6d92350b3004bca3e0c335c15c42b3be.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

The development of a computerized library in a primary school Presenter: Leung Wai Shing, Raymond Facilitator: Mr. Teddy So

Introduction

Background n IT usage in education n Common in classroom School office administration work Impact to libraries n Computerized libraries are needed in primary school

Background (cont. ) n Self Improvement Program (SIP) n n n Building New blocks Build a central library Buy books and furniture Achieve Computerization New Era Five-Year Strategy Plan n 294. 5 millions

Study Objective n n To find out the tasks needed to be computerized in primary school libraries the priorities of performing these tasks

Findings and Analysis
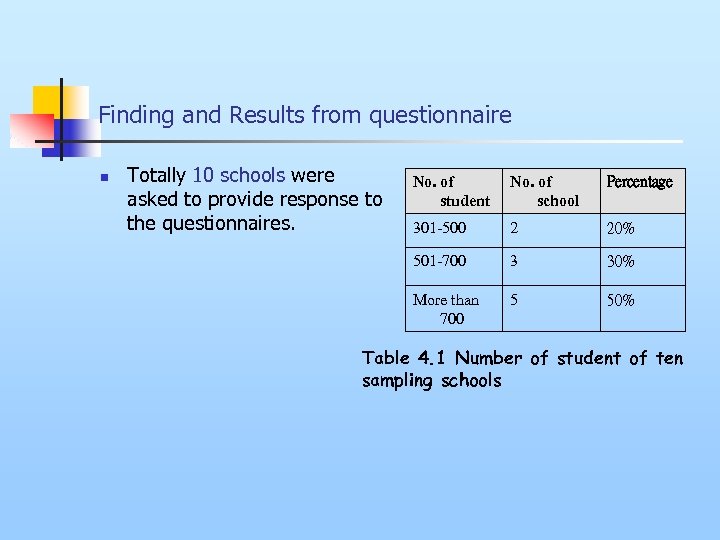
Finding and Results from questionnaire n Totally 10 schools were asked to provide response to the questionnaires. No. of student No. of school Percentage 301 -500 2 20% 501 -700 3 30% More than 700 5 50% Table 4. 1 Number of student of ten sampling schools
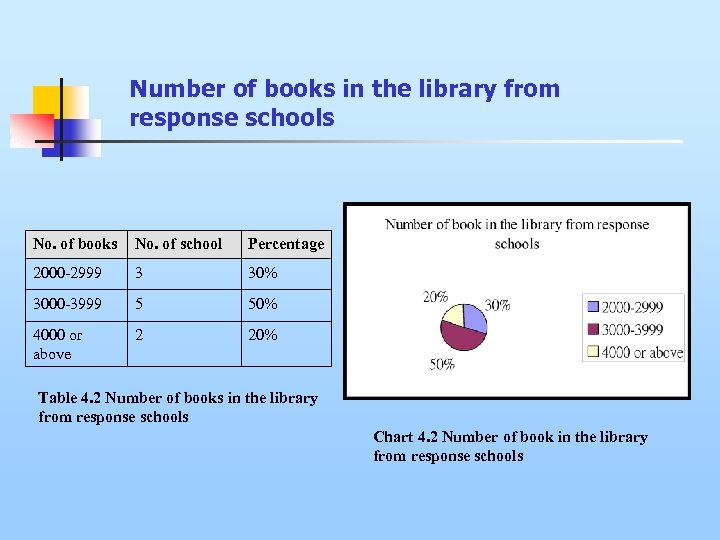
Number of books in the library from response schools No. of books No. of school Percentage 2000 -2999 3 30% 3000 -3999 5 50% 4000 or above 2 20% Table 4. 2 Number of books in the library from response schools Chart 4. 2 Number of book in the library from response schools

Existing Facilities n n It is important to select a proper model of computer used in the school library. From the survey, all schools have computers of Pentium 3 or Pentium 4 computer with 833 MHz or above. These configurations are enough to install automation software, to browse the Internet and to access digital multimedia material. Also, all of them are Internet access ready.

Profile of response schools n n n From the response schools, more than 80% of schools have more than 500 students. 80% of the response schools have already set up a central library. . The response school have a minimum of three computers in central library.
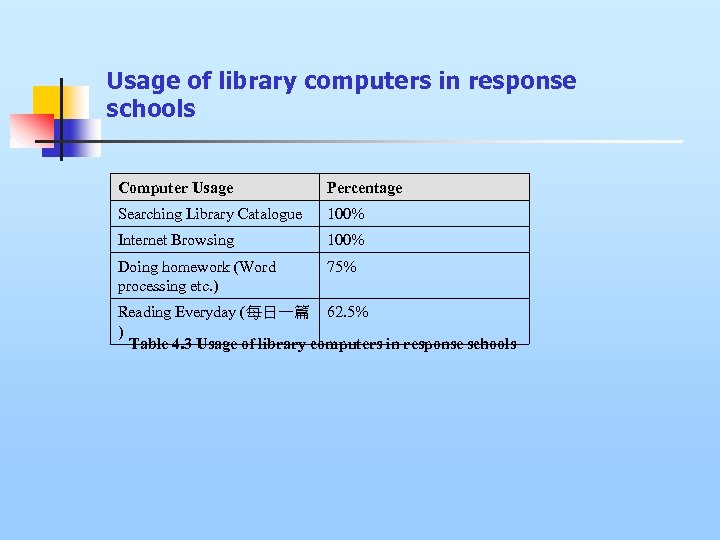
Usage of library computers in response schools Computer Usage Percentage Searching Library Catalogue 100% Internet Browsing 100% Doing homework (Word processing etc. ) 75% Reading Everyday (每日一篇 62. 5% ) Table 4. 3 Usage of library computers in response schools
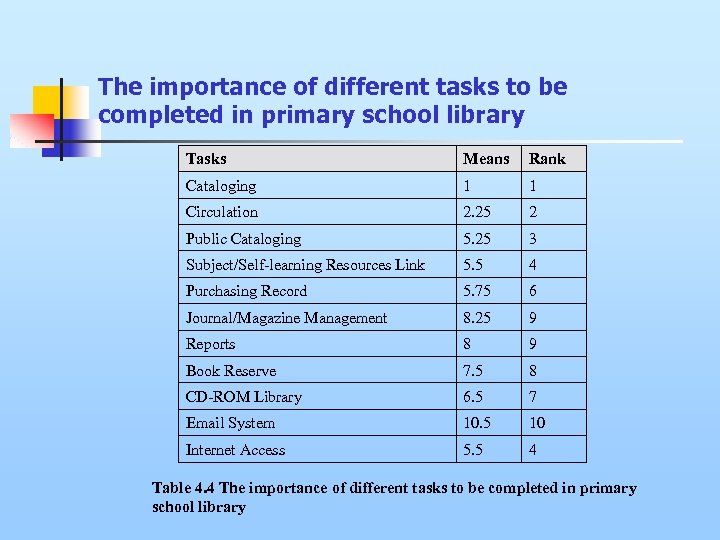
The importance of different tasks to be completed in primary school library Tasks Means Rank Cataloging 1 1 Circulation 2. 25 2 Public Cataloging 5. 25 3 Subject/Self-learning Resources Link 5. 5 4 Purchasing Record 5. 75 6 Journal/Magazine Management 8. 25 9 Reports 8 9 Book Reserve 7. 5 8 CD-ROM Library 6. 5 7 Email System 10. 5 10 Internet Access 5. 5 4 Table 4. 4 The importance of different tasks to be completed in primary school library

Information Technology Usage in the libraries n n n Both users and staffs use the Library Automation System to search for library catalogue, circulation conditions, Internet browsing, to do homework and have some online readings. Library homepage provide relevant link on the school curriculum and project learning. Students and teachers can benefit from this. Digitalized the purchasing Record, reports, email and using multimedia material such as CD-ROM, VCD etc.
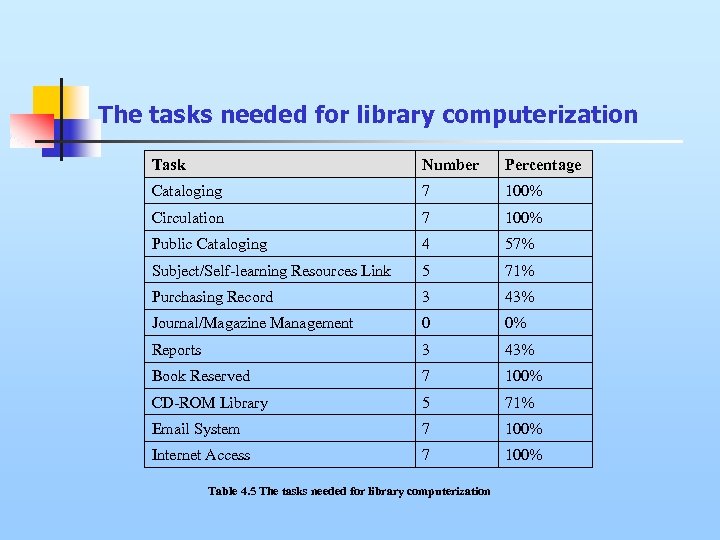
The tasks needed for library computerization Task Number Percentage Cataloging 7 100% Circulation 7 100% Public Cataloging 4 57% Subject/Self-learning Resources Link 5 71% Purchasing Record 3 43% Journal/Magazine Management 0 0% Reports 3 43% Book Reserved 7 100% CD-ROM Library 5 71% Email System 7 100% Internet Access 7 100% Table 4. 5 The tasks needed for library computerization

Levels of library computerization n n Employ library automation systems for circulation, cataloguing etc. Internet Services Online learning through library homepage Using other functions of the library automation system such as purchasing record, book reserve etc.
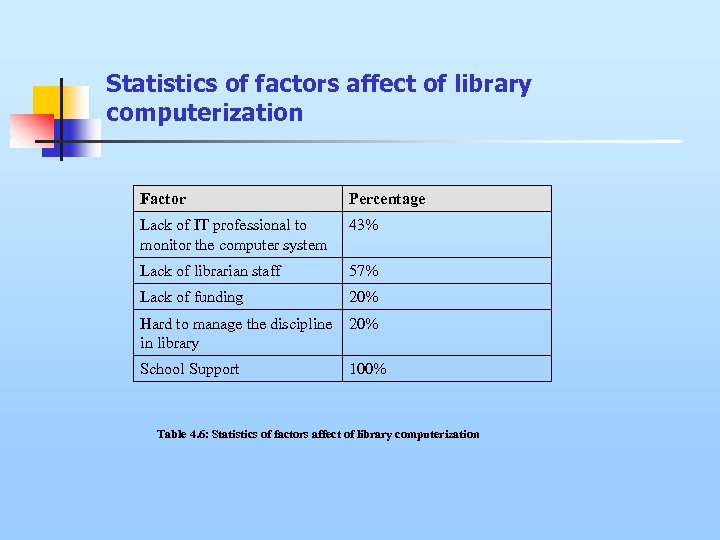
Statistics of factors affect of library computerization Factor Percentage Lack of IT professional to monitor the computer system 43% Lack of librarian staff 57% Lack of funding 20% Hard to manage the discipline in library 20% School Support 100% Table 4. 6: Statistics of factors affect of library computerization
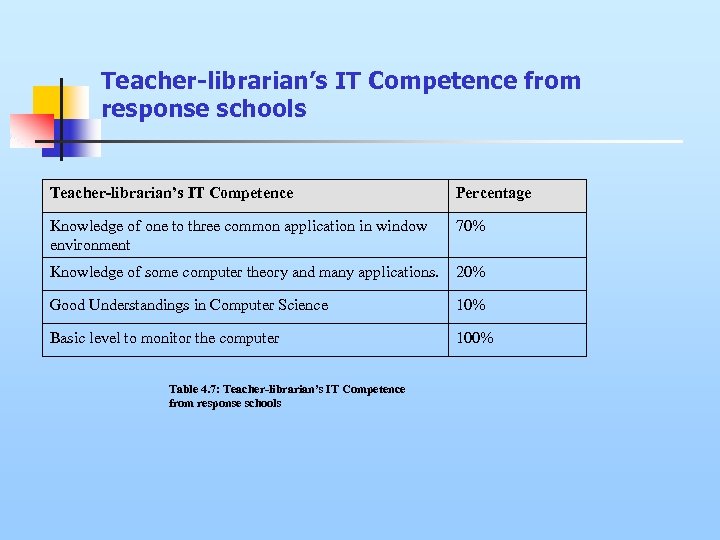
Teacher-librarian’s IT Competence from response schools Teacher-librarian’s IT Competence Percentage Knowledge of one to three common application in window environment 70% Knowledge of some computer theory and many applications. 20% Good Understandings in Computer Science 10% Basic level to monitor the computer 100% Table 4. 7: Teacher-librarian’s IT Competence from response schools

People who encourage the use of computers from response schools Those who encourage the use of computers in school library Percentage Teacher-librarian 80% Principle 71% Teacher 20% Donation 10% Table 4. 8: People who encourage the use of computers from response schools

Peoples help in the planning process of library computerization Staffs involved in planning Percentage of response school Principle 71% IT coordinator 71% Teacher librarian 100% IT Teacher(s) 43% Others teachers 20% Teaching assistant 53% Library assistant 71% TSS 80% Consultant 0% Table 4. 9: Peoples help in the planning process of library computerization

Choice of library automation system n n n SLS Library Master 75% of the response schools selected SLS and 25% of them selected Library Master.

Retrospective conversion n the retrospective conversion between handwriting record and MARC records, which are used in the library automation system. To speed up this process, some staffs may transfer the data from other source and keep the records for the use in their own library system. This is much more convenient and it will save much of the time. The staff can get the data from various sources like n n n Hong Kong Public Libraries, University Libraries, Others School Libraries and Union Catalog. Otherwise the staff has to input the data by themselves and this may cause a lot of time and not efficient enough.
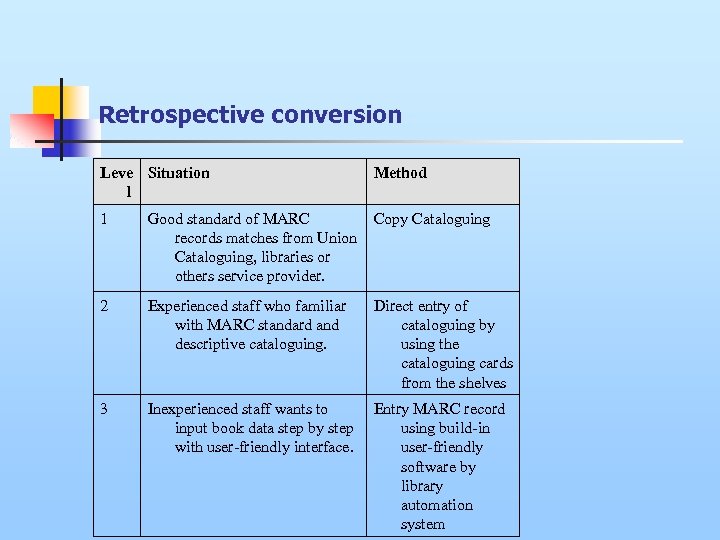
Retrospective conversion Leve Situation l Method 1 Good standard of MARC records matches from Union Cataloguing, libraries or others service provider. Copy Cataloguing 2 Experienced staff who familiar with MARC standard and descriptive cataloguing. Direct entry of cataloguing by using the cataloguing cards from the shelves 3 Inexperienced staff wants to input book data step by step with user-friendly interface. Entry MARC record using build-in user-friendly software by library automation system

Additional Comment from the questionnaire n the system cannot identify capital letter from some source of MARC records.
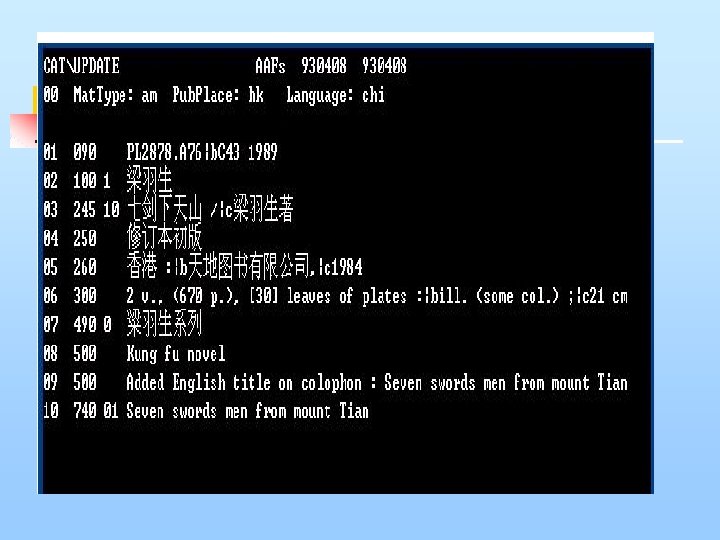

Additional Comment from the questionnaire information such as barcode number and classification number is different in different library. n After staffs download the MARC records, they need to modify some data before using it. The library assistant thinks that it is time consuming to modify the data. n Finally, they may input the full record manually instead of copying the cataloging. library automation system provides some build-in tools that are user friendly for users who do not know MARC standard.

How to solve? n n descriptive cataloging course in-house training copying catalog and giving training and practices of input MARC records manually set priority when importing book catalogue to the system

Finding from the Interview n Total of seven open-ended questions are asked by researcher.

Q 1: When you planned to set up a computerized library, what should you consider? n n Staffs get ready Teacher-librarian should gain more knowledge on library computerization n Existing System from others Literature Various supplier

Q 2: Which factors would you consider when you prepare the budget of computer automation? n n n n teacher-librarian should consider the following costs: Planning and Consultation fee, hardware, software and library automation system fee, cabling and networking related fee, Internet fee, costs for data conversion between manual system to automation system, hardware and maintenance fee and daily automation fee.

Q 3: What computer facilities are you suggesting for library computerization? n Different Type of computers n n n Circulation workstation Staff workstation, public workstation, file server, etc. File Server n n Windows NT/2000 Servers Linux Server (7. 3/8. 0/9. 0) n n Free of charge Work. Station n Windows ME/XP User-friendly for users Handwriting and drawing pad n

n Storage n Server n n Workstation n DVD-RW, Tape Recorder for data backup CD-RW/Zip Drive, USB Slot for card reader or RAM Stick The circulation workstations should have a CCD scanner for reading barcode. the decoration and position of library should be considered for library computerization.

Q 4: What kinds of preparation works need to be done before you select a library automation system? n n n n different types of library automation systems setting up some specifications to evaluate different library systems, listing set of tasks to check the competence of the computer system and rank the priority of different tasks contact the supplier and ask for relevant questions visit to other computerized school libraries teacher-librarian compare the price of different systems.

Q 5: What sorts of services should be provided by the supplier? n n on-site services, enquiry hotline and free upgrade to new version of the system are required. software installation on site?

Q 6: The budget plan for the library computerization n The budget plan should included n n n the bar-coding cost, the library card, the library the automation system, and the computer systems, the networking costs and the cost of human resources. But the cost of networking, computer systems have already included under the IT funding which is also the funding for the IT group. So, the cost could exclude these items.
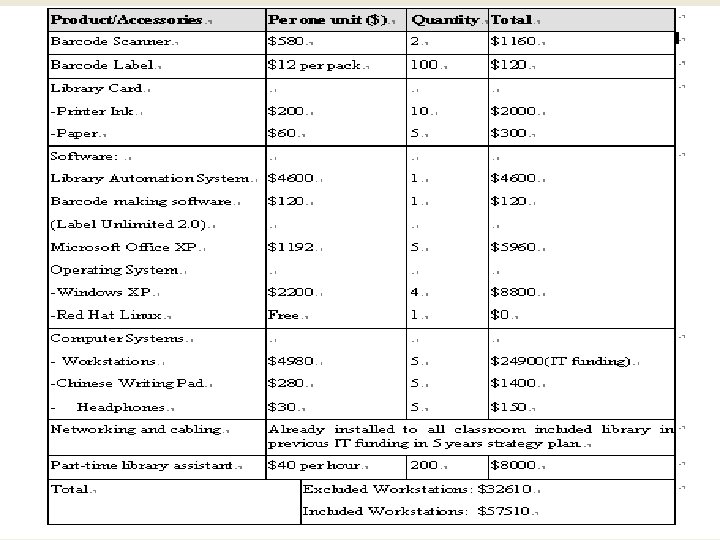

Budgeting n n From the document review of School Improvement Programme (SIP) and funding of reading scheme for English and Chinese, it is concluded that a medium sized school with central library has a total funding of $156000. If teacher-librarian takes about 25% from SIP and 10% from reading scheme, the amount that can be spent for library computerization is $33600. the total amount spent is $32610 and the amount that can be used is around $33600. It is thus within budget.

Q 7: What are the steps and problems faced when performing link-referral services in library homepage? n n n The teacher-librarian feels that there is lack of communication between teachers and librarian. Even there are bunch of links provided on the school library webpage, teachers and students may not find them useful because they cannot fulfill their needs. So, the librarian may need to revise it many times. Moreover, the major problem of doing this is that some websites no longer exists after a while.

Link Referral Service n n n From the survey, schools are ready for Internet connection. Teacher-librarian construct a library homepage to support the school curriculum and project learning. The homepage should include web-referral services to support students’ self-learning purpose. The web page reference should be checked periodically with link checker program, and good coordination between teachers and teacher-librarian is needed.

Training is needed for different level of staffs and users. teachers and students can receive training in the following modes: n n n n n Online Learning Reference from library homepage Information Technology and Library Lesson Seminars Training the trainer program On-the-job training Learning through activities such as project

Recommendations for future research

Recommendations for future research n n Online Evaluation for reading Statistics of reading habit Digitalized the purchasing record Electronic Paper

Q&A
6d92350b3004bca3e0c335c15c42b3be.ppt