dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, talking) – accumulation of food particles enhanced bacterial growth halitosis • Salivary glands Infection – Mumps (myxovirus infection) spread to testes in male adults 25% chance of sterility
 Deglutition (Swallowing) • Three phases – Voluntary • Bolus of food moved by tongue from oral cavity to pharynx – Pharyngeal Reflex: Upper esophageal sphincter relaxes, elevated pharynx opens the esophagus, food pushed into esophagus – Esophageal • Reflex: Epiglottis is tipped posteriorly, larynx elevated to prevent food from passing into larynx
Deglutition (Swallowing) • Three phases – Voluntary • Bolus of food moved by tongue from oral cavity to pharynx – Pharyngeal Reflex: Upper esophageal sphincter relaxes, elevated pharynx opens the esophagus, food pushed into esophagus – Esophageal • Reflex: Epiglottis is tipped posteriorly, larynx elevated to prevent food from passing into larynx
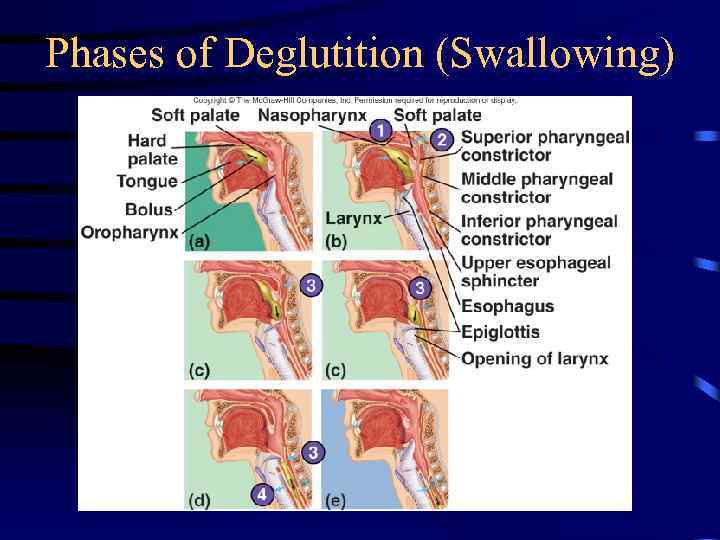 Phases of Deglutition (Swallowing)
Phases of Deglutition (Swallowing)
 Esophagus • Heartburn - burning, radiating, substernal pain caused by acid reflux into esophagus, can lead to inflammation & ulceration • Causes: – excessive eating, severe obesity, pregnancy, exercise after meals, hiatus hernia (structural abnormality, stomach protrudes above diaphragm, insufficient cardiac sphincter function, esp. when lying down)
Esophagus • Heartburn - burning, radiating, substernal pain caused by acid reflux into esophagus, can lead to inflammation & ulceration • Causes: – excessive eating, severe obesity, pregnancy, exercise after meals, hiatus hernia (structural abnormality, stomach protrudes above diaphragm, insufficient cardiac sphincter function, esp. when lying down)
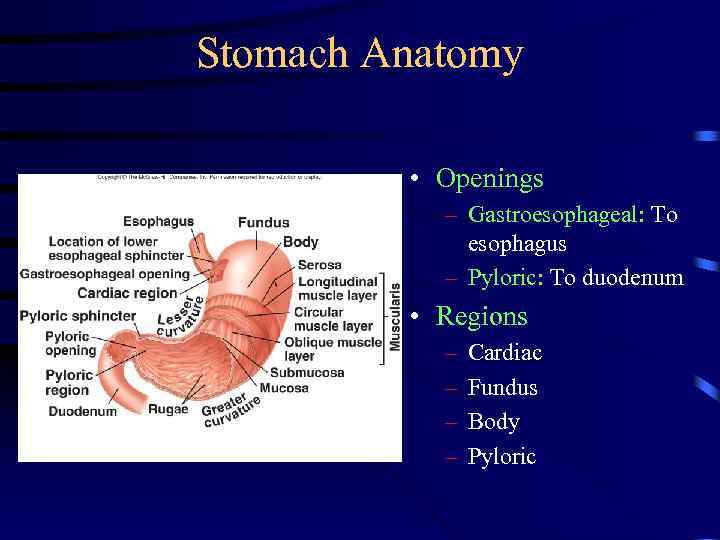 Stomach Anatomy • Openings – Gastroesophageal: To esophagus – Pyloric: To duodenum • Regions – – Cardiac Fundus Body Pyloric
Stomach Anatomy • Openings – Gastroesophageal: To esophagus – Pyloric: To duodenum • Regions – – Cardiac Fundus Body Pyloric
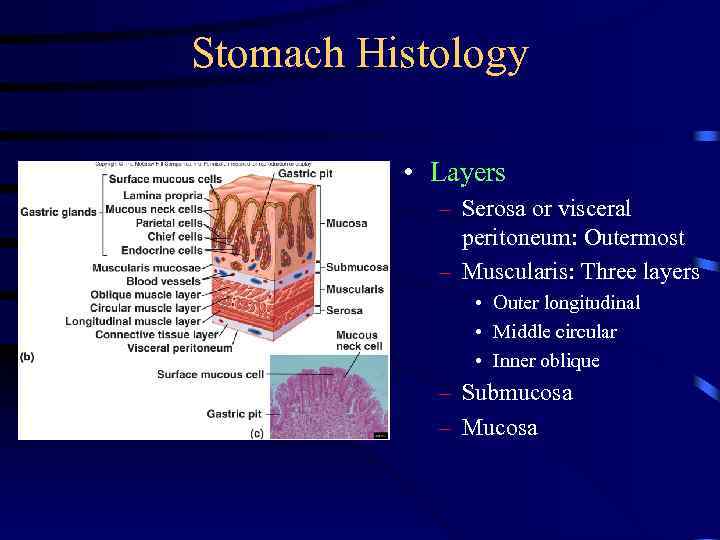 Stomach Histology • Layers – Serosa or visceral peritoneum: Outermost – Muscularis: Three layers • Outer longitudinal • Middle circular • Inner oblique – Submucosa – Mucosa
Stomach Histology • Layers – Serosa or visceral peritoneum: Outermost – Muscularis: Three layers • Outer longitudinal • Middle circular • Inner oblique – Submucosa – Mucosa
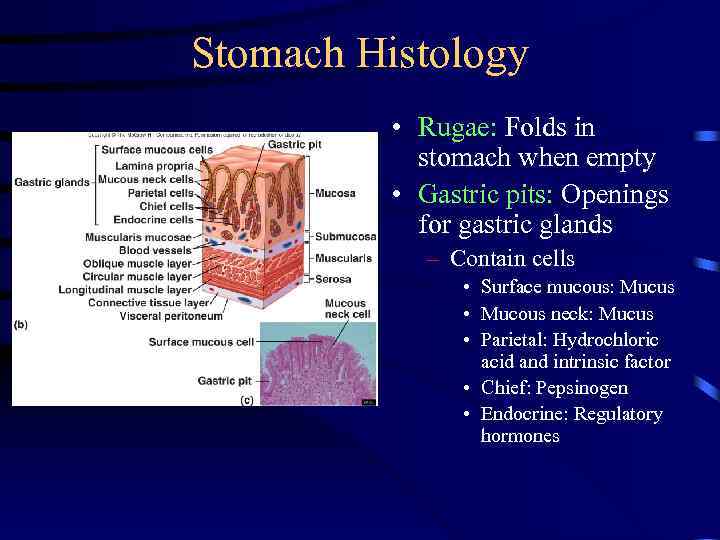 Stomach Histology • Rugae: Folds in stomach when empty • Gastric pits: Openings for gastric glands – Contain cells • Surface mucous: Mucus • Mucous neck: Mucus • Parietal: Hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor • Chief: Pepsinogen • Endocrine: Regulatory hormones
Stomach Histology • Rugae: Folds in stomach when empty • Gastric pits: Openings for gastric glands – Contain cells • Surface mucous: Mucus • Mucous neck: Mucus • Parietal: Hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor • Chief: Pepsinogen • Endocrine: Regulatory hormones
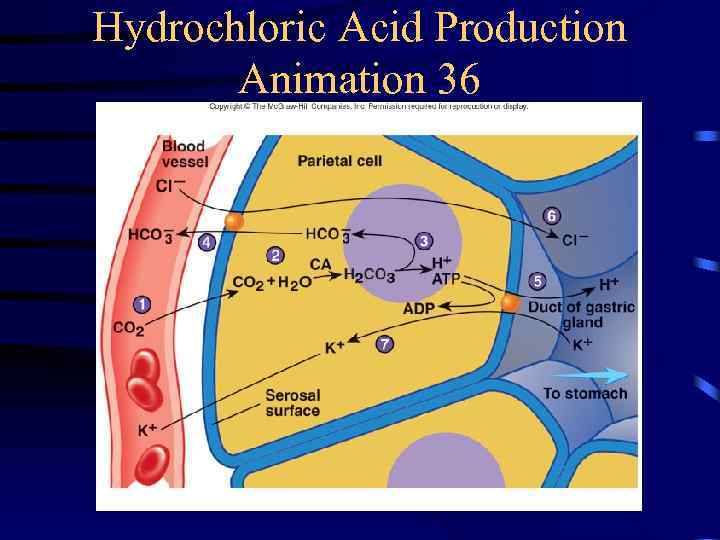 Hydrochloric Acid Production Animation 36
Hydrochloric Acid Production Animation 36
 Phases of Gastric Secretion Animation 37
Phases of Gastric Secretion Animation 37
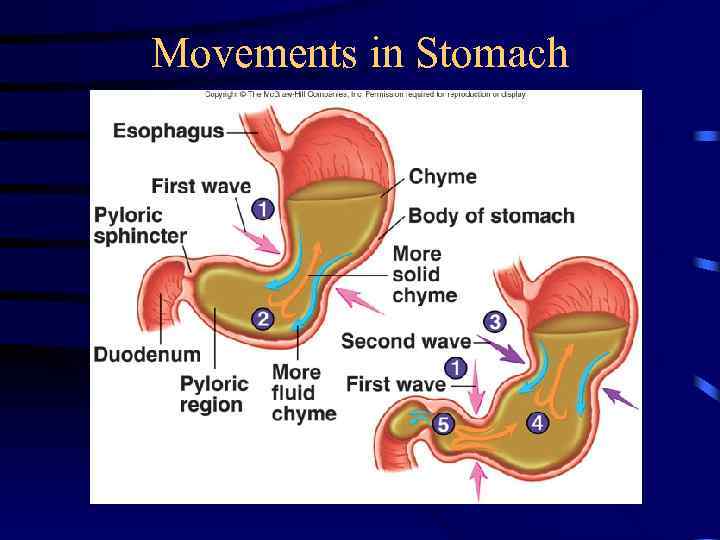 Movements in Stomach
Movements in Stomach
 Gastritis, Gastric Ulcers – breaching of the mucosal barrier inflammation persistent gastritis erosion of underlying tissue ulcer – pain, risk of hemorrhage – triggered by hypersecretion of HCl, hyposecretion of mucus, 90% of affected patients carry Helicobacter pylori
Gastritis, Gastric Ulcers – breaching of the mucosal barrier inflammation persistent gastritis erosion of underlying tissue ulcer – pain, risk of hemorrhage – triggered by hypersecretion of HCl, hyposecretion of mucus, 90% of affected patients carry Helicobacter pylori
 Gastritis, Gastric Ulcers • Bacteria release cytotoxins and chemotactic proteins immune response (suspected of increasing risk for stomach cancer) • ? Bacterium also found in >40% of healthy people • Treatment: Antibiotics, H 2 -antihistamines, cimetidine (Tagamet ), ranitidine (Zantac ) • Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol ) Bi 3+ toxic to Helicobacter • Antacids neutralize HCl - (Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2 – Maalox. TC®, Rolaids ®
Gastritis, Gastric Ulcers • Bacteria release cytotoxins and chemotactic proteins immune response (suspected of increasing risk for stomach cancer) • ? Bacterium also found in >40% of healthy people • Treatment: Antibiotics, H 2 -antihistamines, cimetidine (Tagamet ), ranitidine (Zantac ) • Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol ) Bi 3+ toxic to Helicobacter • Antacids neutralize HCl - (Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2 – Maalox. TC®, Rolaids ®
 Vomiting (Emesis) • Triggers – excessive stretching of stomach, alcohol, chemical irritants such as bacterial toxins, drugs, etc. impulse to emetic center (medulla) • Motor response – skeletal muscles of abdominal wall & diaphragm contract, cardiac sphincter relaxes, soft palate rises closing off nasal passages
Vomiting (Emesis) • Triggers – excessive stretching of stomach, alcohol, chemical irritants such as bacterial toxins, drugs, etc. impulse to emetic center (medulla) • Motor response – skeletal muscles of abdominal wall & diaphragm contract, cardiac sphincter relaxes, soft palate rises closing off nasal passages
 “there she blows”
“there she blows”
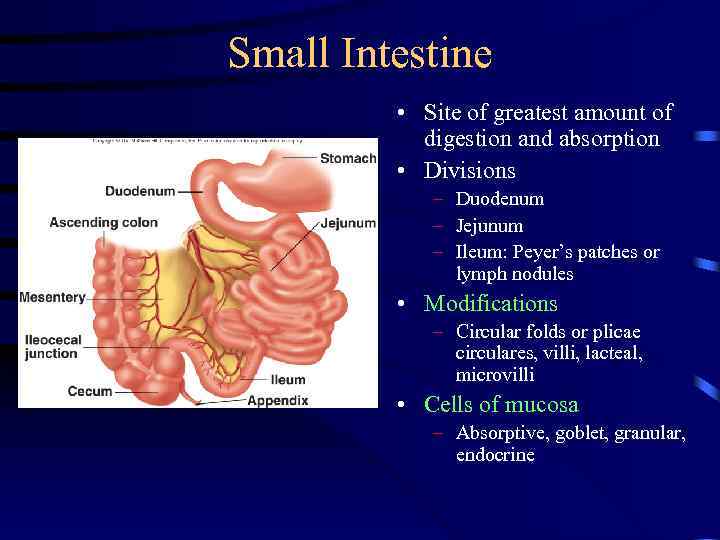 Small Intestine • Site of greatest amount of digestion and absorption • Divisions – Duodenum – Jejunum – Ileum: Peyer’s patches or lymph nodules • Modifications – Circular folds or plicae circulares, villi, lacteal, microvilli • Cells of mucosa – Absorptive, goblet, granular, endocrine
Small Intestine • Site of greatest amount of digestion and absorption • Divisions – Duodenum – Jejunum – Ileum: Peyer’s patches or lymph nodules • Modifications – Circular folds or plicae circulares, villi, lacteal, microvilli • Cells of mucosa – Absorptive, goblet, granular, endocrine
 Small Intestine Secretions • Mucus – Protects against digestive enzymes and stomach acids • Digestive enzymes – Disaccharidases: Break down disaccharides to monosaccharides – Peptidases: Hydrolyze peptide bonds – Nucleases: Break down nucleic acids • Duodenal glands – Stimulated by vagus nerve, secretin, chemical or tactile irritation of duodenal mucosa
Small Intestine Secretions • Mucus – Protects against digestive enzymes and stomach acids • Digestive enzymes – Disaccharidases: Break down disaccharides to monosaccharides – Peptidases: Hydrolyze peptide bonds – Nucleases: Break down nucleic acids • Duodenal glands – Stimulated by vagus nerve, secretin, chemical or tactile irritation of duodenal mucosa
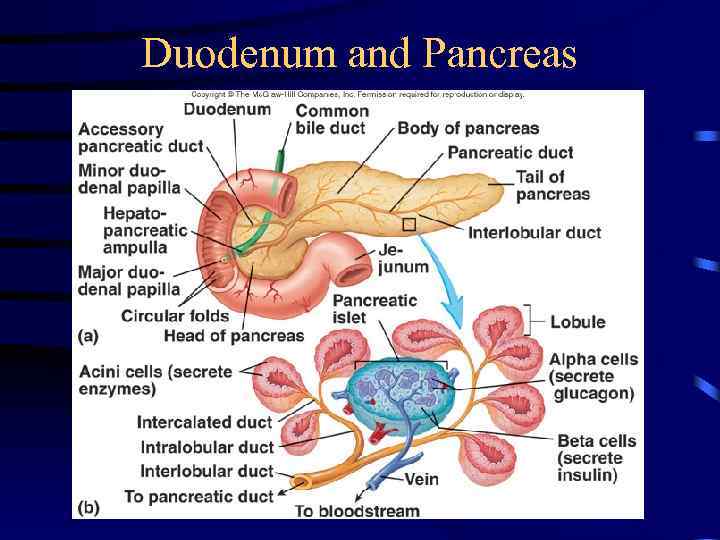 Duodenum and Pancreas
Duodenum and Pancreas
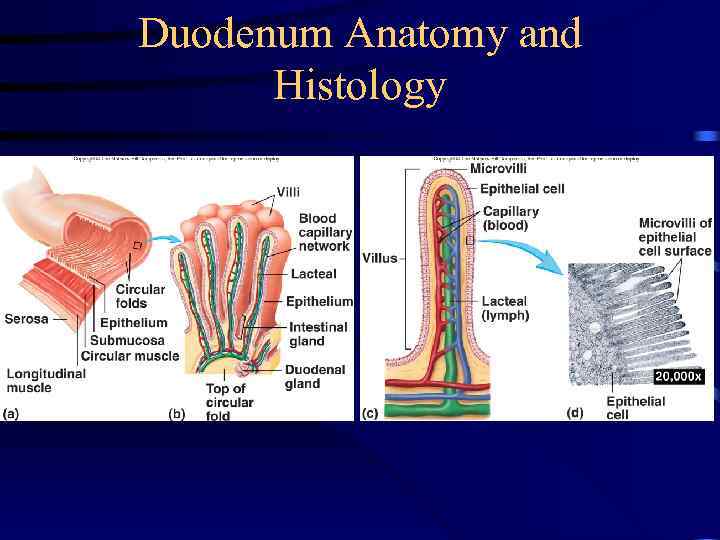 Duodenum Anatomy and Histology
Duodenum Anatomy and Histology
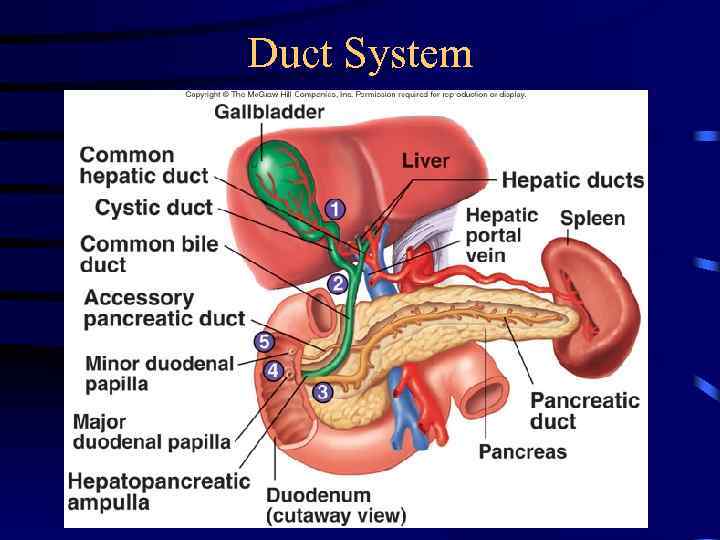
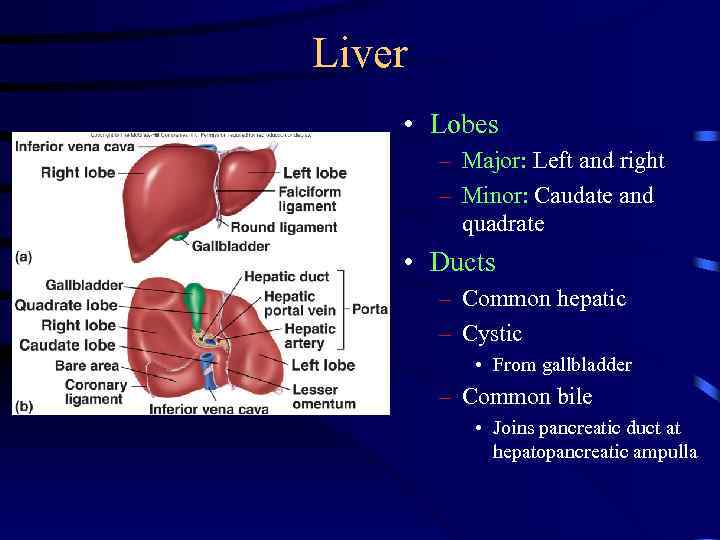 Liver • Lobes – Major: Left and right – Minor: Caudate and quadrate • Ducts – Common hepatic – Cystic • From gallbladder – Common bile • Joins pancreatic duct at hepatopancreatic ampulla
Liver • Lobes – Major: Left and right – Minor: Caudate and quadrate • Ducts – Common hepatic – Cystic • From gallbladder – Common bile • Joins pancreatic duct at hepatopancreatic ampulla
 Functions of the Liver • Bile production – Salts emulsify fats, contain pigments as bilirubin 0. 5 – 1 l/day • Storage – Glycogen, fat, vitamins A, D, E, copper and iron • Nutrient interconversion • Detoxification – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea • Phagocytosis – Kupffer cells phagocytize worn-out and dying red and white blood cells, some bacteria • Synthesis – Albumins, fibrinogen, globulins, heparin, clotting factors
Functions of the Liver • Bile production – Salts emulsify fats, contain pigments as bilirubin 0. 5 – 1 l/day • Storage – Glycogen, fat, vitamins A, D, E, copper and iron • Nutrient interconversion • Detoxification – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea • Phagocytosis – Kupffer cells phagocytize worn-out and dying red and white blood cells, some bacteria • Synthesis – Albumins, fibrinogen, globulins, heparin, clotting factors
 Hepatitis • Inflammation of liver, mostly due to – Viral infection (strains A-F), some drugs, mushroom toxins • 40% (US) Hepatitis B (blood contact, infusions, needles, sex) • 32% (US) Hepatitis A (less severe, transmitted water born, sewage, lack of hygiene, raw shell fish, (feces-mouth) • Recombinant-DNA produced vaccine against both made in yeast
Hepatitis • Inflammation of liver, mostly due to – Viral infection (strains A-F), some drugs, mushroom toxins • 40% (US) Hepatitis B (blood contact, infusions, needles, sex) • 32% (US) Hepatitis A (less severe, transmitted water born, sewage, lack of hygiene, raw shell fish, (feces-mouth) • Recombinant-DNA produced vaccine against both made in yeast
 Hepatitis • Hepatitis C common epidemic in developing countries, water born – no vaccine, but successful drug treatment with anti-inflammatory/immunesuppressive steroids (prednisone), recombinant-DNA made interferon
Hepatitis • Hepatitis C common epidemic in developing countries, water born – no vaccine, but successful drug treatment with anti-inflammatory/immunesuppressive steroids (prednisone), recombinant-DNA made interferon
 Liver Cirrhosis & Cancer • Cirrhosis - chronic, progressive inflammation, via chronic alcoholism, hepatitis, and other toxins regeneration of connective tissue faster than hepatocytes scar tissue contracts fibrosis obstruction of hepatic portal veins portal hypertension varicosis - may rupture bleeding, vomiting of blood • Hepatitis B often leads to hepatocarcinoma
Liver Cirrhosis & Cancer • Cirrhosis - chronic, progressive inflammation, via chronic alcoholism, hepatitis, and other toxins regeneration of connective tissue faster than hepatocytes scar tissue contracts fibrosis obstruction of hepatic portal veins portal hypertension varicosis - may rupture bleeding, vomiting of blood • Hepatitis B often leads to hepatocarcinoma
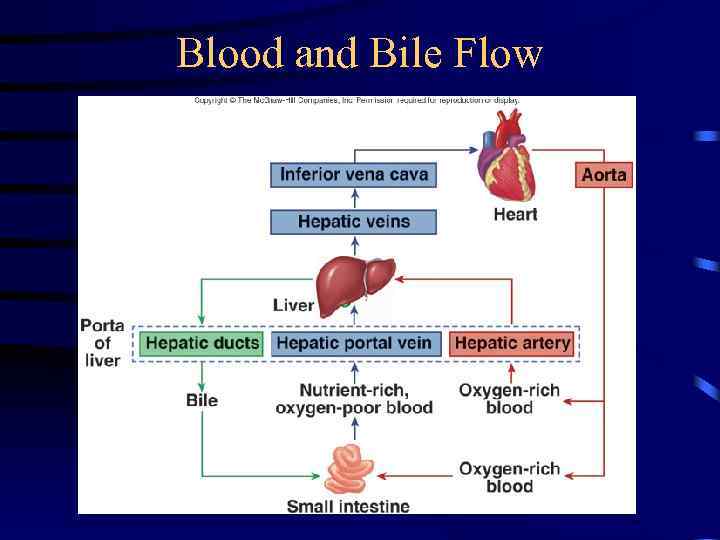 Blood and Bile Flow
Blood and Bile Flow
 Duct System
Duct System
 Gallbladder • Bile is stored and concentrated • Stimulated by cholecystokinin and vegal stimulation • Dumps into small intestine • Production of gallstones possible – Drastic dieting with rapid weight loss
Gallbladder • Bile is stored and concentrated • Stimulated by cholecystokinin and vegal stimulation • Dumps into small intestine • Production of gallstones possible – Drastic dieting with rapid weight loss
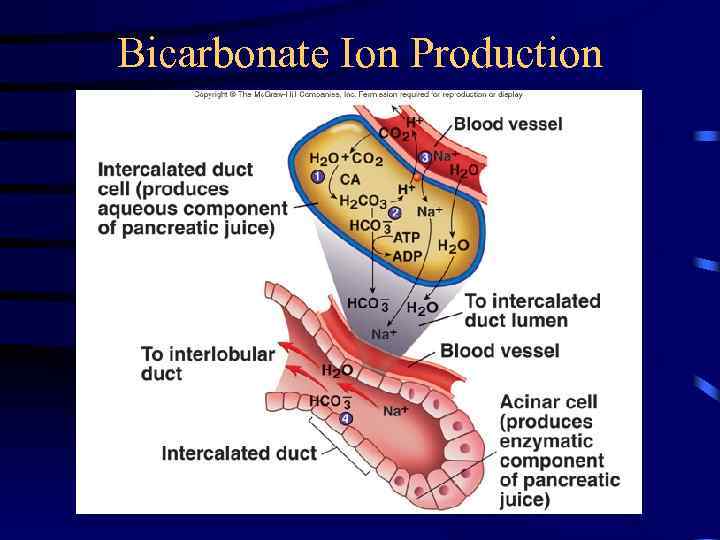
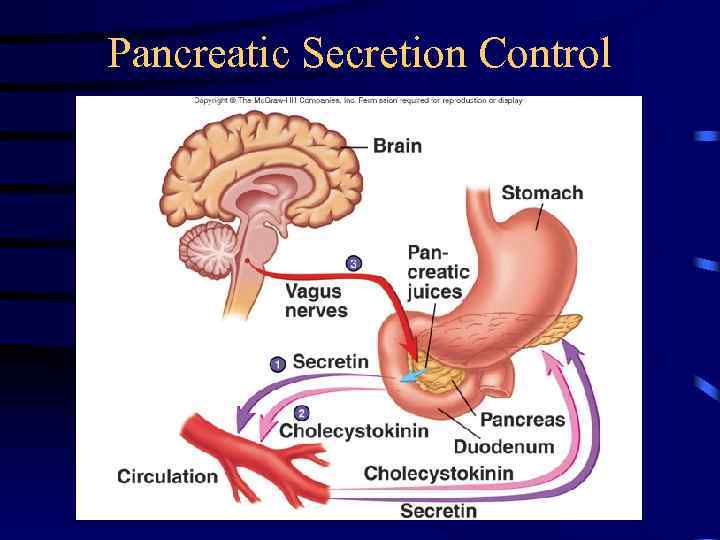
 Pancreas • Anatomy – Endocrine • Pancreatic islets produce insulin and glucagon – Exocrine • Acini produce digestive enzymes – Regions: Head, body, tail • Secretions – Pancreatic juice (exocrine) • • • Trypsin Chymotrypsin Carboxypeptidase Pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipases Enzymes that reduce DNA and ribonucleic acid
Pancreas • Anatomy – Endocrine • Pancreatic islets produce insulin and glucagon – Exocrine • Acini produce digestive enzymes – Regions: Head, body, tail • Secretions – Pancreatic juice (exocrine) • • • Trypsin Chymotrypsin Carboxypeptidase Pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipases Enzymes that reduce DNA and ribonucleic acid
 Bicarbonate Ion Production
Bicarbonate Ion Production
 Pancreatic Secretion Control
Pancreatic Secretion Control
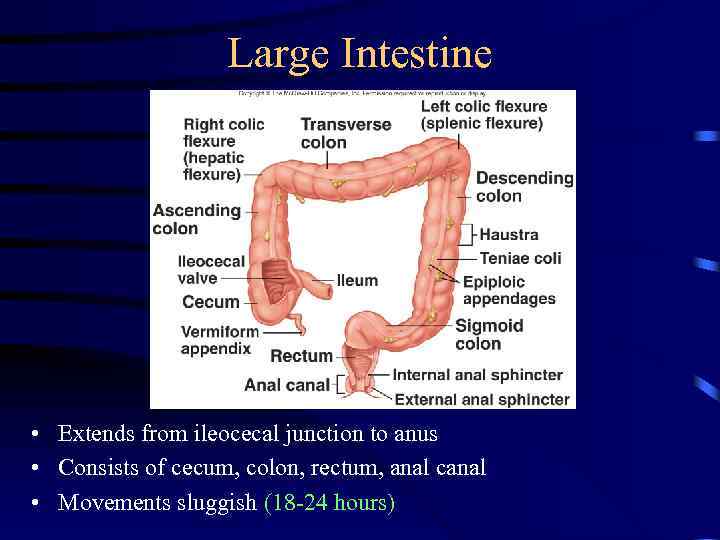 Large Intestine • Extends from ileocecal junction to anus • Consists of cecum, colon, rectum, anal canal • Movements sluggish (18 -24 hours)
Large Intestine • Extends from ileocecal junction to anus • Consists of cecum, colon, rectum, anal canal • Movements sluggish (18 -24 hours)
 Large Intestine • Cecum – Blind sac, vermiform appendix attached • Colon – Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid • Rectum – Straight muscular tube • Anal canal – Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle) – External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle) – Hemorrhoids: Vein enlargement or inflammation
Large Intestine • Cecum – Blind sac, vermiform appendix attached • Colon – Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid • Rectum – Straight muscular tube • Anal canal – Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle) – External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle) – Hemorrhoids: Vein enlargement or inflammation
 Secretions of Large Intestine • Mucus provides protection – Parasympathetic stimulation increases rate of goblet cell secretion • Pumps – Exchange of bicarbonate ions for chloride ions – Exchange of sodium ions for hydrogen ions
Secretions of Large Intestine • Mucus provides protection – Parasympathetic stimulation increases rate of goblet cell secretion • Pumps – Exchange of bicarbonate ions for chloride ions – Exchange of sodium ions for hydrogen ions
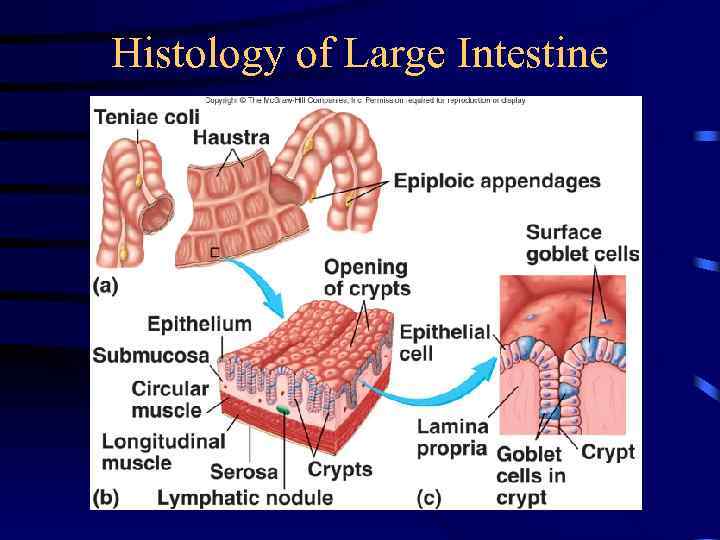 Histology of Large Intestine
Histology of Large Intestine
 Movement in Large Intestine • Mass movements – Common after meals • Local reflexes in enteric plexus – Gastrocolic: Initiated by stomach – Duodenocolic: Initiated by duodenum • Defecation reflex – Distension of the rectal wall by feces • Defecation – Usually accompanied by voluntary movements to expel feces through abdominal cavity pressure caused by inspiration
Movement in Large Intestine • Mass movements – Common after meals • Local reflexes in enteric plexus – Gastrocolic: Initiated by stomach – Duodenocolic: Initiated by duodenum • Defecation reflex – Distension of the rectal wall by feces • Defecation – Usually accompanied by voluntary movements to expel feces through abdominal cavity pressure caused by inspiration
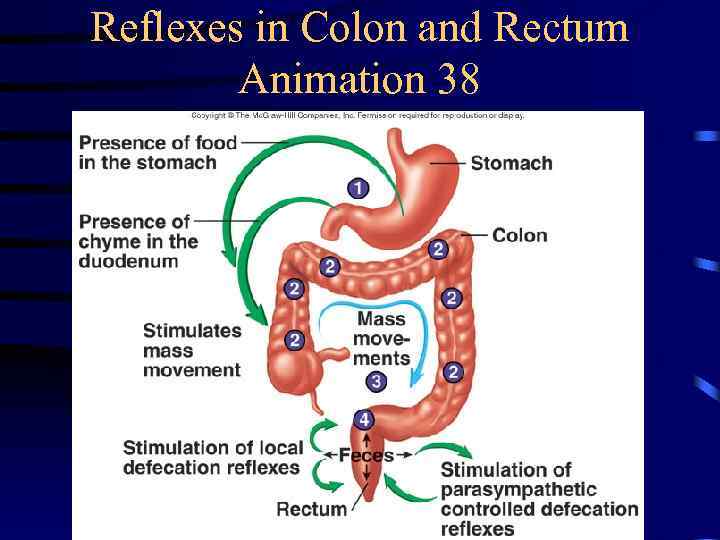 Reflexes in Colon and Rectum Animation 38
Reflexes in Colon and Rectum Animation 38
 Large Intestine Bacterial Flora – live off undigested material, e. g. complex carbohydrates, cellulose, etc. – produce gases: CH 4, CO 2, H 2, N 2, dimethyl sulfide (CH 3 -S-CH 3) called flatus – synthesize crucial vitamin Bs & K • Diarrhea, constipation
Large Intestine Bacterial Flora – live off undigested material, e. g. complex carbohydrates, cellulose, etc. – produce gases: CH 4, CO 2, H 2, N 2, dimethyl sulfide (CH 3 -S-CH 3) called flatus – synthesize crucial vitamin Bs & K • Diarrhea, constipation
 Salmonella Food Poisoning • Many different strains of Salmonella, some cause typhoid fever, other common gastroenteritis – emesis, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, common in children under 10, even more in infants – bacteria common on poultry, eggs, sometimes in unpasteurized milk – rarely causes bacteremia, can affect heart, joints, and brain (meningitis) mostly selflimiting disease (symptoms ca. 5 - 7 d, bacteria present up to 6 month)
Salmonella Food Poisoning • Many different strains of Salmonella, some cause typhoid fever, other common gastroenteritis – emesis, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, common in children under 10, even more in infants – bacteria common on poultry, eggs, sometimes in unpasteurized milk – rarely causes bacteremia, can affect heart, joints, and brain (meningitis) mostly selflimiting disease (symptoms ca. 5 - 7 d, bacteria present up to 6 month)
 Lactose Intolerance • Decrease production of lactase in adulthood – lack of hydrolysis of lactose in into galactose and glucose – accumulation of lactose in intestine (after ingesting dairy products) – acts as osmotic laxative (retains H 2 O in lumen) – metabolized by intestinal flora - production of gases - cramps, abdominal pain • Therapy: Lactase tablets
Lactose Intolerance • Decrease production of lactase in adulthood – lack of hydrolysis of lactose in into galactose and glucose – accumulation of lactose in intestine (after ingesting dairy products) – acts as osmotic laxative (retains H 2 O in lumen) – metabolized by intestinal flora - production of gases - cramps, abdominal pain • Therapy: Lactase tablets
 Gluten Enteropathy • Gluten - protein common in cereals (wheat, rye, barely & oats) • some people - hypersensitive, diarrhea & malabsorption (mechanism? ) • Therapy: Gluten free food products
Gluten Enteropathy • Gluten - protein common in cereals (wheat, rye, barely & oats) • some people - hypersensitive, diarrhea & malabsorption (mechanism? ) • Therapy: Gluten free food products
 Genetic Defects affecting GI-tract • Structural malformations e. g. cleft palate, lip, patent opening b/w esophagus and trachea • Cystic Fibrosis – all secretions affected, major symptoms in lung – in GI-tract, pancreatic secretion abnormal, indigestion, severely compromised fat digestion, malabsorption of Vits. A, D, K – in utero: possible blockage of intestine, rupture
Genetic Defects affecting GI-tract • Structural malformations e. g. cleft palate, lip, patent opening b/w esophagus and trachea • Cystic Fibrosis – all secretions affected, major symptoms in lung – in GI-tract, pancreatic secretion abnormal, indigestion, severely compromised fat digestion, malabsorption of Vits. A, D, K – in utero: possible blockage of intestine, rupture
 Colon Cancer • Second most frequent (after lung cancer) in males • without symptoms for long time • when symptoms appear, mostly metastases have formed (liver, etc. ) • gradual progression of series of mutations • starting as polyps • prevention by early detection, yearly colon examination, surgery • correlation to diet?
Colon Cancer • Second most frequent (after lung cancer) in males • without symptoms for long time • when symptoms appear, mostly metastases have formed (liver, etc. ) • gradual progression of series of mutations • starting as polyps • prevention by early detection, yearly colon examination, surgery • correlation to diet?
 Digestion, Absorption, Transport • Digestion – Breakdown of food molecules for absorption into circulation • Mechanical: Breaks large food particles to small • Chemical: Breaking of covalent bonds by digestive enzymes • Absorption and transport – Molecules are moved out of digestive tract and into circulation for distribution throughout body
Digestion, Absorption, Transport • Digestion – Breakdown of food molecules for absorption into circulation • Mechanical: Breaks large food particles to small • Chemical: Breaking of covalent bonds by digestive enzymes • Absorption and transport – Molecules are moved out of digestive tract and into circulation for distribution throughout body
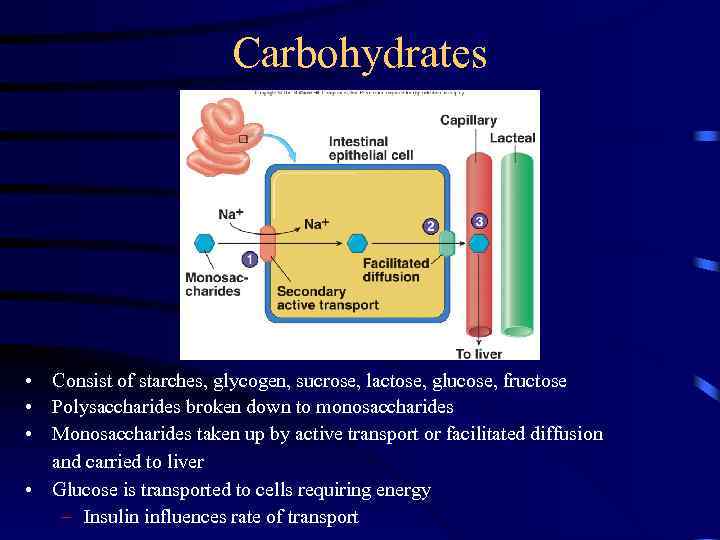 Carbohydrates • Consist of starches, glycogen, sucrose, lactose, glucose, fructose • Polysaccharides broken down to monosaccharides • Monosaccharides taken up by active transport or facilitated diffusion and carried to liver • Glucose is transported to cells requiring energy – Insulin influences rate of transport
Carbohydrates • Consist of starches, glycogen, sucrose, lactose, glucose, fructose • Polysaccharides broken down to monosaccharides • Monosaccharides taken up by active transport or facilitated diffusion and carried to liver • Glucose is transported to cells requiring energy – Insulin influences rate of transport
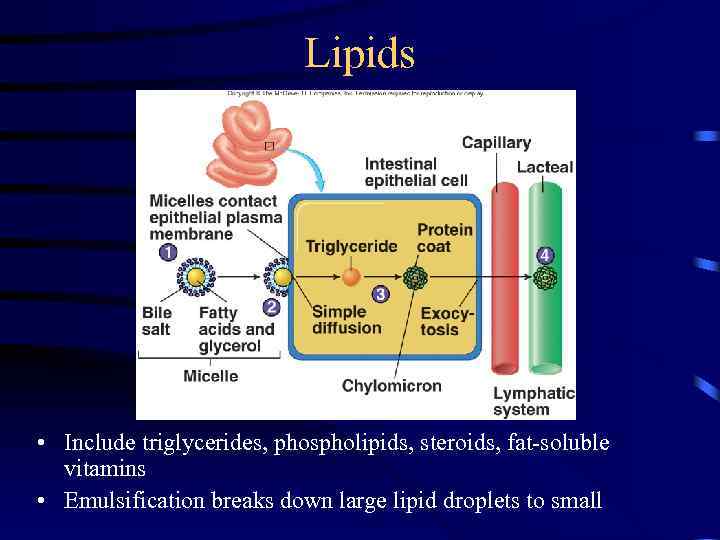 Lipids • Include triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins • Emulsification breaks down large lipid droplets to small
Lipids • Include triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins • Emulsification breaks down large lipid droplets to small
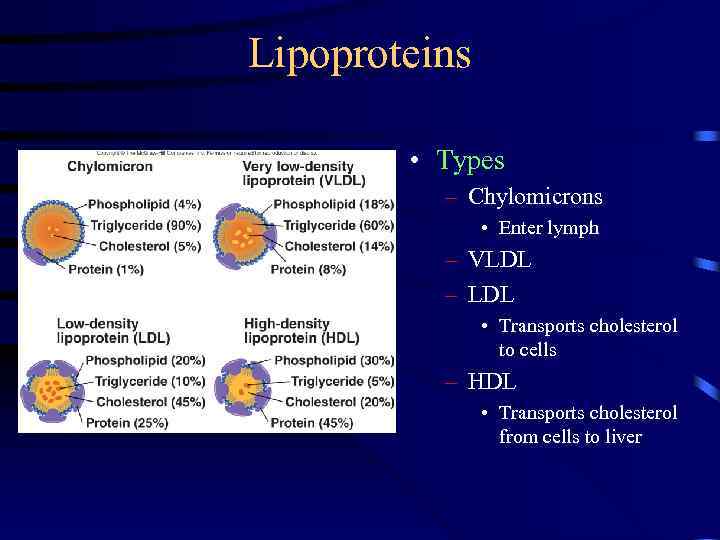 Lipoproteins • Types – Chylomicrons • Enter lymph – VLDL – LDL • Transports cholesterol to cells – HDL • Transports cholesterol from cells to liver
Lipoproteins • Types – Chylomicrons • Enter lymph – VLDL – LDL • Transports cholesterol to cells – HDL • Transports cholesterol from cells to liver
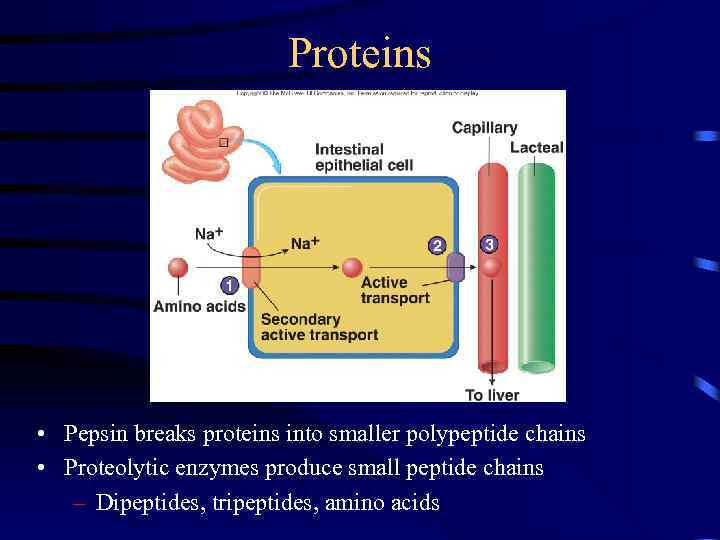 Proteins • Pepsin breaks proteins into smaller polypeptide chains • Proteolytic enzymes produce small peptide chains – Dipeptides, tripeptides, amino acids
Proteins • Pepsin breaks proteins into smaller polypeptide chains • Proteolytic enzymes produce small peptide chains – Dipeptides, tripeptides, amino acids
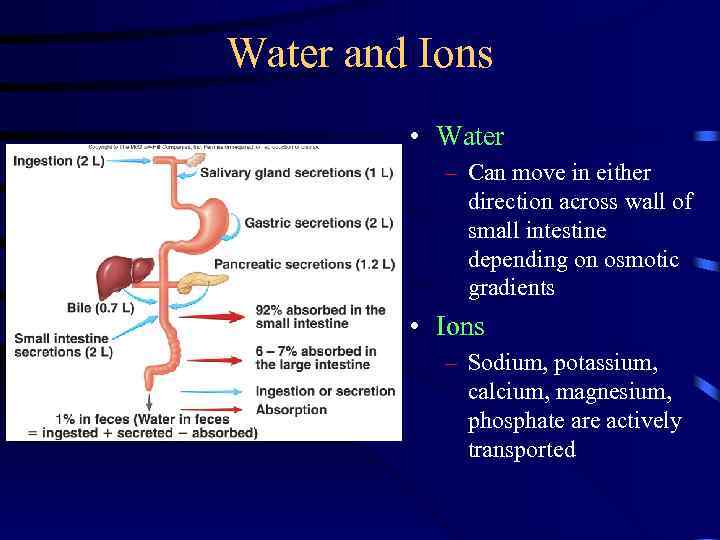 Water and Ions • Water – Can move in either direction across wall of small intestine depending on osmotic gradients • Ions – Sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate are actively transported
Water and Ions • Water – Can move in either direction across wall of small intestine depending on osmotic gradients • Ions – Sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate are actively transported


