717f9e40e121b7721e13f37cb5124674.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence by Kathleen Stassen Berger Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Prenatal Development and Birth Slides prepared by Kate Byerwalter, Ph. D. , Grand Rapids Community College

A remarkable journey…are you ready? PHOTODISC Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
Stages of Prenatal Development n Germinal Period (0 -2 weeks) ¨ Conception occurs in fallopian tubes ¨ Cell differentiation and multiplication ¨ 42% of conceptions successfully implant in uterus Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
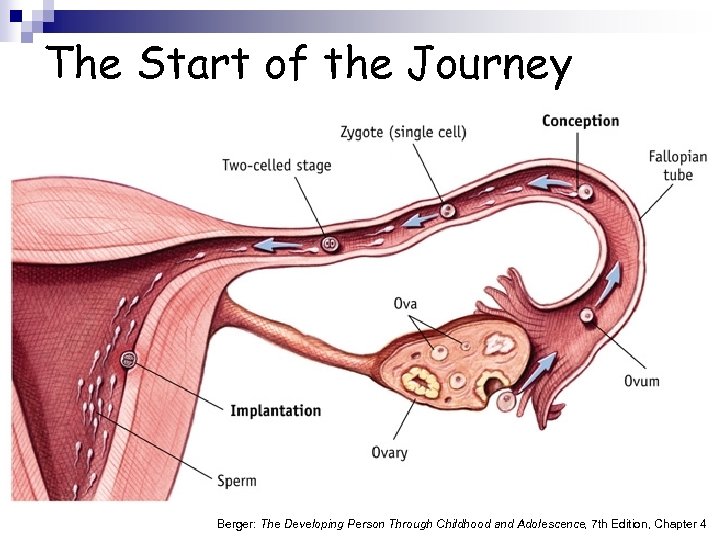
The Start of the Journey Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
Stages of Prenatal Development (cont. ) n Embryonic Period (3 -8 weeks) ¨ Major organs develop ¨ At 8 weeks, organism is less than 2˝ long! n Fetal Period (9 weeks-birth) ¨ Sex organs develop ¨ Brain development is significant ¨ Age of viability occurs around 22 weeks Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
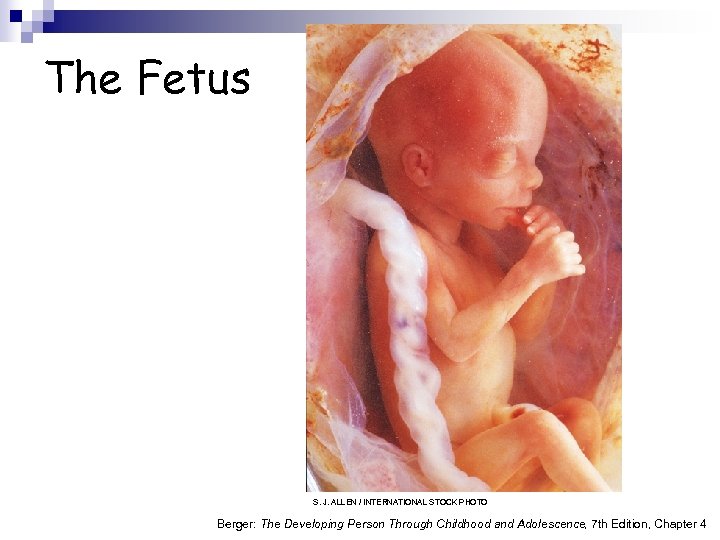
The Fetus S. J. ALLEN / INTERNATIONAL STOCK PHOTO Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
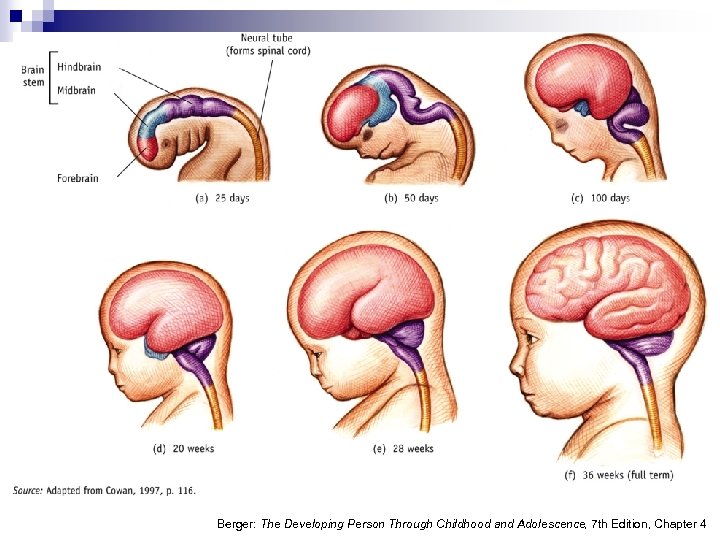
Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
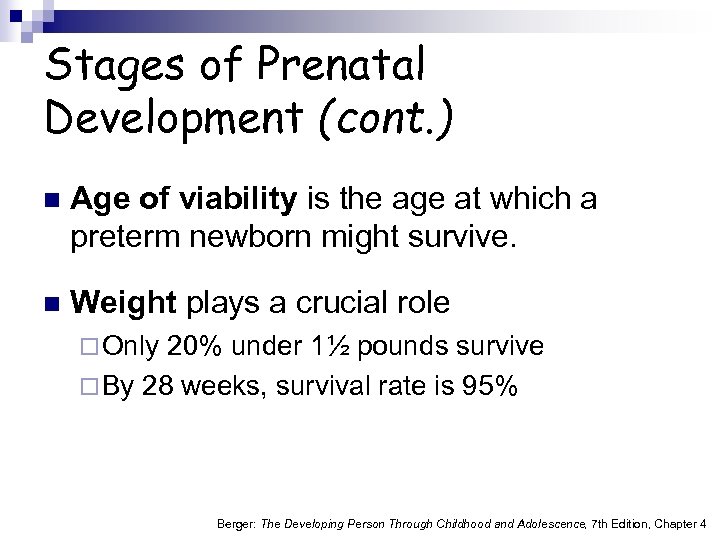
Stages of Prenatal Development (cont. ) n Age of viability is the age at which a preterm newborn might survive. n Weight plays a crucial role ¨ Only 20% under 1½ pounds survive ¨ By 28 weeks, survival rate is 95% Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Make it Real: Do’s and Don’ts of Pregnancy n List some things you have heard that a woman should or shouldn’t do while pregnant. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Risk Reduction Teratology = the study of birth defects n Teratogens = harmful agents to the developing organism n ¨ Examples: diseases (e. g. , rubella), lifestyle choices (e. g. , drug use), medications, toxins n Teratology is a science of risk analysis. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Determining Risk n Timing of exposure ¨ Critical period is the time of greatest vulnerability (for each body structure) n Amount of exposure ¨ Threshold n effect and interaction effect Genetic vulnerability ¨ Ethnicity, sex (males as greater risk) Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
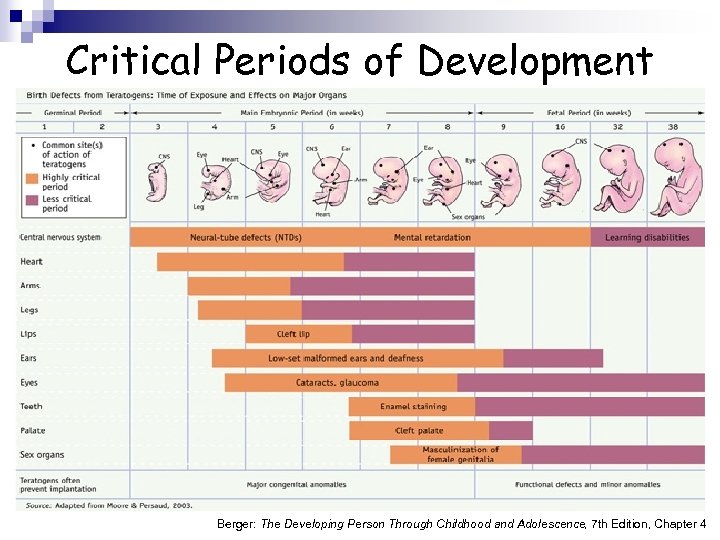
Critical Periods of Development Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Fetal Alcohol Syndrome n Caused by heavy drinking (> 5 drinks/day) n Causes severe cognitive, physical, and behavioral deficits n Is the leading behavioral cause of mental retardation Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Fetal Alcohol Syndrome BOTH: GEORGE STEINMETZ Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Cigarette Smoking n Cigarette smoking cuts off oxygen to the developing baby by 20%, significantly increasing the risk of having a low birthweight newborn. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Birthweight n The average weight of a newborn is 7½ lbs. n LBW is considered less than 5½ lbs. n Preterm is less than 35 weeks. PHOTODISC Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Possible Causes of LBW n Lifestyle choices ¨ e. g. , cigarette smoking accounts for 25% of LBW births worldwide! Maternal malnutrition n Multiple births n Prescription drugs n Unknown causes n Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
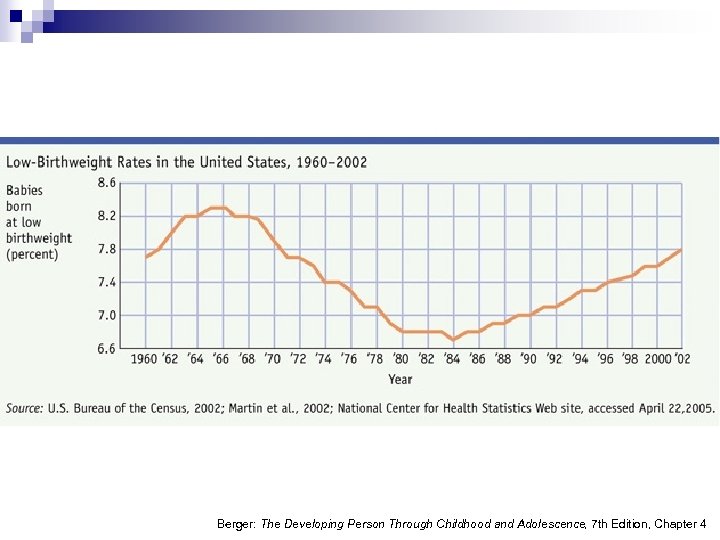
Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
The Birth Process: Methods of Delivery Hospital (majority of U. S. births) n Birthing centers (5%) n At home (1%) n Doula: someone who helps women with labor, delivery, breastfeeding n Cesarean Section (28%) n ¨ Intended for emergencies Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

“Look out world, here I come!” PHOTODISC Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Newborn’s First Minutes n Apgar Scale ¨ An assessment of risk taken 1 and 5 minutes after birth ¨ Measures 5 vital signs ¨ Score of 7 or higher = infant is fine ¨ Score below 7 = infant needs help breathing ¨ Score below 4 = infant needs critical care Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
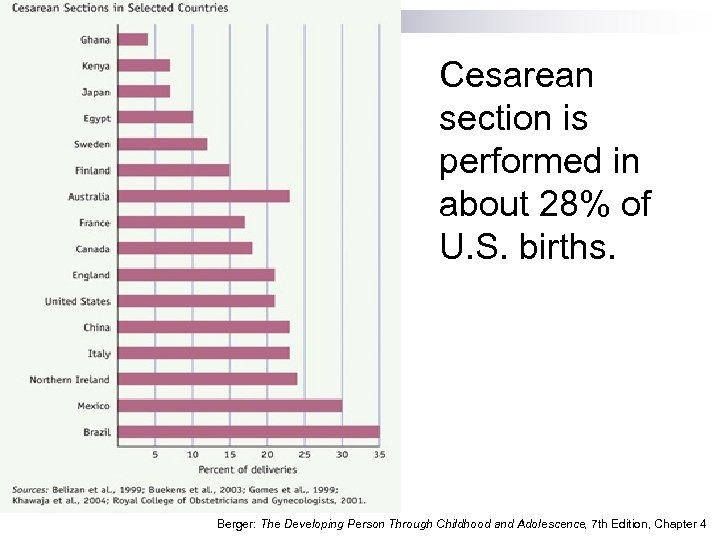
Cesarean section is performed in about 28% of U. S. births. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Birth Complications n Cerebral Palsy includes difficulties with movement control, often resulting from a combination of genetic vulnerability and anoxia (lack of oxygen). n Bacterial infection caused by GBS Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Intensive Care for Infants n Kangaroo care: allows the parents of an infant in intensive care to be involved, holding the newborn at least an hour a day n This helps the newborns sleep better and become more alert when awake. It also helps with bonding. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Long-Term Effects of Intensive Care n There are some long-term delays for preterm infants (e. g. , slower to communicate, hold bottle). n Infants with serious defects who survive often have long-lasting disabilities. n However, ongoing family support and services make a big difference in outcome. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

The Importance of Support n Mothers in Mexico receive exceptional support during pregnancy (familia)–this correlates with fewer LBW births, despite lower incomes and less prenatal care than Mexican immigrants in the U. S. n A parental alliance between father and mother of the developing baby is key! Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
Postpartum Depression n 8 -15% of women experience postpartum depression, a sense of inadequacy and sadness after birth. n Possible causes: preexisting depression, stress, marital problems, infant difficulties Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4

Postpartum Depression (cont. ) n Symptoms include irritability, sleep and eating disruptions, sadness, feeling overwhelmed and inadequate as a mom, no interest in baby, or overly worried about baby. n Antidepressants and support help. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7 th Edition, Chapter 4
717f9e40e121b7721e13f37cb5124674.ppt