f4b5ed6122a08ce446b0f235d1dcb9da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The Danish CDM Project Development Facility Financing CDM in Indonesia Erik Dugstad, Sr. Economist, ECON Analysis Agus Sari, Climate change specialist, Pelangi Contact: erik. dugstad@econ. no – Phone: 021 5221930
The Danish CDM Project Development Facility Financing CDM in Indonesia Erik Dugstad, Sr. Economist, ECON Analysis Agus Sari, Climate change specialist, Pelangi Contact: erik. dugstad@econ. no – Phone: 021 5221930
 Danish Climate Strategy Published by Danish Government in February 2003 Key issue: Introducing Kyoto Mechanisms to achieve cost efficiency Balance between domestic action and buying of credits defined in economic terms. m Maximum cost of domestic measures set at 120 DKK or approximately 20 USD pr ton of CO 2 -eq 2
Danish Climate Strategy Published by Danish Government in February 2003 Key issue: Introducing Kyoto Mechanisms to achieve cost efficiency Balance between domestic action and buying of credits defined in economic terms. m Maximum cost of domestic measures set at 120 DKK or approximately 20 USD pr ton of CO 2 -eq 2
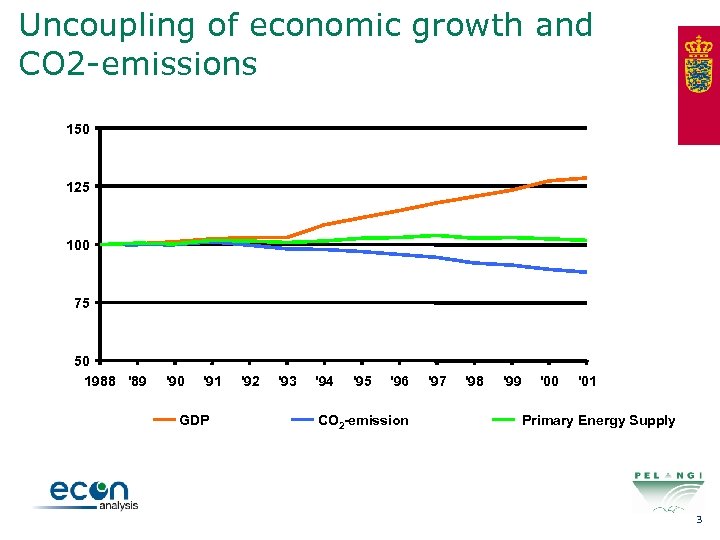 Uncoupling of economic growth and CO 2 -emissions 150 125 100 75 50 1988 '89 '90 '91 GDP '92 '93 '94 '95 '96 CO 2 -emission '97 '98 '99 '00 '01 Primary Energy Supply 3
Uncoupling of economic growth and CO 2 -emissions 150 125 100 75 50 1988 '89 '90 '91 GDP '92 '93 '94 '95 '96 CO 2 -emission '97 '98 '99 '00 '01 Primary Energy Supply 3
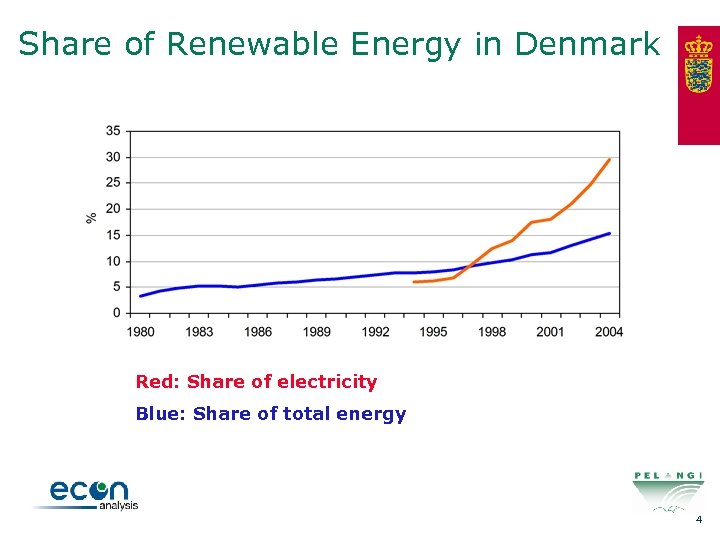 Share of Renewable Energy in Denmark Red: Share of electricity Blue: Share of total energy 4
Share of Renewable Energy in Denmark Red: Share of electricity Blue: Share of total energy 4
 Danish demand for Carbon Credits Danish EU-burden sharing target is reduction of 21% in 2008 -2012 compared to 1990 -level Three sources of ”deficit” compared to target: m 10 mill. Tons CO 2/year from lack of success in achieving reductions i. e. in the transport sector m 10 mill. Tons CO 2/year from expected electricity export m 5 mill. Tons CO 2/year from (lack of) base year adjustment Projected total demand 25 mill tons CO 2/year for 5 years or a total of 125 mill tons Government expected to buy 20% - The rest by private sector (mainly electricity sector) 5
Danish demand for Carbon Credits Danish EU-burden sharing target is reduction of 21% in 2008 -2012 compared to 1990 -level Three sources of ”deficit” compared to target: m 10 mill. Tons CO 2/year from lack of success in achieving reductions i. e. in the transport sector m 10 mill. Tons CO 2/year from expected electricity export m 5 mill. Tons CO 2/year from (lack of) base year adjustment Projected total demand 25 mill tons CO 2/year for 5 years or a total of 125 mill tons Government expected to buy 20% - The rest by private sector (mainly electricity sector) 5
 Bilateral collaboration in focus Government purchases through pipelines of m Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Bilateral collaboration on CDM in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, China and South Africa m Environmental Protection Agency: JI-projects in Eastern Europe m Multilateral Carbon Funds – A Danish Fund in the World Bank Incentives for private sector m EU Emissions trading scheme started 1. January 2005 m Directive implemented that links emission trading and JI/CDM A Memorandum of Understanding between Denmark and Indonesia has been signed between Ambassador Andersen and Minister Witoelar on July 27, 2005 6
Bilateral collaboration in focus Government purchases through pipelines of m Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Bilateral collaboration on CDM in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, China and South Africa m Environmental Protection Agency: JI-projects in Eastern Europe m Multilateral Carbon Funds – A Danish Fund in the World Bank Incentives for private sector m EU Emissions trading scheme started 1. January 2005 m Directive implemented that links emission trading and JI/CDM A Memorandum of Understanding between Denmark and Indonesia has been signed between Ambassador Andersen and Minister Witoelar on July 27, 2005 6
 Huge CDM potential in Indonesia 125 - 300 million ton CERs in the period 2008 -2012 Could create a value of 625 -1200 million USD via sales + large local benefits for sustainable development Opportunities in many sectors m Cement m Oil and gas m Landfill and waste m Pulp and paper m Steel m Palm Oil m Electricity m Energy saving m Etc 7
Huge CDM potential in Indonesia 125 - 300 million ton CERs in the period 2008 -2012 Could create a value of 625 -1200 million USD via sales + large local benefits for sustainable development Opportunities in many sectors m Cement m Oil and gas m Landfill and waste m Pulp and paper m Steel m Palm Oil m Electricity m Energy saving m Etc 7
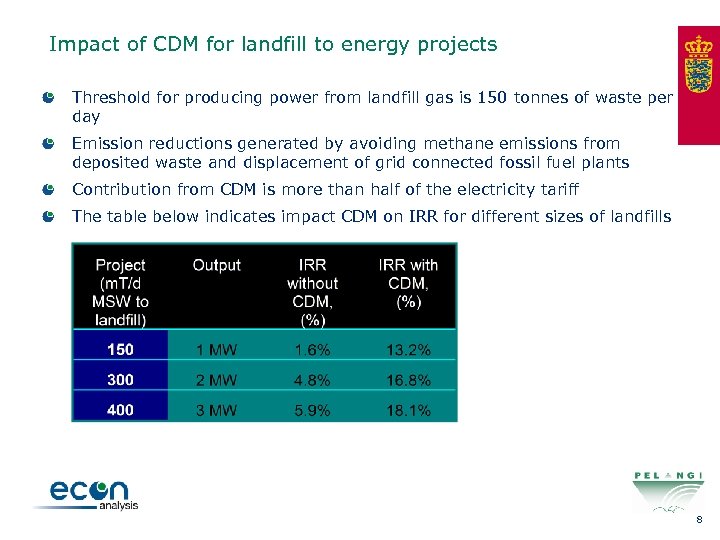 Impact of CDM for landfill to energy projects Threshold for producing power from landfill gas is 150 tonnes of waste per day Emission reductions generated by avoiding methane emissions from deposited waste and displacement of grid connected fossil fuel plants Contribution from CDM is more than half of the electricity tariff The table below indicates impact CDM on IRR for different sizes of landfills 8
Impact of CDM for landfill to energy projects Threshold for producing power from landfill gas is 150 tonnes of waste per day Emission reductions generated by avoiding methane emissions from deposited waste and displacement of grid connected fossil fuel plants Contribution from CDM is more than half of the electricity tariff The table below indicates impact CDM on IRR for different sizes of landfills 8
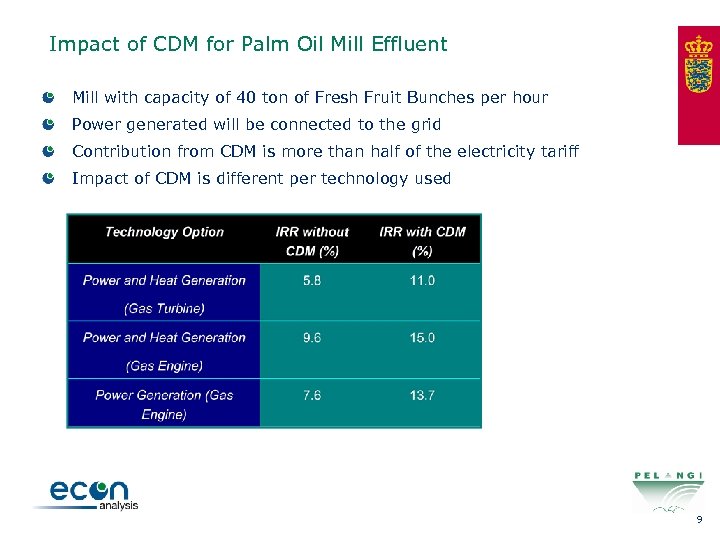 Impact of CDM for Palm Oil Mill Effluent Mill with capacity of 40 ton of Fresh Fruit Bunches per hour Power generated will be connected to the grid Contribution from CDM is more than half of the electricity tariff Impact of CDM is different per technology used 9
Impact of CDM for Palm Oil Mill Effluent Mill with capacity of 40 ton of Fresh Fruit Bunches per hour Power generated will be connected to the grid Contribution from CDM is more than half of the electricity tariff Impact of CDM is different per technology used 9
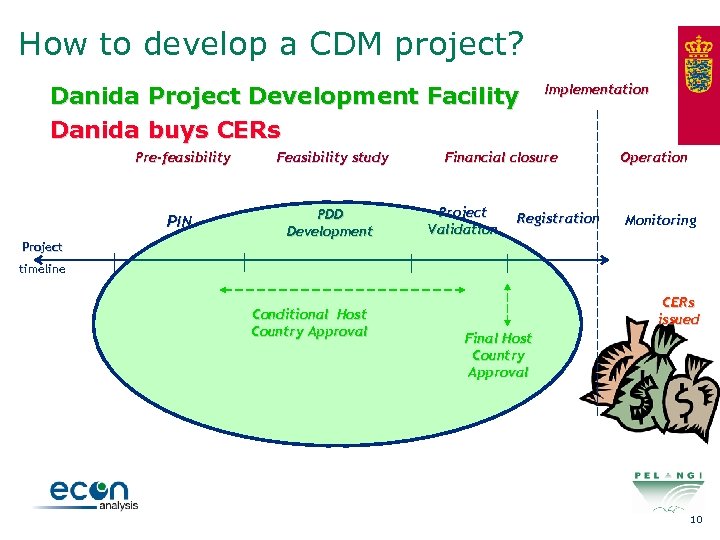 How to develop a CDM project? Danida Project Development Facility Danida buys CERs Pre-feasibility Feasibility study PIN PDD Development Implementation Financial closure Project Validation Registration Operation Monitoring Project timeline Conditional Host Country Approval CERs issued Final Host Country Approval 10
How to develop a CDM project? Danida Project Development Facility Danida buys CERs Pre-feasibility Feasibility study PIN PDD Development Implementation Financial closure Project Validation Registration Operation Monitoring Project timeline Conditional Host Country Approval CERs issued Final Host Country Approval 10
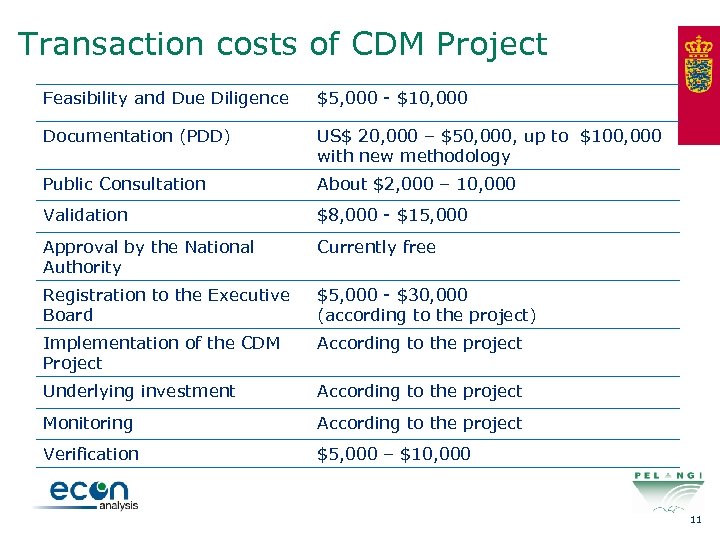 Transaction costs of CDM Project Feasibility and Due Diligence $5, 000 - $10, 000 Documentation (PDD) US$ 20, 000 – $50, 000, up to $100, 000 with new methodology Public Consultation About $2, 000 – 10, 000 Validation $8, 000 - $15, 000 Approval by the National Authority Currently free Registration to the Executive Board $5, 000 - $30, 000 (according to the project) Implementation of the CDM Project According to the project Underlying investment According to the project Monitoring According to the project Verification $5, 000 – $10, 000 11
Transaction costs of CDM Project Feasibility and Due Diligence $5, 000 - $10, 000 Documentation (PDD) US$ 20, 000 – $50, 000, up to $100, 000 with new methodology Public Consultation About $2, 000 – 10, 000 Validation $8, 000 - $15, 000 Approval by the National Authority Currently free Registration to the Executive Board $5, 000 - $30, 000 (according to the project) Implementation of the CDM Project According to the project Underlying investment According to the project Monitoring According to the project Verification $5, 000 – $10, 000 11
 Benefits of participating You get a new income stream for your project – with no risk for you Danida takes all the CDM related risk Danida takes all the trouble getting the paper work done m Preparing a Project Design Document m Getting the PDD validated m Getting an Indonesian National Approval m Getting the registration at the CDM Executive Board Danida buys the CERs when they are delivered 12
Benefits of participating You get a new income stream for your project – with no risk for you Danida takes all the CDM related risk Danida takes all the trouble getting the paper work done m Preparing a Project Design Document m Getting the PDD validated m Getting an Indonesian National Approval m Getting the registration at the CDM Executive Board Danida buys the CERs when they are delivered 12
 Criteria for participating The underlying project must be technically and financially viable m The technical design m Financial viability/project financing m Legal and commercial status of the project The project should be likely to be approved as CDM project m Contribution to sustainable development m Likelihood of being additional m Existence of baseline methodology The project proponent is capable to implement the project m Technical and management capability m Financial solidity of the company 13
Criteria for participating The underlying project must be technically and financially viable m The technical design m Financial viability/project financing m Legal and commercial status of the project The project should be likely to be approved as CDM project m Contribution to sustainable development m Likelihood of being additional m Existence of baseline methodology The project proponent is capable to implement the project m Technical and management capability m Financial solidity of the company 13
 The formalities Action Date Announcement of call for proposals 27 July 2005 Closing for proposals 3 October 2005 Pre-assessment/selection 4 October - 21 November 2005 Announcement of results 22 November 2005 Signing of Letter of Intent 22 November – 29 November 2005 Second call with tentative closing date: 1 February 2006 14
The formalities Action Date Announcement of call for proposals 27 July 2005 Closing for proposals 3 October 2005 Pre-assessment/selection 4 October - 21 November 2005 Announcement of results 22 November 2005 Signing of Letter of Intent 22 November – 29 November 2005 Second call with tentative closing date: 1 February 2006 14
 Possible next step in the wastemanagement sector A number of workshops will be organised giving more information on the Project Development Facility m. A follow-up workshop to develop Project Idea Notes (PINs) in the waste-management sector. If you have a project already then contact the project secretariat to get a template for a PIN. m. A one-on-one consultation on project development and writing of PIN is possible. 15
Possible next step in the wastemanagement sector A number of workshops will be organised giving more information on the Project Development Facility m. A follow-up workshop to develop Project Idea Notes (PINs) in the waste-management sector. If you have a project already then contact the project secretariat to get a template for a PIN. m. A one-on-one consultation on project development and writing of PIN is possible. 15
 Contact Secretariat of Danish CDM Project Facility c/o Royal Danish Embassy Menara Rajawali 25 th Floor Jl. Mega Kuningan Jakarta 12590 Telephone: + 62 21 576 1478 ext 114 Fax: + 62 21 576 1535 E-mail: jktamb@um. dk Website: www. emb-denmark. or. id Or ECON (in Jakarta) – emd@econ. no – Hp: 0815 8155048 Pelangi - rde@pelangi. or. id – Phone: 021 - 72801172
Contact Secretariat of Danish CDM Project Facility c/o Royal Danish Embassy Menara Rajawali 25 th Floor Jl. Mega Kuningan Jakarta 12590 Telephone: + 62 21 576 1478 ext 114 Fax: + 62 21 576 1535 E-mail: jktamb@um. dk Website: www. emb-denmark. or. id Or ECON (in Jakarta) – emd@econ. no – Hp: 0815 8155048 Pelangi - rde@pelangi. or. id – Phone: 021 - 72801172


