cea28351bfc4c3e637d3801d2438501c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 The Data Center of the Future Steve Duplessie Founder & Senior Analyst Enterprise Strategy Group, Inc.
The Data Center of the Future Steve Duplessie Founder & Senior Analyst Enterprise Strategy Group, Inc.
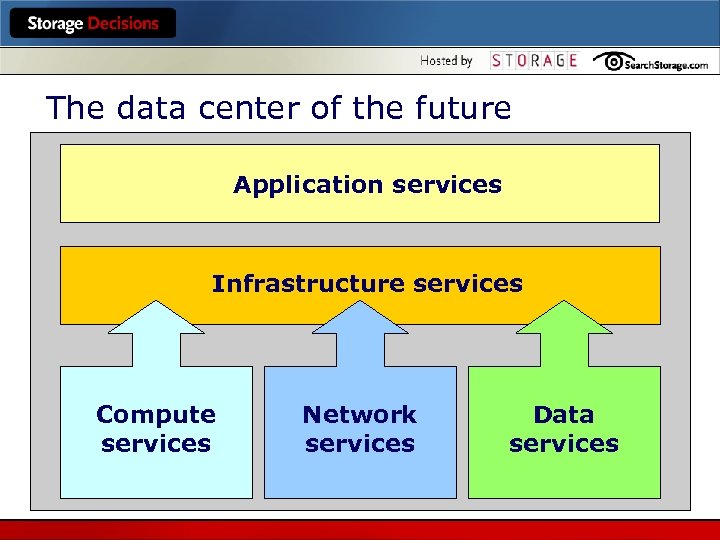
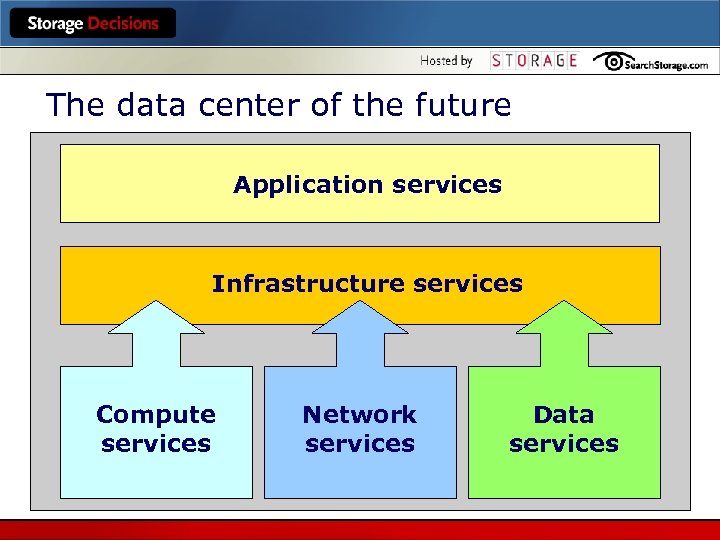 The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services Data services
The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services Data services
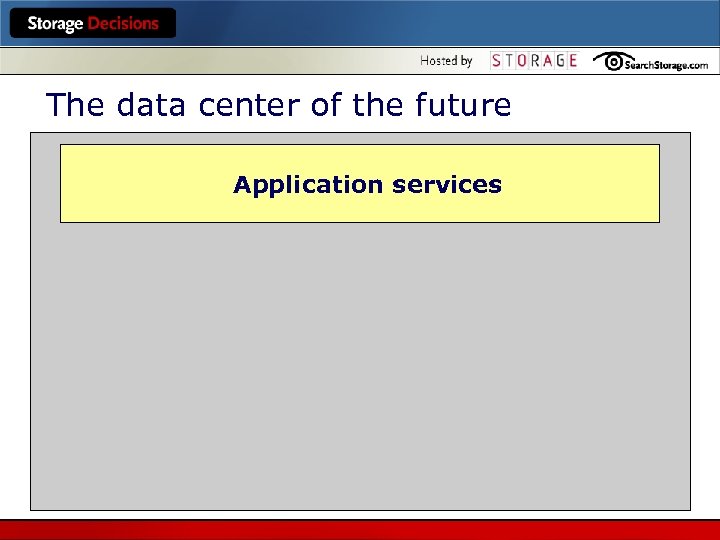 The data center of the future Application services
The data center of the future Application services
 Application services l Our reason for being l The tools our clients use to do their jobs l The ONLY thing our client cares about (in terms of IT)
Application services l Our reason for being l The tools our clients use to do their jobs l The ONLY thing our client cares about (in terms of IT)
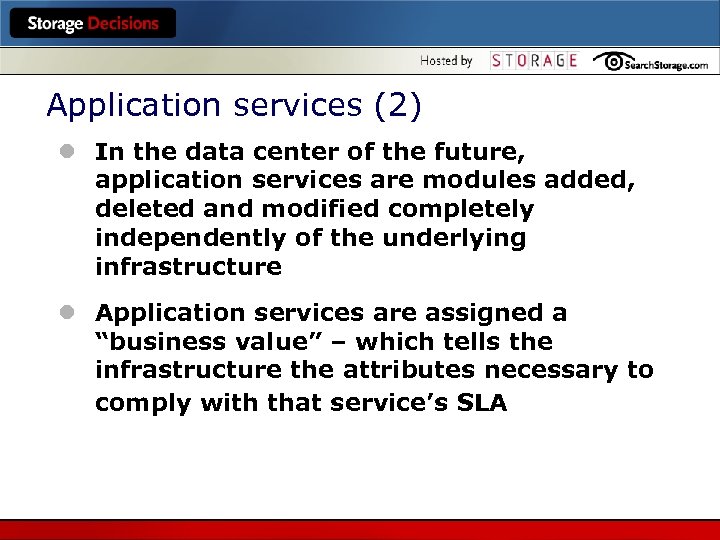 Application services (2) l In the data center of the future, application services are modules added, deleted and modified completely independently of the underlying infrastructure l Application services are assigned a “business value” – which tells the infrastructure the attributes necessary to comply with that service’s SLA
Application services (2) l In the data center of the future, application services are modules added, deleted and modified completely independently of the underlying infrastructure l Application services are assigned a “business value” – which tells the infrastructure the attributes necessary to comply with that service’s SLA
 Application services (3) l The application services layer is COMPLETELY abstracted (and virtualized) from the infrastructure layers l Applications interface to the physical via APIs to call function – not to provide function outside of their intended use. We don’t even use volume manager anymore.
Application services (3) l The application services layer is COMPLETELY abstracted (and virtualized) from the infrastructure layers l Applications interface to the physical via APIs to call function – not to provide function outside of their intended use. We don’t even use volume manager anymore.
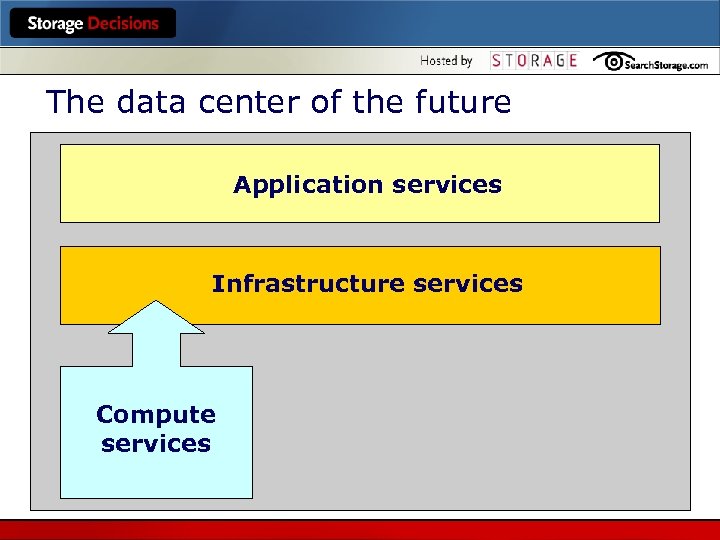 The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services
The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services
 Compute services l A collection of processors – blades most likely l Interconnected through the network services layer through both high- and lowspeed interconnects – IB and Ethernet (IP) near term, who knows (or cares) long term l The “grid” is capable of looking like anything – a single machine that looks like a lot of machines or a single machine comprised of many “component” machines - or any combination
Compute services l A collection of processors – blades most likely l Interconnected through the network services layer through both high- and lowspeed interconnects – IB and Ethernet (IP) near term, who knows (or cares) long term l The “grid” is capable of looking like anything – a single machine that looks like a lot of machines or a single machine comprised of many “component” machines - or any combination
 Compute services (2) l Blades are: a) Disposable, b) Hot pluggable, and c) Never obsolete l As long as they are operable, they are part of a pool of compute resources used by the “grid manager” l The grid manager controls the inventory of compute assets, assimilates virtual compute instances for periods of time, dictated by SLA requirements of the “application services manager” l The grid manager controls the liquidity of the server farm – how the server farm presents itself to the application services layer
Compute services (2) l Blades are: a) Disposable, b) Hot pluggable, and c) Never obsolete l As long as they are operable, they are part of a pool of compute resources used by the “grid manager” l The grid manager controls the inventory of compute assets, assimilates virtual compute instances for periods of time, dictated by SLA requirements of the “application services manager” l The grid manager controls the liquidity of the server farm – how the server farm presents itself to the application services layer
 The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services
The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services
 Network services Physical connectivity layer connecting everything to everything • • • Multiple current and future technologies (IP, IB, FC) Multiple concurrent protocol support (FC, SCSI, i. SCSI, FICON, IB) Smarts to know what’s what and why Smarts to utilize, provision, and provide true Qo. S (by individual application service) Intelligence lives here
Network services Physical connectivity layer connecting everything to everything • • • Multiple current and future technologies (IP, IB, FC) Multiple concurrent protocol support (FC, SCSI, i. SCSI, FICON, IB) Smarts to know what’s what and why Smarts to utilize, provision, and provide true Qo. S (by individual application service) Intelligence lives here
 Network services (2) Intelligence in the network • Smarts exist both here and at the data services layer, with the heavy lifting happening at the network layer
Network services (2) Intelligence in the network • Smarts exist both here and at the data services layer, with the heavy lifting happening at the network layer
 Network services (3) The network will control: • • Macro data placement (what goes on what, when) Volume management (who sees what) Data migration (routing) Replication Quality of Service to the application services layer ILM/DLM policy execution Backup/Recovery/DR • Security management
Network services (3) The network will control: • • Macro data placement (what goes on what, when) Volume management (who sees what) Data migration (routing) Replication Quality of Service to the application services layer ILM/DLM policy execution Backup/Recovery/DR • Security management
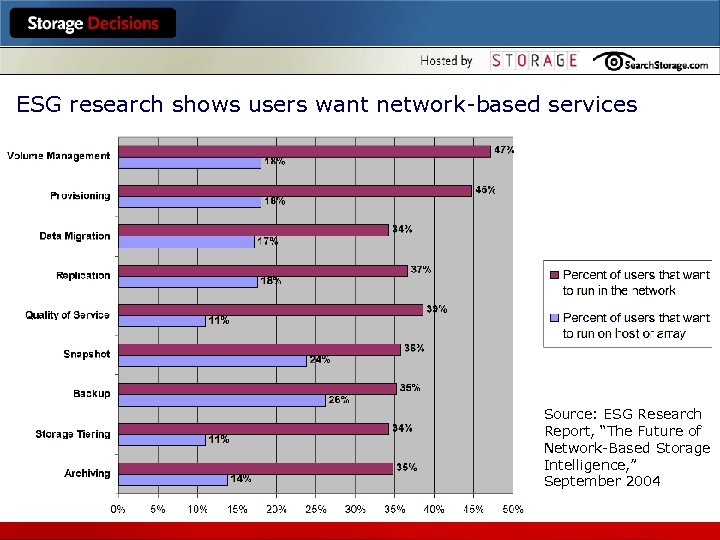 ESG research shows users want network-based services Source: ESG Research Report, “The Future of Network-Based Storage Intelligence, ” September 2004
ESG research shows users want network-based services Source: ESG Research Report, “The Future of Network-Based Storage Intelligence, ” September 2004
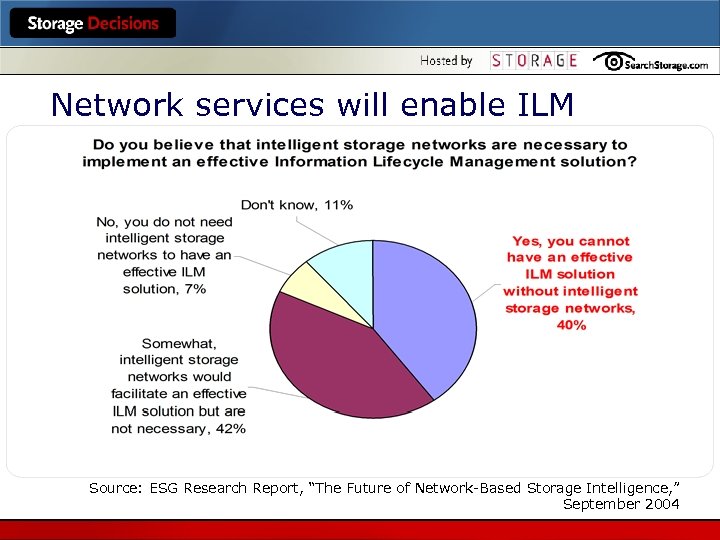 Network services will enable ILM Source: ESG Research Report, “The Future of Network-Based Storage Intelligence, ” September 2004
Network services will enable ILM Source: ESG Research Report, “The Future of Network-Based Storage Intelligence, ” September 2004
 The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services Data services
The data center of the future Application services Infrastructure services Compute services Network services Data services
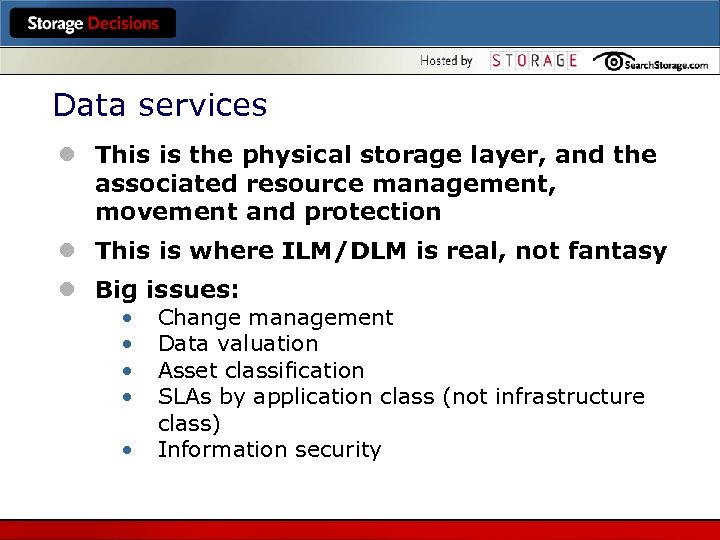 Data services l This is the physical storage layer, and the associated resource management, movement and protection l This is where ILM/DLM is real, not fantasy l Big issues: • • • Change management Data valuation Asset classification SLAs by application class (not infrastructure class) Information security
Data services l This is the physical storage layer, and the associated resource management, movement and protection l This is where ILM/DLM is real, not fantasy l Big issues: • • • Change management Data valuation Asset classification SLAs by application class (not infrastructure class) Information security
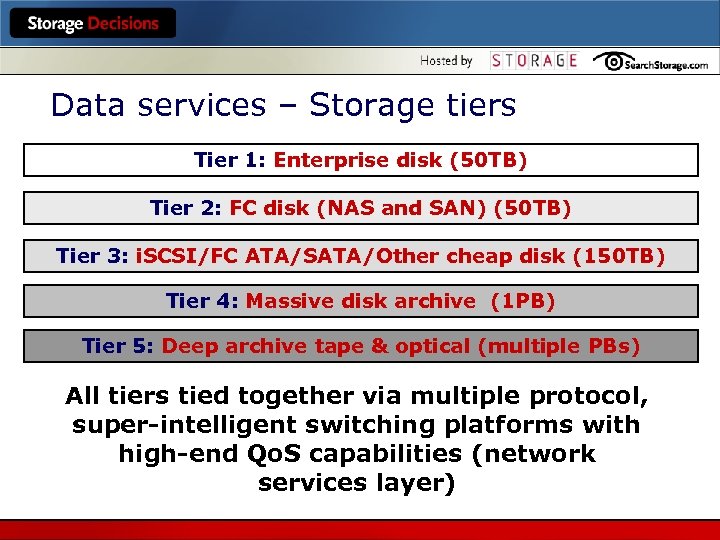 Data services – Storage tiers Tier 1: Enterprise disk (50 TB) Tier 2: FC disk (NAS and SAN) (50 TB) Tier 3: i. SCSI/FC ATA/SATA/Other cheap disk (150 TB) Tier 4: Massive disk archive (1 PB) Tier 5: Deep archive tape & optical (multiple PBs) All tiers tied together via multiple protocol, super-intelligent switching platforms with high-end Qo. S capabilities (network services layer)
Data services – Storage tiers Tier 1: Enterprise disk (50 TB) Tier 2: FC disk (NAS and SAN) (50 TB) Tier 3: i. SCSI/FC ATA/SATA/Other cheap disk (150 TB) Tier 4: Massive disk archive (1 PB) Tier 5: Deep archive tape & optical (multiple PBs) All tiers tied together via multiple protocol, super-intelligent switching platforms with high-end Qo. S capabilities (network services layer)
 Common factors among tiers l All tiers fault-tolerant l All systems future proofed – never get old - just get newly “tiered” l Tiers may have overlapped components l Access to each tier will include block, file AND object
Common factors among tiers l All tiers fault-tolerant l All systems future proofed – never get old - just get newly “tiered” l Tiers may have overlapped components l Access to each tier will include block, file AND object
 Tier 1 l High-performance (perhaps not the highest) l Super-scale in 3 dimensions (capacity, I/O, throughput) l Mainframe AND open connectivity
Tier 1 l High-performance (perhaps not the highest) l Super-scale in 3 dimensions (capacity, I/O, throughput) l Mainframe AND open connectivity
 Tier 2 l High-performance (probably the highest) l Will need to present single system image from small to huge – single box to many l Flexible capacity entry points
Tier 2 l High-performance (probably the highest) l Will need to present single system image from small to huge – single box to many l Flexible capacity entry points
 Tier 3 l Low-cost, idiot-proof, automatic add, management “free” – self-actualizing storage l ISCSI mandatory l Thousands of server connections
Tier 3 l Low-cost, idiot-proof, automatic add, management “free” – self-actualizing storage l ISCSI mandatory l Thousands of server connections
 Tier 4 l Scale to multi-petabytes l Massive density – super low acquisition cost AND operating cost (power) l Kills the big tape library market
Tier 4 l Scale to multi-petabytes l Massive density – super low acquisition cost AND operating cost (power) l Kills the big tape library market
 Tier 5 l Deep archive tape & optical – smaller libraries, bigger fatter cheaper media l Performance is irrelevant (it almost is already) l 50 TB/cartridge plus l Will have to have object indexing offload right in the media – which will require standards
Tier 5 l Deep archive tape & optical – smaller libraries, bigger fatter cheaper media l Performance is irrelevant (it almost is already) l 50 TB/cartridge plus l Will have to have object indexing offload right in the media – which will require standards
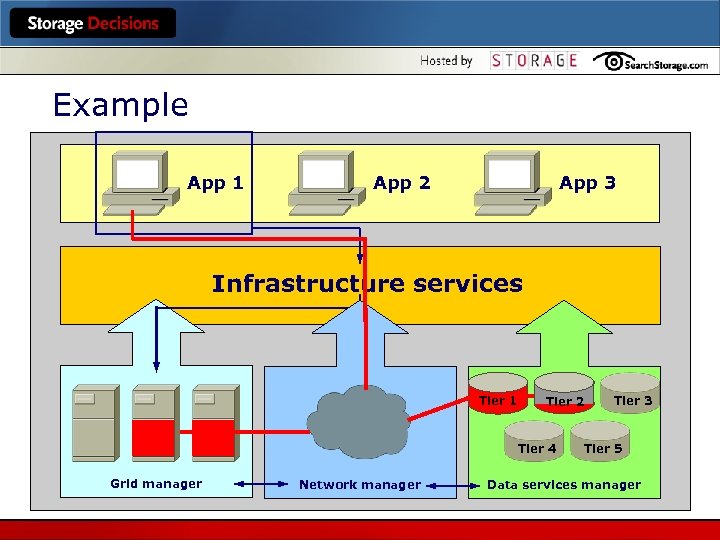 Example App 1 App 2 App 3 Infrastructure services Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 4 Grid manager Network manager Tier 3 Tier 5 Data services manager
Example App 1 App 2 App 3 Infrastructure services Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 4 Grid manager Network manager Tier 3 Tier 5 Data services manager
 Storage manager skill requirements For the next 5 years: Control the baseline Build the tiered infrastructure Connect everything to everything Master physical management Create classifications of infrastructure/data services l Create the cross-functional committee to determine application service “values” l Understand costs per class l l l
Storage manager skill requirements For the next 5 years: Control the baseline Build the tiered infrastructure Connect everything to everything Master physical management Create classifications of infrastructure/data services l Create the cross-functional committee to determine application service “values” l Understand costs per class l l l
 Storage manager skill requirements (2) After 5 years: l All infrastructure/data services WILL be automated – traditional storage administrations services will have gone the way of the dodo. Any manual labor job is no longer in existence. There are no more tape guys. There are no more “sys admins” either. The box is smarter at the mundane than the human.
Storage manager skill requirements (2) After 5 years: l All infrastructure/data services WILL be automated – traditional storage administrations services will have gone the way of the dodo. Any manual labor job is no longer in existence. There are no more tape guys. There are no more “sys admins” either. The box is smarter at the mundane than the human.
 Storage manager skill requirements (3) After 5 years: l The “Data Services Manager” (DSM) will be responsible for adding/removing/changing and integrating new technologies into the Liquid Infrastructure l The DSM will “monitor” SLAs, given to the application services layer – and make changes as needed. The DSM spends his/her time on creating and implementing POLICY changes.
Storage manager skill requirements (3) After 5 years: l The “Data Services Manager” (DSM) will be responsible for adding/removing/changing and integrating new technologies into the Liquid Infrastructure l The DSM will “monitor” SLAs, given to the application services layer – and make changes as needed. The DSM spends his/her time on creating and implementing POLICY changes.
 Storage manager skill requirements (4) After 5 years: The upside l The upside for the DSM is the network services layer. The critical smarts WILL execute in the network – so the DSM who speaks the networking language is in the driver’s seat – and owns ALL of the strategic responsibilities of the infrastructure – which is much more valuable than owning the tactical responsibilities. l THE LESSON: Get your networking act together. Now.
Storage manager skill requirements (4) After 5 years: The upside l The upside for the DSM is the network services layer. The critical smarts WILL execute in the network – so the DSM who speaks the networking language is in the driver’s seat – and owns ALL of the strategic responsibilities of the infrastructure – which is much more valuable than owning the tactical responsibilities. l THE LESSON: Get your networking act together. Now.
 This has been done before! Application Services Infrastructure Services Compute Services Network Services Data Services
This has been done before! Application Services Infrastructure Services Compute Services Network Services Data Services
 Questions? Thank you! steved@enterprisestrategygroup. com 508 -482 -0188
Questions? Thank you! steved@enterprisestrategygroup. com 508 -482 -0188


