6527fcc24b6ce4344bd0157725b7d066.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

The Database Development Process MGIS 641 Koç University

Learning objectives l l l l Define the following key terms : Information System Architecture (ISA), methodology, business function, business process, functional decomposition & repository Lists benefits of ISA describe three components of Zachman framework for ISA Describe stages of information engineering Describe major components of an enterprise model Describe briefly planning matrices used in strategic IS planning Describe system development life cycle Explain prototyping approach

Introduction l l The scope of ISs today is the whole organisation Managers/knowledge workers expect easy access to information Islands of information retire in favour of cooperative, integrated, interoperable enterprise systems The goal of enterprise-wide computing presents a significant challenge for ISs management – Problems in controlling & maintaining data stored throughout the organisation l Describe key components to required to develop ISs that support enterprise-wide computing – – Concept of ISA - framework information engineering - formal methodology for developing ISs Strategic business planning+ Strategic ISs planning Describe CASE tools & repository

A framework for ISA l l New home - set of architectural plans before construction Any large scale endeavour requires early development of a vision/architectural plan Information Systems Architecture (ISA) : conceptual blueprint/plan that expresses the desired future of an IS Design/implementation of effective ISs a great challenge – many organisations do not have an ISA l no standard format for an ISA l costly in time & other resources l may seem difficult/counterproductive if conditions change rapidly l ISA creates the context within which managers can make consistent decisions concerning their ISs

Benefits of ISA Provides l l l basis for strategic planning of ISs basis for communicating with top-management & a context for budget decisions for ISs unifying concept for the various stakeholders in ISs help to achieve information integration when ISs are distributed basis for evaluating technology options (e. g. downsizing, distributed processing) communicates the overall direction of information technology & a context for a major decision in this area.

Overview of the framework l There is no standard means for portraying ISA – Zachman developed a comprehensive framework l l not an ISA but a context to develop one Zachman ISA framework components – data – process – network
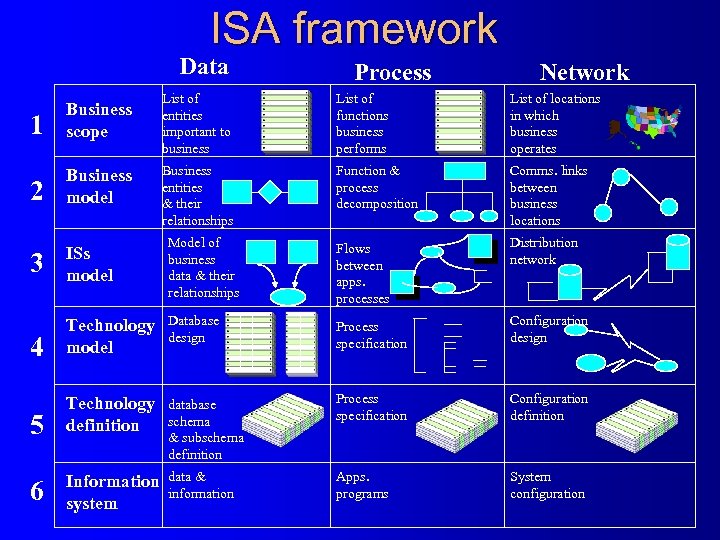
ISA framework Data Process Network List of entities important to business List of functions business performs List of locations in which business operates Business entities & their relationships Function & process decomposition Comms. links between business locations Model of business data & their relationships Flows between apps. processes Distribution network 1 Business scope 2 Business model 3 ISs model 4 Technology model Database design Process specification Configuration design 5 Technology definition database schema & subschema definition Process specification Configuration definition 6 Information system data & information Apps. programs System configuration
ISA framework components l Every IS is visualised as a combination of three components – Data represents what - bill of materials listing the components in a manufacturing system (M. S. ) – Process represents how - list of instructions in M. S. – Network represents - where data stored/processed including comms. links - locations where components are manufactured (in M. S. ) l l Business rules are embedded in the form of logic, constraints & knowledge throughout the columns. Data column concerns us most. But there is a close interrelationship among data / process / network components

Architecture roles & perspective l l Each row represents the role/perspective of each individual concerning three components Each cell contains a representation of a model for a component – any model representation may be used (more than one possible) Model name Role/perspective Business Scope Owner Business model Architect ISs model Designer Technology model Builder Technology definition Contractor IS User Role description Provides a strategic overview including business scope/mission & direction develops business models that describe the business scope/mission & direction Develops an IS model that supports the business Converts ISs model into a design that conforms to the features/constraints of the technology Converts technology models into statements to generate the actual IS Manages, uses & operates the completed IS

Evolution through the framework l Evolve through the cells from top to bottom – In simple systems one person - many roles – In complex systems - one role many people – Each row is not merely developed by adding extra detail but by transforming it consistently to suit to the person concerned l framework should be used to enforce a discipline in IS development, two simple rules : – Objects within rows are mapped horizontally. each process is mapped to the data it uses & both data & process are mapped to the network locations where they are distributed - ensure integration – Ideally components in each row should be simultaneously developed & one should not proceed to next row before the current row development is completed - avoid inconsistencies > rework.

Roles of methodologies & tools l l The framework suggests the data model but does not provide the means to to develop these models One needs a methodology/set of tools to develop architectural representation for each perspective – Methodology : Process/related set of steps to accomplish a stated goal with a set of design objects to support the process l l consistent standards & procedures used throughout development process similar to recipe = a set of instructions + set of ingredient => product – Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools : S/W tools that provide automated support for some portion of the system development process. ( diagramming, screen/report painters, code generation etc. ) – Integrated CASE (I- CASE) toolset : S/W tools that provide automated support for all phases of the system development process l CASE tools speed up development, improve quality

CASE tools - tasks Diagramming Tools for drawing structured diagrams & creating pictorial specifications Screen & report painters Tools for prototyping the user interface & creating system specification Repository & reports Facility for storing, reporting & querying all system information Checking & analysis Tools to check the consistency, completeness & correctness of system specification Code generator Tools to generate executable code from system specification Maintenance Tools to document, restructure & analyse existing systems

Information engineering methodology l Information engineering : A methodology that uses a data-orientation to create & maintain ISs. – top down approach – enterprise-wide in scope – data-driven – compatible with the ISA framework introduced
Phases of information engineering Planning l Analysis l Design l Implementation l

Phases of information engineering - Planning l Planning – Identify strategic planning factors l l l Goals CSFs Problem areas – Identify planning objects l l Organisational units Locations Business functions Entity types – Develop enterprise model l Functional decomposition E-R diagram Planning matrices
Phases of information engineering - Analysis Develop conceptual model (detailed E-R diagram) l Develop process model (data flow diagrams) l
Phases of information engineering - Design databases (normalised relations) l Design processes l – Action diagrams – user interfaces, menus, screens, reports. . .
Phases of information engineering - Implementation Build database definitions (tables, indexes. . ) l Generate applications (program code, macros. . . ) l
Similar phases in DB development & information engineering Information Engineering DB development Planning Enterprise modeling Analysis Conceptual data modeling & part of logical DB design Design Parts of both logical & physical DB design Implementation DB implementation No similar phase DB maintenance

IE methodology l Major strength of IE is its emphasis on strategic planning for ISs. – goal : align IT with business strategies l l close cooperation between business & IS managers Competitive advantage possible if strategic ISs plans are converted into a series of practical ISs projects – 3 steps : l l l develop the planning context, link ISs plans to strategic business plans Identify the important planning objects (org. units, locations, high-level business functions & entity types) - 1 st row in ISA framework (business scope) Develop an enterprise model - 2 nd row in ISA framework (business model) – Functional decomposition diagram high-level functions -> low-level functions – A high-level E-R diagram – A set of planning matrices that link the various components in the sub models

PVF & strategic planning factors l 1. Goals : – – l maintain 10% per annum growth rate maintain 15% before-tax ROI No layoffs responsible corporate citizenship 2. Critical Success Factors (CSFs) : (in achieving goals) – high quality products – on-time deliveries – high productivity l 3. Problem Areas : – inaccurate sales forecasts – increasing competition – stockouts leading to backorders/lost sales

Alignment of Business Goals and IS (CSFs) l l Hierarchy of Objectives Consider a motor car manufaturer – Raise market share to 20% from 10% in 5 years l More frequent choice of new models – Thus reduce time to develop new model 5 to 2 years (designers) – Thus switch over assembly lines in less time, reduce to 3 months from 6 (production department) • Need IS that can produce manufacturing instructions, documents to support tendering, components listings and setup instructions for the assembly lines from drawings. l Critical Success Factors (CSF): Lower level objectives that must be achieved if the top-level objective is to be met

Identify Corporate Planning Objects Organizational units l Organizational locations l Business functions l Entity types – the things we are trying to model l Information (application) systems l

PVF & planning objects Organisational units l l Sales Dept. Orders Dept. Accounting Dept. Manufacturing Dept. – Fabrication Dept. – Assembly Dept. – Finishing Dept. l l Purchasing Dept. Receiving / Shipping Dept. Business Functions l l l l Business Planning Product Development Materials Management Marketing & Sales Production Operations Finance & Accounting Human Resources Entity Types l l l l l CUSTOMER PRODUCT VENDOR RAW MATERIAL ORDER WORK CENTRE WORK ORDER INVOICE EQUIPMENT EMPLOYEE
Develop Enterprise Model l Decomposition of business functions l Enterprise data model l Planning matrixes
Enterprise Data Model l l l First step in database development Specifies scope and general content Overall picture of organizational data, not specific design Entity-relationship diagram Descriptions of entity types Relationships between entities Business rules

Enterprise model l Business Planning l l Concept analysis Product design Materials Management l l l Marketing research Order fulfillment Distribution l l l Finance & Accounting l l l Capital budgeting Accounts receivable Accounts payable l l l Materials requirement planning Purchasing Receiving Production Operations Marketing & Sales l l Market analysis Sales forecasting Product Development l l l Production scheduling Fabrication Assembly Finishing Human Resources l l Recruiting Training
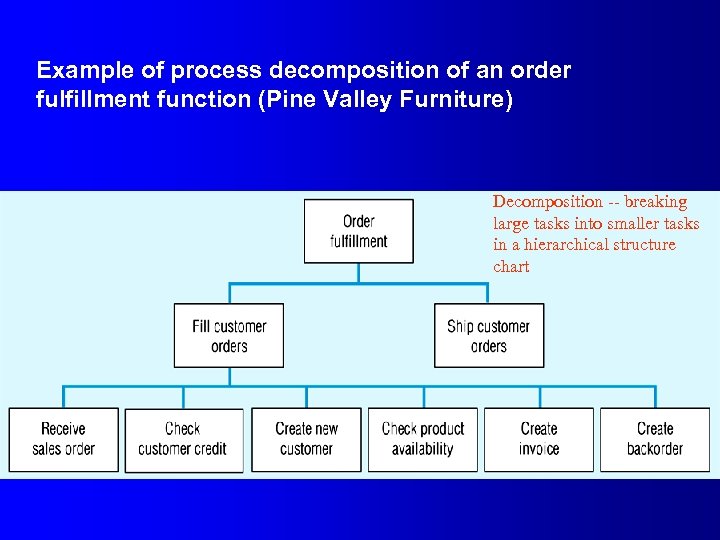
Example of process decomposition of an order fulfillment function (Pine Valley Furniture) Decomposition -- breaking large tasks into smaller tasks in a hierarchical structure chart
![Segment from enterprise data model (Pine Valley Furniture Company) [simplified E-R diagram] Enterprise data Segment from enterprise data model (Pine Valley Furniture Company) [simplified E-R diagram] Enterprise data](https://present5.com/presentation/6527fcc24b6ce4344bd0157725b7d066/image-29.jpg)
Segment from enterprise data model (Pine Valley Furniture Company) [simplified E-R diagram] Enterprise data model describes the entities in an organization and the relationship between these entities
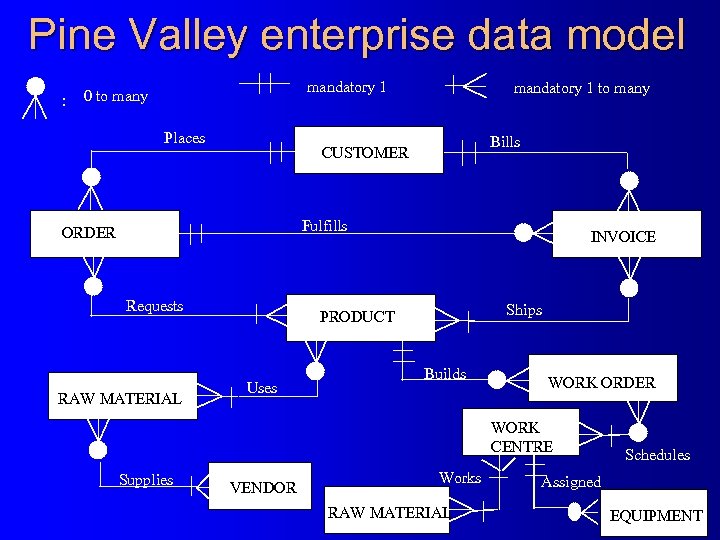
Pine Valley enterprise data model : mandatory 1 0 to many Places mandatory 1 to many Bills CUSTOMER Fulfills ORDER Requests RAW MATERIAL INVOICE Ships PRODUCT Uses Builds WORK ORDER WORK CENTRE Supplies VENDOR Works RAW MATERIAL Schedules Assigned EQUIPMENT

Planning Matrices examples Function-to-data entity l Location-to-function l Unit-to-function l IS-to-data entity l IS-to-business objective l
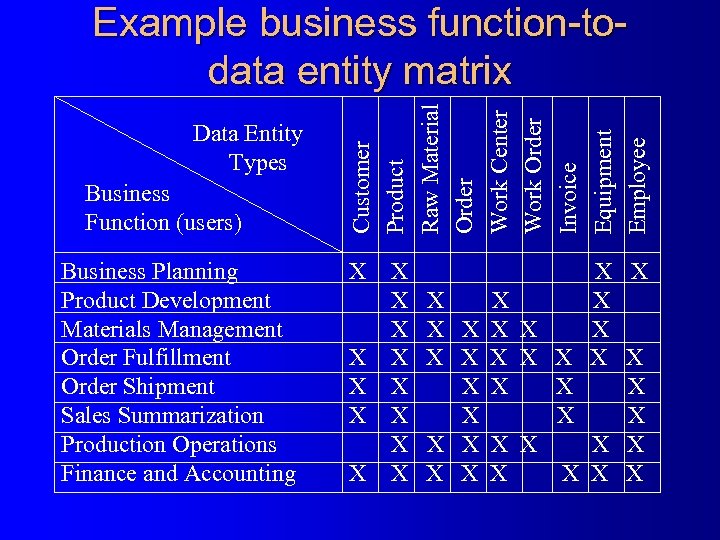
Data Entity Types Business Function (users) Business Planning Product Development Materials Management Order Fulfillment Order Shipment Sales Summarization Production Operations Finance and Accounting Customer Product Raw Material Order Work Center Work Order Invoice Equipment Employee Example business function-todata entity matrix X X X X X X X X X X X X X

Alternative Approaches to Database and IS Development l SDLC – – l System Development Life cycle Detailed, well-planned development process Time-consuming, but comprehensive Long development cycle Prototyping – – Rapid application development (RAD) Cursory attempt at conceptual data modeling. Define database during development of initial prototype. Repeat implementation and maintenance activities with new prototype versions.
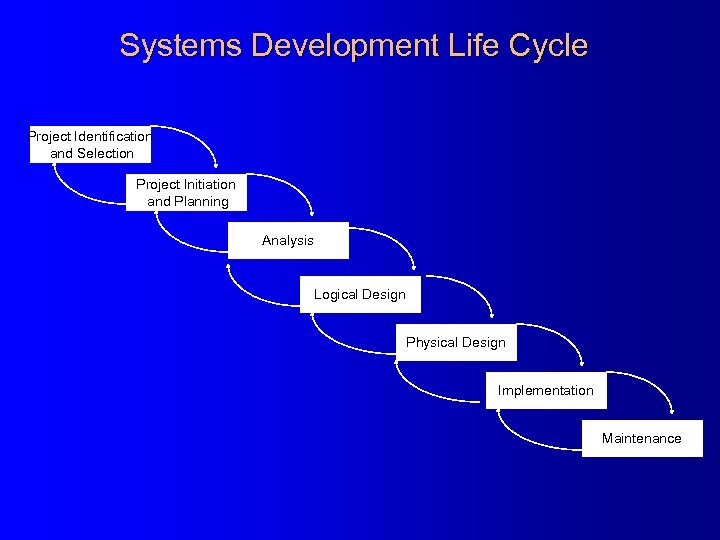
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Implementation Maintenance
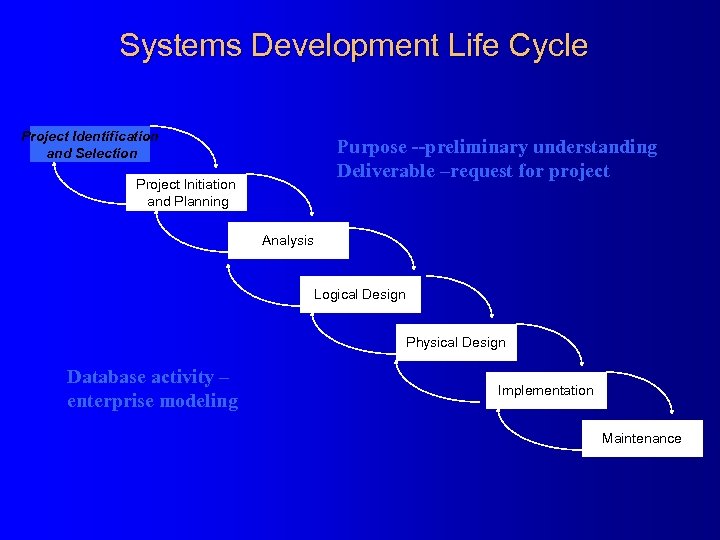
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Purpose --preliminary understanding Deliverable –request for project Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – enterprise modeling Implementation Maintenance
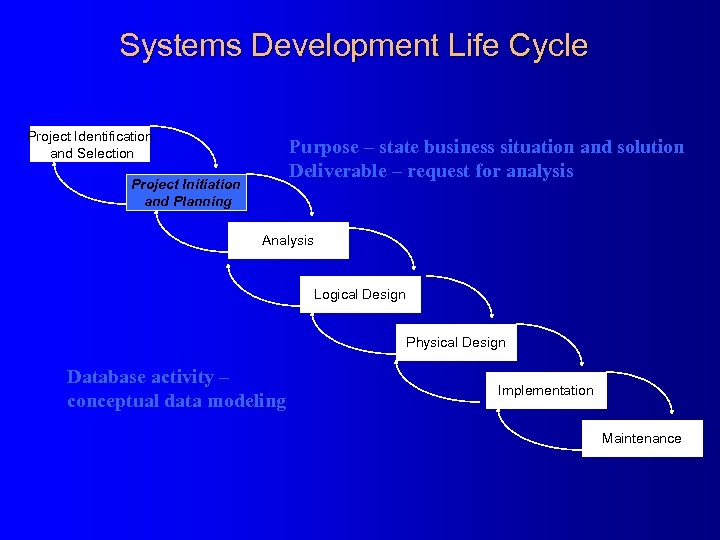
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Purpose – state business situation and solution Deliverable – request for analysis Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – conceptual data modeling Implementation Maintenance
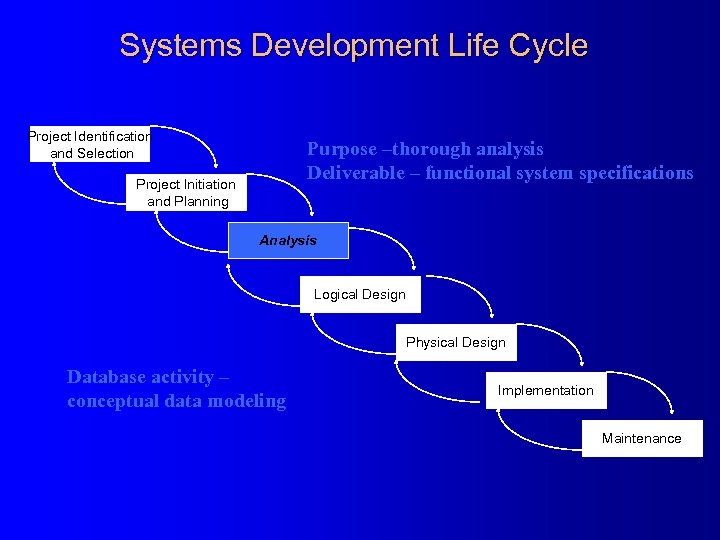
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Purpose –thorough analysis Deliverable – functional system specifications Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – conceptual data modeling Implementation Maintenance
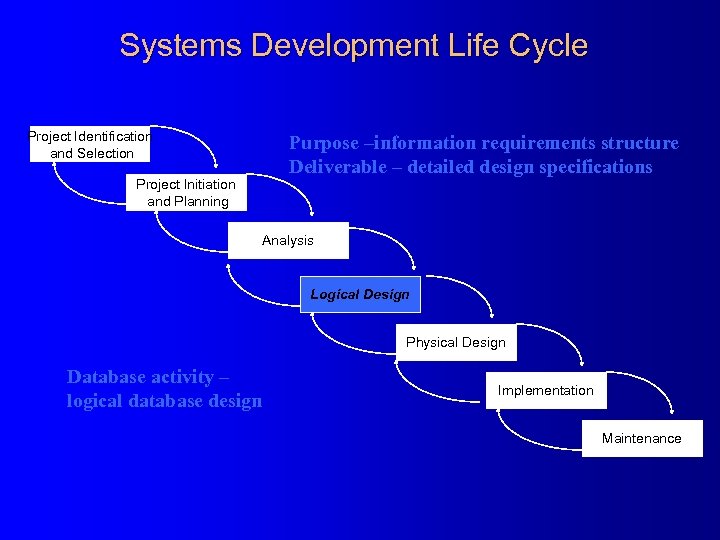
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Purpose –information requirements structure Deliverable – detailed design specifications Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – logical database design Implementation Maintenance
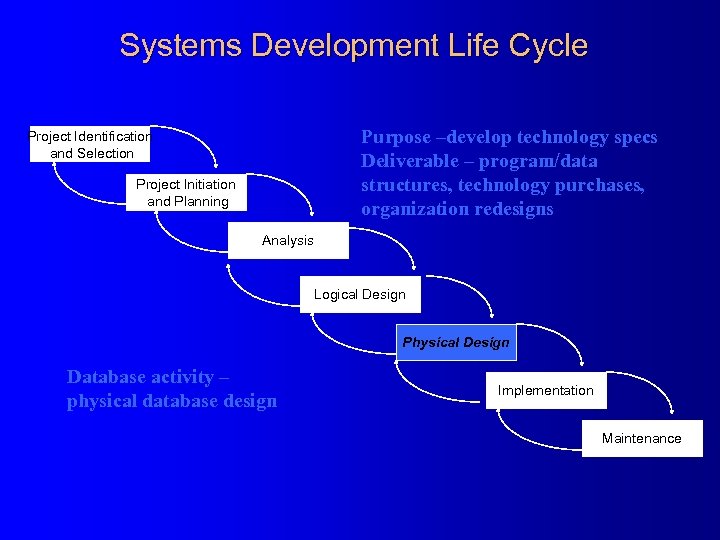
Systems Development Life Cycle Purpose –develop technology specs Deliverable – program/data structures, technology purchases, organization redesigns Project Identification and Selection Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – physical database design Implementation Maintenance
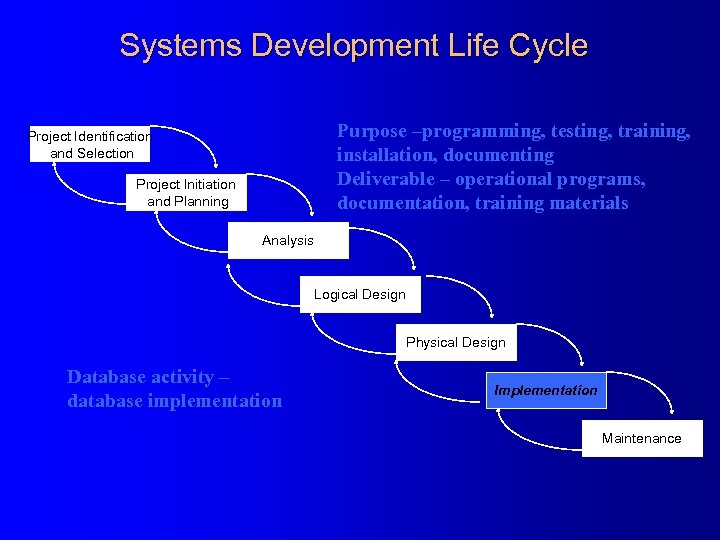
Systems Development Life Cycle Purpose –programming, testing, training, installation, documenting Deliverable – operational programs, documentation, training materials Project Identification and Selection Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – database implementation Implementation Maintenance
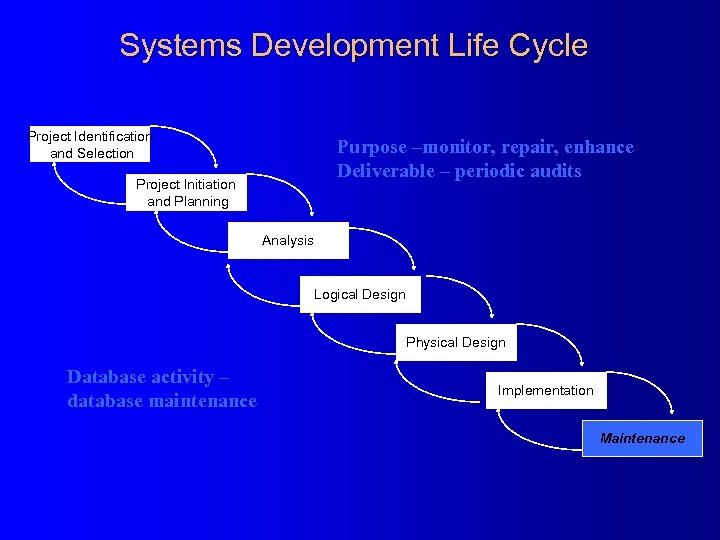
Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification and Selection Purpose –monitor, repair, enhance Deliverable – periodic audits Project Initiation and Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Database activity – database maintenance Implementation Maintenance
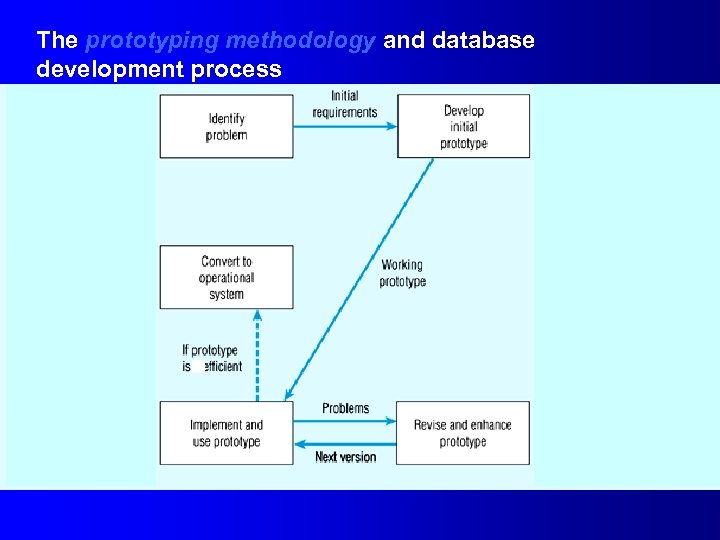
The prototyping methodology and database development process
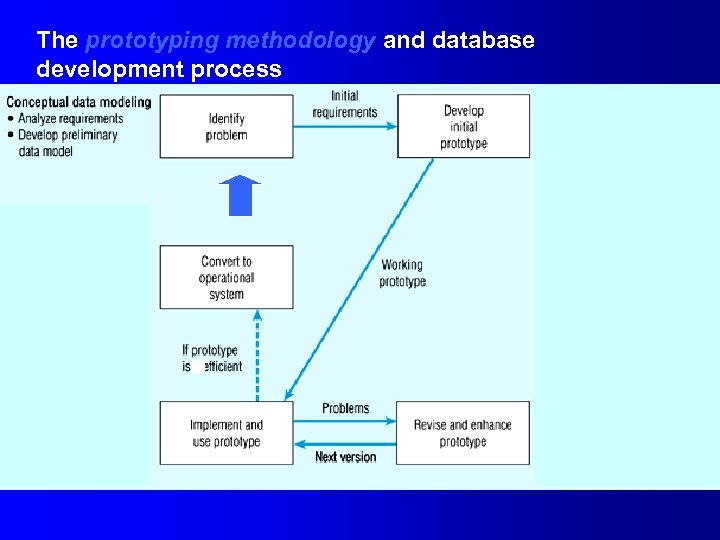
The prototyping methodology and database development process
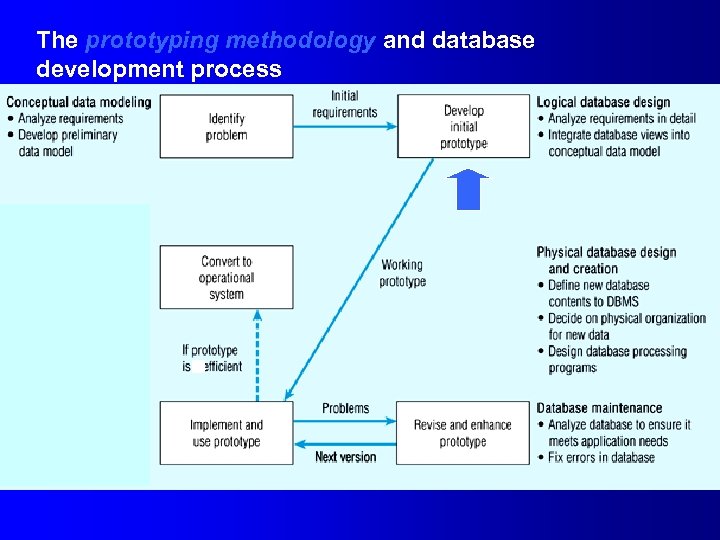
The prototyping methodology and database development process
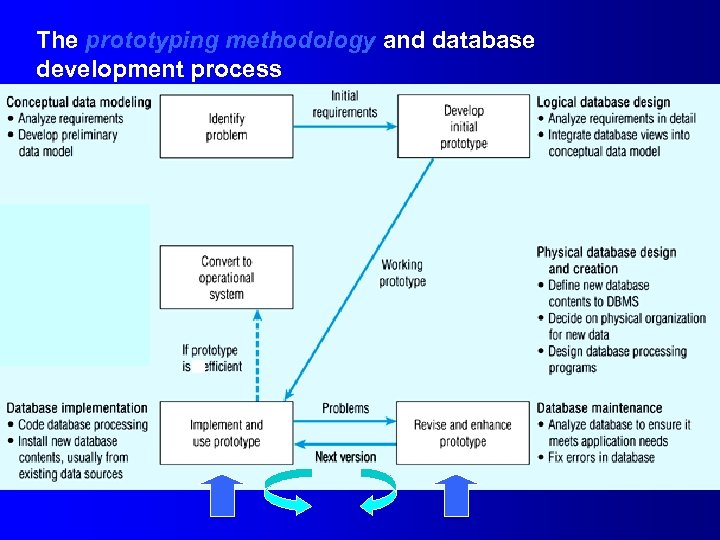
The prototyping methodology and database development process
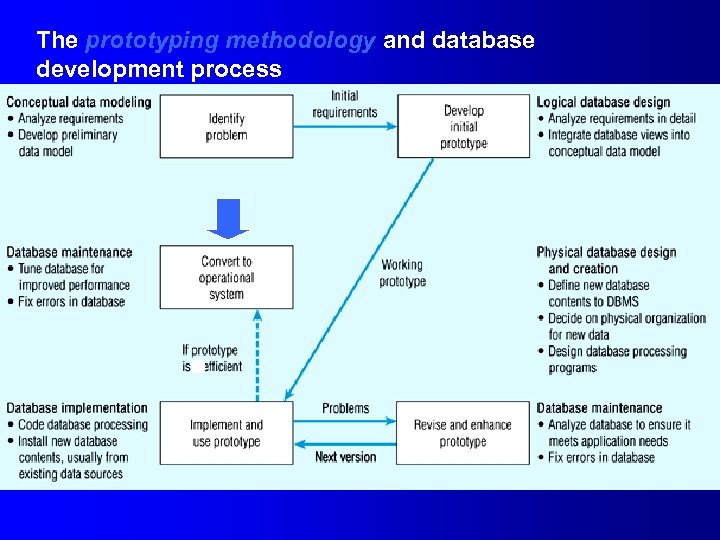
The prototyping methodology and database development process

Managing Projects: People Involved Systems analysts l Database analysts l Users l Programmers l Database/data administrators l Systems programmers, network administrators, testers, technical writers l
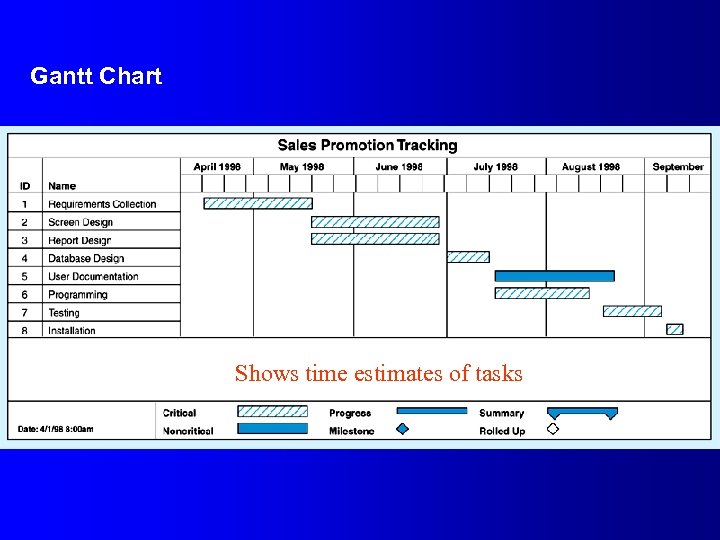
Gantt Chart Shows time estimates of tasks
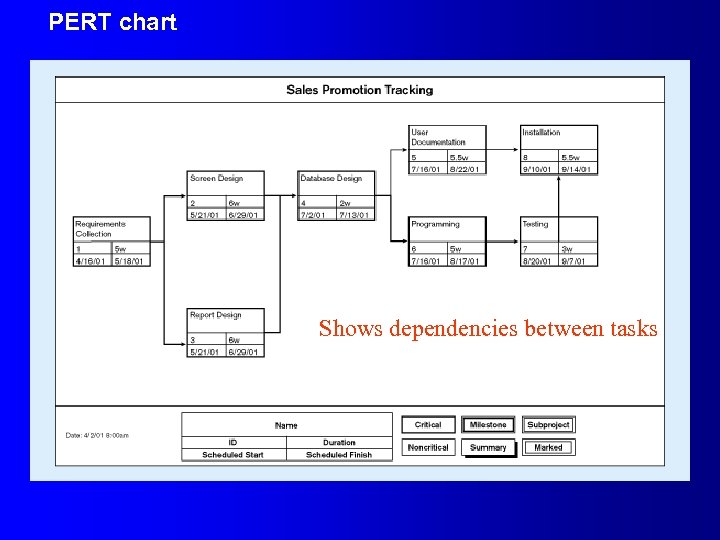
PERT chart Shows dependencies between tasks
Database Schema l Physical Schema – Physical structures l Conceptual Schema – ER models l External Schema – User Views – Subsets of Conceptual Schema – Can be determined from business-function/data entity matrices – DBA determines schema for different users – This is part of people-management in databases
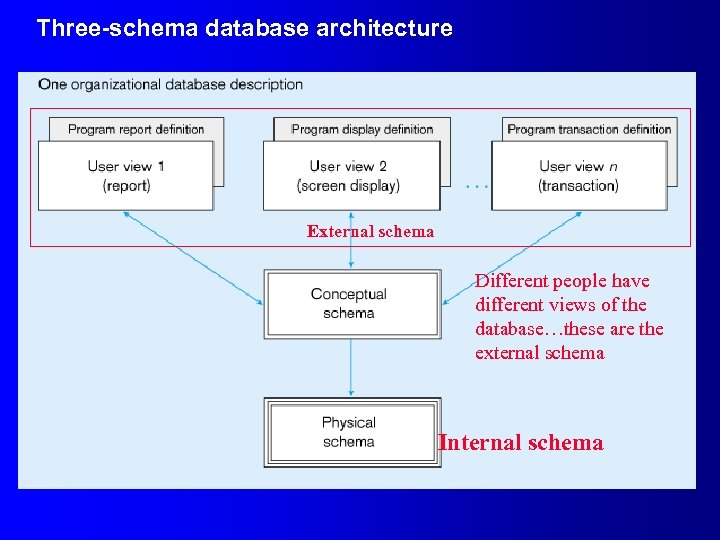
Three-schema database architecture External schema Different people have different views of the database…these are the external schema Internal schema
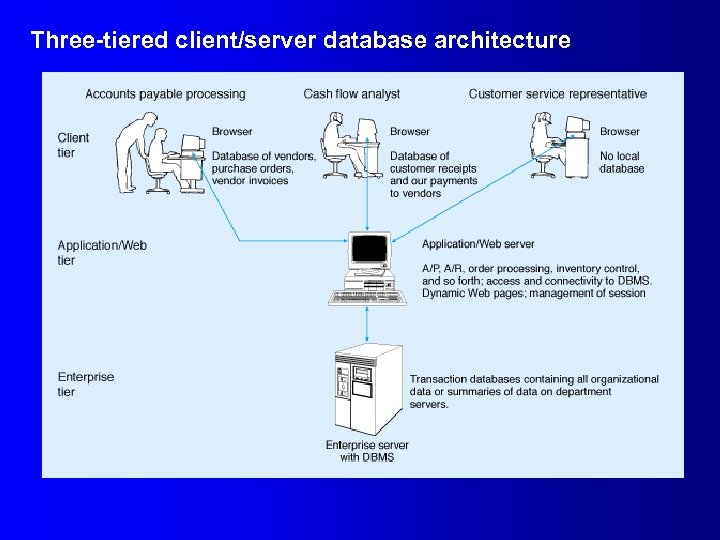
Three-tiered client/server database architecture
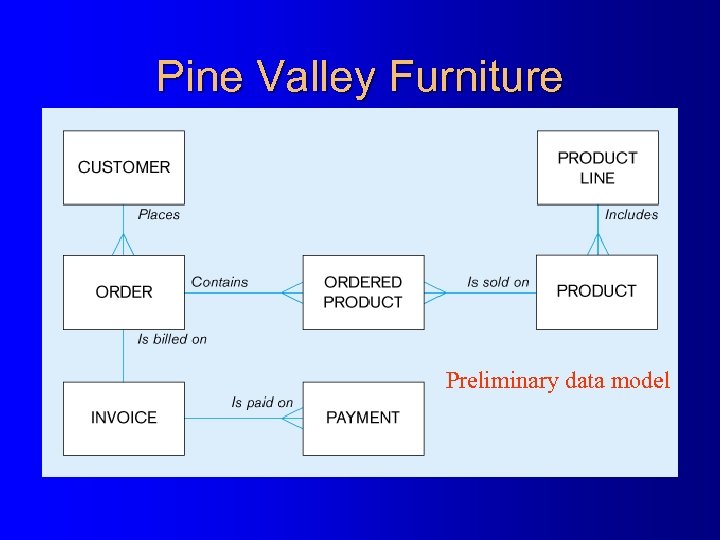
Pine Valley Furniture Preliminary data model
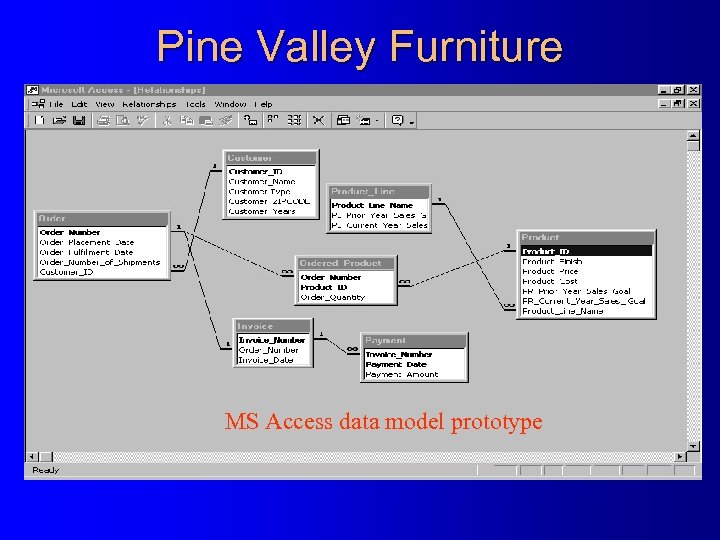
Pine Valley Furniture MS Access data model prototype
6527fcc24b6ce4344bd0157725b7d066.ppt