0df2abf5d8212224d830bd5e97558c71.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

The Data Warehouse: a Transitional Bridge between Legacy and People. Soft 11: 20 – 12: 10 May 16, 2005 CUMREC 2005 Conference Keystone, Colorado

Your Presenter Art Brooks, Director of Applications University of Missouri – Rolla • 12 years in Registrar’s Office • 26 years in Information Technology • Involved in data warehousing since 1986 • Instructor of Data Warehouse course 2

University of Missouri - Rolla • Founded 1871 as the Missouri School of Mines and Metallurgy • Smallest of 4 campus system. • Enrollment around 5500. • Predominantly engineering and science. 3

University of Missouri and People. Soft University of Missouri has implemented Finance and HR across the enterprise. Admit/Recruit is in production at UMKC, UMR and UMSL. Student Records is in production only at UMR (since January, 2004) NO campus has Student Financial Aid implemented nor scheduled at this time. 4

The Evolving Data Warehouse • UMR Started data warehouse adventure in • 1986. Over 18 years the data warehouse and reporting has transitioned: – from local mainframe SQL/DS to local client/server with Informix – from Informix to Oracle – from native SQL for report creation to Info. Maker – through four strategic methodological changes – through three version upgrades in the Advance system – through implementation of People. Soft – through one People. Soft version upgrade. 5

Presentation Topics • Basic reporting perspective • UMR’s unique approach • The Registrar’s conversion 6

Basic Reporting Perspective KEEP IT SIMPLE 7

The Players and their roles • Technical staff – address the data infrastructure, provide a user friendly reporting software and provide training as well as consulting services. • Functional office – identify and define reporting needs. Produce new reports, handle production scheduling and submit reports. 8

Reporting: • Is user oriented. • Is an entity separate from the transactional system. • Must be insulated from transactional system changes. • Must include a transitional bridge. • Can begin BEFORE a system conversion. 9

Data Warehouse dividends • Is an evolutionary phenomenon. • Insulates business processes (reporting side) from • • • changes in hardware or software. (and in some cases process changes) Provides extended flexibility. Produces a point in time reference for reporting. Produces a single point for change. Can provide consistency across reports and time. Can eliminate some logic errors. Can simplify the data. 10
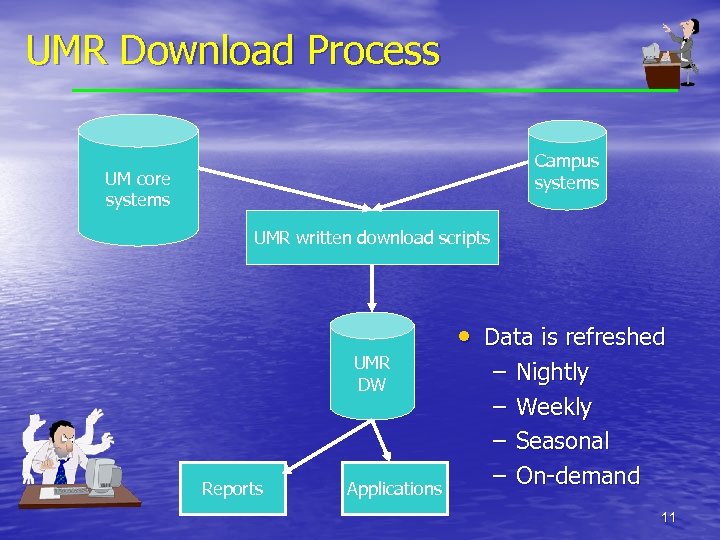
UMR Download Process Campus systems UM core systems UMR written download scripts UMR DW Reports Applications • Data is refreshed – – Nightly Weekly Seasonal On-demand 11

Staff for reporting and data warehouse • 4 fulltime staff • Schedule downloads from • • • core systems Maintain download scripts Local DW table support Create new tables Write reports Define data to users Advise and assist users 12

UMR’s Unique Approach FOCUSED ON THE USERS 13

The UMR Approach • Free standing • Ambiguously • Related • Entities • In contrast to such conventional approaches as star schemas, fact tables and dimension tables. 14

The Reporting Foundation • ‘Event oriented, functional tables’: relational tables designed for a specific reporting need that draws data from multiple data warehouse tables, focusing on the needs of the user and not the technical staff. Goal – reduce technical requirements to formatting the output page. SIMPLICITY!! 15

‘Functional’ Table Concept was developed to: – 1. ‘Empower the users’ – 2. Simplify the data structure – 3. Reduce report development time – 4. Reduce processing time for the server (quicker response) – 5. Improve programmer efficiency – 6. Provide another tool for reporting YOU can do this! 16

Concept – Simplicity – Zero table joins – Zero ‘Where’ statements – Event oriented – Report design centric – User takes less than five minutes to develop query – User concentrates on report appearance – Data source is the data warehouse 17

Advantages of the Functional Table Strategy – 1. Simplicity in data presentation and development. – 2. Reports run significantly faster. – 3. Changes in data standards much more adaptable (One place to make changes in data interpretation and NOT in every report. ) – 4. Provides a transitional bridge from legacy to new system – 5. Provides a greater potential to ‘empower the users’. – 6. Reporting accuracy improved and many potential errors removed. – 7. Reporting consistency is greatly enhanced 18

Plus – 8. Shorter learning curve (no requirements on the part of the report writer to learn the core system data structure or methodology) – 9. Allows for continuation of longitudinal studies – 10. Estimated eleven fold reduction in code to create a report – 11. Allows for the creation of hybrid tables and thereby creating a TRANSITIONAL BRIDGE to SPAN the REPORTING ABYSS. 19
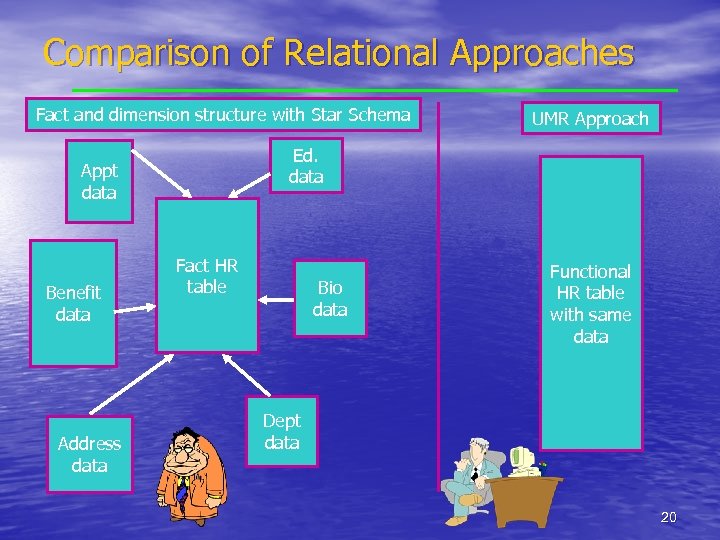
Comparison of Relational Approaches Fact and dimension structure with Star Schema Ed. data Appt data Benefit data Address data UMR Approach Fact HR table Bio data Functional HR table with same data Dept data 20
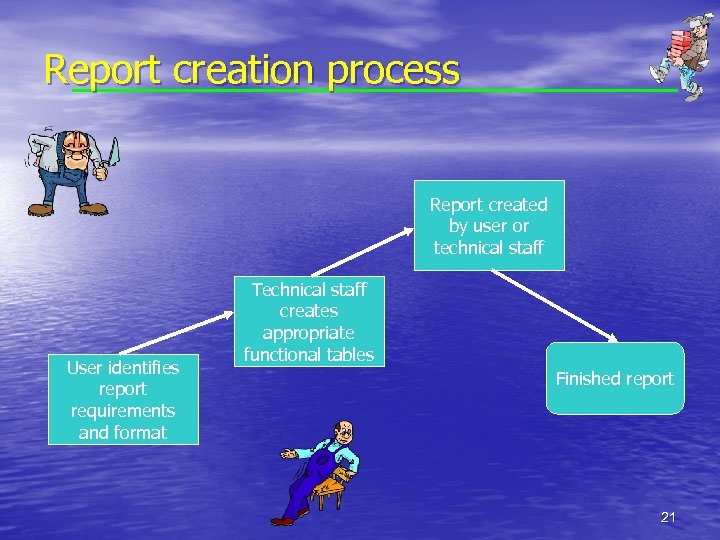
Report creation process Report created by user or technical staff User identifies report requirements and format Technical staff creates appropriate functional tables Finished report 21

Proven Approach • Concept developed in 1998 • First put into use in 1999 with conversion of University Advancement system from mainframe to client/server • Over 500 new reports created for that department using this technique • Utilized in 2000 to retain orientation system when Admissions implemented People. Soft • An integral part of reporting solution at UMR prior to 2004 Registrar’s People. Soft implementation 22 22

Example report: User requests a count of all new freshmen University of Missouri – Rolla New Freshman Applicant Count FS 2005 Major Count Biology 21 C Sc 53 IST 78 MIS 39 23

Report Creation Comparisons UMR Functional Table Query select a. admajor, count(*) from admfresh a where a. adterm=’FS 2001’ and a. fraction=’A’ and a. fractiondate<=sysdate group by a. admajor”; Direct People. Soft Query Each of these queries counts the number of freshmen admitted for a specified term. The results are the same. 1 table 1 query 0 joins 3 'where' statements 6 lines 1 query 7 distinct tables 12 process tables 6 joins 50 'where' statements 5 sub queries 70 lines select f. acad_plan, count(*) from ps_pers_data_effdt a, ps_pers_dtef_sa_vw a 1, ps_stdnt_career b, ps_adm_appl_data c, ps_adm_app_car_seq d, ps_adm_appl_prog e, ps_adm_appl_plan f, where a. emplid=a 1. emplid and from ps_pers_data_effdt a_eda. effdt=a 1. effdt and (a. effdt=(select max(a_ed. effdt) where a. emplid=a_ed. emplid anda_ed. effdt<=sysdate) and a. emplid=b. emplid and b. acad_career=c. acad_career and c. emplid=d. emplid and c. acad_career=d. acad_career and c. stdnt_car_nbr=d. stdnt_car_nbr and c. adm_appl_nbr=d. adm_appl_nbr and d. emplid=e. emplid and d. acad_career = e. acad_career and d. stdnt_car_nbr = e. stdnt_car_nbr and d. adm_appl_nbr = e. adm_appl_nbr and d. appl_prog_nbr = e. appl_prog_nbr and e. effdt=(select max(e_ed. effdt) from ps_adm_appl_prog e_ed where e. emplid=e_ed. emplid and e. acad_career=e_ed. acad_career and e. stdnt_car_nbr=e_ed. stdnt_car_nbr and e. adm_appl_nbr=e_ed. adm_appl_nbr and e. appl_prog_nbr = e_ed. appl_prog_nbr and e_ed. effdt <=sysdate) and from ps_adm_appl_prog e_es where e. emplid=e_es. emplid and e. acad_career=e_es. acad_career and e. stdnt_car_nbr=e_es. stdnt_car_nbr and e. adm_appl_nbr=e_es. adm_appl_nbr and e. appl_prog_nbr=e_es. appl_prog_nbr and e. effdt=e_es. effdt and e. prog_status=e_es. prog_status) and e. admit_term=’FS 2001’ and e. prog_status in (‘AC’, ‘AD’) and e. action_dt <= sysdate and c. admit_type=’FTC’ and d. acad_career=’UGRD’ and e. emplid = f. emplid and e. acad_career=f. acad_career and e. stdnt_car_nbr=f. stdnt_car_nbr and e. adm_appl_nbr=f. adm_appl_nbr and e. appl_prog_nbr = f. appl_prog_nbr and f. effdt=(select max(f_ed. effdt) from ps_adm_appl_plan f_ed where f. emplid=f_ed. emplid and f. acad_career=f_ed. acad_career and f. stdnt_car_nbr=f_ed. stdnt_car_nbr and f. adm_appl_nbr=f_ed. adm_appl_nbr and f. appl_prog_nbr=f_ed. appl_prog_nbr and f_ed. effdt<=e. effdt) and f. effseq=(select max(f_es. effseq) from ps_adm_appl_plan f_es where f. emplid=f_es. emplid and f. acad_career=f_es. acad_career and f. stdnt_car_nbr=f_es. stdnt_car_nbr and f. adm_appl_nbr=f_es. adm_appl_nbr and f. appl_prog_nbr=f_es. appl_prog_nbr and f. effdt=f_es. effdt)) group by f. acad_plan; 24
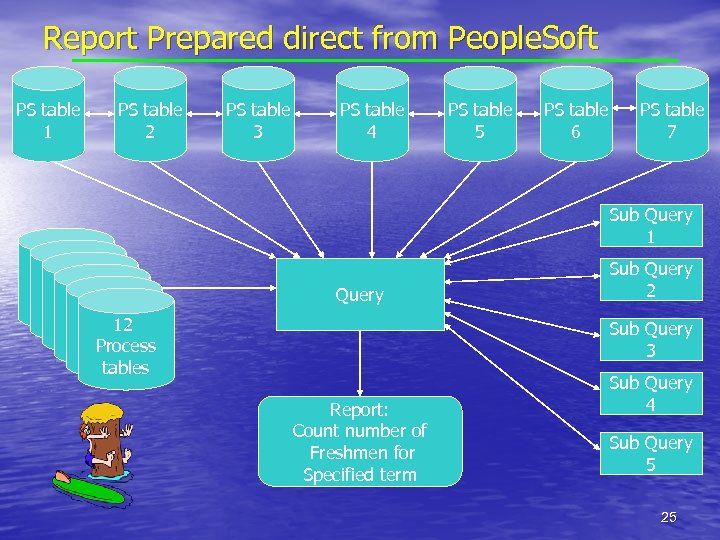
Report Prepared direct from People. Soft PS table 1 PS table 2 PS table 3 PS table 4 PS table 5 PS table 6 PS table 7 Sub Query 1 12 12 Process tables 12 Process tables Query Sub Query 2 Sub Query 3 Report: Count number of Freshmen for Specified term Sub Query 4 Sub Query 5 25
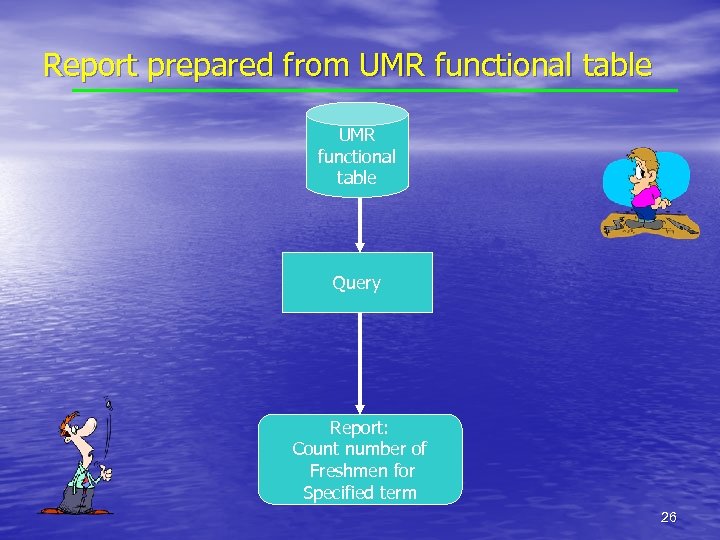
Report prepared from UMR functional table Query Report: Count number of Freshmen for Specified term 26
Hybrid tables – After further experience and discussion it was realized the functional tables could be hybridized to satisfy specific reporting needs and to provide a transitional bridge to the future. – Definition – a hybrid functional table is one that has data derived from disparate systems. (normally legacy and People. Soft) – Hybrid tables can become transitional tables. – With time, hybrid tables can become normal functional tables. (When the legacy data is no longer required, the columns cease to be filled or are removed. ) 27
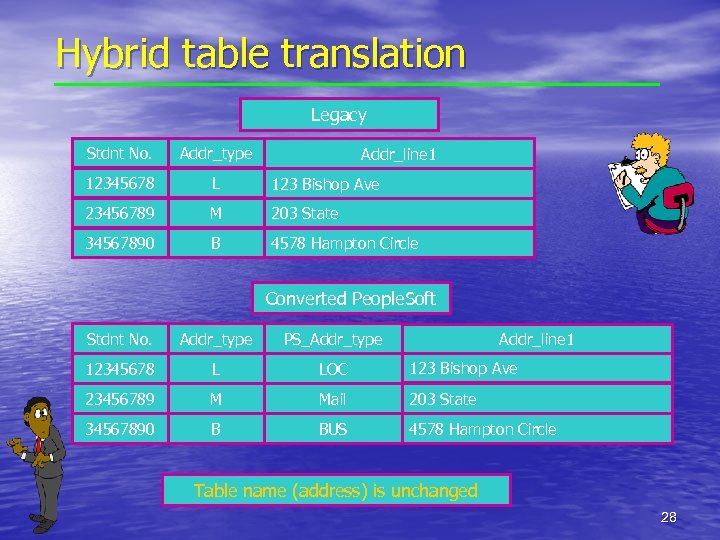
Hybrid table translation Legacy Stdnt No. Addr_type 12345678 L 123 Bishop Ave 23456789 M 203 State 34567890 B 4578 Hampton Circle Addr_line 1 Converted People. Soft Stdnt No. Addr_type PS_Addr_type 12345678 L LOC 123 Bishop Ave 23456789 M Mail 203 State 34567890 B BUS 4578 Hampton Circle Addr_line 1 Table name (address) is unchanged 28
Hybrid table flexibility Legacy reports Code changes kept to a minimum Hybrid Tables Output New reports 29
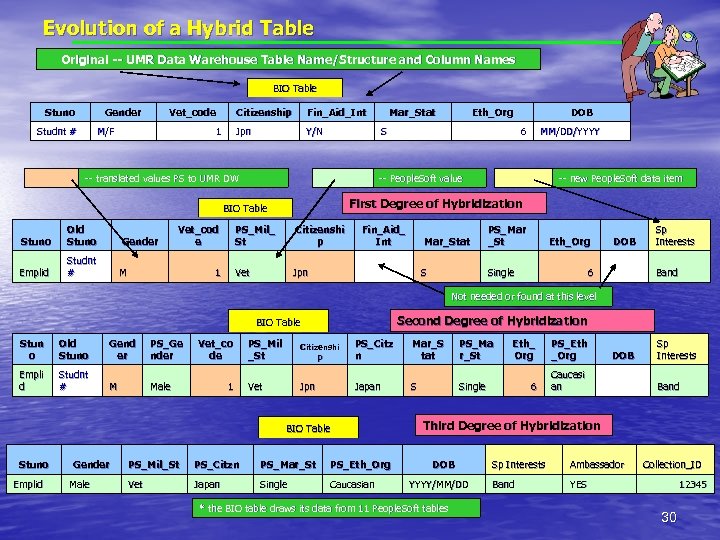
Evolution of a Hybrid Table Original -- UMR Data Warehouse Table Name/Structure and Column Names BIO Table Stuno Gender Studnt # Vet_code M/F Citizenship Jpn 1 Fin_Aid_Int Y/N -- translated values PS to UMR DW Old Stuno Emplid Studnt # Gender Vet_cod e M DOB 6 -- People. Soft value MM/DD/YYYY -- new People. Soft data item First Degree of Hybridization PS_Mil_ St Citizenshi p Fin_Aid_ Int Vet 1 Eth_Org S BIO Table Stuno Mar_Stat Jpn Mar_Stat S PS_Mar _St Eth_Org Single DOB 6 Sp Interests Band Not needed or found at this level Second Degree of Hybridization BIO Table Stun o Old Stuno Gend er PS_Ge nder Empli d Studnt # M Vet_co de Male 1 PS_Mil _St Citizenshi p PS_Citz n Mar_S tat PS_Ma r_St Vet Jpn Japan S Single BIO Table Stuno Emplid Gender Male PS_Mil_St PS_Citzn PS_Mar_St PS_Eth_Org Vet Japan Single Caucasian Eth_ Org PS_Eth _Org 6 Caucasi an DOB Sp Interests Band Third Degree of Hybridization DOB YYYY/MM/DD * the BIO table draws its data from 11 People. Soft tables Sp Interests Ambassador Band Collection_ID YES 12345 30
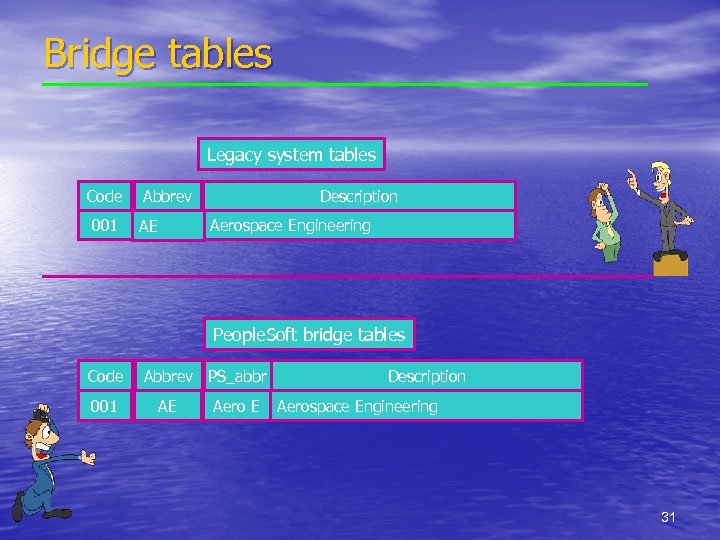
Bridge tables Legacy system tables Code 001 Abbrev Description Aerospace Engineering AE People. Soft bridge tables Code 001 Abbrev PS_abbr AE Aero E Description Aerospace Engineering 31
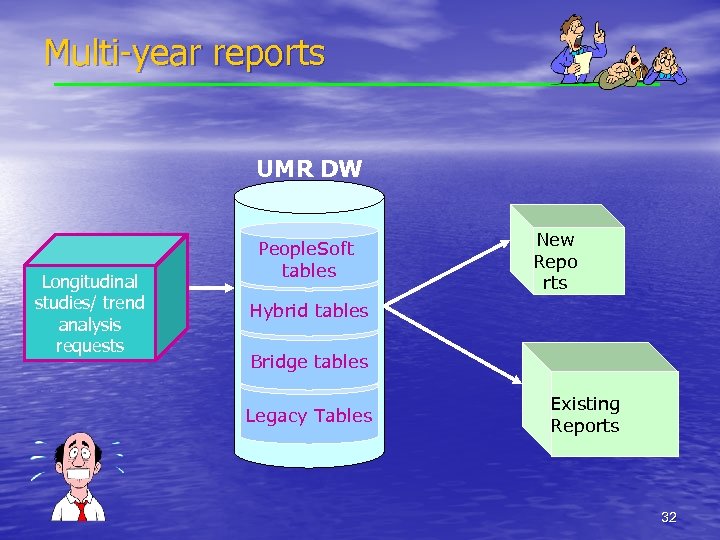
Multi-year reports UMR DW Longitudinal studies/ trend analysis requests People. Soft tables New Repo rts Hybrid tables Bridge tables Legacy Tables Existing Reports 32

The Registrar’s Conversion KEEP THE BUSINESS PROCESSES FUNCTIONING 33

Road Closed -- Construction • When transitioning from a legacy system to a new system, you CANNOT shut reporting down. • Tantamount to shutting down an Interstate for road construction. • MUST find an alternate solution. 34

Registrar’s Environment • Legacy system in production since 1975 • Mainframe based • Four campus system • Nearly all UMR campus reports utilizing local data warehouse since late 1980 s. 35

Strategic Statement for Registrar’s Conversion • “If data can be converted from legacy to People. Soft, then data can be translated from People. Soft to legacy. ” (We NEVER stated ALL of the data could be translated. ) • Terms: – Converted – data in a legacy format, modified and loaded in People. Soft tables – Translated – data in a People. Soft format, modified and loaded in legacy defined tables. 36

The Challenge • With modules being implemented over a six year period • • of time, applications and reports had to continue to function when some data was in the mainframe in a legacy format and other data was in People. Soft in a client server/relational environment. This required applications and reports to draw data from tables that had diverse sources. Inventory indicated over 3, 000 reports and 25 applications built over a 10+ year period of time would cease to function. • No defined subset of reports required or in use. 37

Implementation tactics • Wanted to ‘BUY TIME’ to keep reports running until • • replacements could be written. Focused on identifying People. Soft data to re-create legacy tables for reports needed within first 2 weeks of the semester. All staff dedicated to effort: – Programming staff worked on bringing tables up, AB tested and modified needed existing reports. After 2 weeks focused on next set of most critical tables. Found some data just could not be re-created. Developed a work around. 38
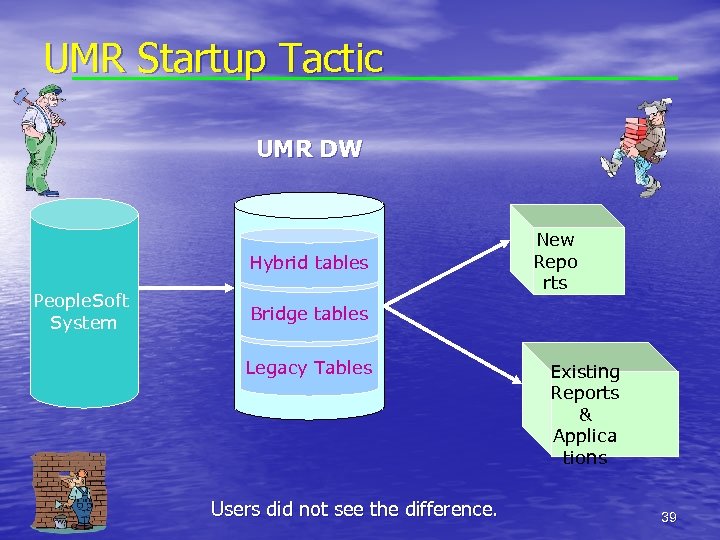
UMR Startup Tactic UMR DW Hybrid tables People. Soft System New Repo rts Bridge tables Legacy Tables Users did not see the difference. Existing Reports & Applica tions 39

Results • Translated People. Soft admissions data for 3 years • • • without interrupting production. Integrated People. Soft HR with student legacy for 2 years without interrupting production. Integrated legacy and People. Soft grant data for a fiscal year report. Amended HR data without affecting applications. Had 400 reports and all applications needing student data in production by the end of the 4 th week of classes. Integrated admissions People. Soft data with legacy student data for 18 months until student system went live with People. Soft 40

Questions? 41

Contact Art Brooks Director of Applications Information Technology University of Missouri – Rolla E-mail: artb@umr. edu 42
0df2abf5d8212224d830bd5e97558c71.ppt