29070e940c9af72cecac79362d1926df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

The Cost of Doing Business Fixed vs. Variable Expenses
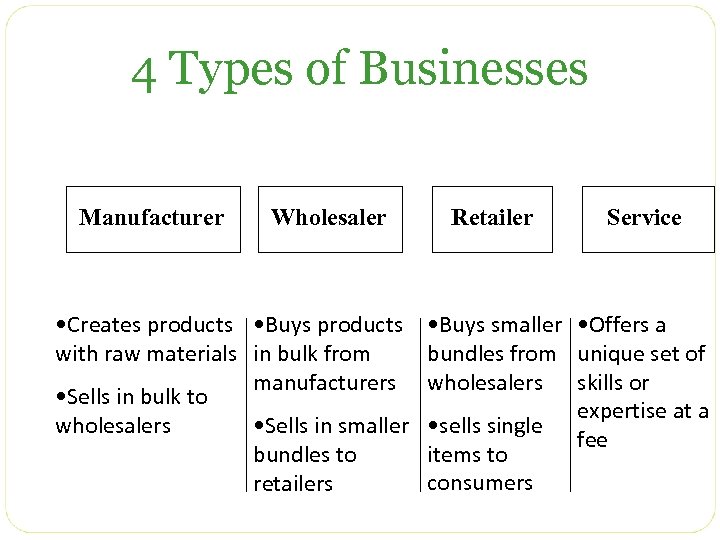
4 Types of Businesses Manufacturer Wholesaler • Creates products • Buys products with raw materials in bulk from manufacturers • Sells in bulk to wholesalers • Sells in smaller bundles to retailers Retailer Service • Buys smaller • Offers a bundles from unique set of wholesalers skills or expertise at a • sells single fee items to consumers
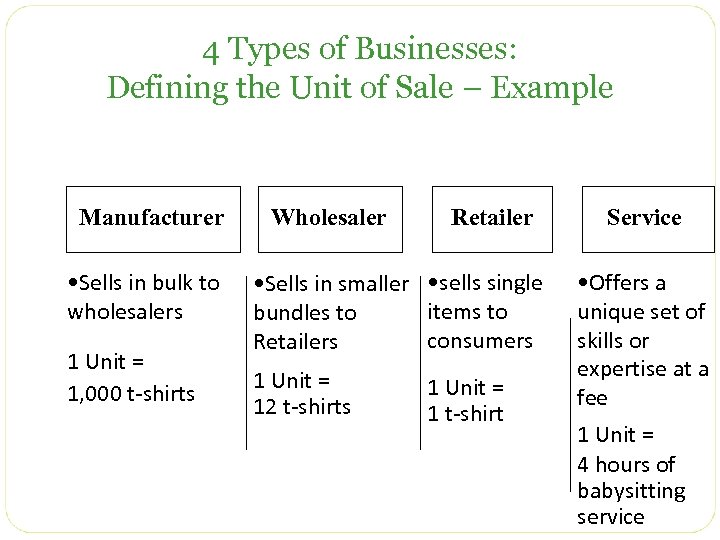
4 Types of Businesses: Defining the Unit of Sale – Example Manufacturer • Sells in bulk to wholesalers 1 Unit = 1, 000 t-shirts Wholesaler Retailer • Sells in smaller • sells single items to bundles to consumers Retailers 1 Unit = 12 t-shirts 1 Unit = 1 t-shirt Service • Offers a unique set of skills or expertise at a fee 1 Unit = 4 hours of babysitting service
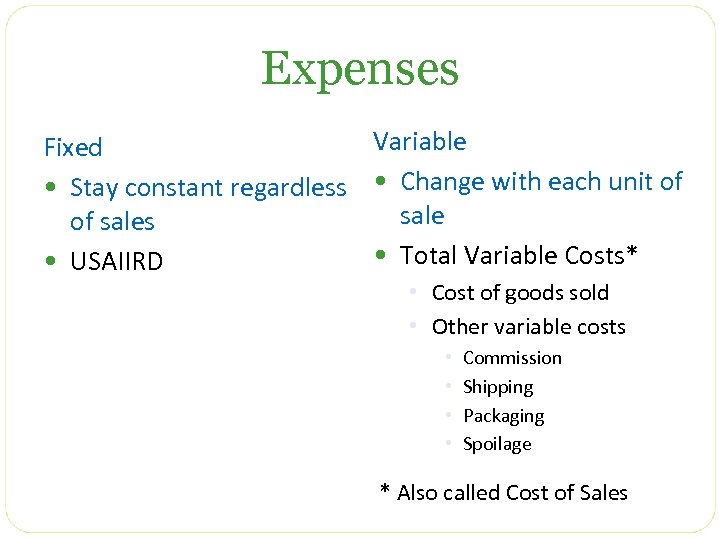
Expenses Variable Fixed • Stay constant regardless • Change with each unit of sales • Total Variable Costs* • USAIIRD • Cost of goods sold • Other variable costs • • Commission Shipping Packaging Spoilage * Also called Cost of Sales

Fixed Expenses to Operate Business Interest Salaries Advertising Insurance Depreciation Utilities Rent Other EXpense

Fixed Expenses • Focus on fixed expenses • USAIIRD ISAIDUROX • Depreciation - use straight line calculation • Other Costs • Transportation, Supplies, Maintenance • Professional Development, Education
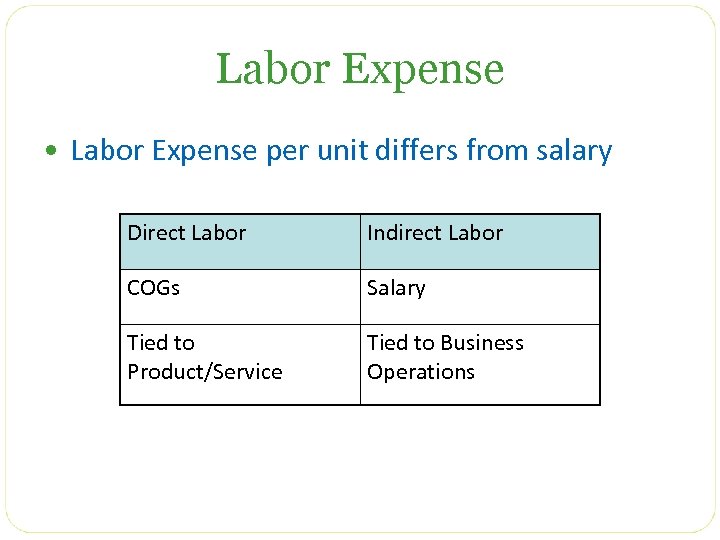
Labor Expense • Labor Expense per unit differs from salary Direct Labor Indirect Labor COGs Salary Tied to Product/Service Tied to Business Operations

Lego Activity Objectives NFTE’s Objectives: • Introduce students to classifying costs • Engage students in fun Economics of One Unit exercise

Lego Activity • In groups, create a toy made by Lego • • • Survey Lego available in market Determine target consumer Design and name the toy Assemble toy Determine: • Material cost • Labor cost • Variable cost • Fill out the simple worksheet

Lego Activity • Present back: • The Name of the toy • Target consumer • Your worksheet

Lego Activity Debrief • What did you think about the activity? • As a Student? • As a Teacher? • What was the purpose/objective? • How would this work in your classroom? • Any Modifications?

Economics of 1 Unit Formula: Contribution Margin = Selling Price – Var. Exp. per unit (COGS/ + other var. Expense) per unit Also called “Cost of Sales/unit”
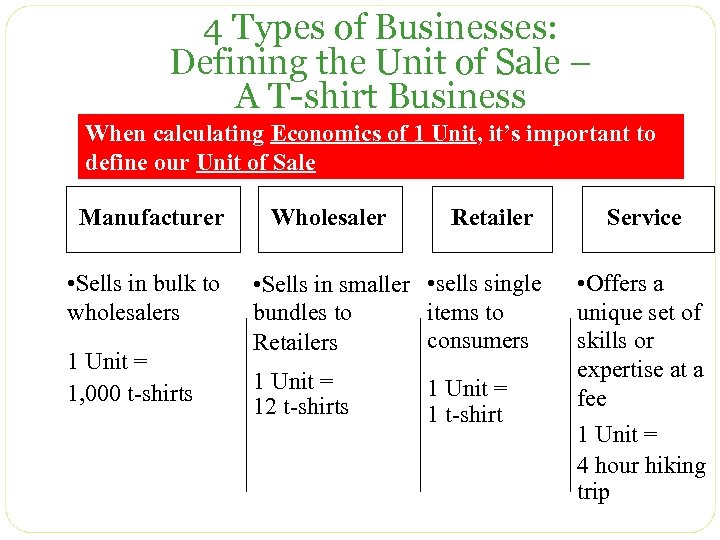
4 Types of Businesses: Defining the Unit of Sale – A T-shirt Business When calculating Economics of 1 Unit, it’s important to define our Unit of Sale Manufacturer • Sells in bulk to wholesalers 1 Unit = 1, 000 t-shirts Wholesaler Retailer • Sells in smaller • sells single items to bundles to consumers Retailers 1 Unit = 12 t-shirts 1 Unit = 1 t-shirt Service • Offers a unique set of skills or expertise at a fee 1 Unit = 4 hour hiking trip
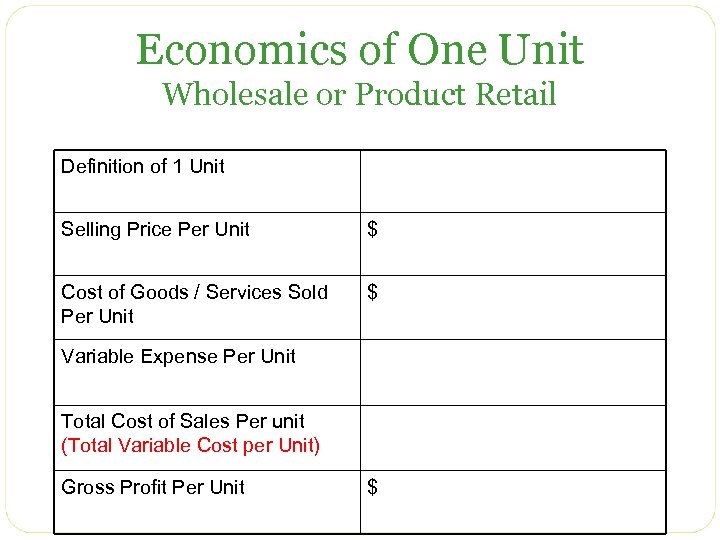
Economics of One Unit Wholesale or Product Retail Definition of 1 Unit Selling Price Per Unit $ Cost of Goods / Services Sold Per Unit $ Variable Expense Per Unit Total Cost of Sales Per unit (Total Variable Cost per Unit) Gross Profit Per Unit $
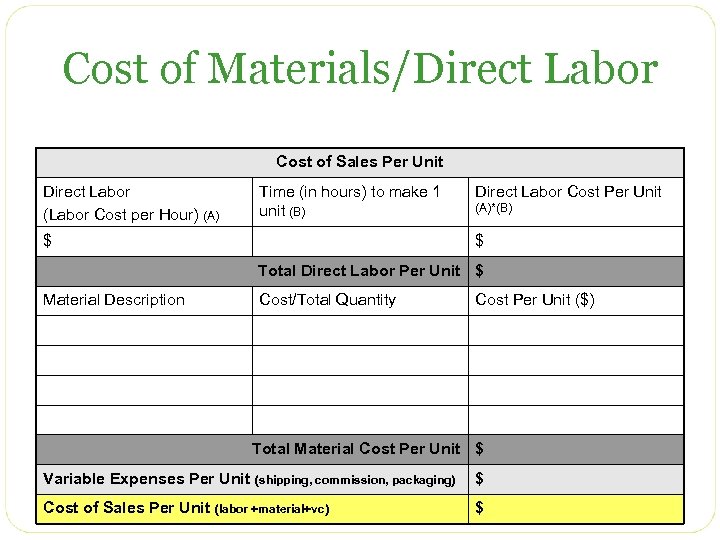
Cost of Materials/Direct Labor Cost of Sales Per Unit Direct Labor (Labor Cost per Hour) (A) Time (in hours) to make 1 unit (B) $ Direct Labor Cost Per Unit (A)*(B) $ Total Direct Labor Per Unit $ Material Description Cost/Total Quantity Cost Per Unit ($) Total Material Cost Per Unit $ Variable Expenses Per Unit (shipping, commission, packaging) $ Cost of Sales Per Unit (labor +material+vc) $
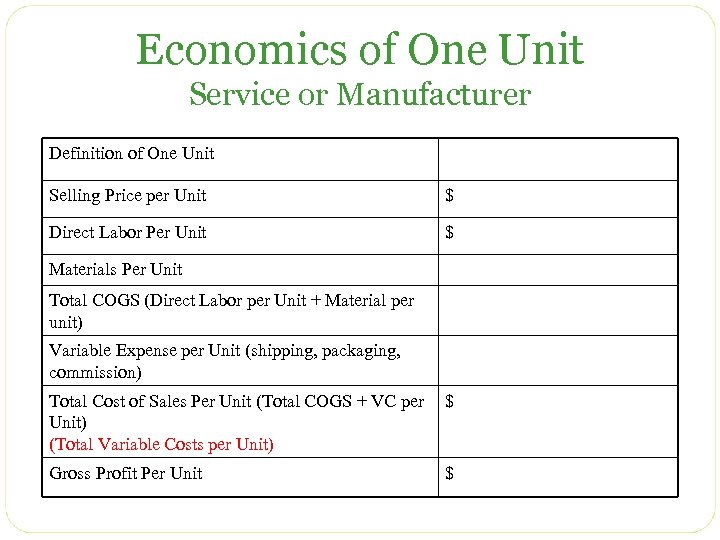
Economics of One Unit Service or Manufacturer Definition of One Unit Selling Price per Unit $ Direct Labor Per Unit $ Materials Per Unit Total COGS (Direct Labor per Unit + Material per unit) Variable Expense per Unit (shipping, packaging, commission) Total Cost of Sales Per Unit (Total COGS + VC per Unit) (Total Variable Costs per Unit) $ Gross Profit Per Unit $

Economics of 1 Unit

Economics of 1 Unit Customized Gift Basket • Things to consider: • Direct labor • How long does it take to assemble one basket? • Customization • What is the average cost per unit? Find the range • How much customization is affordable? • Multiple economics of 1 unit • How many economics of 1 unit should there be?

Economics of 1 Unit Customized Gift Basket • Calculate economics of 1 unit: • Materials • 10 Baskets = $10 • Ribbons and cellophane wrap for 10 baskets= $20. 00 • Items for 10 baskets = $170. 00 • Labor per hour = $6. 00 • 15 minutes to assemble • Commission = 10% of sale

Economics of 1 Unit 1. What is the unit of sale for our gift basket? 2. What is our Contribution Margin per Unit?

Turkey Sandwich Exercise
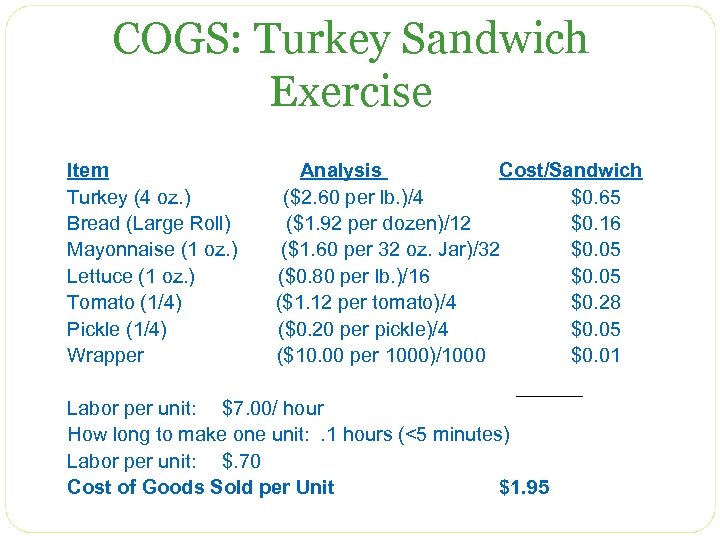
COGS: Turkey Sandwich Exercise Item Turkey (4 oz. ) Bread (Large Roll) Mayonnaise (1 oz. ) Lettuce (1 oz. ) Tomato (1/4) Pickle (1/4) Wrapper Analysis Cost/Sandwich ($2. 60 per lb. )/4 $0. 65 ($1. 92 per dozen)/12 $0. 16 ($1. 60 per 32 oz. Jar)/32 $0. 05 ($0. 80 per lb. )/16 $0. 05 ($1. 12 per tomato)/4 $0. 28 ($0. 20 per pickle)/4 $0. 05 ($10. 00 per 1000)/1000 $0. 01 Labor per unit: $7. 00/ hour How long to make one unit: . 1 hours (<5 minutes) Labor per unit: $. 70 Cost of Goods Sold per Unit $1. 95

Total Sales for One Month Market analysis • Assume school of 500 students • How many buy lunch? • How many bring lunch? • How many complain about quality of cafeteria food? • How many participate in after school activities? • How many selling days in one month? • How many sandwiches can I make per day? • How many sandwiches can I sell per day?

Example: Economics of 1 Unit Lawn care Service

Economics of 1 Unit Lawn care Service • Things to consider: • Average Unit • What is the average size of a lawn? • What services will you provide the lawn? • Labor Cost • How do you value your labor per hour? • How many hours of labor will you need to provide? • Supply cost • What materials will you need to provide? • What is the average amount of materials used on one lawn?

Economics of 1 Unit Lawn care Service • Calculate economics of 1 unit • Average size lawn takes 2 hours • Labor cost per hour = $7. 50 • Supply Cost • 3 lawn bags for 1 hour work • 5. 99 for 100 heavy duty bags • 1/4 gallon of gas per 1/2 acre lawn
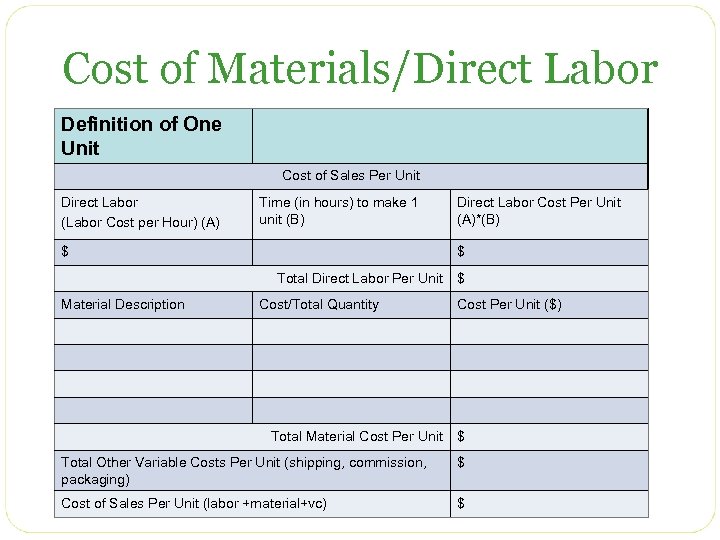
Cost of Materials/Direct Labor Definition of One Unit Cost of Sales Per Unit Direct Labor (Labor Cost per Hour) (A) Time (in hours) to make 1 unit (B) $ $ Total Direct Labor Per Unit Material Description Direct Labor Cost Per Unit (A)*(B) Cost/Total Quantity Total Material Cost Per Unit $ Cost Per Unit ($) $ Total Other Variable Costs Per Unit (shipping, commission, packaging) $ Cost of Sales Per Unit (labor +material+vc) $
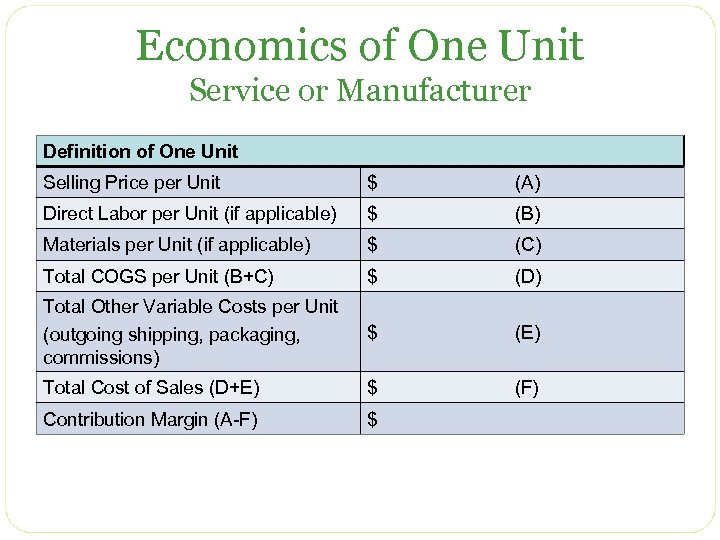
Economics of One Unit Service or Manufacturer Definition of One Unit Selling Price per Unit $ (A) Direct Labor per Unit (if applicable) $ (B) Materials per Unit (if applicable) $ (C) Total COGS per Unit (B+C) $ (D) Total Other Variable Costs per Unit (outgoing shipping, packaging, commissions) $ (E) Total Cost of Sales (D+E) $ (F) Contribution Margin (A-F) $

Sales Assumptions • What are the assumptions that inform your projections? • Size of market (Target Market) • Full capacity • How much time can you spend (see time management slide)? • Do you have help? • Seasonality • When is the busiest time of year for you, your industry? • Time to develop a brand presence and establish customer base (ie. No business sells at full capacity immediately)
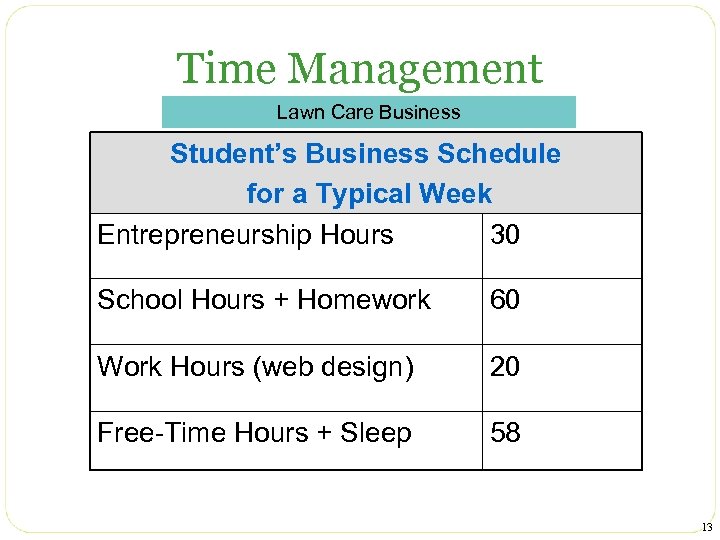
Time Management Lawn Care Business Student’s Business Schedule for a Typical Week Entrepreneurship Hours 30 School Hours + Homework 60 Work Hours (web design) 20 Free-Time Hours + Sleep 58 13
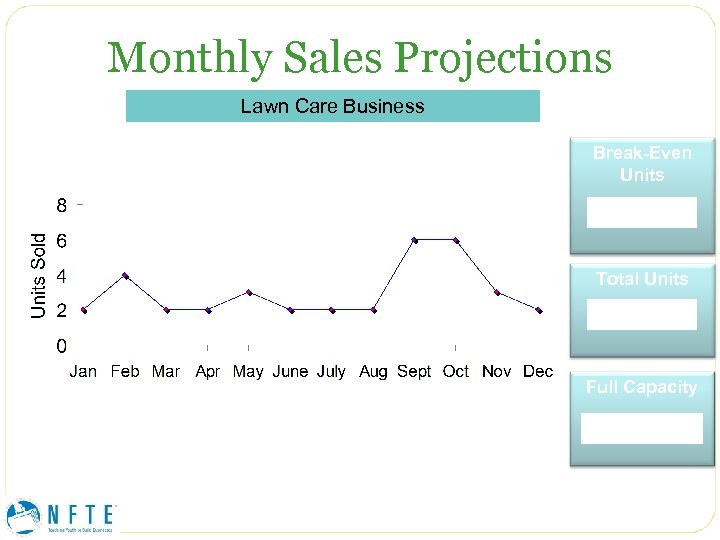
Monthly Sales Projections Lawn Care Business Break-Even Units Total Units Full Capacity
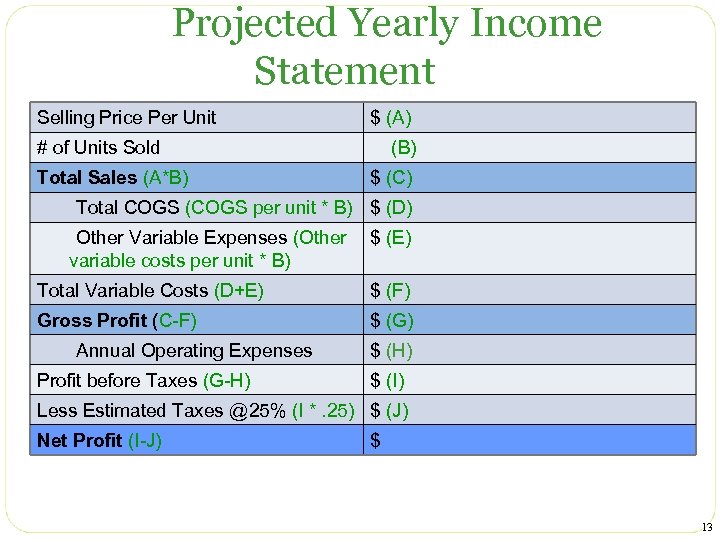
Projected Yearly Income Statement Selling Price Per Unit $ (A) # of Units Sold Total Sales (A*B) (B) $ (C) Total COGS (COGS per unit * B) $ (D) Other Variable Expenses (Other variable costs per unit * B) $ (E) Total Variable Costs (D+E) $ (F) Gross Profit (C-F) $ (G) Annual Operating Expenses Profit before Taxes (G-H) $ (I) Less Estimated Taxes @25% (I *. 25) $ (J) Net Profit (I-J) $ 13

Final Financial Thoughts • Guide Students to the lowest unit • Makes it easier to project costs and describe business • Have students map out the entire business process before even looking at any numbers • Play with numbers in Excel • Remember Financials are fun and tell the businesses story!
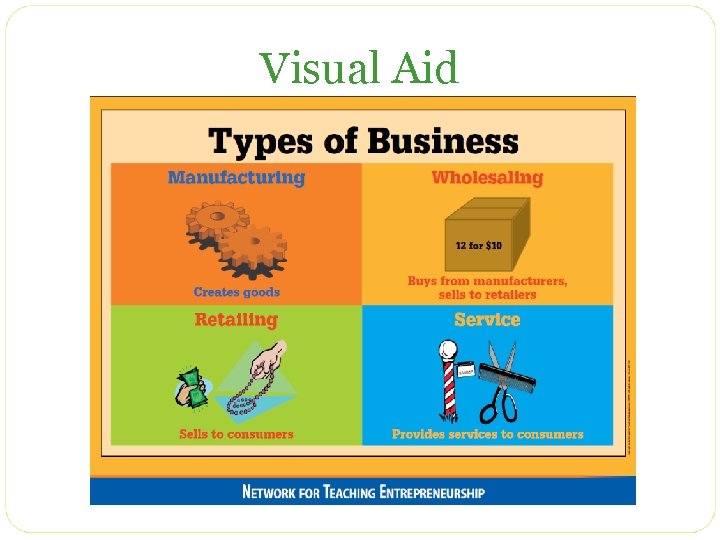
Visual Aid
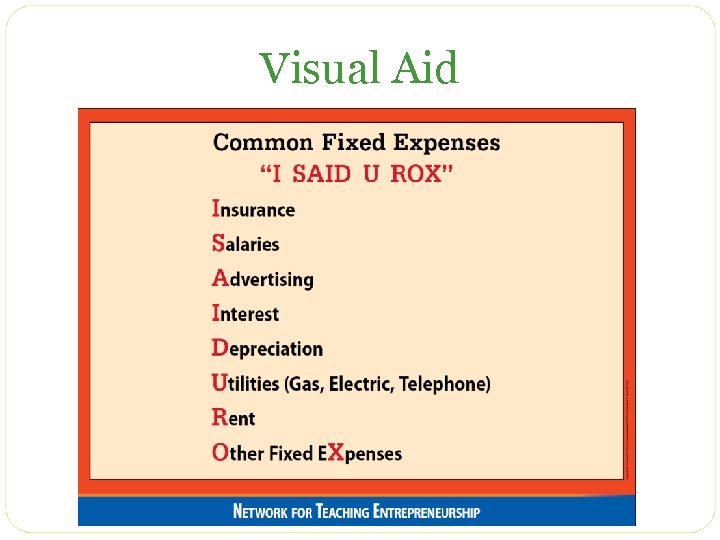
Visual Aid

Visual Aid
29070e940c9af72cecac79362d1926df.ppt