1d123b36723e7a2c61c57d3e893dc435.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

The Cost of Raising Replacement Dairy Heifers Brian Lang, OMAFRA, Woodstock Bill Grexton, Can. West DHI, Guelph
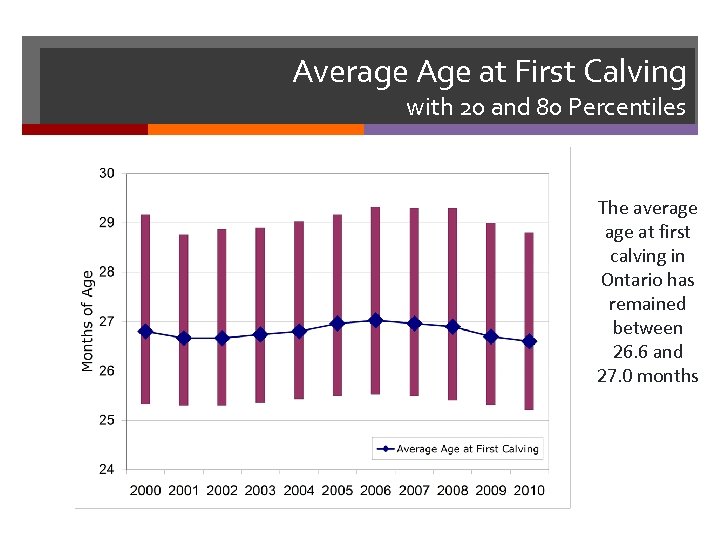
Average Age at First Calving with 20 and 80 Percentiles The average at first calving in Ontario has remained between 26. 6 and 27. 0 months
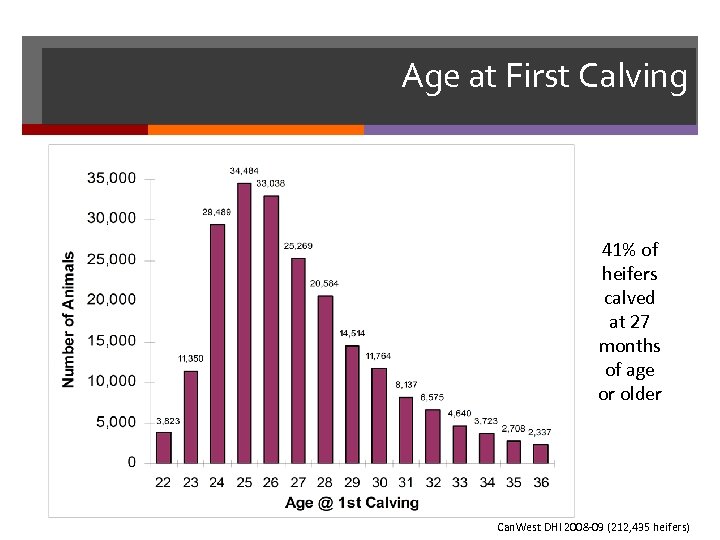
Age at First Calving 63% of 41% of heifers calved at 27 months of age or older Can. West DHI 2008 -09 (212, 435 heifers)

Comparison of Age at First Calving and Productive Life Productive life in a dairy herd is similar across all ages with a range of less than 4 months Heifers calving at 25 -26 months have the longest herd life Can. West DHI 2008 -09
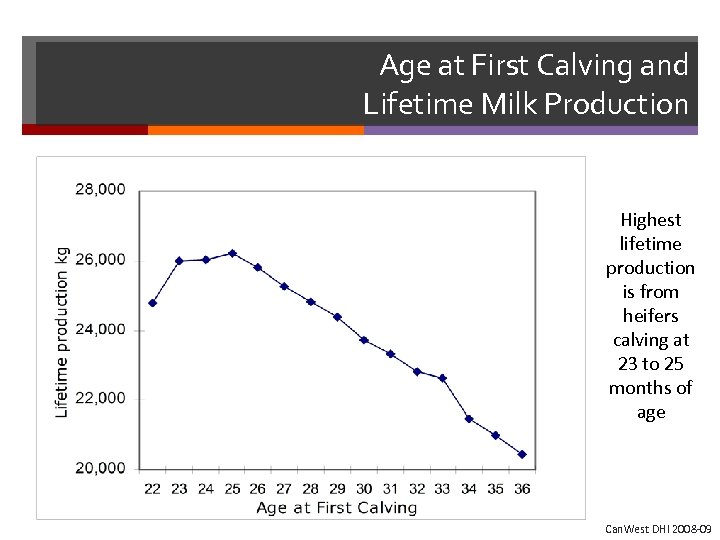
Age at First Calving and Lifetime Milk Production Highest lifetime production is from heifers calving at 23 to 25 months of age Can. West DHI 2008 -09

Heifers required to supply replacements for 100 -cow herd 15% allowance for culling, non-breeders and death loss

Replacements Required If calving interval is 14 months for both farms and 15% allowance for culling A Farm 1 has 12 heifers to sell each year A Farm 2 must buy 5 heifers each year
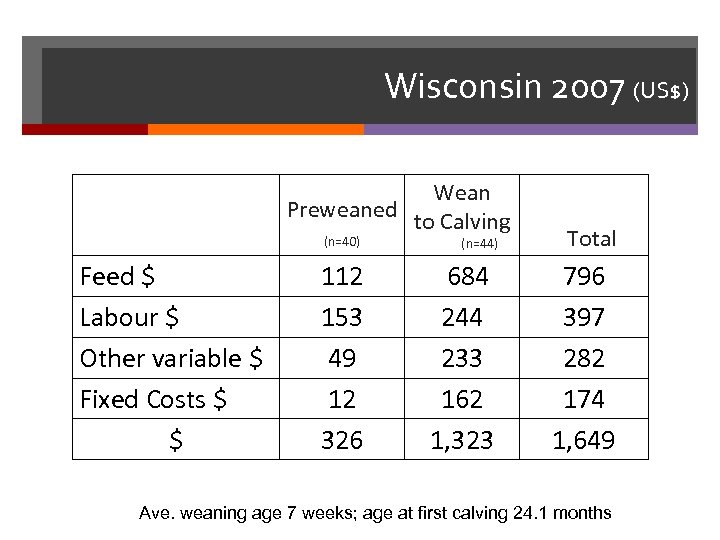
Wisconsin 2007 (US$) Wean Preweaned to Calving (n=40) Feed $ Labour $ Other variable $ Fixed Costs $ $ 112 153 49 12 326 (n=44) 684 244 233 162 1, 323 Total 796 397 282 174 1, 649 Ave. weaning age 7 weeks; age at first calving 24. 1 months
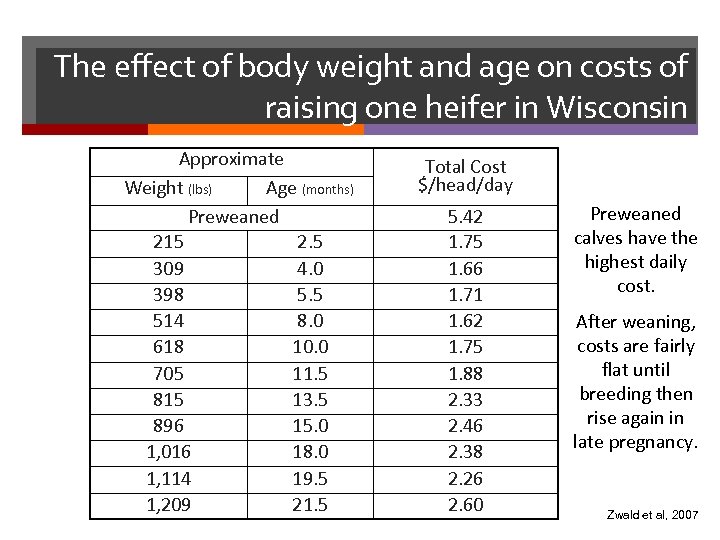
The effect of body weight and age on costs of raising one heifer in Wisconsin Approximate Weight (lbs) Age (months) Preweaned 215 2. 5 309 4. 0 398 5. 5 514 8. 0 618 10. 0 705 11. 5 815 13. 5 896 15. 0 1, 016 18. 0 1, 114 19. 5 1, 209 21. 5 Total Cost $/head/day 5. 42 1. 75 1. 66 1. 71 1. 62 1. 75 1. 88 2. 33 2. 46 2. 38 2. 26 2. 60 Preweaned calves have the highest daily cost. After weaning, costs are fairly flat until breeding then rise again in late pregnancy. Zwald et al, 2007
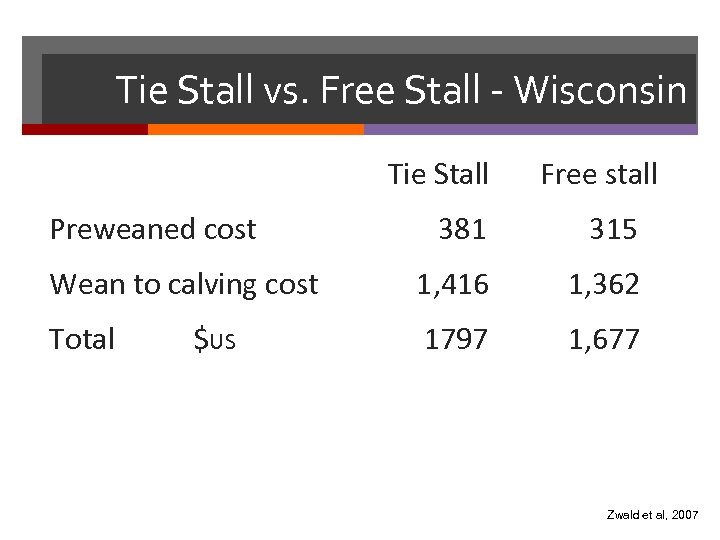
Tie Stall vs. Free Stall - Wisconsin Tie Stall Preweaned cost Free stall 381 315 Wean to calving cost 1, 416 1, 362 Total 1797 1, 677 $US Zwald et al, 2007
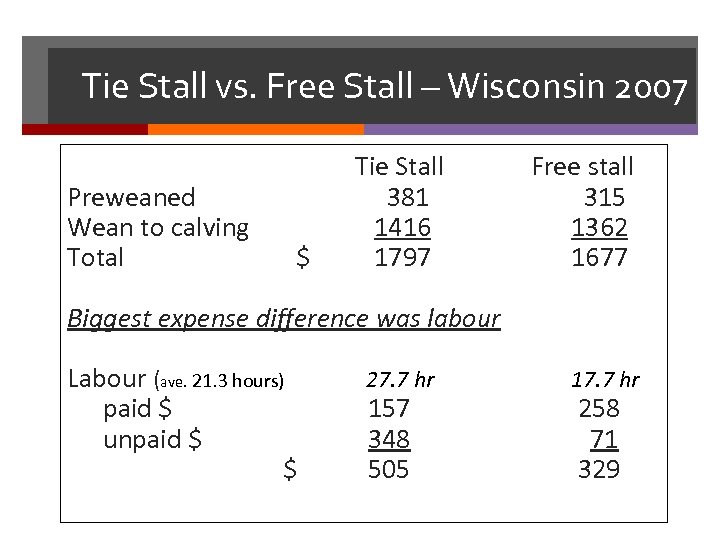
Tie Stall vs. Free Stall – Wisconsin 2007 Preweaned Wean to calving Total $ Tie Stall 381 1416 1797 Free stall 315 1362 1677 Biggest expense difference was labour Labour (ave. 21. 3 hours) paid $ unpaid $ $ 27. 7 hr 157 348 505 17. 7 hr 258 71 329
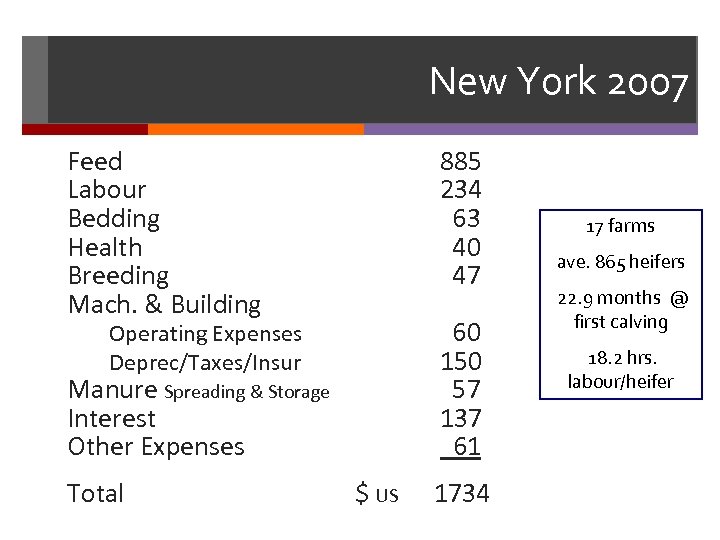
New York 2007 Feed Labour Bedding Health Breeding Mach. & Building 885 234 63 40 47 60 150 57 137 61 Operating Expenses Deprec/Taxes/Insur Manure Spreading & Storage Interest Other Expenses Total $ US 1734 17 farms ave. 865 heifers 22. 9 months @ first calving 18. 2 hrs. labour/heifer
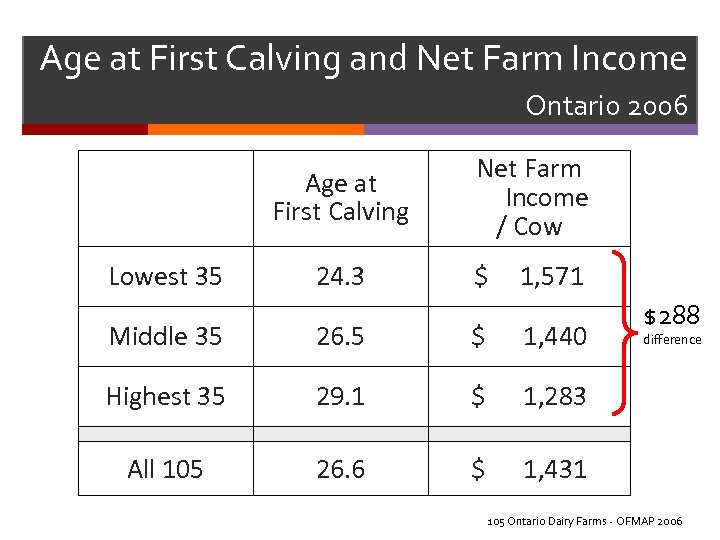
Age at First Calving and Net Farm Income Ontario 2006 Age at First Calving Lowest 35 24. 3 Net Farm Income / Cow $ 1, 571 Middle 35 26. 5 $ 1, 440 Highest 35 29. 1 $ 1, 283 All 105 26. 6 $ $288 1, 431 difference 105 Ontario Dairy Farms - OFMAP 2006
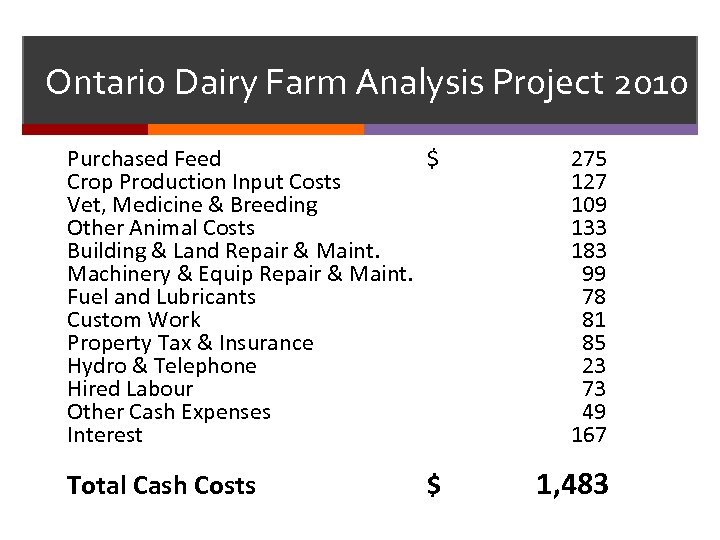
Ontario Dairy Farm Analysis Project 2010 Purchased Feed $ Crop Production Input Costs Vet, Medicine & Breeding Other Animal Costs Building & Land Repair & Maint. Machinery & Equip Repair & Maint. Fuel and Lubricants Custom Work Property Tax & Insurance Hydro & Telephone Hired Labour Other Cash Expenses Interest Total Cash Costs $ 275 127 109 133 183 99 78 81 85 23 73 49 167 1, 483
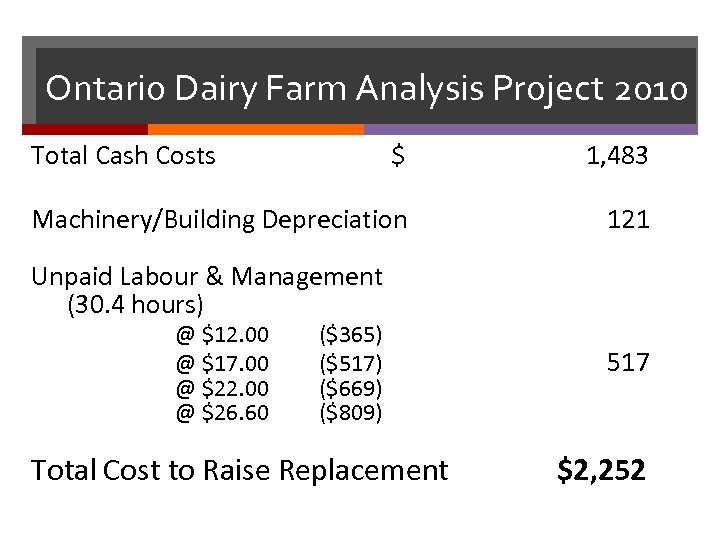
Ontario Dairy Farm Analysis Project 2010 Total Cash Costs $ 1, 483 Machinery/Building Depreciation 121 Unpaid Labour & Management (30. 4 hours) @ $12. 00 @ $17. 00 @ $22. 00 @ $26. 60 ($365) ($517) ($669) ($809) Total Cost to Raise Replacement 517 $2, 252

Hours of Labour to Required to Raise a Heifer from Birth to Calving 2000 -2010 In recent years, the labour required to raise a heifer has ranged from 35 to 48 hours (includes family and employee labour) Ontario Dairy Farm Accounting Project
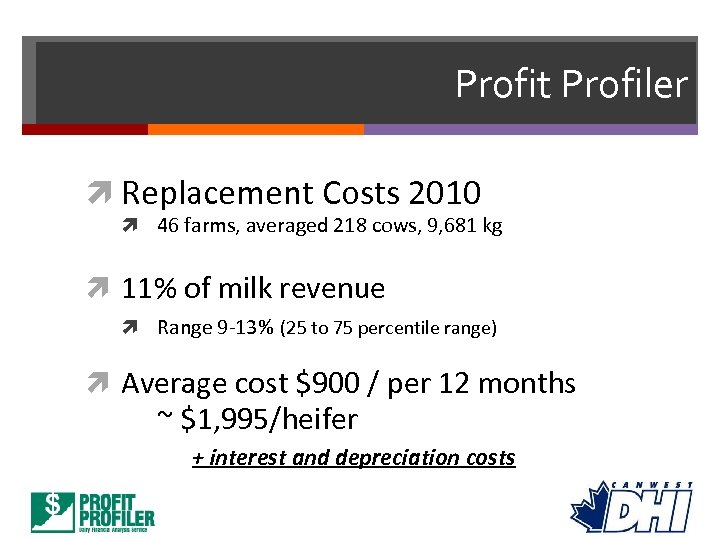
Profit Profiler Replacement Costs 2010 46 farms, averaged 218 cows, 9, 681 kg 11% of milk revenue Range 9 -13% (25 to 75 percentile range) Average cost $900 / per 12 months ~ $1, 995/heifer + interest and depreciation costs

How to Measure Impact COP of heifer may not be the best indicator of success 1 st Lactation Production compared to herd average is needed to see other side Most herds = 89% Range 87 - 91% (25 to 75 percentile range) Some herds as low as 80% = program is not working You need a good indicator to know if your heifer program is working
Impact of Age @ Calving 2 groups of herds based on age @ 1 st Calving (24 and 28 mo) Low Age Group … Produced 1400 kg milk more per cow ($885) with higher % margin Spent. 9% of milk cheque LESS to raise a heifer Spent $14 more per heifer per year but… Spent $281 LESS overall to bring heifer into milking line 1 st lactation production was 1, 170 kg higher Good overall management dictates that in addition to getting economical high milk production, you need to get higher production heifers into the milking line sooner - it can be done!

Summary $2, 000 - $2, 500 average cost to raise a replacement heifer Remember overhead costs Unpaid labour Plus value of calf

Summary Herds that calve earlier get higher 1 st lactation and lifetime production There is a wide range of costs between farms to raise heifers. There is no advantage to delaying the age to 1 st calving. Herds with good management can raise heifers which perform better than those who do not. Herds that combine good management with wise cost of production decisions not only have good results but also add considerably the overall profit of the business. The difference in cost can be in excess of $25, 000 per year for the heifer program and $60, 000 in the overall farm profit for a herd size of 100 cows.

Thank you
1d123b36723e7a2c61c57d3e893dc435.ppt