a97cf0e806321fc823284a336b205201.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 The Critical Era 1783 -1787
The Critical Era 1783 -1787
 The Revolution Changes American Society
The Revolution Changes American Society
 New Political Ideas n Republic n n NOT a democracy Elected representatives Protection of minority rights State Constitutions n n “Separation of Powers” Bicameral assemblies 1780 – Massachusetts Constitution Bills of Rights
New Political Ideas n Republic n n NOT a democracy Elected representatives Protection of minority rights State Constitutions n n “Separation of Powers” Bicameral assemblies 1780 – Massachusetts Constitution Bills of Rights
 Religion n Freedom of Religion n n Disestablishmentarianism – End of established religion Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom n n n 1786 Thomas Jefferson Deism n n Distant, impersonal god Founded in science and reason Not widespread Jefferson and Franklin
Religion n Freedom of Religion n n Disestablishmentarianism – End of established religion Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom n n n 1786 Thomas Jefferson Deism n n Distant, impersonal god Founded in science and reason Not widespread Jefferson and Franklin
 Equality n Expansion of franchise n n White males Some property qualifications
Equality n Expansion of franchise n n White males Some property qualifications
 Equality? : African-Americans n British freed slaves 1. 2. 3. n Undermine Southern economy Gain soldiers Ship them to British Caribbean plantations George Washington n n Permitted African Americans to join the Continental Army Encouraged state militias to admit African Americans Offered freedom to all who served Quakers, Baptists and Methodists condemned slavery Gradual emancipation in the North
Equality? : African-Americans n British freed slaves 1. 2. 3. n Undermine Southern economy Gain soldiers Ship them to British Caribbean plantations George Washington n n Permitted African Americans to join the Continental Army Encouraged state militias to admit African Americans Offered freedom to all who served Quakers, Baptists and Methodists condemned slavery Gradual emancipation in the North
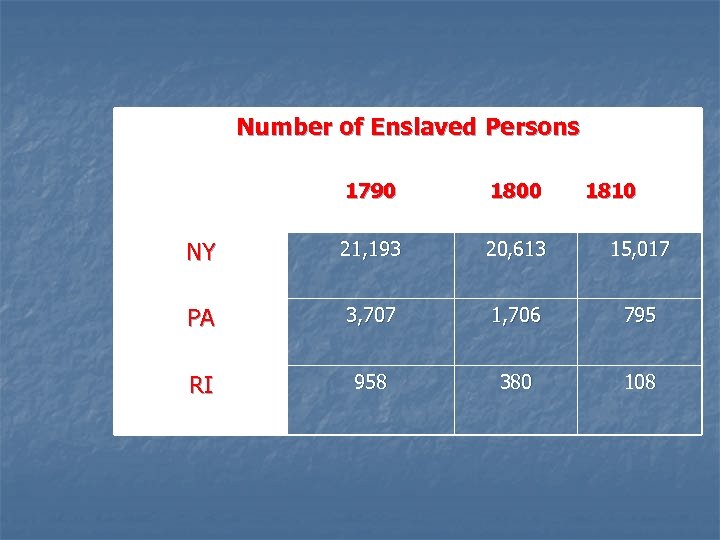 Number of Enslaved Persons 1790 1800 1810 NY 21, 193 20, 613 15, 017 PA 3, 707 1, 706 795 RI 958 380 108
Number of Enslaved Persons 1790 1800 1810 NY 21, 193 20, 613 15, 017 PA 3, 707 1, 706 795 RI 958 380 108
 Equality? : African Americans n North n Difficulties n n n Voting restrictions Segregation Re-enslavement African Methodist Episcopal Church – AME South n Manumission
Equality? : African Americans n North n Difficulties n n n Voting restrictions Segregation Re-enslavement African Methodist Episcopal Church – AME South n Manumission
 American Culture n Nationalism n n n American painters n n n Common enemy Common folklore John Trumbull Charles Willson Peale Education n 1795 – University of North Carolina
American Culture n Nationalism n n n American painters n n n Common enemy Common folklore John Trumbull Charles Willson Peale Education n 1795 – University of North Carolina
 The Confederation “A firm league of friendship…”
The Confederation “A firm league of friendship…”
 The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union n n Adopted in 1777 Weak central government n Confederation Congress n n n Unicameral legislature One representative from each state 9/13 majority needed to pass laws Unanimity needed for amendments No executive or judicial branch
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union n n Adopted in 1777 Weak central government n Confederation Congress n n n Unicameral legislature One representative from each state 9/13 majority needed to pass laws Unanimity needed for amendments No executive or judicial branch
 Confederation Powers granted to the Confederation Congress n n n n Declare war Raise armies Make treaties Create a postal system Raise loans Issue bills of credit Native American relations Resolve disputes between the states n Congress lacked power to: n n n Levy taxes Regulate of trade and tariffs Enforce provisions of treaties
Confederation Powers granted to the Confederation Congress n n n n Declare war Raise armies Make treaties Create a postal system Raise loans Issue bills of credit Native American relations Resolve disputes between the states n Congress lacked power to: n n n Levy taxes Regulate of trade and tariffs Enforce provisions of treaties
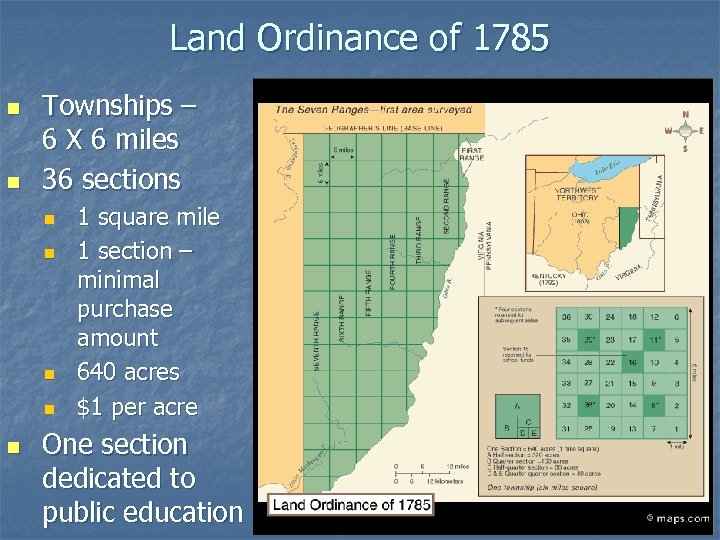 Land Ordinance of 1785 n n Townships – 6 X 6 miles 36 sections n n n 1 square mile 1 section – minimal purchase amount 640 acres $1 per acre One section dedicated to public education
Land Ordinance of 1785 n n Townships – 6 X 6 miles 36 sections n n n 1 square mile 1 section – minimal purchase amount 640 acres $1 per acre One section dedicated to public education
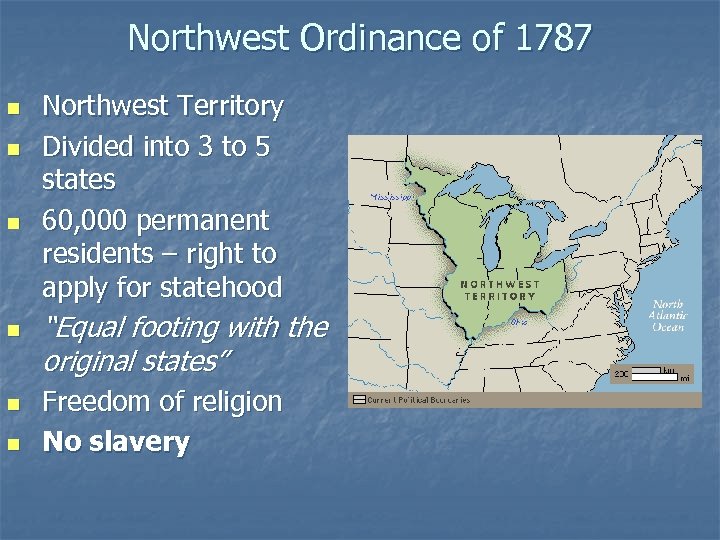 Northwest Ordinance of 1787 n n n Northwest Territory Divided into 3 to 5 states 60, 000 permanent residents – right to apply for statehood “Equal footing with the original states” Freedom of religion No slavery
Northwest Ordinance of 1787 n n n Northwest Territory Divided into 3 to 5 states 60, 000 permanent residents – right to apply for statehood “Equal footing with the original states” Freedom of religion No slavery
 Commerce Under the Confederation n Successful trade treaties with: n n n Holland Prussia Sweden n Problems n With Britain n Trade restrictions Flood of imports States acted like independent nations n Duties imposed, but not uniformly n n Interstate customs posts Interstate tariffs
Commerce Under the Confederation n Successful trade treaties with: n n n Holland Prussia Sweden n Problems n With Britain n Trade restrictions Flood of imports States acted like independent nations n Duties imposed, but not uniformly n n Interstate customs posts Interstate tariffs
 The Economic Crisis n Recession n Farmers were most severely affected n n n Cyclical debtors Mortgages National and state debts n Bonds n States printed money n Inflation n Property is endangered by democracy
The Economic Crisis n Recession n Farmers were most severely affected n n n Cyclical debtors Mortgages National and state debts n Bonds n States printed money n Inflation n Property is endangered by democracy
 Shays’s Rebellion n Massachusetts n n Taxes raised Farmers in Western Massachusetts most severely affected n Daniel Shays n n n August, 1786 – Attack local courthouses January 1787 – 1200 farmers march to Boston Put down by MA militia
Shays’s Rebellion n Massachusetts n n Taxes raised Farmers in Western Massachusetts most severely affected n Daniel Shays n n n August, 1786 – Attack local courthouses January 1787 – 1200 farmers march to Boston Put down by MA militia
 The Constitutional Convention
The Constitutional Convention
 The Philadelphia Convention n May-September 1787 n “Constitutional Convention” n All states except RI n 55 delegates (“Framers”) n Washington chosen President n Not open to public n Write an entirely new Constitution n 3 Major issues n n n National powers vs. States’ Rights Large states vs. small states Slave states vs. Free states
The Philadelphia Convention n May-September 1787 n “Constitutional Convention” n All states except RI n 55 delegates (“Framers”) n Washington chosen President n Not open to public n Write an entirely new Constitution n 3 Major issues n n n National powers vs. States’ Rights Large states vs. small states Slave states vs. Free states
 The Virginia Plan n Drafted by Madison n Powerful national n Structure n government n n n Three branches n n Impose laws on states Levy taxes Regulate commerce n Single executive National courts Bicameral legislature § Lower house chosen directly by the people § State legislatures nominate candidates for upper house § Lower house elects upper house from these candidates § Representation based on population or financial contributions n Favored by large states
The Virginia Plan n Drafted by Madison n Powerful national n Structure n government n n n Three branches n n Impose laws on states Levy taxes Regulate commerce n Single executive National courts Bicameral legislature § Lower house chosen directly by the people § State legislatures nominate candidates for upper house § Lower house elects upper house from these candidates § Representation based on population or financial contributions n Favored by large states
![The Virginia Plan Upper House [proportioned by population] elects nominate candidates State Legislatures elect The Virginia Plan Upper House [proportioned by population] elects nominate candidates State Legislatures elect](https://present5.com/presentation/a97cf0e806321fc823284a336b205201/image-21.jpg) The Virginia Plan Upper House [proportioned by population] elects nominate candidates State Legislatures elect Lower House [proportioned by population] elect People
The Virginia Plan Upper House [proportioned by population] elects nominate candidates State Legislatures elect Lower House [proportioned by population] elect People
 The New Jersey Plan n William Paterson (NJ) n Small states n Modify the Articles n n Unicameral Congress Equal representation New powers to levy taxes and to regulate trade Multi-person executive
The New Jersey Plan n William Paterson (NJ) n Small states n Modify the Articles n n Unicameral Congress Equal representation New powers to levy taxes and to regulate trade Multi-person executive
 The Great Compromise “Mankind may hereafter, from n Benjamin Franklin n Bicameral legislature this unfortunate instance, despair n House of Representatives n n n Based on population Directly elected Senate n n Each state equally represented Senators selected by the state legislature of establishing governments by human wisdom, and leave it to chance, war, and conquest” ~ Benjamin Franklin ~
The Great Compromise “Mankind may hereafter, from n Benjamin Franklin n Bicameral legislature this unfortunate instance, despair n House of Representatives n n n Based on population Directly elected Senate n n Each state equally represented Senators selected by the state legislature of establishing governments by human wisdom, and leave it to chance, war, and conquest” ~ Benjamin Franklin ~
![The Great Compromise Senate [two senators per state] choose State Legislatures elect House of The Great Compromise Senate [two senators per state] choose State Legislatures elect House of](https://present5.com/presentation/a97cf0e806321fc823284a336b205201/image-24.jpg) The Great Compromise Senate [two senators per state] choose State Legislatures elect House of Representatives [proportioned by population] elect People
The Great Compromise Senate [two senators per state] choose State Legislatures elect House of Representatives [proportioned by population] elect People
 Three-Fifths Compromise n How do you count Slaves? n n South: Slaves should count as part of the populations North: n n “[Populations] shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service Slaves should not count for a Term of Years, and If they do, they should excluding Indians not taxed, count in apportioning three fifths of all other Persons. ” taxes as well ~Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 ~ n Compromise n Every five enslaved persons would count as three free persons
Three-Fifths Compromise n How do you count Slaves? n n South: Slaves should count as part of the populations North: n n “[Populations] shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service Slaves should not count for a Term of Years, and If they do, they should excluding Indians not taxed, count in apportioning three fifths of all other Persons. ” taxes as well ~Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 ~ n Compromise n Every five enslaved persons would count as three free persons
 Commerce Compromises n Southern fears n If national government controls trade, it can n n Ban slave trade Tax exports n Compromise n n Exports cannot be taxed Slave trade cannot be banned for 20 years n North very willing to compromise n n Necessity Slavery a dying institution
Commerce Compromises n Southern fears n If national government controls trade, it can n n Ban slave trade Tax exports n Compromise n n Exports cannot be taxed Slave trade cannot be banned for 20 years n North very willing to compromise n n Necessity Slavery a dying institution
 The Executive n Chosen by legislature or independently elected? n n Both! Electoral College n n Multiple regional candidates Difficult to receive majority House of Representatives chooses Vice President § Runner-up in electoral college § Tie: Senate chooses “The British government forms the best model the world has ever produced. ” ~ Alexander Hamilton ~
The Executive n Chosen by legislature or independently elected? n n Both! Electoral College n n Multiple regional candidates Difficult to receive majority House of Representatives chooses Vice President § Runner-up in electoral college § Tie: Senate chooses “The British government forms the best model the world has ever produced. ” ~ Alexander Hamilton ~
 Thoughts from Franklin Close of the Convention n Major omissions: n n Bill of Rights Political parties n “Factions” n September 17, 1787 (Constitution Day) "I have often looked at that picture behind the president without being able to tell whether it was a rising or setting sun. Now at length I have the happiness to know that it is indeed a rising, not a setting sun. " Signed by 37 of the 55 delegates Eliza Powell: “Well, Doctor, n “Bundle of Compromises”? what have we got—a Republic or a Monarchy? ” “It…astonishes me, sir, to find this system Franklin: “A Republic, if approaching so near to you can keep it. ” perfection as it does. ” n
Thoughts from Franklin Close of the Convention n Major omissions: n n Bill of Rights Political parties n “Factions” n September 17, 1787 (Constitution Day) "I have often looked at that picture behind the president without being able to tell whether it was a rising or setting sun. Now at length I have the happiness to know that it is indeed a rising, not a setting sun. " Signed by 37 of the 55 delegates Eliza Powell: “Well, Doctor, n “Bundle of Compromises”? what have we got—a Republic or a Monarchy? ” “It…astonishes me, sir, to find this system Franklin: “A Republic, if approaching so near to you can keep it. ” perfection as it does. ” n
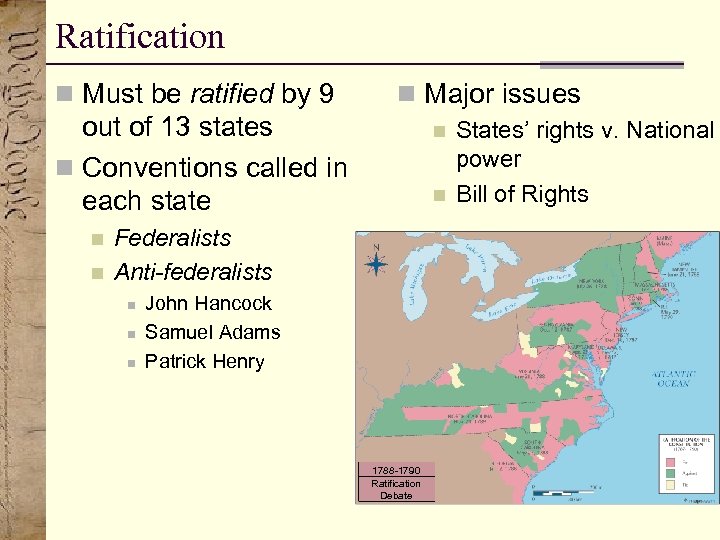 Ratification n Must be ratified by 9 n Major issues out of 13 states n Conventions called in each state n n Federalists Anti-federalists n n n John Hancock Samuel Adams Patrick Henry 1788 -1790 Ratification Debate States’ rights v. National power Bill of Rights
Ratification n Must be ratified by 9 n Major issues out of 13 states n Conventions called in each state n n Federalists Anti-federalists n n n John Hancock Samuel Adams Patrick Henry 1788 -1790 Ratification Debate States’ rights v. National power Bill of Rights
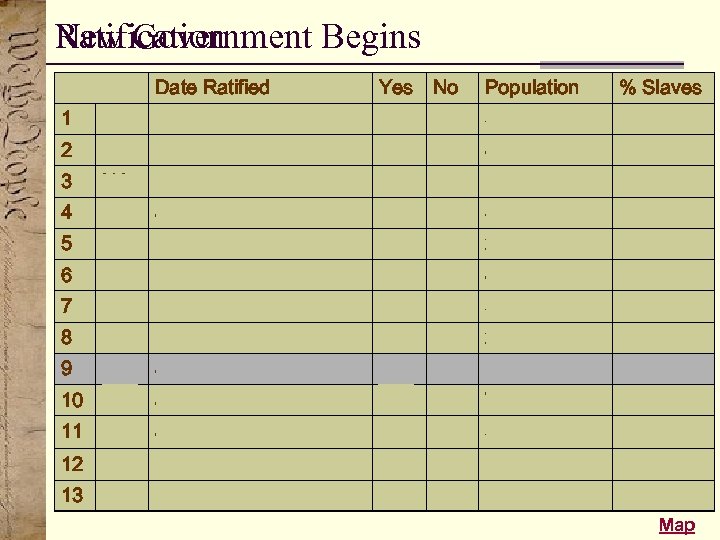 New Government Begins Ratification Date Ratified Yes No Population % Slaves 1 DE December 7, 1787 30 0 59, 096 (13) 15% 2 PA December 12, 1787 46 23 433, 611 (3) >1% 3 NJ December 18, 1787 38 0 184, 839 (9) 6% 4 GA January 2, 1788 26 0 82, 548 (11) 35. 5% 5 CT January 9, 1788 128 40 237, 655 (8) 1% 6 MA February 6, 1788 187 168 475, 199 (2) 0% 7 MD April 28, 1788 63 11 319, 728 (6) 32% 8 SC May 23, 1788 149 73 249, 073 (7) 43% 9 NH June 21, 1788 57 47 141, 899 (10) 0. 1% 10 VA June 25, 1788 89 79 747, 550 (1) 39% 11 NY July 26, 1788 30 27 340, 241 (5) 6% 12 NC November, 21, 1789 194 77 395, 005 (4) 26. 5% 13 RI May 29, 1790 34 32 69, 112 (12) 1% Map
New Government Begins Ratification Date Ratified Yes No Population % Slaves 1 DE December 7, 1787 30 0 59, 096 (13) 15% 2 PA December 12, 1787 46 23 433, 611 (3) >1% 3 NJ December 18, 1787 38 0 184, 839 (9) 6% 4 GA January 2, 1788 26 0 82, 548 (11) 35. 5% 5 CT January 9, 1788 128 40 237, 655 (8) 1% 6 MA February 6, 1788 187 168 475, 199 (2) 0% 7 MD April 28, 1788 63 11 319, 728 (6) 32% 8 SC May 23, 1788 149 73 249, 073 (7) 43% 9 NH June 21, 1788 57 47 141, 899 (10) 0. 1% 10 VA June 25, 1788 89 79 747, 550 (1) 39% 11 NY July 26, 1788 30 27 340, 241 (5) 6% 12 NC November, 21, 1789 194 77 395, 005 (4) 26. 5% 13 RI May 29, 1790 34 32 69, 112 (12) 1% Map
 Basic Principles of the Constitution n n Popular Sovereignty Republicanism Federalism Separation of Powers n n Baron de Montesquieu Spirit of Laws n Checks and Balances n Amendment Procedure “We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. ” ~ The Preamble of the Constitution ~
Basic Principles of the Constitution n n Popular Sovereignty Republicanism Federalism Separation of Powers n n Baron de Montesquieu Spirit of Laws n Checks and Balances n Amendment Procedure “We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. ” ~ The Preamble of the Constitution ~
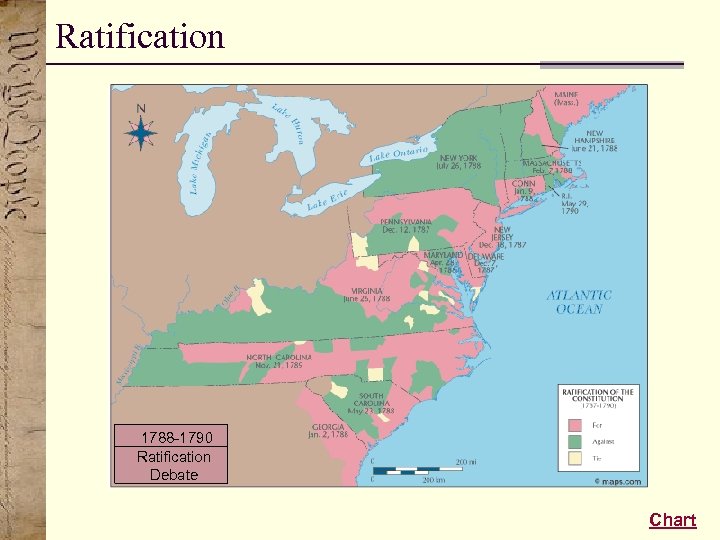 Ratification 1788 -1790 Ratification Debate Chart
Ratification 1788 -1790 Ratification Debate Chart
 The Federalist Papers n New York n Gov. George Clinton n 85 essays n Publius n n n Alexander Hamilton James Madison John Jay “Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. ” ~ Federalist 51 ~ n Federalist 10: n n Control of factions “Pluralism” n Federalist 51: n Separation of powers “The influence of factious leaders may kindle a flame within their particular States, but will be unable to spread a general conflagration through the other States” ~ Federalist 10 ~ Map Chart
The Federalist Papers n New York n Gov. George Clinton n 85 essays n Publius n n n Alexander Hamilton James Madison John Jay “Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. ” ~ Federalist 51 ~ n Federalist 10: n n Control of factions “Pluralism” n Federalist 51: n Separation of powers “The influence of factious leaders may kindle a flame within their particular States, but will be unable to spread a general conflagration through the other States” ~ Federalist 10 ~ Map Chart


