ee3d2c4b93afca331a35a7ba7373b604.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 THE CONSTITUTION
THE CONSTITUTION
 What is a Constitution Fundamental law Law determining the fundamental political principles of a government Often codified as a written document Purpose To create a framework of government
What is a Constitution Fundamental law Law determining the fundamental political principles of a government Often codified as a written document Purpose To create a framework of government
 The U. S. Constitution Independence Hall, Philadelphia, PA, September, 1787 The Signing of the United States Constitution by Thomas Pritchard Rossiter
The U. S. Constitution Independence Hall, Philadelphia, PA, September, 1787 The Signing of the United States Constitution by Thomas Pritchard Rossiter
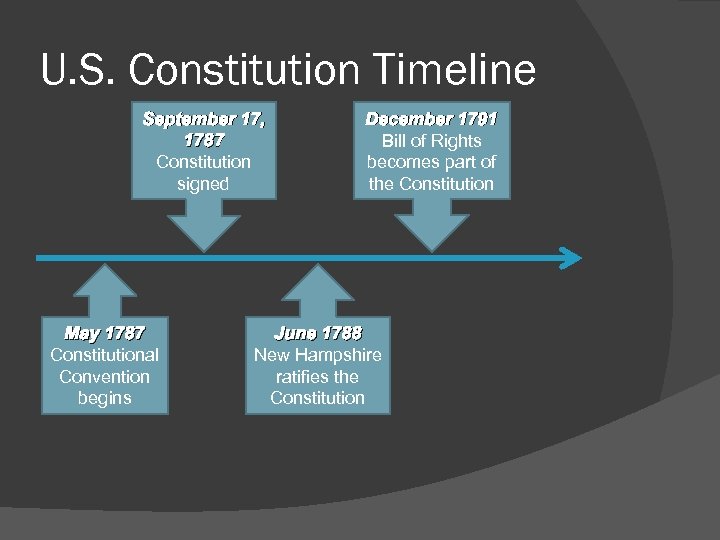 U. S. Constitution Timeline September 17, 1787 Constitution signed May 1787 Constitutional Convention begins December 1791 Bill of Rights becomes part of the Constitution June 1788 New Hampshire ratifies the Constitution
U. S. Constitution Timeline September 17, 1787 Constitution signed May 1787 Constitutional Convention begins December 1791 Bill of Rights becomes part of the Constitution June 1788 New Hampshire ratifies the Constitution
 Creation of the US Constitutional Convention Philadelphia, PA 55 Delegates from 12 states James Madison, Father of the Constitution
Creation of the US Constitutional Convention Philadelphia, PA 55 Delegates from 12 states James Madison, Father of the Constitution
 Constitutional Compromises Virginia Plan Designed largely by James Madison Presented by Gov. Edmund Randolph ○ Called for a federal legislative, executive, & judicial branches ○ Scrap the Articles of Confederation ○ New federal government Could impose laws on the states Collect taxes ○ Bicameral Legislature Upper house elected by the people Lower house elected by the upper house ○ Number of representatives based on population ○ Favored large states (VA, NY, MA)
Constitutional Compromises Virginia Plan Designed largely by James Madison Presented by Gov. Edmund Randolph ○ Called for a federal legislative, executive, & judicial branches ○ Scrap the Articles of Confederation ○ New federal government Could impose laws on the states Collect taxes ○ Bicameral Legislature Upper house elected by the people Lower house elected by the upper house ○ Number of representatives based on population ○ Favored large states (VA, NY, MA)
 Constitutional Compromises New Jersey Plan Presented by William Patterson of NJ Keep the Articles of Confederation ○ Modify them to make federal government stronger Unicameral Legislature ○ Equal representation for all states Federal government ○ Raise taxes ○ Regulate trade
Constitutional Compromises New Jersey Plan Presented by William Patterson of NJ Keep the Articles of Confederation ○ Modify them to make federal government stronger Unicameral Legislature ○ Equal representation for all states Federal government ○ Raise taxes ○ Regulate trade
 Constitutional Compromises Connecticut or Great Compromise Committee headed by Ben Franklin Proposed by Roger Sherman of CT ○ Bicameral Legislature House of Representatives - Based on population - Elected by the people Senate - Equal representation - Elected by the state legislatures
Constitutional Compromises Connecticut or Great Compromise Committee headed by Ben Franklin Proposed by Roger Sherman of CT ○ Bicameral Legislature House of Representatives - Based on population - Elected by the people Senate - Equal representation - Elected by the state legislatures
 Constitutional Compromises Slavery One member of the House of Representatives for every 40, 000 people The South ○ Count each slave for representation The North ○ Slaves cannot vote and should not be counted ○ If slaves count for representation count them for taxes as well Three-Fifths Compromise Every five slaves would count as three free white persons for representation and taxes
Constitutional Compromises Slavery One member of the House of Representatives for every 40, 000 people The South ○ Count each slave for representation The North ○ Slaves cannot vote and should not be counted ○ If slaves count for representation count them for taxes as well Three-Fifths Compromise Every five slaves would count as three free white persons for representation and taxes
 Three-Fifths Compromise
Three-Fifths Compromise
 Constitutional Compromises Other Compromises Federal government ○ Could not tax exports ○ Would not ban the slave trade until 1808 Nine of thirteen states had to ratify the Constitution for it to take effect
Constitutional Compromises Other Compromises Federal government ○ Could not tax exports ○ Would not ban the slave trade until 1808 Nine of thirteen states had to ratify the Constitution for it to take effect
 Other Constitutions C. S. A. (1861) We the people of the Confederacy Russia (1993) We, the multinational people of the Russian Federation Brazil (1998) We, the representatives of the Brazilian People Afghanistan (2004) We the people of Afghanistan
Other Constitutions C. S. A. (1861) We the people of the Confederacy Russia (1993) We, the multinational people of the Russian Federation Brazil (1998) We, the representatives of the Brazilian People Afghanistan (2004) We the people of Afghanistan
 Alabama Constitution of 1901
Alabama Constitution of 1901
 Alabama Constitution (1901) 357, 157 words (4, 400 US Constitution) 798 Amendments (27 US Constitution) Why was it written? White Supremacy, Honest Elections and the New Constitution, One and Inseparable Why is it so long? Power is concentrated in the state government Counties lack home rule How does the US Constitution address this? The 10 th Amendment
Alabama Constitution (1901) 357, 157 words (4, 400 US Constitution) 798 Amendments (27 US Constitution) Why was it written? White Supremacy, Honest Elections and the New Constitution, One and Inseparable Why is it so long? Power is concentrated in the state government Counties lack home rule How does the US Constitution address this? The 10 th Amendment
 Constitutional Compromises Legislatures still operate the same way Meet in committees to discuss measures Present ideas to assembly for a vote
Constitutional Compromises Legislatures still operate the same way Meet in committees to discuss measures Present ideas to assembly for a vote
 Group Assignment Quickly divide into groups of three Each group will get one amendment from the Alabama Constitution of 1901 Read it Debate: Is this amendment important to everyone in the state Would you change it? How? Update the language Present it to the class for a vote
Group Assignment Quickly divide into groups of three Each group will get one amendment from the Alabama Constitution of 1901 Read it Debate: Is this amendment important to everyone in the state Would you change it? How? Update the language Present it to the class for a vote
 Sample Assessment
Sample Assessment


